2023 Champion Trainer profiles - Peter Schiergen (Germany) / Kadir Baltaci (Turkey) / Claudia Erni (Switzerland)
NATIONAL CHAMPION TRAINERS IN FOCUS
In this issue, we take a look at some more of Europe’s champion national trainers, courtesy of the latest data compiled by Dr Marian Surda, doyen of Slovakian racing.
A notable feature of the tables, when comparing the last two years, is the infrequency of trainers retaining their crowns. Only in 7 of the 18 countries that featured in both years did this happen (France, Jean-Claude Rouget; Ireland, Aidan O’Brien; Spain, Guillermo Arizkorreta; Germany, Peter Schiergen; Norway, Niels Petersen and Greece, Charalambos Charalambus). The baton changed in all other countries, including in Great Britain, the country whose trainer earned the most money, for the second year running. This time, that trainer was the father and son combination of John and Thady Gosden, who wrested the title from Charlie Appleby.
Among the jockeys, Maxim Guyon, in France and William Buick, in Britain headed the table once again. But the dominance of the big three countries – France, Britain and Ireland – was interrupted by an extraordinary performance by Turkey’s Champion, 20-year-old Vedat Abis, who clocked up a remarkable 283 wins – far more than any of his fellow champions.
Our featured trainers this year are Peter Schiergen (Germany / 5th in the table), Kadir Baltaci (Turkey / 6th) and Claudia Erni (Switzerland / 11th).
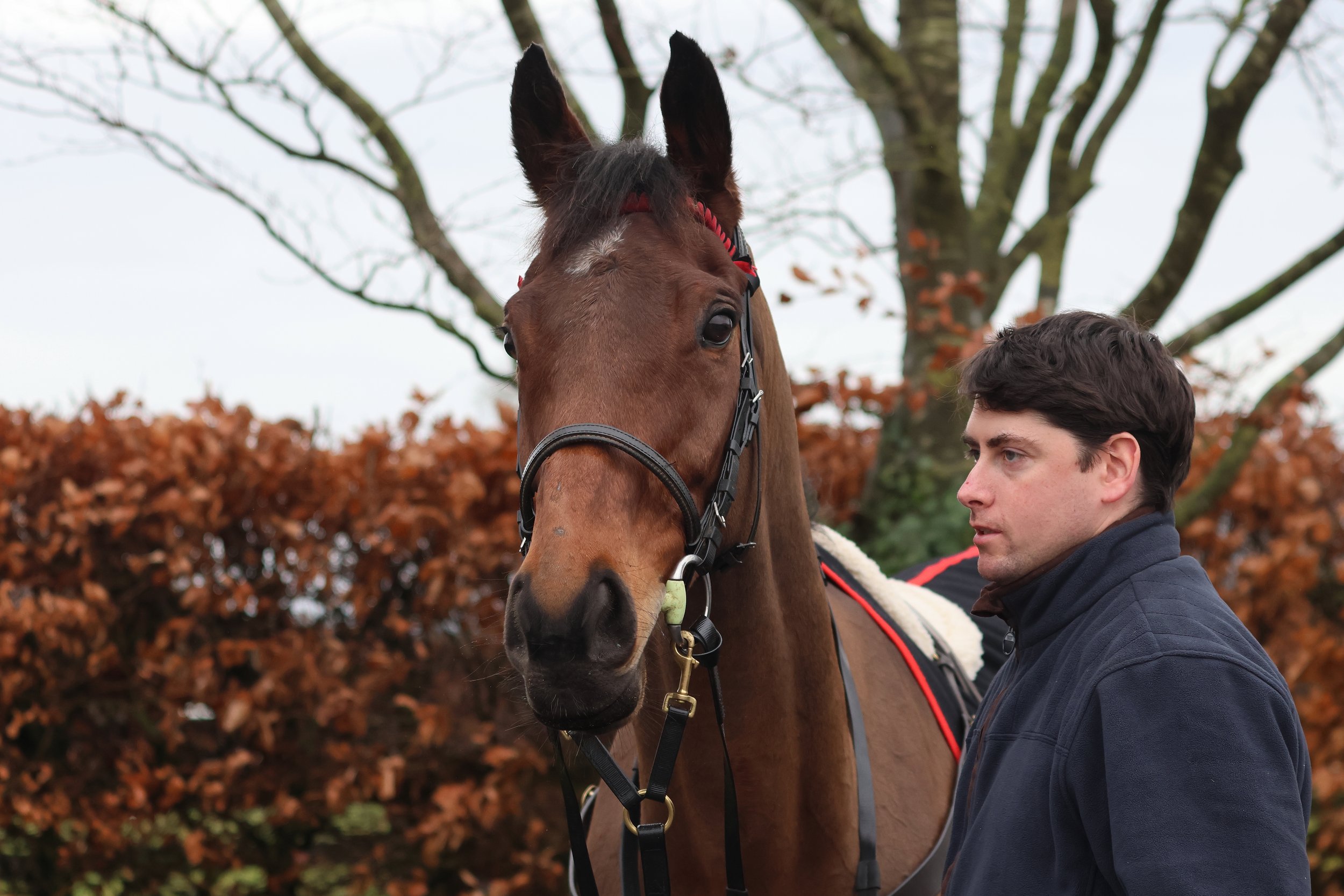
PETER SCHIERGEN
The name of Peter Schiergen is a familiar one across the European racing scene and beyond, with Group wins in France, Britain, Italy and Dubai as well as his native Germany. At time of writing, that Group race tally stands at 199. Champion Trainer in Germany no fewer than eight times (2002, 2005, 2006, 2013, 2015, 2021, 2022 and 2023), with six German Derby wins to his name (Boreal 2001, Schiaparelli 2006, Kamsin 2008, Lucky Speed 2013, Nutan 2015 and Sammarco 2022), his crowning single achievement remains his Arc win with Danedream in 2011.
But before becoming one of the most successful German trainers of recent generations, Peter had been one of his country’s most successful jockeys. His outstanding record in the saddle encompassed five jockeys’ championships – 1992 to 1996 – and nearly 1500 wins, including a record 271 successes in 1995.
I asked Peter about his journey into racing and what had led to his becoming a jockey at the age of 16. “I always wanted to become a show jumper. My plan was just to do my apprenticeship in racing and after that to go back to show jumping. But it turned out differently and I had quite a bit of success as an apprentice and stayed in the game”.
The transition from jockey to trainer (taking over from fellow legend Heinz Jentzsch in 1998) was made at a younger age – just 33 – than is often the case.
“The opportunity came up to take over from Heinz Jentsch. I knew that this was a huge chance and even though it was quite early I decided to take over. I started in 1998 in Köln and still train there today. In 2009 we built a new stable next to the old one so that’s really the main thing that has changed”.
“I had a great time as a jockey and was five consecutive years champion jockey and broke the European record in 1995. But the owners didn’t give me the chance to ride in the big races abroad such as Lando in the Japan Cup. This is something I don’t want to happen to my stable jockeys and therefore I use them both in Germany and abroad.
What does Schiergen consider the pros and cons of training on the track? “The horses are used to the racetrack. A great benefit is that it’s easier to get staff. Furthermore, the racecourse is in charge of preparing the training facilities. A disadvantage would be that we have certain times at which we must be at the track, as there are many trainers who use the facilities. On a private track you have more peace”.
“The team consists of 25 staff. It gets more and more difficult to get good staff and competent work riders. We have a great team and many people have been staff members for many years. There are plenty of Germans working with us. Other than Germans, most of the staff tend to be from the eastern European countries such as Poland, Czech Republic, Bulgaria etc.”.
When asked which trainer he admires the most, Schiergen replies: “I didn’t have a jockey I admired the most when I was a jockey, and now, as a trainer, neither do I have a trainer I would single out as admiring. I look at many others and try to take the best of each”.
“The state of racing in Germany isn’t great, but there are many ambitious people who are trying to bring the sport back to better times. It’s difficult with social change and especially the animal welfare movement. Racing’s lobby sometimes appears to be too weak to work against these forces. Therefore, we need a change. It’s difficult to compare our racing jurisdiction to other countries. We don’t have training facilities such as Newmarket or Chantilly.”
As well as the 200 Group race milestone, Schiergen has another in his sights. Ending last year on 1,907 wins on the flat and 31 over jumps, it is a real possibility that he could send out his 2,000th winner this year. “Certainly is a milestone and a great achievement. But it is more important to win big races.”
KADIR BALTACI
Kadir Baltaci’s 31 wins last year came at the hooves of just 37 individual starters (his stable currently houses just 30 horses in training). His tally included seven domestic Group races, including three at Group 1.
From Baltaci’s base in Turkey’s capital, Ankara, it is a long haul to the tracks where he does most of his racing: a 5-hour drive north-west takes him to the nation’s racing headquarters, Veliefendi in Istanbul, or a lengthier run yet in the opposite direction finds the track in Adana.
“I was born in Adana”, Baltaci begins. “I lived in Adana until 2010. Adana is my city, my place but Ankara is now ‘my city’ and ‘my place’, where I live with my two sons and my wife. Though I train my horses here, when they are ready to race I mostly prefer to run in Istanbul because of the classic and other big races that are run at Veliefendi racecourse”.
“I began as an Assistant Trainer in 2011. After spending seven seasons as an Assistant, I started training in my own right, in 2017.
“When I was at high school, I was best friends with the son of the owner of the famous Turkish-Arabian horse Nurhat. I often went with my friend to (Adana’s) Yesiloba Racecourse to see the horse. As a child, I loved the horses. I used to watch racing on the television, especially the classic and GAZI races.
“Workwise, I started out working at my father's painting company, but it collapsed. I then worked as a driver for one of my now-owners, Mr Fedai Kahraman. When working as his driver, he often used to send me to the races at Ankara, in order to help his trainer out. After a couple of years, he asked me if I would move to the track to assist the trainer. I said ‘yes’ and that’s how my journey started.
“I don’t have a private training centre. Like all trainers in Turkey, I must be based at one of the Jockey Club racecourses. We chose Ankara for the wintertime: because the racetrack is empty then, I can easily prepare my horses.
“I have 20 people working for me. My staff are all Turkish. We did try employees of other nationalities, but I did not like the way they worked. Most of my crew have been with me since I started training. Because we have been working together for so long, it is a great relief to me that they know exactly what I want. It is hard to find new people to take care of horses. Really hard. I have five exercise riders. You can find exercise riders very easily, but most are not proficient. The Jockey Club of Turkey trains exercise riders. One of mine came from there – he graduated last year. But they are young and need time to learn the job properly. We have also got a broader problem with finding stable staff generally. Not only me, other trainers have the same problem”.
To date, Baltaci has ventured abroad to race but once, sending a runner to Meydan to contest the Grade 2 Cape Verdi and Ballanchine Stakes. “I believe my horses will run more often abroad. My big ambition is to run in - and win - a European Classic.
“We are not well educated about training practices in other countries, so I will not make comparisons. All I would say is that many are lucky to have private training facilities. I think our trainers probably spend more time in nursing horses which have suffered minor injuries back into racing”.
Baltaci places much hope for the future in Serdal Adali, Adana-born President of the Turkish Jockey Club. “Mr Serdal Adali is spending time ensuring a better future for us. I believe he will succeed. Then my countrymen will be more interested in racing outside of Turkey.”
Balaci’s strike rate, particularly at the top level, is impressive indeed, but he is modest when asked to explain the secret of his success. “It’s down to the efforts of everyone, from my horse owner to my team. That's why I can't give any specific reasons for my success. I have 30 in training right now. Thirty different horses, which all act differently, and that is why I train each horse differently”.
CLAUDIA ERNI
Over in Switzerland, there has seen a changing of the guard. After several years of domination by Miro Weiss, there is a new woman in town. Step forward, Claudia Erni. Her yard of 20 horses – ranging from 2yo’s to a 10yo sprinter and stayer, ranks fourth by size within the country, but in 2023 punched above its weight to capture the championship.
“I grew up with horses. My father had a riding school. I took part in some national dressage competitions. My father’s girlfriend was in racing, and this was how I found my way into racing. I rode as an amateur, both on the flat and over jumps, and also held an amateur training license before taking out my professional trainer’s licence in 2006”.
“I am also a physical therapist and still devote two afternoons a week to working in this profession”.
Erni trains from Switzerland’s westernmost racetrack, Avenches, south of Lake Neuchatel. This impressive complex (a good idea of which can be gleaned from www.iena.ch), extends to 140 hectares/350 acres and accommodates multiple equine disciplines. It is important to the finances of Swiss racing, many of its race days being taken by the French betting operator, PMU.
“It is really nice to train here. We have a lot of space. We have two tracks of 1600m and 1800m circumference, with paddocks and a horse-walker. And I am almost alone here! At present, I have four employees, from France, Switzerland and Chechia. I do find it difficult to find good riders. For so many, money is more important than passion - sad, but that’s how it is”.
“My owners have been in the business for a long time. It is difficult to find young owners. But I am fortunate, in that mine came to me – I didn’t have to go looking for them!”
“I often race in France, Germany and Italy, when the owners allow it. I love Longchamp. We are very close to France – for example, it takes just three hours to reach Lyon.”
And what of the outlook for the sport in her country? “As in every country, racing in Switzerland is getting harder. It is harder to find sponsors and new owners, and the number of racehorses is reducing. The Swiss racing authority is trying to find ways to increase the popularity of the sport. Maybe, jockeys will be prevented in future from using the whip?”
Emmet Mullins - the Irish National Hunt trainer who has had no shortage of success - a common trait in the Mullins clan!
Article by Daragh Ó Conchúir
Emmet Mullins possesses the sense of mischievousness that is common in many of the Mullins clan, and there are times when one wonders if it might be a contributory factor in his approach to training racehorses. Or at least his race planning.
We know from a significant sample of more than eight years as a trainer, that Mullins doesn’t throw darts without having given them due consideration. It’s just that his way of getting to the double is more Mensur Suljoviç than Michael van Gerwen. Convention is a constraint he sees no sense in burdening himself with.
So, it is not just plucking outlandish plans out of the ether. That would be idiotic and Mullins is no idiot. He is not unaware that he might be doing something others would not consider however, and when he delivers with an apparently off-kilter plot, he most definitely gets a kick out of it.
Examples of eschewing custom? Landing a listed three-year-old fillies’ hurdle race in Auteuil in 2019 with Fujimoto Flyer, acquired as a yearling on a trip to Japan two years previously. Scoring in a Grade 2 three-year-old hurdle race at the same venue last year with McTigue.
Winning a Grade 1 novice chase at Punchestown last April with Feronily, a horse having his second ever run over fences, just a month after shedding his maiden hurdle status, having been given his debut over both national hunt disciplines at graded level. That elite Punchestown triumph was less than five months removed from the Getaway gelding winning a point-to-point on his first ever public appearance at Rathcannon.
How about preparing ten-year-old The Shunter to bag the £103,080 first prize in the Cesarewitch at Newmarket last October? In March 2021, the same horse plundered a £100,000 bonus on offer for any winner of the Morebattle Hurdle that subsequently won at the Cheltenham Festival, doing so over fences in the Plate.
And then there’s capturing the Grand National with Noble Yeats in 2022, the first seven-year-old to be victorious in the Aintree feature since Bogskar, 82 years previously. And that came just 14 months after running in a bumper, 13 from obliging in his maiden hurdle.
For the most part, these aren’t campaigns his uncle Willie would consider and he is the most successful trainer in jumps racing. That said, when it comes to campaigning internationally at least, Willie has been all over the world and taken a punt in places like Nakayama and Merrano, and his own father Paddy (Emmet’s grandfather) did it before him, winning the $750,000 Grabel International Hurdle at Dueling Grounds – now Kentucky Downs – in 1990.
So there is a bit of nature in the ambition, the refusal to be hemmed in by the norm. He’s even had a runner in an Irish Derby, legging up Rachael Blackmore on King Of The Throne in 2020. But certainly, he has taken pioneering thinking to another level. It is his oeuvre. It takes a lot of confidence but the self-assurance is well placed. The CV tells us the methods produce results at a sustained and very exalted level.
For all that, and despite an average strike rate of around one in five over jumps in Ireland since he began in 2015, 28% over jumps in Britain over the same period (four from six at the time of writing this season alone) and a career high eight winners on the flat in Ireland this year (15% SR). Success for the Closutton 34-year-old – his 30 boxes are located at the HQ of his father, George’s equine transport business and next door to the gallops used by Uncle Willie to condition his legion of champions –is primarily about getting horses sold.
Sometimes they stay in the yard, which is the case if JP McManus gets involved as he has done on a number of occasions with The Shunter, Filey Bay, So Scottish, Corbett’s Cross and Feronily, and with Noble Yeats after the Waley-Cohens acquired the subsequent Grand National hero.
Most of them don’t though, particularly the flat horses, with a global market. Of the jumpers, McTigue is one of the more recent to have been bought to race in America.
In an interview in last year’s Irish Racing Yearbook, Mullins said he wasn’t good enough to be a jockey, even though he was a Cheltenham Festival winner in the Martin Pipe Conditional Jockeys’ Hurdle on Sir Des Champs for Willie in 2011.
He won a graded novice chase on the same horse at Limerick the following December and then two years later at the same meeting, was entrusted with the responsibility of steering Faugheen around in a graded novice hurdle. But he couldn’t see himself having enough of those sorts of days.
“I didn’t want to be mediocre. Move on to the next thing and do better,” he explained in that feature.
So he retired at 24, just as his younger cousin David did, having won a Grand National as a teenager. They know their own minds, the Mullins boys.
That independent streak is evident in his second career. Being given the responsibility by Willie of travelling with Blackstairmountain to Japan and overseeing the eight-year-old’s preparations prior to landing the valuable Nakayama Grand Jump planted the seed for training, as well as leaving a very positive impression of racing in the land of the rising sun.
He knew he wasn’t going to be champion trainer but given his disinterest in being a journeyman, resolved to operate commercially and improve the quality while he could.
Making money on a horse is success in his eyes, as evidenced when in the aforementioned Irish Racing Yearbook feature, he posited that saddling a two-year-old to score in an auction maiden on the flat at Gowran Park was arguably his most important winner of a year that also included Noble Yeats’ Liverpool romp.
“Grand National prize money wouldn’t get you a deposit on a house,” he reasoned, referring to the filly’s subsequent sale.
Asked now to sum up his model, he uses one word initially.
“Flexible.”
That, as they say, is an understatement.
“It was always to buy and to sell. Try and advertise your horse and sell it on for a profit. You’ve a lot of advantages with the surname Mullins but there’s a downfall with the selling part. I think most of the market would feel if Willie doesn’t buy it, it’s no good. That’s a drawback. It’s tricky.”
But it’s gone well. He would like to retain the calibre of horse, but it is not at the top of the list.
“I want the quality of the horses to be as high as possible but I don’t think I’ll ever go down the road of too many horses. I’m happy enough with the workload that I have. I went to Kentucky in September and October for the guts of five or six days each time, which you could never do if you had too many horses. There’s a good team at home but the bigger you get, no matter what systems you have in place, the more diluted it gets, I feel.”
As for being hands-on, he says: “I like to know, but I like to delegate. If I’ve all the right information I can make the decisions.”
He only rides work now when they are short of bodies, but is fortunate to have eight full-time staff, while his number one jockey, Donagh Meyler arrives three times a week.
He has just resurfaced a five-furlong gallop he had installed originally in 2018, and describes his method of conditioning as interval training.
“All I know really is Willie outside the back door of our house. It’s all I’ve seen and it’s a good model to be working on.”
While the conditioning, fitness and schooling aspects are imperatives, they are useless without the raw material and it is here that Mullins seems to really deliver at an incredible level for a small-scale operation. He is very clear about what he is looking for when making acquisitions.
“When it comes to horses in training, it’s when they hit the line. There’s nothing worse than something tying up that might fall across the line and hold on to win. I would definitely be waiting for the horse in third that was too far back and flew home and ran through the line. I’d value him more than the horse that actually won but the market might consider the winner the best horse. There are plenty of different factors gone into where each horse was but horses that run through the line, there’s another day in them.
“With unraced horses, I suppose it’s a lucky dip but if they can’t walk, they can’t gallop. It’s all about the action. When you’re looking at horses that ran, the page is 90% irrelevant because they’ve either outrun their page or underrun it and there’s probably more underrun their page than outrun it. Once there’s black and white form, the page drops way down the list. But with unraced horses, it’s one of your only markers. You’ve got your conformation and pedigree and you haven’t much else to go on.”
Paul Byrne is a key investor, a friend of cousin Patrick (son of Willie), who clearly liked what Emmet Mullins was doing and whose light blue colours have become very recognisable on the likes of Feronily, Corbett’s Cross and The Shunter prior to their sales to McManus, as well as Slate Lane, among many others. Meyler is a key contributor too, obviously.
“We’re on the same wavelength I think,” he says of the experienced pilot. “Sometimes I mightn’t say much and I think I’ve said what needs to be said. If you’re not on the same wavelength, the jockey hasn’t got it. That’s my fault. It hasn’t been communicated the right way. With Donagh, we’re on the same wavelength and a facial expression could say as much as a word.
“McTigue in Auteuil, I walked the track with him [Meyler]. Don’t think he’d ridden there before. I’d won there with Fujimoto, had ridden there and we’d been watching Willie’s horses win there over the years. I told him how I would ride the race, and hurdle by hurdle it was just textbook, following the conversation we had the whole way around.
“Once we come out after getting the saddle, I ask him about the race. I might have my homework done but I want to see what he says first anyway. Nine times out of ten, we come up with a plan together. A few times, I throw a spanner in the works, like with Slate Lane in Haydock when I say, ‘We’re gonna make it today.’
“Donagh thought we’d be switching off as usual, down the paint, but I just thought there wasn’t much pace in the race so I said, ‘No. Line up wide. Go with them. If they’re going too hard, you can always sit in behind them. If you’re going too slow, you’ll get a freebie up front. It’s up to you to figure it out from then. I just wanted him to have those options rather than being locked in a pocket in behind if they were going too slow. But the main thing is we are on the same wavelength.”
When we speak, Slate Lane has just delivered on another target, his fourth consecutive triumph, bagging the £71,188 first prize of that premier handicap at Haydock he has referred to. It is bittersweet though as, barring a miraculous recovery from a very bad tendon injury suffered at some point during that race, he won’t compete again.
“I don’t know how he got to the line. Fifty per cent of the tendon is gone, into the tendon sheath and the big worry with that is infection. He’s in a cast now so as not to put the weight on it. The BHA vets were very good, flushed it out and gave him antibiotics on the racecourse and he went to Leahurst (Equine Hospital in Liverpool). It’s fairly certain he’ll never race again but it’s good news that he avoided the infection and saving the horse was the most important thing. With tendon sheaths it’s often 50-50 whether you’ll survive it because of the risk of infection.”
It is a reminder that even when things are going outstandingly well, in racing, above all other pursuits it seems, the leveller is just around the corner. Only the day before, Jeroboam Machin won a Fairyhouse bumper on debut. He too suffered a nasty cut on his tendon, a bigger one than suffered by Slate Lane but not as deep. It will sideline the youngster for some time and there is a double whammy in terms of a potential sale but he should hopefully return to the track at least.
Some were talking up Slate Lane as a potential Stayers’ Hurdle candidate, cognisant of Mullins’ propensity to press fast forward with his neophytes but the intention had been to stay in novice company and to see just how far up the ladder the five-year-old son of Ask could go.
He only had him six months, and though there were three underwhelming performances on the track for Paul Hennessy, the third had been an improved sixth in a two-mile Gowran Park maiden hurdle in March though that ended in disqualification when jockey Niall Prendergast weighed in incorrectly. That actually brought Mullins’ attention to him however, and when he delved a bit deeper to look at his third-place finish in a Moig South maiden point, the manner in which Slate Lane finished strongly was enough for him to press the button.
“He flew home. I know he finished third but he was the horse to buy out of the race. There were no hiccups from then. We were probably on the mark after Newton Abbot but it was 75 days out to the race. As it transpired, the race didn’t fill and he’d only have been a pound or two out off 113 but you couldn’t take that risk and you’d have been longer again out. So in between Newton Abbot and Haydock, we took in the (Corinthian Challenge) charity race at Leopardstown (which he won) to keep him ticking over. Michael O’Neill, who won on him, comes in to ride work for us a good bit.
“Haydock wasn’t mentioned until after Cartmel but first, it was Cartmel for the sticky toffee pudding. That was the big draw! As soon as he crossed the line - it was a 2m6f maiden hurdle - we said, ‘Big pot, three miles, Haydock, November’. I had a runner in it once (2021), Righplacerighttime. I tend not to forget where the money is!
“We couldn’t enter him in Irish handicaps because if you ran him in Ireland, the English handicapper has his own interpretation so we campaigned him exclusively in England over hurdles to keep on their handicap system and we wouldn’t be guessing about what rating we’d have.
“He was working well when we decided to go for the maiden hurdle. We thought he’d win and he kept improving the whole time and he had to. The same horse that won in Haydock, wouldn’t have come off the bridle in the Cartmel race and he came off it on the home bend and had to be scrubbed against a 78-rated horse. So he’s clearly improved. He wasn’t a 127-rated horse. It has been a natural progression.”
Using a charity race to keep him ticking over is unconventional, to say the least, but Mullins readily concedes that “we don’t do much normal”. The outside-the-box planning seems like genius given how often it comes off.
“You’re just looking for those niches. It was 2017 I think I went to those yearling sales in Japan... They are, I would say, on top of the world now with their system, their tiered racing, their midweek racing and their weekend racing, the prize money. It’s ten years this year since I was at the Japan Cup and the racing fraternity were like the Premier League stars. The following was phenomenal.
“I bought Fujimoto Flyer. Another foal I bought privately over there was Crowns Major (owned by long-time patron Annette Mee, who provided him with his first winner St Stephen’s Green). He won the big premier handicap at Galway (in 2021) with Wesley Joyce. Now, the third, I sold to Poland or the Czech Republic fairly quickly after but two out of three isn’t bad.”
No other trainer around would have campaigned Feronily like he did and that they picked him up for just £45,000 at Cheltenham, five days after cantering to victory under Derek O’Connor in his point-to-point was a fantastic start.
“It’s funny, on the day of the sale, I was going over thinking he was the best horse in the sale. Told the clients, ‘Couple of hundred thousand, this is the real deal.’ I hadn’t seen him but looked at the vet report on the phone, saw the video of the race but the rumour machine was going around that he had bad tendons. Two vets were after standing over him and cleared him! I spoke with Ellmarie Holden who won the point-to-point with him. They’d scanned the tendons at home, they showed me them, it was perfect.
“Paul was beside me and I says, ‘We’re buying the next one in.’ He says, ‘What is it?’ I says, ‘You’ll see when you sign for it.’ There were a few mates of his with us and I said to them, ‘Put up your hand now. We’re gone past the reserve and you’ll get him on the next one.’ One of the guys bid, so we got him. They didn’t know what was after happening. I was giggling away and Tattersalls had the buyers as Hughes, Smith and Stokes - three friends of Paul’s!
“He’d won ten lengths. He’d a big advantage going to the last. Popped it. Lost all the ground. Derek sat down on his back and he took off and went again. And you don’t go a second time unless you’ve got a big engine and he galloped through the line after losing all momentum. It was a no-brainer.”
Okay, buying him was, but you cannot tell me the subsequent course of action was obvious.
“It was Paul that wanted to go to Kelso after two good bumper runs (second to Isle Atlantique and third to A Dream To Share). He didn’t run too bad (finishing fourth) because it was a graded handicap on his first start over hurdles. We got the maiden hurdle in Limerick out of the way. I think the entries for Punchestown were closing after that and I don’t know why, but I just thought that the three-mile novice chase division was vulnerable. Stuck him in, then rang Paul and told him, ‘I might have done something crazy again.’ When the entries came out then he said, ‘That wasn’t one of your worst ideas.’
“We got the run into him in Cork (in a Grade 3 chase). We didn’t want to run in a beginner’s chase because if he won, he wasn’t a novice the following season. So you wanted it to be justifiable to lose it. If we won, well and good, if not, you had the experience. He ran very nicely in second and it was on to Punchestown from that.”
Sometimes things just fall into place. The Shunter was slated for a major staying handicap from the time he won his maiden in Sligo in May 2022.
“He wasn’t right for the Irish Cesarewitch and for luck, he went to Newmarket. The extra two weeks probably helped and it rained then as well.
“It was Paul that had spotted the bonus with the Morebattle. He had won the Greatwood already. You can’t be expecting him to be that far ahead of the handicapper to win three premier handicap hurdles so that’s why we had to take up the chase option in Cheltenham after he won the Morebattle. He probably wouldn’t have run over fences at all, he was still in a 0-116 bracket and there was a beginners’ chase at Punchestown for horses rated 116 or less over hurdles. I said to Paul we probably wouldn’t win a beginners’ chase in a month’s time when Willie and Gordon (Elliott) had their horses out and 140 horses were getting beaten in beginners’ chase. That opened that possibility for us. So it wasn’t that we were planning hurdles and fences with the Morebattle and Cheltenham. With that one, it just panned out that we had somehow done the right thing.
“He’ll get a break now and maybe come back for the Chester Cup. He’s an older horse, he’s had plenty of issues and I’d say his jumping days might be behind him.”
Corbett’s Cross is moving the right way and a return for one of the Grade 1 novice chases at Cheltenham is a more straightforward plan.
Noble Yeats is likely to miss the Gold Cup this time around, having finished fourth last year before filling the same position in his bid to go back-to-back in the National.
“I think we found a little race for him to start back over hurdles at Christmas. It’ll be a start. He had a tough year last year. Gold Cup, Grand National, Grand Steep de Paris. He had an extended break and didn’t come back to me till the first of October. At the moment it’s the National. I don’t think we can do both. He won’t be helped by being so consistent in his races, with his handicap mark and plenty of weight but as they say, horses for courses and he definitely has Aintree sussed.
“He’s a funny horse in that he needs a hood or ear plugs for the preliminaries, but when he’s going he needs cheekpieces. There’s no other horse you’d do it with. It’s just figuring them out.”
Just another element of the job Emmet Mullins seems to be very good at.
Topspec Trainer of the Quarter - Mick Appleby
Article by Lissa Oliver
It wasn’t hard to single out Mick Appleby for our quarterly award, given such top-level international success in such a short space of time, leaving the yard “buzzing”, as Appleby says. With 105 boxes, The Homestead stables in Rutland, Leicestershire, is hardly a “small” stable, and Appleby is renowned for his All-Weather success, having been Champion Trainer for six years. But Group One successes on such an international scale are taking the team to new heights.
“Big Evs’ win at the Breeders’ Cup has been a great boost to the team and there’s a huge buzz around the yard,” says Appleby, “it’s good for all the team, they work so hard all year round.” Just to emphasise that, team-member Madan Singh has just reached the six Finalists for the prestigious Thoroughbred Industry Employee Awards, sponsored by Godolphin, in the Rider/Groom category.
Add to Big Evs’ grand end-of-season finale the success of Roberto Escobarr in the Premio St Leger Italiano, on his first run for the Appleby stable, and the final months of 2023 really have been quite a purple-patch for Appleby, who isn’t afraid of taking horses abroad for better prize money.
With over 30-years’ experience in racing, Appleby has gone from such roles as stable jockey to John Manners, head lad to Roger Curtis and Andrew Balding, to taking out his own licence in 2010. In 2014, he trained his first Group winner when Danzeno won the Grade 3 Chip Chase at Newcastle.
The yard is set in 80 acres of Rutland countryside, with 20 paddocks and 40 acres of summer turnout fields. Appleby has also added schooling fences, hurdles and cross-country jumps around the fields and is working on re-opening an historic bridleway to allow further access for hacks across road-free countryside. Together with an undulating one-mile all-weather gallop, he has a five-furlong (1000m) oval gallop and a seven-furlong (1400m) straight grass gallop; with a solarium and a theraplate installed to allow different training regimes.
Appleby describes Big Evs’ run-up to the Breeders’ Cup as, “pretty straightforward, really. We didn’t do anything different with him, but we did use the bell for him to practise coming out of the stalls. We borrowed that from Adam West! But, to be fair, I don’t think it made any difference. He was absolutely grand, he took the travelling all in his stride and the experience didn’t faze him at all. Big Evs is on his holiday now, but he’ll be back for all the big 5f (1000m) races next year.”
Roberto Escobarr had only been bought by the yard in July, so the Premio St Leger Italiano hadn’t really been a target, Appleby says. “We saw that race and thought it might be good for him and luckily it all worked out well. He might go to Dubai now and, long-term, we might even think about the Melbourne Cup next year.”
Group One glory hasn’t changed anything at The Homestead. “It’s business as usual. Hopefully we might get offered more two-year-olds on the back of Big Evs,” Appleby hopes. “I’d just like to thank everyone for all their support and for all the congratulations that poured in for Big Evs, it was overwhelming really, and great for the staff who work hard all year round.”
Steps to take in order to prevent respiratory disease after a poor harvest
Article by Alan Creighton (Head of environment and nutrition at the Irish Equine Centre)
I don’t want to sound alarmist because I am generally a very positive person, but I have no doubt that there will be an increase in racehorse respiratory issues this winter and next spring due to a combination of poor hay and straw harvests in conjunction with a very damp autumn.
Through our everyday testing at the Irish Equine Centre we have already seen higher than average fungal contaminated hay, haylage and straw submitted for testing this autumn. Our routine monitoring of racing yard environments in Ireland, the UK and France are also showing increases in fungal contamination in air samples and surface swabs taken throughout the yards. The damp weather conditions from the second week of June right through the summer in western Europe resulted in fields of grass and cereal crops which were showing major signs of fungal contamination while still standing in the field.
It didn’t get much better when the dry spells came in early September. Land was already saturated which meant the crops once mowed were extremely difficult to dry which has resulted in discoloured, dusty, high moisture straw, many hay stacks which heated and oats with high moisture content. Even haylage, which is the normal go to method of preserving forage when conditions are poor has shown much higher levels of contamination thus far. Damp weather in this period also meant that stables themselves were often damp which encouraged fungal growth on the internal surfaces.
Racehorses are athletes that need a fully functioning respiratory system to maximise performance. IAD, COPD, RAO (all forms of equine asthma) and EIPH (bleeding) are respiratory conditions which are major causes of poor performance in racehorses. Fungi and mycotoxins are now recognised as a major cause of these conditions and in particular the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus being the main culprit.
Fungi that penetrate the airways can cause unwanted inflammation and can be infective, toxic, allergenic or all 3 combined. The further the distance a racehorse is asked to race, the more detrimental this inflammation will be to performance. The main sources of this fungus are in hay, haylage, straw and oats.
This fungus is a storage fungus and so it propagates in stored foodstuffs overtime where the moisture level is above 14%. When the fungus contaminates a foodstuff or bedding the horse has no choice but to breathe in the harmful spores in their stable environment. The fungus also causes a level of immunosuppression which can often be the precursor to secondary bacterial and viral disease.
The cost of bedding for racehorses has been steadily rising over the last number of years. Wood shavings have become very expensive to buy but are now also very expensive to dispose of. Straw is still more cost effective to buy and much more cost effective to dispose of.
I will often get asked the question “what is the best bedding for horses?” - my answer is consistently “good straw”. When I get asked the question “what is the worst bedding for horses?” my answer is consistently “bad straw”. The cost saving in purchasing and disposing of straw has made it attractive to trainers in a time when all other costs are rising. Finding good straw this year will be very difficult.
In many countries in Europe, we have a government policy called SIM, the Straw Incorporation Measure which is a payment for chopping straw and incorporating it into the soil. SIM has been designed to encourage tillage farmers to increase soil organic carbon levels by chopping and incorporating straw from cereal crops and oilseed rape.
Unfortunately, an unintended consequence of that policy is the reduction in availability of straw for bedding purposes. This is particularly problematic this year because now we have a shortage of straw and the straw which is available for bedding has much higher levels of harmful moulds due to the poor harvest conditions.
When feeding haylage, the spoilage process can begin quickly if the bale is exposed to air, this may be due to damage of the wrapping or not using the bale quick enough once opened. Fungal spores will develop and this should be carefully assessed before feeding. This is a major problem we encounter on a regular basis. Often trainers are feeding big bales of haylage to a small number of horses which means the bales are exposed to air for a prolonged period of time.
Pathogenic fungi will develop very quickly and often lead to both respiratory and gastric problems. For that reason, the IEC will recommend to use haylage once opened inside of 4 days in the winter and 3 days in the summer. This recommendation will often determine the choice between hay and haylage as you would therefore need to be feeding a larger number of horses to feed large bale haylage.
Hay production requires 7-10 days of continuous good weather unless you are barn drying. In Ireland and the UK we got a two week spell of suitable weather in the last week of May until the end of the first week of June. Many meadows were not ready, and the ones that needed patience from the farmer not to bale too early as hay at that time of the year is very difficult to dry properly due to the lushness of the grass.
Having said all that, the best hay of this season was made in that period. That was the only spell until a two week spell in September. Historically, the best hay in western Europe is made from the middle of June to the end of July. That was not possible this season. The hay made in that early spell is very good in terms of quality but very poor in terms of volume. The hay made in the second spell in September was very high in volume but very poor in terms of quality. The nutrition levels of this September hay is also poor and the fungal levels are very high.
At the Irish Equine centre we analyse thousands of samples of hay, haylage, chaffs, straw and oats every year for both hygiene (mould and bacteria levels) and nutritional content. The reality is that in a normal year with good spells of weather we still get both hay and haylage with extremely good nutritional and hygiene values and we get hay and haylage with very poor nutritional and hygiene values.
This year the percentage of poor is outweighing the percentage of good. Normally we would advise that trainers should produce or purchase enough of the same batch of quality forage for the whole season. That may not be possible this year. It is our experience from testing forage that getting haylage with consistent nutritional values can be very difficult even in a good year. This is mainly due to the variants in moisture content which will certainly be the case this season. Hay which is well made and stored well does tend to be much more consistent and therefore better for overall horse health.
Both hay and haylage are prone to fungal contamination in different ways. With haylage the fungal contamination occurs as a result of inadequate fermentation or when air pockets or punctures occur in the plastic.
Fungal problems in hay occur because of high moisture levels during the baling process and because of inadequate storage during winter months. We have shown in the past that those fungal problems are compounded and elevated since farmers have moved away from the traditional small bale and moved to large round and rectangular bales. Farmers who traditionally barn dry small square bales, who ensure that hay is dried below 14% moisture and then covered (a layer of clean bales of straw) in storage remains the most hygienic hay for racehorses.
During storage the moisture level on the outside of uncovered bales significantly increases over damp winter months, leading to a significant increase in fungal growth. Round bales suffer the worst during storage. Hay in large bales needs to have a very low moisture level when baling, which just wasn’t possible in most cases this year when field drying.
When this type of bale has a high moisture level in the centre of the bale it results in significant increases of pathogenic fungi contamination during storage. We have shown through studies that keeping the moisture level of hay below 14% moisture will significantly reduce Aspergillus contamination. It was very difficult to achieve this moisture reduction this summer and often farmers had no choice but to treat the hay with buffered propionic acid which is an effective preservation method which reduces fungal growth during the early stages of storage but its effect diminishes over time.
Good quality tested hay is still the most beneficial to horses when all factors are taken into account. Once purchased hay should be stored properly by the supplier to ensure that it remains consistent. The hay supplier should ideally guarantee the trainer a supply of hay which is consistent for the whole season rather than swapping and changing batches constantly.
All hay should be covered from the end of September once the moisture content has stabilised to protect it from damp air during winter months. Trainers with inadequate storage may have no choice than to feed haylage. If this is the case, buy the right size of bales for the amount of horses you are feeding.
Steaming of hay in the correct manner can be a very useful process to reduce the fungal load in contaminated hay. Some producers of hay harvested very early this year to take advantage of that good weather spell. First crop hay when harvested early can be difficult to save and can have a very high protein content. That high protein is good if you test it to quantify the actual protein content and you then balance your feeds accordingly.
If high protein hay or haylage is used and feeds are not adjusted accordingly it can overload the digestive system with nitrogen. Excess of protein will also lead to an over production of urea, leading to an excess of ammonia emissions in the stable which can also cause respiratory irritation.
So, what is the advice from the IEC? Trainers will need to test their hay and haylage at multiple stages during their season as the dangerous fungi will develop over time. The volume of suitable forage and bedding will be low, so trainers should act quickly to secure the best that’s available.
The nutrition department at the IEC provides full nutritional and hygiene testing for hay, haylage, straw and oats. It is vital that you test forage pre-purchase when trying to buy a season's supply. Hay, haylage or bedding contaminated with pathogenic fungi will cause respiratory disease which will affect racehorse performance.
For that reason, the cost of testing forage is a small price to pay rather than losing significant portions of the season due to poor performance as a result of respiratory disease. How you store and feed hay, haylage, and oats will have a huge impact on the level of exposure your animals will have to harmful moulds. Stable hygiene and ventilation will be even more critically important when the risk of contaminated inputs is so high.
To conclude, trainers should always acquire the best possible forage and bedding available and test it prior to purchase. You can and should inspect and test any batch of hay or bedding properly prior to delivery. You can take a representative sample for the testing lab which can then be the deciding factor for your purchase. When taking a sample, take a fistful from 6-8 different bales in the stack to ensure you get a representative sample.
We monitor the stable environments of over 200 racing yards in Ireland, the UK, France and in the Middle East. That monitoring includes hygiene sampling of feed, forage, bedding, water, stable surfaces, walker surfaces and air quality in barns. The benefits of that monitoring for the trainer is that you highlight issues which can cause respiratory disease, proactively prevent disease problems and finally have a mechanism which quantifies the effectiveness of stable disinfection routines.
The most consistent trainers in terms of performance have good hygiene practices. If anybody would like to discuss the above issues or need help with assessing the quality of forage and bedding in use, please contact myself or any of my team at nutrition@irishequinecentre.ie and we would be glad to help.
“It’s a struggle…” The mental wellbeing of trainers and how to support them.
Article by Rupert Arnold
Training racehorses is a stressful occupation. There’s nothing wrong with that - until there is. In today’s world, mental health is front of stage in conversations about occupational health. Though horse racing might often appear to lag behind more progressive parts of society, attention is increasingly being focused on its participants’ capacity to withstand the stresses of a busy, challenging life where performance is in the public eye.
In Britain and Ireland, jockeys have been the first sector to benefit from support structures instigated by their trade associations and governing bodies. They have been encouraged to speak publicly about the causes of depression, anxiety and substance dependence, and in this way have begun to erode the stigma that stifles potentially healing conversations. A pathway has been opened for trainers to follow.
Three racing nations have spearheaded the research on trainers’ mental health. The first studies were conducted in Australia in 2008 by Speed and Anderson on behalf of Racing Victoria. It’s findings that “two-thirds of trainers never or rarely had one day off per week”, and “Trainers also face increased pressure from owners (e.g. pressure to win competitive races), shoulder the burden of responsibility for keeping horses healthy and sound, as well as financial difficulties” will strike a chord with trainers across all racing jurisdictions and sets the precedent for other research.
In July 2018, again in Australia, research on “Sleep and psychological wellbeing of racehorse industry workers” surveyed Australian trainers and found “Trainers reported significantly higher depression and anxiety scores compared with other racing industry workers, racehorse owners, and the general population. They had less sleeping hours and higher daytime dysfunction due to fatigue.”
Simone Seer’s University of Liverpool MBA dissertation of September 2018 “Occupational Stressors for Racehorse Trainers in Great Britain and their Impact on Health and Wellbeing” (supported by Racing Welfare) used qualitative research via unstructured interviews from which themes were analysed to identify patterns and differences between trainers’ experiences.
“Examples included business and finance worries, bureaucracy, the rules of racing, the fixture list, a lack of resources and busy work schedules, managing stressful episodes with racehorse owners and staff and in balancing emotions. The most dominant stressors were those that were felt to be out of a participant’s control and particularly related to racehorses: keeping horses healthy, free from injury, disease and illness, and the pressure to perform in relation to both the participant and their horses…participants were found to be engaged in intensive emotional labour combined with long work hours and busy schedules resulting in a ‘time famine’. All participants had experienced abusive messages by voicemail, email or social media.
“Participants reported mental ill health symptoms brought on by emotional toll, sleep deprivation, insomnia and isolation resulting in outcomes such as low self-esteem, depression, anxiety, low confidence and recurrent headaches.”
In 2021, following the watershed of the Covid-19 pandemic, research on Irish racehorse trainers by King et al published in the Journal of Equine Veterinary Science examined the “prevalence and risk factors” associated with racehorse trainer mental health. Among their headline findings were some familiar features:
“A prevalence of symptoms associated with common mental disorders was identified. Specifically, depression (41%), adverse alcohol use (38%), psychological distress (26%), and generalised anxiety (18%).
“Career dissatisfaction, financial difficulties, and lower levels of social support increased the likelihood of meeting the criteria for depression, psychological distress and generalised anxiety.”
As Ryan McElligott, Chief Executive of the Irish Racehorse Trainers Association, says: “Training is a tough business. Even the top trainers lose more often than they win. It’s extra competitive so fear keeps training fees down while costs are increasing…it’s a struggle.”
Away from the published science-based research, we must rely on anecdotes to get a picture of the experience of trainers in other European countries.
Perhaps surprisingly, no studies are available on the situation in France. Gavin Hernon, who represents the Association des Entraineur de Galop (AEDG) at the European Trainers Federation (ETF), suggests this may be because France Galop sees itself primarily as a regulator so wouldn’t include trainers’ health and well-being in its remit.
Gavin reports that trainers in France share the same pressures as colleagues in other countries. He says, “A major factor is the high financial cost of doing business. Well-funded prize money may cast a rosy glow across the sport, but this leads to trainers relying on their percentage to make a profit. It also gives them an incentive to own more horses than is the case in other countries. The combination becomes toxic if the horses are not winning, creating a culture of performance anxiety.”
According to Gavin, a common response to the occupational pressure is for trainers to shut themselves away and bottle up their true feelings. This belief is endorsed by Tom Luhnenschloss, the ETF representative in Norway. “Trainers are living in a bubble”, he explains. “Trainers have a certain mentality. Their life is very repetitive, they put their heads down and carry on, without sharing their problems. There are a lot of hidden issues.”
In the smallest racing nations, the subject of trainers’ mental health may not be enough of a priority for specific attention. Karin Lutmanova in the Czech Republic points out “The problem definitely exists, but I do not think anybody has capacity to care about it. Our racing has so many other crucial and elementary problems such as funding, closure of the main thoroughbred stud, and a decrease of racehorses and racing days.”
So there is a consensus that racehorse trainers are susceptible to particular forms of mental health conditions. The obvious follow-up question is, what can be done to support trainers facing these conditions?
At first glance, there seems to be a gap in racing’s provision for trainers. On governing body and charity websites it isn’t difficult to track down welfare/wellbeing support for jockeys and stable staff, less so for trainers. As Tom Lunhenschloss observed, “There is no one to catch you when you fall.” However, further investigation reveals that initiatives are underway.
From a European perspective, Britain and Ireland are adopting slightly different approaches.
Having contributed extensively to the research in Britain, the National Trainers Federation was keen to collaborate with Racing Welfare, the Jockey Club charity that aims to support the workforce of British racing and backed the research. Simone Sear’s paper concluded that “a bespoke, confidential service should be designed in order to support this workforce to gain insight and build resilience… and will need to provide support across a range of issues such as mental health, physical health, sports psychology, business management, HR and legal advice, financial assistance and time management.”
An informal arrangement between Racing Welfare and the NTF began in 2020 with referrals being made via both parties to Michael Caulfield, a sports psychologist with deep connections to horseracing through a previous role heading the Professional Jockeys Association. Racing Welfare also set up the Leaders Line, a centralised structure for supporting people in management positions. Neither of these initiatives achieved a breakthrough in terms of reach and recognition.
Drawing on Racing Foundation-funded research by Dan Martin at the Liverpool John Moores University, the NTF, through its charity Racehorse Trainers Benevolent Fund (RTBF), began working on a different approach inspired by Dan’s recommendation:
“Create a trainer-specific referral system, exclusive to trainers and separate from Racing Welfare, for mental health support. Given the multiple roles of the racehorse trainer, the support should provide organisational psychology, sports psychology, counselling, and clinical support. Former trainers should be considered to receive training to provide some of this support.”
The twist is that instead of building something and expecting the people to come, the RTBF model was about outreach – creating a network of knowledgeable and empathetic people to be visible in the trainer community, starting the conversations that trainers, by their own admission, were unlikely to reach out for on their own.
Michael Caulfield and David Arbuthnot, whose career as a trainer spanned 38 years and who later undertook counselling qualifications through the NTF Charitable Trust, were recruited to go out and about, chatting to trainers in the Lambourn training centre and surrounding area and at race meetings and bloodstock sales.
Harry Dunlop, a former trainer and recently recruited trustee of the RTBF, explains, “It’s well known that however serious the problem, taking that first step to ask for support with a mental health issue is hard to take. People are afraid to show what they perceive as weakness. By getting Caulfield and Arbuthnot into the places where trainers circulate in their daily working lives, we hope to break down barriers and give trainers a chance to share their problems. That might be all it takes to lighten the load. Or it might lead to scheduling a one-to-one at another time.”
Set up as a six-month pilot from July 2023, this initiative has already expanded to Yorkshire in the North and Newmarket, with trainers Jo Foster and Chris Wall respectively providing the support. Initial response from trainers was amused scepticism but this proved to be a superficial reaction. Very quickly, on a private and confidential basis, trainers have begun opening up to members of the support team. One-to-one sessions were scheduled. Trainers who admitted to putting off seeking help, contacted one of the team for a conversation. Thankfully, there has not been a rush of acute cases of serious mental health pathology. But there is clear evidence that “Trainers just want someone to talk to” as Michael Caulfield describes it. It’s worth noting that Caulfield warns against medicalising all the mental health conditions experienced by trainers. “There is a world of difference between a clinical mental illness such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, and being overwhelmed by the weight of responsibility and/or despair brought on by sheer exhaustion. Most of the time people need an outlet to vent their worries, and more sleep.”
The need for someone familiar to lend a friendly ear is confirmed by Ryan McElligott. “Trainers are a traditional cohort; they have rather conservative values. They don't like to admit they are in trouble; they worry that it's a sign of weakness. It's a close-knit community so generally the first call for help would be to people close to them.” McElligott says the Irish trainers are fortunate to have two sources of support – the Industry Assistance Programme, which gives access to counselling and therapy; and the availability of Jennifer Pugh, the Senior Medical Officer for the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board. He describes her as “a prominent presence” at race meetings, and clearly trainers feel able to communicate with her.
Pugh contributed to the “prevalence and risk factor” paper mentioned above. She points out that with a background as an amateur rider, coming from a training family, and having worked as a racecourse doctor, she was already a recognisable person before taking on her present official role. The need for access to trusted figures appears to be a common factor in effective mechanisms of support.
The Industry Assistance Programme sits under the umbrella of Horse Racing Ireland’s EQUUIP service, described as ‘The People Behind the People’ in the Irish Horse Racing & Breeding Industry. One of its three offers is “health and wellbeing services for everyone who wants it.” As the British experience shows, encouraging trainers to make use of the formalised support system is not straightforward. Though predating EQUUIP’s creation, the Irish research indicated that “only a fifth of trainers had sought support for their personal and emotional problems.”
For this reason, Pugh endorses the social support approach. She says there is a plan to recruit wellbeing “champions” for people to approach out in the community. And having learned much more about trainers’ mental health through the strong communications established to manage racing’s response to the Covid pandemic, a programme of support is being worked on so that trainers’ needs are given the same importance as for jockeys and stable staff.
For a major racing nation comparatively rich in resources, some recognition of the psychological challenges facing trainers might be expected in France. After all, on its website France Galop lists “Ensuring the health of its professionals” in its responsibilities. It goes on to refer only to jockeys and stable staff. Other than redirecting fines levied on trainers under the disciplinary system towards support for retired trainers, France Galop makes no provision for the welfare of trainers. Furthermore, unlike Britain and Ireland, France Galop does not employ an official medical adviser, preferring to provide a list of authorised doctors. That said, this is a new policy area for everyone; France Galop is generally a first mover when it comes to policy initiatives so it can’t be long before a collaboration with the AEDG emerges.
This article has focussed on what we know about trainers’ mental health and ways to help them deal with the impact. What it does not address is the strategic question, how could the sport, the trainer’s business model and – as importantly – trainers’ professional development be structured differently to minimise the risks to trainers’ mental health and therefore reduce the need for intervention when things fall apart?
The role of the lymphatic system in energy metabolism
Article by Peter Bollen, head nutritionist Cavalor
In recent years, focus has turned towards the emerging science of the lymphatic system. It is as important as the circulatory system (which includes the heart and the blood vessels), and is fundamental to the functioning of the body and central to the immune system, energy metabolism, detoxification and energy availability in the horse’s body.
A horse with a well-functioning lymphatic system can metabolise energy and clear metabolic waste more efficiently, leading to enhanced performance and faster recovery.
So how can we tap into the benefits of an effective lymphatic system? Well, the first step is in understanding what it is. We might know that nutrients and oxygen are carried in the bloodstream towards our tissues, but what about how they are actually delivered to the cells?
This is where the lymphatic system comes in. Broadly speaking, it runs in parallel to the circulatory system and creates the point of delivery to the cells and tissues. The circulatory system carries the blood via arteries and vessels, which get smaller as they reach the muscle tissue as capillaries - where the wall is only one cell thick.
This enables smaller molecules such as nutrients and oxygen to be pushed out of the capillaries and into the fluid around the cells - or lymph - while retaining larger cells like erythrocytes (red blood cells).
The lymphatic system is an extensive network of vessels and nodes that transports lymphatic fluid around the body and it has two main functions:
1. Energy metabolism - transporting nutrients and oxygen to the cells
All the cells and tissues of a horse’s body are surrounded by a watery gel-like substance called interstitial fluid. This provides a medium for dissolved oxygen and nutrients to travel across to the cells. Lymph capillaries, carrying these substances, run through the interstitial fluid. The walls of these capillaries are also only one cell thick and have overlapping junctions, which make them highly permeable and allow easy transfer of materials.
In practical terms, this means the horse’s muscles and tissues get all the energy they require to carry out all their metabolic processes. As well as being responsible for giving cells the oxygen and nutrients they need, the interstitial fluid transports salts, hormones, neurotransmitters, coenzymes, amino acids, sugars and fatty acids around the body via the lymphatic system.
“A horse with a well-functioning lymphatic system can benefit from increased energy and enhanced performance, but without feeling too fresh or fizzy”
2. Detoxification: processing waste products
During the season, horses are placed under physiological demands and their body has a lot to process. In hard exercise and in races, their body will produce a lot of waste products. Their thin-walled lymph vessels also allow interstitial fluid into them to remove the waste products of cell metabolism (such as cell debris, bacteria, dead blood cells, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid and protein molecules) from each cell. This process is just as important as carrying necessary materials to the tissues to provide energy.
These metabolic waste products are carried in the lymph away from the cells for detoxification. This is the term used for the continuous processes in the horse’s body to remove those waste products or metabolites that are naturally produced.
Detoxification takes place mainly in the liver, kidneys and intestines, so it is really important to ensure that those organs in the horse are healthy and functioning well. By supporting the liver and kidneys, you can help this breakdown process and allow the horse to better metabolise compounds that would otherwise be toxic if they remained in the body.
Gut health is also very important to the lymphatic system and detoxification, given that more than half of the lymphatic vessels of the horse are located within the gastrointestinal tract.
Peristalsis (the natural contraction and relaxation of the gut wall) drives the return of lymph to the rest of the body. Movement in the gut is stimulated by food consumption (mainly long fibres) and is crucial to lymphatic system function as there is very limited muscular contraction in the horse’s lymphatic vessels themselves. This means it relies on passive forces from movement of other systems in the horse’s body as opposed to active muscle contractions.
Ensuring sufficient feed for a horse around the clock is crucial, not only for maintaining gut health, but to maintain a healthy immune system and detoxification process as well.
Lymphatic system and immune function
In addition to lymph and lymph vessels, the horse has around 8000 lymph nodes. These bundles of lymphoid tissue and proteins act as a filter for foreign substances that travel through the lymphatic fluid and contain lymphocytes (white blood cells) that help the body fight infection and disease. This means that the lymphatic system is also key to the functioning of the immune system.
As the lymph tissue approaches each lymph node, it slows down and collects in that area. Horses have so many lymph nodes that they are extremely susceptible to lymph node blockage. Lymph nodes can actually be felt or sometimes seen at various points around the horse’s body, particularly around the head and neck or when they are swollen.
Keep on moving
Movement is so important for horses, precisely because of the fact that there are no direct muscular contractions within the walls of the lymph vessels to promote the flow of lymph. The functioning of their lymphatic system relies on the force of movement of other structures in the body, such as the movement of the skin to apply pressure to the underlying tissues and stimulate the transport of lymph through the vessels.
In the modern day, racehorses can be stabled for longer periods of time. It is very common to see leg swelling, which has a very simple explanation in terms of the immune system. This principle of continuous movement being necessary applies especially to the legs, where this elastic movement of the skin is assisted by a pump mechanism in the hoof and fetlock joint. It is thought that this is the case due to there being no muscles in the lower limbs of the horse to aid the movement of lymph from this area.
Horses therefore need to move extensively and perhaps almost constantly (up to 16 hours per day) to keep the lymph circulating around the body, and standing still for too long significantly impairs the functioning of the lymphatic system.
Practical tips for a healthy lymphatic system
1. Turn horses out as much as possible
Horses that are standing still for long periods of time are at risk of an impaired lymphatic system, which can impact the immune system, recovery time and ultimately performance. Turnout makes a happier horse and a healthier horse.
2. Cool down for at least 15 minutes after exercise
The period of time immediately after training is important for removal of metabolic waste products and keeping a horse moving after a hard training session stimulates the lymphatic system to continue to remove waste products from cells, which includes the removal of lactic acid. By cooling down properly after every session, you can significantly improve recovery times.
3. Consider feeding supplements that can directly benefit the lymphatic system
Functional herbal ingredients in innovative supplements can support lymphatic system function. Cleavers (Galium aparine) is known to bring benefits to the lymphatic system. Couch grass (Elymus repens), Nettle (Urtica dioica), and Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) are all known to have purifying effects which can support metabolism and detoxification.
Even Lionel Messi, Usain Bolt or Iga Swiatek have picked up issues through their sporting careers, despite having elite support teams behind them. Unfortunately injuries do just happen, but with foresight, preparation and providing the best nutritional support to their horses, trainers will give themselves the greatest chance of avoiding yet another bad news phone call to an owner.
What we learnt at the first carbon-neutral horseracing industry conference
Article by Rhianydd Lee-Jones
Delegates from across the racing industry attended the first carbon-neutral Horseracing Industry Conference at York Racecourse on Tuesday, October 24.
Over 250 delegates from across the industry registered for the event: from racecourse representatives to racehorse trainers, funders to charities and racing schools to suppliers. The cross-section of British racing and the wider sporting landscape attendees engaged with keynote talks from specialists and experts from within and outside of the sport.
When developing the agenda for this year’s conference, the Racing Foundation and University of Liverpool Management School did so with the belief that in order to discuss the future of the sport, it was imperative to engage younger audiences and make their voices heard. Each agenda item featured a ‘next generation panellist’ who represented the next generation of racing's fan base and workforce. Complimentary delegate tickets were offered to under 25-year-olds to encourage engagement and debate with the challenges and opportunities discussed at the conference.
Environmental sustainability was embedded into the conference this year not only through its inclusion on the agenda, but by its sustainable practices. The conference used reusable signage, encouraged delegates to travel by train, collected carbon data and used a digital-only brochure. Lanyards made from recycled bottles replaced traditional plastic name badges. A lunch using produce from Yorkshire was served as the Racing Foundation and University of Liverpool Management School addressed all aspects of environmental impact in delivering the event. The carbon used will be offset using an approved scheme.
Senior Independent Director and Chair of the Commercial Committee David Jones kicked off the conference with the keynote address, offering a commercial view of the forthcoming industry strategy and stressing the importance of significant innovation through collaboration.
The Racing Product agenda item commenced with Racing League founder Jeremy Wray discussing the importance of trying new ideas within the sport of racing and calling for more data and more technology to capture the next generation of racing fans. He said that while we haven’t managed to engage millennials or Gen Z with the sport yet, there is hope and time to win them back. Wray cited ITV’s new six-part primetime docuseries, that focuses on jump racing, as crucial to address racing’s “massive existential crisis.”
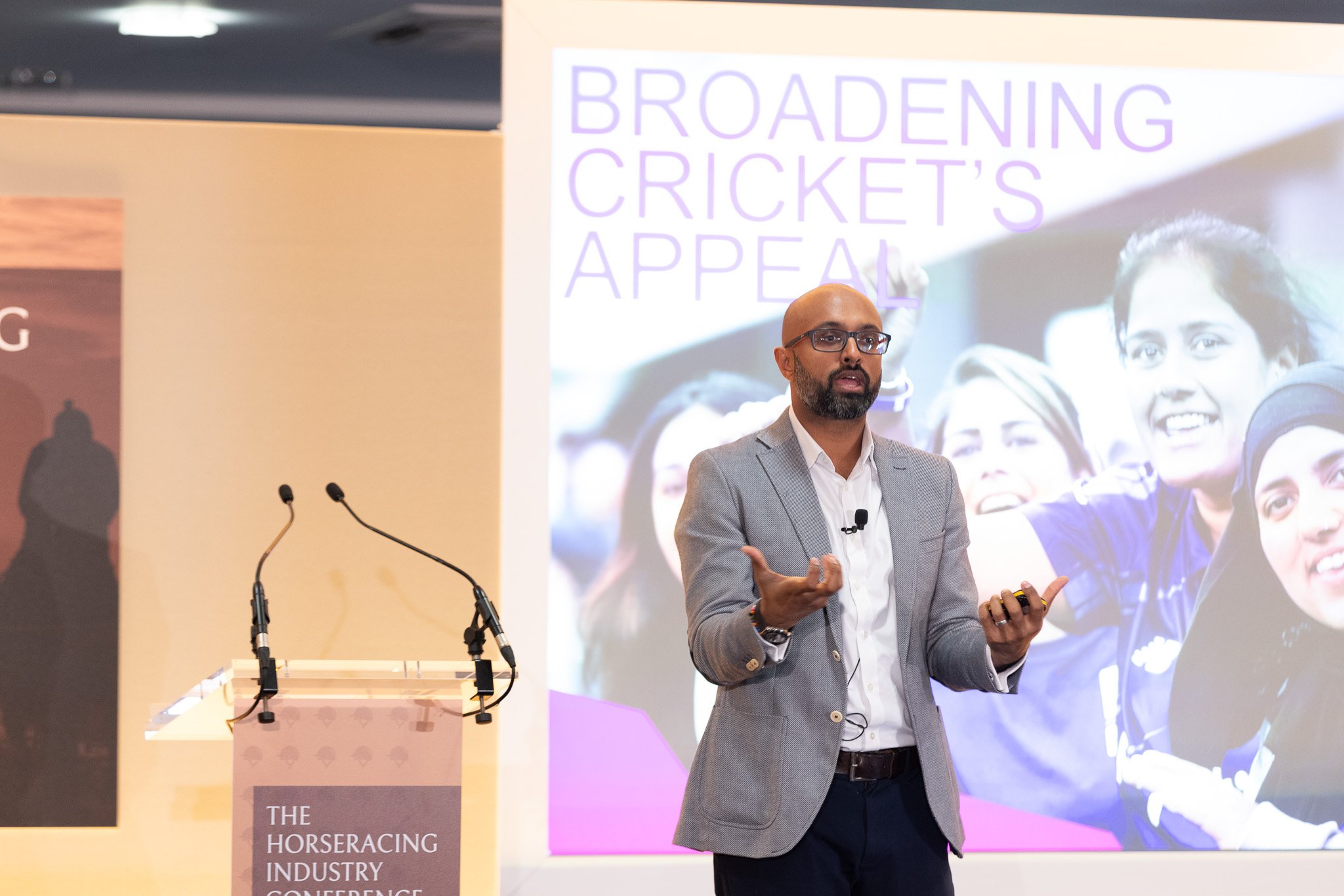
Vikram Banerjee is Director of Business Operations at the England and Wales Cricket Board. Instrumental in the delivery of cricket’s modernised format ‘The Hundred’, Vikram talked about breaking down perceptions of cricket as elitist and how the ECB broadened cricket’s appeal and engaged families with young children.
‘Equine Breeding: Past, Present and Future’ was the first session after lunch. Vice-Chair and Veterinary Chair of the International Thoroughbred Breeders’ Federation Dr Des Leadon delivered an educational keynote talk on the history of thoroughbred breeding and the integrity of the breed. In keeping with the conference structure of considering the wider sporting landscape, breeding specialists James Crabtree and Fred Barrelet then explored equine breeding techniques in the non-thoroughbred, reflecting on outcomes in other equestrian disciplines.
Ruth Dancer is the Director of White Griffin who delivered the racing industry’s sustainability assessment results and recommendations in 2022. She delivered a keynote talk at this year’s conference. After giving an update and insight into best practice across various industry sectors, Dancer posed the question ‘Where are you in your journey?’ Subsequently encouraging delegates to educate themselves, get started, and talk about what they’re doing and celebrate every single sustainability win.
Football followed Dancer’s talk. Ben Fisher, Environmental Sustainability Officer of the English Football League, talked about the power of sport to engage communities in the area of environmental sustainability, its connection to social aim, and the opportunity to use sustainability to leverage fan buy-in.
The final item of the day was the industry leadership panel. Its aim was to offer all delegates the opportunity to quiz racing’s decision makers in an open forum. Keynote address David Jones was joined by Claire Sheppard (Thoroughbred Breeders’ Association Chief Executive), Charlie Liverton (Chief Executive of the Racehorse Owners Association), Dale Gibson (interim CEO of the Professional Jockeys Association), Jemma Marshall (President of the National Association of Stable staff), Neil Hayward (Chair the Industry People Boar) and David Armstrong (Racecourse Association Chief Executive) joined Rishi Persad onstage to answer questions from the audience. The discussion included data, training and retaining the industry’s workforce and community engagement for racecourses. This session, alongside other select keynote talks, is available to watch online at https://www.racingfoundation.co.uk/conference-2023
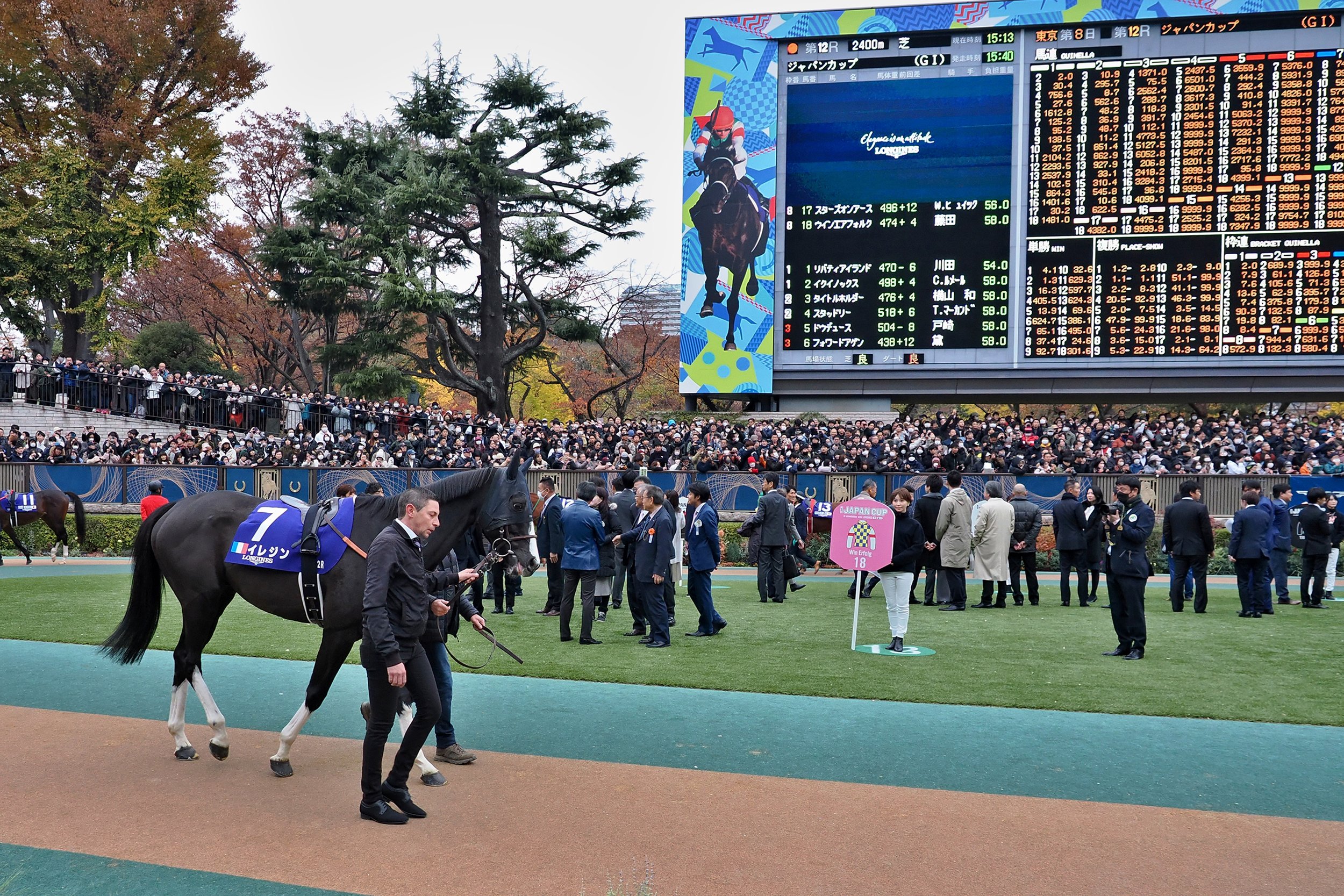
Tokyo Calling – Documenting Iresine’s journey from rural France to the Japan Cup
Article by Katherine Ford
This is the fairytale of a Japanese adventure for a team of family and friends who could never have anticipated being treated like emperors in Tokyo as privileged guests of the JRA.
Iresine, a six-year-old gelding who cost just €6000 as a yearling before climbing the ranks to a pair of Group 1 successes in France, brought the dream to life for hands-on trainer Jean-Pierre Gauvin, France’s leading lady jockey Marie Velon and a group of low-key owners and supporters eager for the experience of a lifetime.
Rags to riches stories are nothing new to Jean-Pierre Gauvin, famed in France as the handler of Saonois, the “Cheval du Boulanger”, who was bought for a song and won the 2012 Prix du Jockey-Club for local baker Pascal Treyve, and renowned for his success with the unfashionably-bred mare Siljan’s Saga, multiple Group 1 placed and 4th at 100/1 in the 2016 Arc.
Winner of the Prix Royal-Oak in 2022 and Prix Ganay in 2023, his latest star, Iresine, has been high on the wish list of the Japan Racing Association for the Japan Cup for many months and this autumn, Gauvin decided the time was right.
“Ever since last year, the JRA French representative Soichiro Matsumae, has been encouraging us to run in the Japan Cup! He has done a good job! As a six-year-old gelding he has the right profile to travel to Asia and the date of the Japan Cup is ideal before he goes on his winter break.”
Family Connections
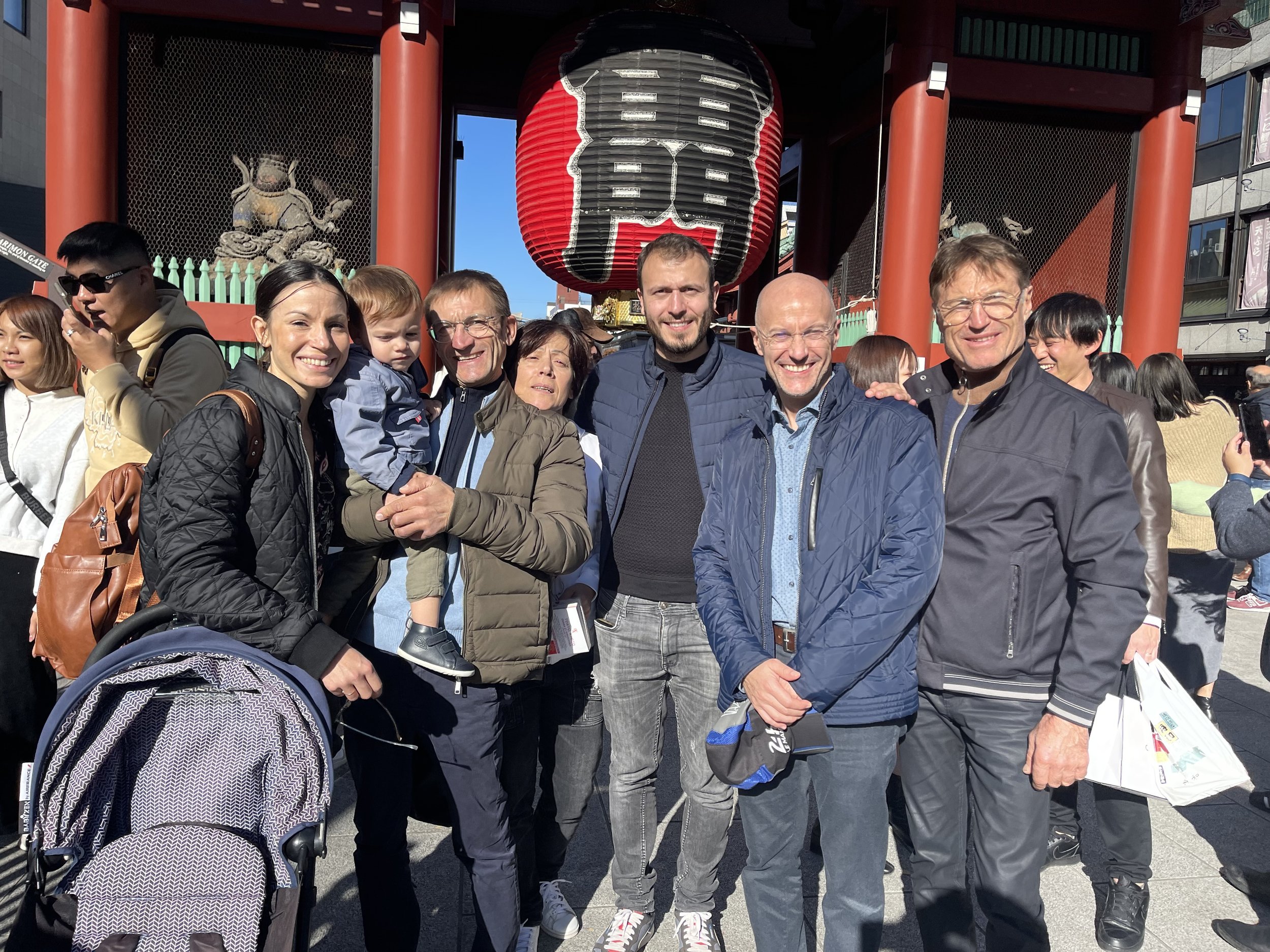
“Above all the aim is to enjoy the adventure. My son and daughter are co-owners of the horse and they are both coming, as well as my grandson who is just 18 months old, my wife, my brother who is a co-owner too, plus another brother who lives in the USA. If it hadn’t been for Iresine, we would never have undertaken such a trip as a family.”
60 year-old Gauvin is a horseman through and through. Born and raised in the Centre-East region of France by parents who “like many farmers in the region, had a couple of trotting broodmares. At age 15 I went to the apprentice school to learn the trotting trade but at only 33kg, I was advised to try the flat!” Except for a brief stint in Marseille, he has spent his entire career, from apprentice to trainer, at the stable he still occupies in the rural hamlet of Saint-Cyr les Vignes.
With limited facilities but plenty of turnout paddocks and a hands-on approach, Jean-Pierre Gauvin is not afraid to test alternative routes, and was not deterred by conditions in Tokyo.
“The ground will be fast and the competition will be very tough, but if we only raced when everything was in our favour and we were sure to win we’d never go anywhere. The JRA agreed to all our requests, including the possibility of taking a companion horse, so there was no reason not to go!”
JRA Generosity
“For Iresine’s participation, the JRA offer the same bonus as for the winner of the Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe and other bonus races, of which the Ganay is not one. He will receive $200,000 just for participating, plus there is prize money down to tenth place. So from a financial perspective, it represents a considerable sum even if we finish tenth. It’s an adventure but the organisation has been perfect. Now the final concern is the travel, which after a change of plan from Air France, will be from Frankfurt to Tokyo. I’m looking forward to Eric calling me to tell me that all has gone well.”
Eric Vandra, Gauvin’s travelling head lad, is about to undertake his second far-flung journey with a horse as he was present when Saonois ran (10th) in Hong Kong 11 years earlier. A former jockey who left racing twice only to return each time, he is determined to ensure that all goes smoothly with Iresine.
“We’re going on an adventure. But there are already details which reassure me. On the plane Iresine will be accompanied by Edouard Lyon who is a trainer but does some work for the STH transport company. I used to be an apprentice for his father and looked after Edouard when he was a kid. All these years later, we meet again on a plane to Japan, and it’s him who will be looking after me!
Iresine will come off the horsebox and be stabled for a few hours in Frankfurt airport, then the flight to Tokyo takes about 14 hours. He’s a horse who can be nervous when he travels, and it seems he inherits his stressed nature from his dam. I didn’t know her in training but we have got to know Iresine’s breeders and they have told us about her character.”
Vandra has prepared 250kg of equipment to travel with Iresine and stablemate Marcan, “I’ve tried to think of every eventuality. Having been to Hong Kong, I know more or less what we’ll need, and of course the most important thing is the passport!”
All the foodstuff has already been taken care of, as Jean-Pierre Gauvin explains, “The JRA requested a full inventory of all our feed, plus any complementary products, because nothing can come off the plane with Iresine. The JRA supply everything, and this will be either the equivalent product from Japan, or imported items if necessary.”
Vandra continues, “The JRA have explained what it will be like over there. We have to leave our riding clothes in the quarantine area, there are showers on site and we have to wash and change before leaving the stable complex. The protocol is very strict. I’ve seen some photos, it all looks very new.”
Indeed, the equine import procedure for the Japan Cup has been simplified with the opening in 2022 of a new quarantine stable in the infield of Tokyo racecourse, eliminating the need for horses to respect a quarantine period at a separate site upon arrival in Japan before moving on to Tokyo days later.
Nerves fraying early in the week
Iresine travelled “perfectly” to Japan but after clearing quarantine gave trainer Jean-Pierre Gauvin a major scare. At a press conference for “international visiting horses” three days before the race, the eyes of around 100 media and other onlookers were all focused upon connections of sole visitor, Iresine.
“On Monday, Iresine suffered from tying up syndrome after his work.”, the trainer explained with refreshing transparency. “He got nervous when going through the tunnel to access the track, but then he cantered fine. Back at the stable, all seemed to be OK initially but then he started to tie up as we took him to wash down. I was very worried but the vet took a blood test and we treated him, essentially to rehydrate him. On Tuesday he had to undergo his stalls test so we had no choice but to take him through the tunnel again, but we led him through in hand and mounted him on the other side, and he reassured us with his exercise. All went smoothly again on Wednesday and today (Thursday) he was completely back to himself, asking to go faster. His coat is shiny again and he looks happy to be here.”
The same can be said for his trainer, who was out on the track each day aboard lead horse Marcan. “I would have come here just for the opportunity to ride out at this amazing racecourse!” he joked to an interested reporter.
In addition to the assembled media, Team Iresine had taken time out from sightseeing to attend the training session and press conference. “I’ve never seen so many media in all my life. Wow!” exclaimed wide-eyed co-owner Bertrand Millière. “For small owners like us, we weren’t programmed to have a horse like this. At the sales, he didn’t have the profile to end up where he is today. But as is often the case with the Gauvin method, he has climbed the ladder step by step. Each time we just said “wow”, but he has never stopped progressing and now here we are in Japan, the centre of attention of a crowd of journalists. We are living in a dream and are making the most of it.”
Another co-owner is Jean-Pierre’s brother, trotting trainer Jean-Paul Gauvin, “I’m on a different planet, even further than the moon! I wanted to have horses in training with Jean-Pierre to share experiences, but I was thinking of small provincial race tracks at home, we never imagined ending up here. The two disciplines, trotting and flat, are so different, but we do take ideas from each other and I think that Jean-Pierre has gained a lot of inspiration from the trotting world. We exchange a lot, notably about shoeing… It’s an opportunity for us to talk, because we both have all-consuming jobs. Training is more than a passion, it’s a way of life, and having horses with Jean-Pierre gives us an opportunity to see each other and share emotions. We’re making the most of it at 200%, visiting Tokyo, enjoying good food and discovering a whole new world.”
“Iresine is a champion. He has a huge heart and a great attitude. It wasn’t written on him at the sales.. or else we wouldn’t have been able to buy him so cheaply. But Jean-Pierre has a real horseman’s intuition. Don’t forget he also picked out Saonois and Siljan’s Saga. Saonois cost €8000, “Siljan” just €2500 and she finished fourth in the Arc. That’s proof that you can always dream with horses, and here we are!”
Bargain buy from novice breeders
Jean-Pierre Gauvin goes on to explain the purchase of Iresine, for €6000 at Arqana’s October yearling sale. “He caught my eye in the collecting area before entering the ring. He had four white stockings which is often considered to be a negative but Bertrand Millière’s children fell in love with his markings and we were able to buy him cheaply.”
Breeders Marie-Louise Van Dedem and her husband Pierre Joyaux are also part of the support team in Tokyo and Dutch-born Marie-Louise remembers, “Iresine was the first generation to be born at our Haras de Grandouet in Normandy and he always had a lot of personality. The Haras de Montaigu presented him at the sale and Jean-Pierre Gauvin was the only one to show any interest in the horse. I didn’t know him at the time, but Aliette Forien (of Haras de Montaigu) said to me after the sale, “you did the right thing to let him go at that price, as he is a very good trainer.””
Like the rest of the team, Marie-Louise Van Dedem was far from imagining that one day she would be invited by the JRA as a connection of a Japan Cup runner. “I became a breeder by chance, and we bought the property on (resale website) Le Bon Coin and built it from scratch. My husband Pierre bought Iresine’s dam and he chooses the matings. I remember early on he explained to me about the Group race system and I didn’t understand a thing! But I’ve learnt quickly and do everything now. It’s all about observation and attention to detail.”
More drama as dream almost turns to nightmare
Attention to detail is a maître-mot for the JRA who cannot receive enough praise from Jean-Pierre Gauvin and his team, especially after a second unwelcome setback. “On Friday evening, as Iresine was being led out, he wasn’t sound. We couldn’t believe it, another problem after him tying up on Monday,” recounts Vandra.
Jean-Pierre Gauvin received the bad news just moments before attending the Japan Cup gala event, “it was a difficult moment at the formal dinner as I would have preferred to be at the stable close to the horse, but I had a lot of confidence in the JRA veterinary team. The vet proposed solutions but also listened to our suggestions. We always agreed about the best treatment to adopt.”
After fears of an infection were discounted, confidence grew that Iresine would make the starting line after all. “He had leather pads on all four feet. These can have a tendency to harden and one of them had become distorted, making a lump which was putting pressure on the sole. In agreement with the veterinarian, we applied a linseed poultice, and on Saturday morning, even without his shoe he trotted out sound. The blacksmith was superb, he is the son of the best farrier in Japan, and I even heard that he shoes Equinox. He reshod Iresine, taking care to avoid pressure on the sensitive part, and things soon worked out. But it was a worry as we were less than two days from the race.”
“For me, the victory is that we were able to run,” says Vandra, “it didn’t look good during the week. The JRA teams did everything they could to help us.”
A memorable occasion for a united team
Come raceday, in a state of relief, excitement and wonder, the team of co-owners, breeders and trainer were welcomed into a private box overlooking Tokyo’s gigantic track and stands filled with 85,000 fans. Jockey Marie Velon’s parents, who live close to the Gauvin stable, were also part of the supporting group throughout the week. “Marie turned up one morning at the stable after finishing her apprenticeship with Alain de Royer Dupré, and until recently worked for me whenever racing allowed. She has grown with Iresine and this is her adventure too,” says Gauvin before adding with emotion, “I am her racing dad. I was touched the day she came out with that…”
As is the way in Japan, horses enter the parade ring 35 minutes before the race, giving fans time to digest all the information available on the giant screens and admire their champions before placing a bet and taking position in the stands. Focus is on favourite Equinox, the Longines World’s Best Racehorse, but there is respect and admiration for the foreign visitor.
“In the parade ring, the only noise I could hear was of cameras clicking all the way around for 15 minutes,” recalls Vandra. “The public are real fans; they must have taken hundreds of photos, and I’ve received some of them. They love their racing and are pleased to have an international horse in the race.”
In what will be remembered as an iconic edition of the Japan Cup, won in superlative style by the world champion Equinox, Iresine ran credibly to finish ninth.
“He ran honourably. It’s difficult to say whether the complications affected his performance, but Marie was happy with how he ran and he recorded his best time over the distance of 2400m.”
For his efforts, connections take home to France the $200,000 participation bonus plus €107,000 for ninth place. But far more important than the prize money, Iresine’s Japan Cup was an unforgettable team adventure.
“We would have liked to stay longer… We all had an incredible experience, both professionally and personally… We were the only international horse so maybe they made an extra effort for us, but the support from the JRA was second to none. Day by day, within our group, we reassured each other about the likelihood of being able to race, which wasn’t guaranteed at times, and despite the worries we were able to relax and enjoy the week together.”
After Iresine landed back in France safe and sound several days after the Japan Cup and began his annual winter break in the Puy de Dome, the final word goes to his trainer, “Merci Iresine!”, or should that be Arigatou Iresine?
Updates from the EMHF and we learn about Europe's latest beach racecourse - Zahara de los Atunes
Article by Paull Khan
The European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation first started providing regular articles for European Trainer back in 2016. I thought, after eight years, it was time to have a look ‘under the bonnet’ of the federation, to see how it works.
EXECUTIVE COUNCIL MEETING, MADRID, SPAIN OCTOBER 14th
The Executive Council of the EMHF comprises nine members, elected by our General Assembly from among its members. The ‘ExCo’ sets the policy tone of the federation, agrees its budget and what the membership fees should be, etc. ExCo members elect, from amongst their own number, the EMHF’s Chair and its three Vice-Chairs.
Brian Kavanagh, now CEO of The Curragh Racecourse and formerly CEO of Horse Racing Ireland, has held the position of EMHF Chair since its inception, in 2010. Brian has indicated that he will stand down at the end of his current term, in mid-2025.
Your correspondent has served as the EMHF’s Secretary-General since 2012. There are no employees, although we do receive valuable help from Horse Racing Ireland, which provides resources for invoicing and handling the Federation’s finances.
Our Vice-Chairs are Rudiger Schmanns, Racing Director at Deutsche Galopp, representing EU countries, Julie Harrington, CEO at the British Horseracing Authority, representing non-EU European countries and Omar Skalli, serving for Mediterranean and Other countries. Rudiger and Omar are, like Brian, founding members of the ExCo.
The other members of the ExCo represent France (Henri Pouret), Poland (Jakub Kasprzak), Norway (Liv Kristiansen), Spain (Paulino Ojanguren Saez) and the Channel Islands, whose Jonathan Perree, in May, became the only person to be re-elected back on to the council, having also served between 2016 and 2019. Three countries – France, Great Britain and Ireland, enjoy automatic representation within ExCo. The other six ExCo places are filled by process of election.
ExCo deliberations span the full range of the responsibilities of our member Racing Authorities – governance, regulation, marketing, financial, legal, social, etc. Specific reports are received from the EMHF’s standing Political and Legislative Committee, together with the committees which sit within the EMHF umbrella – the European Pattern Committee (EPC) and European Horserace Scientific Liaison Committee (EHSLC). The EMHF has also created two special interest associations, the European Beach Racing Association and the European Pony Racing Association.
Much of the Political and Legislative Committee’s work concerns keeping alert to forthcoming legislation, whether within the EU or elsewhere, which may have a bearing on racing. Very often, this centres on the potential unintended consequences of changes which are being suggested with the best intentions. For example, animal health and welfare laws which are drafted with farm animals in mind and are not suited to horses. It was in this context that the EMHF led a delegation to Brussels in the summer, to impress upon policy-makers a number of potential pitfalls in the European Commission’s review of Welfare in Transport.
The European Pattern Committee’s work is not limited to deciding which races across Europe qualify as Group 1, 2, 3 or Listed. The EPC is constantly alive to trends, identifying any areas where the quality of European racing may be under threat or in decline – staying races, perhaps - and agreeing race planning policy initiatives designed to address these by influencing, over time, the behaviour of owners, breeders or trainers.
Doping and medication control sit at the core of the EHSLC’s remit, whether in the detection of substances prohibited at all times, or in the regulation of those therapeutic substances which need to be controlled. Alongside this, increasingly being raised are matters relating to horse welfare more widely and on which a pan-European response and approach is sought. The Chief Veterinary Officers of the major European Racing Authorities sit on the EHSLC and therefore steps are being taken to expand its brief to cover such issues.
At our most recent ExCo Meeting, which took place on October 14th in Madrid, we received a presentation on the report recently published by Horse Racing Ireland, in conjunction with Deloitte, ‘Social and Economic Impact on Irish Breeding and Racing, 2023’. As its title implied, this study took a broader view than the previous HRI/Deloitte report had done – not simply looking at economic factors, but also identifying the considerable and varied social benefits that racing brings, especially to those living in rural areas. This message had resonated strongly in Irish political circles and it was felt that this approach could profitably be replicated by other countries.
At each meeting, the ExCo agrees the shape of the EMHF’s educational programme over the coming twelve months. Last year featured two very successful events: an inaugural EuroMed Stewards’ Conference, hosted by the British Horseracing Authority, and a seminar on Racecourse Surface Management hosted by France Galop. It was decided to repeat the former in Copenhagen in June, where we will be holding our 2024 General Assembly, and to hold a seminar on Starting and Judging Procedures, led by the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board.
The ExCo also seeks to identify which of the pressing issues facing racing could most usefully be focused on at our General Assembly. It was agreed that this year there should be sessions devoted to climate change and sustainability in relation to our sector, as well as the growing threat of illegal betting.
After the business was over, ExCo members were treated to a day’s racing at Spain’s premier track. La Zarzuela impressed on many levels. The luxuriant grass of the turf track belied the drought that had afflicted the region in recent months. The architecture of the gleaming white grandstand is striking, with its arched windows and billowing roof. The demographic was family-orientated, with little peacockery on show. Trees are plentiful, and the footprint of the track is such that there is space for a decent-sized crowd to spread out in the varied outdoor areas provided. And the top floor of the grandstand is now home to a series of airy hospitality areas, with comfy seating and a vibe which is less like a typical racecourse box and more akin to a chilled roof-top bar. All in all, a more than agreeable racing experience.
EUROPE’S YOUNGEST BEACH RACECOURSE: ZAHARA DE LOS ATUNES
The ExCo also receives reports from its two special interest associations, the European Pony Racing Association and the European Beach Racing Association (EBRA). But the latter’s annual meeting was held a couple of weeks after the ExCo – hence this separate bulletin.
The clue is in the name – Zahara de los Atunes is a small town dominated by a large fish! On hiring a car at Malaga airport, en route to this year’s annual EBRA meeting, the woman sorting the paperwork exclaimed jealousy: ‘Oh, you’re going to Zahara. You MUST try the red tuna!’.
‘Red tuna’ in this instance refers, somewhat confusingly, to the Atlantic Bluefin tuna – a prized goliath of the sea, averaging around 6.5 feet/2 metres in length and 550lbs / 250kgs in weight, whose lifespan, at 40 years, is greater than that of a racehorse. Born in the Mediterranean, they then venture out into the broad expanses of the Atlantic, before returning to breed. And, just as they sweep, as they must, through the narrow gap between ocean and sea - the Straits of Gibraltar – there, waiting for them, are the good fishermen of Zahara. They still employ the ancient and more eco-friendly ‘almadraba’ fishing technique, involving a complicated sequence of nets, strategically positioned, the gauge of which allows the younger fish to proceed, whilst trapping those of a certain size and maturity.
The influence and importance of the tuna to the town is all-pervasive. But, for one weekend of the year – the last weekend in October – the focus now moves from fish to thoroughbred. Because the vast strand which stretches both to the north and the south of the resort then becomes home to Europe’s newest official Beach Racecourse and to the staging of the Gran Premio de Zahara.
This is still a very young tradition, with nothing like the rich history of Zahara’s celebrated beach racing neighbour, Sanlúcar de Barrameda, which sits just 100 kms north up the Costa de la Luz, the other side of Cadiz. Sanlucar, which stages six days of racing and partying in the high summer, and which hosted the EBRA in 2019, is approaching its 180th anniversary, no less.
That year – 2019 – Zahara dipped its toe into the sea of beach racing, holding some unofficial exhibition races. But then COVID struck and three years passed before the first official races, (for thoroughbreds and held under the auspices of the Spanish Jockey Club), were run at Zahara. So, 2023 was, to all intents and purposes, ‘Year 2’ in an initiative – sponsored in part by Andalucia Tourism - designed to extend the tourist season, from its previous closure in early-October, for a few more precious and profitable weeks.
Progress over just these two years has been remarkable and testimony to its creator and driving force Pio Gonzales. It already has the feel of an embedded community event. Some 4,500 spectators lined the temporary barriers to watch the races, which were both live-streamed and covered by local television. “Beach Racing has been central to our success in keeping Zahara open for business for longer”, explains Gaspar Castro Valencia, Chair of the Zahara Beach Races Association. “We have just 1,300 inhabitants, but this year there were still 12,200 people here for the Gran Premio de Zahara weekend when, previously, the hotels and restaurants would have been closed. It has been an economic engine for the region. The presence of the European Beach Racing Association further helped to position Zahara, and Andalucia more widely, as an international tourist destination.”
The three thoroughbred races were interspersed with exhibition races, including one pony race for children, featuring a staggered starting-point based on the rider’s age. Two of the main races were over 1500m /7.5f, and the Gran Premio itself over 2000m /10f. Zahara is therefore noteworthy, among the world’s racecourses, in boasting - with Newmarket’s Rowley Mile – a straight 2000m / 10 furlongs! Starter numbers were modest, but included participants bred in France, Great Britain, Ireland and USA. The Gran Premio had the distinction of including Legionario (GB), a Listed Race winner in France the previous year, trained by the Duke of Alburquerque and coming to the sands off the back of a run in a €135K race at Meydan. The intention was to use Zahara as a stepping stone to the International races in Morocco the following month but, sadly, Legionario failed to fire in the race and the plan was abandoned.
Zahara – recently awarded the accolade as one of the ‘Magical Villages of Spain’ - was certainly a hit with the EBRA delegates. Apart from the tuna and the fish restaurants that abound, the village is famed for its live music, and the festival weekend has cleverly brought the jazz and racing worlds together. The Jazzahara Music Festival took place in an atmospheric al fresco setting, surrounded by the towering ancient walls of the Palacio de Pilas, former residence of the Dukes of Medina Sidonia which doubled up as a defence against pirates and a place in which to store the nets of the almadraba. And if your view of tuna is (as was mine) sullied by the canned variety, the Zaharan version is a culinary revelation! The number of different, sumptuous ways in which the fish was presented in the hospitality tents during racing was something to experience.
The additional equestrian attraction of a horse-ball tournament completed the entertainment. Horse-ball requires - of both the horses and their riders - extraordinary agility, and the Thoroughbred has proven wonderfully adept. Many of the horses on show were ex-racehorses, enjoying a second career.
The EBRA meeting received a presentation from Stefan Gast, creator of the vision of Pegasus Land - an ambitious new high-end, equine-focused development in Portugal. Part of that vision is to establish Beach Racing on the expansive and fashionable Comparta Beach, just south of Lisbon and the EBRA stands ready to give advice and share its members’ experiences and expertise.
It is to be hoped that Portugal will embrace the initiative. After all, in neighbouring Spain, Sanlucar and Zahara provide compelling evidence of beach racing’s enormous potential to enhance a coastal area’s touristic appeal and boost the local economy.
Look out for the dates of the 2024 European Beach Racing Fixture List, which will be displayed, when decided, at www.euromedracing.eu/beach-racing. Pop them in your diaries for a holiday or weekend away.
The importance of good hoof balance to improve performance
The equine foot is a unique structure and a remarkable feat of natural engineering that follows the laws of biomechanics in order to efficiently and effectively disperse concussional forces that occur during the locomotion of the horse. Hoof balance has been a term used by veterinarians and farriers to describe the ideal conformation, size and shape of the hoof relative to the limb.
Before horses were domesticated, they evolved and adapted to survive without any human intervention. With respect to their hoof maintenance, excess hoof growth was worn away due to the varied terrain in their habitat. No trimming and shoeing were required as the hoof was kept at a healthy length.
With the domestication of the horse and our continued breeding to achieve satisfactory performance and temperament, the need to manage the horse’s hoof became essential in order to ensure soundness and performance. The horse’s foot has evolved to ensure the health and soundness of the horse; therefore, every structure of the foot has an essential role and purpose. A strong working knowledge of the biology and biomechanics of the horse’s foot is essential for the veterinarian and farrier to implement appropriate farriery. It was soon concluded that a well-balanced foot, which entails symmetry in shape and size, is essential to achieve a sound and healthy horse.
Anatomy and function of the foot
The equine foot is extremely complex and consists of many parts that work simultaneously allowing the horse to be sound and cope with the various terrains and disciplines. Considering the size and weight of the horse relative to the size of the hoof, it is remarkable what nature has engineered. Being a small structure, the hooves can support so much weight and endure a great deal of force. At walk, the horse places ½ of its body weight through its limbs and 2 ½ its weight when galloping. The structure of the equine foot provides protection, weight bearing, traction, and concussional absorption. Well-balanced feet efficiently and effectively use all of the structures of the foot to disperse the forces of locomotion. In order to keep those feet healthy for a sound horse, understanding the anatomy is paramount.
The foot consists of the distal end of the second phalanx (short pastern), the distal phalanx (pedal bone, coffin bone) and the navicular bone. The distal interphalangeal joint (coffin joint) is found between the pedal and short pastern bone and includes the navicular bone with the deep digital flexor tendon supporting this joint. This coffin joint is the centre of articulation over which the entire limb rotates. The navicular bone and bursa sits behind the coffin bone and is stabilised by multiple small ligaments. The navicular bone allows the deep digital flexor tendon to run smoothly and change direction in order to insert into the coffin bone. The navicular bursa is a fluid-filled sac that sits between the navicular bone and the deep digital flexor tendon.
The hoof complex can be divided into the epidermal weight-bearing structures that include the sole, frog, heel, bulbs, bars, and hoof wall and the anti-concussive structures that include the digital cushion, lamina, deep digital flexor tendons, and ungual (lateral) cartilage. The hoof wall encloses the dermal structures with its thickest part at the toe that decreases in thickness as it approaches the heel. The hoof wall is composed of viscoelastic material that allows it to deform and return its shape in order to absorb concussional forces of movement. There is enough deformation to diminish the force from the impact and load of the foot while preventing any damage to the internal structures of the foot and limb. As load is placed on the foot, there is deformation that consists of:
Expansion of the heels
Sinking of the heels
Inward movement of the dorsal wall
Biaxial compression of the dorsal wall
Depression of the coronary band
Flattening of the sole
The hoof wall, bars and their association with the sole form the heel base with the purposes of providing traction, bearing the horse’s weight while allowing the stability and flexibility for the expansion of the hoof capsule that dissipates concussional forces on foot fall. The sole is a highly keratinised structure like the hoof wall but made up of nearly 33% water so it is softer than the hoof wall and should be concave to allow the flattening of the sole on load application. The frog and heel bulbs serve a variety of special functions ranging from traction, protection, coordination, proprioception, shock absorption and the circulation of blood.
When the foot lands on the ground, the elastic, blood-filled frog helps disperse some of the force away from the bones and joints, thus, acting as a shock absorber. The venous plexus above the frog is involved in pumping blood from the foot back to the heart when the foot is loaded. In addition, there is shielding of the deep digital flexor tendon and the sensitive digital cushion (soft tissue beneath the sole that separates the frog and the heel bulb from the underlying tendons and bones). Like the heel bulbs, the frog has many sensory nerve endings allowing the horse to be aware of where his body and feet are and allows the horse to alter landing according to the condition of the ground (proprioception and coordination).
The soft tissue structures comprise and form the palmar/plantar aspect of the foot. The digital cushion lies between the lateral cartilages and above the frog and bars of the horse’s hoof. This structure is composed of collagen, fibrocartilage, adipose tissue and elastic fibre bundles. The digital cushion plays a role in shock absorption when the foot is loaded as well as a blood pumping mechanism. Interestingly, it has been found that the digital cushion composition varies across and within breeds. It is thought the variation of the composition of the digital cushion is partially dictated by a genetic predisposition. In addition, the composition of the digital cushion changes with age. As the horse ages the composition alters from elastic, fat and isolated collagen bundles to a stronger fibrocartilage. Finally, the digital cushion and connective tissue within the foot have the ability to adapt to various external stimuli such as ground contact or body weight. The lateral cartilage is a flexible sheet of fibrocartilage that suspends the pedal bone as well as acting as a spring to store and release energy. The lamina is a highly critical structure for hoof health. The lamina lies between the hoof wall and the coffin bone. There are two types of lamina known as the sensitive (dermal) lamina and insensitive (epidermal) lamina. The insensitive lamina coming in from the hoof wall connects to the sensitive lamina layer that is attached to the coffin bone and these two types of lamina interdigitate with each other to form a bond.
Hoof and Musculoskeletal System
The hoof and the musculoskeletal system are closely linked and this is particularly observed in the posture of the horse when resting or moving. Hoof shape and size and whether they are balanced directly affects the posture of the horse. Ultimately, this posture will also affect the loads placed on the skeletal system, which affects bone remodelling. With an imbalance, bone pathologies of the limbs, spine and pelvis may occur such as osteoarthritis. In addition, foot imbalances result in postural changes that lead to stress to the soft tissue structures that may lead to muscle injuries and/or tendon/ligament injuries.
Conformation and hoof balance
The terms balance and conformation are used frequently and used to describe the shape and size of the limb as a whole as well as the individual components of the limb and the spatial relations between them. Balance is the term often used to describe the foot and can be viewed as a subset of conformation.
Conformation should be considered when describing the static relations within the limb and excludes the foot. Balance should be considered when describing the dynamic and static relationship between the horse’s foot and the ground and limb as well as within the hoof itself.
These distinctions between conformation and balance are important to assess lameness and performance of the horse. Additionally, this allows the veterinarian and farrier to find optimal balance for any given conformation.
The term hoof balance does lack an intrinsic definition. The use of certain principles in order to define hoof balance, which in turn can be extended to have consistent evaluation of hoof balance as well as guide the trimming and shoeing regimens for each individual horse. In addition, these principles can be used to improve hoof capsule distortion, modify hoof conformation and alter landing patterns of the foot. These principles are:
Evaluate hoof-pastern axis
Evaluate centre of articulation
The need for the heels to extend to the base of the frog
Assessing the horse’s foot balance by observing both static (geometric) balance and dynamic balance is vital. Static balance is the balance of the foot as it sits on a level, clean, hard surface. Dynamic balance is assessing the foot balance as the foot is in motion. However, horses normally do not resemble the textbook examples of perfect conformation, which creates challenges for the farriers and veterinary surgeons. The veterinarian should instigate further evaluation of the foot balance and any other ailments, in order to provide information that can be used by the farrier and veterinarian in formulating a strategy to help with the horse’s foot balance. With the farrier and veterinarian working cooperatively, the assessment of the hoof balance and shoeing of the foot should deliver a harmonious relationship between the horse’s limb, the hoof and the shoe.
Dynamic Balance
The horse should be assessed in motion as one can observe the foot landing and placement. A balanced foot when in motion should land symmetrically and flat when moving on a flat surface. When viewed from the side, the heels and toe should land concurrently (flat foot landing) or even a slight heel first landing. It is undesirable to have the toe landing first and often suggests pain localised to the heel region of the foot. When observing the horse from the front and behind, both heel bulbs should land at the same time. Sometimes, horses will land first slightly on the outside or lateral heel bulb of the foot but rarely will a horse land normally on the medial (inside) of the foot. If the horse has no conformational abnormalities or pathologies the static balance will achieve the dynamic balance.
Static Balance
Hoof –pastern axis (HPA)
The hoof pastern axis (HPA) is a helpful guideline in assessing foot balance. With the horse standing square on a hard, level surface, a line drawn through the pastern and hoof should be parallel to the dorsal hoof wall and should be straight (unbroken). The heel and toe angle should be within 5 degrees of each other. An underrun heel has been defined as the angle of the heel being 5 degrees less than the toe angle. The heel wall length should be roughly 1/3 of the dorsal wall. In addition, the cannon (metacarpus/metatarsus) bone is perpendicular to the ground and when observed from the lateral side, the HPA should be a straight line. When assessing the foot from the side, the dorsal hoof wall should be aligned with the pastern. The optimal angle of the dorsal hoof wall is often cited as being 50-54°. The length of the dorsal hoof wall is variable but guidelines have been suggested according to the weight of the horse.
It is not uncommon that the hind feet are more upright compared to the fore feet at approximately 5 degrees. A broken hoof-pastern axis is the most common hoof imbalance. There are two presentations of a broken HPA known as a broken-back HPA and a broken-forward HPA. These changes in HPA are often associated with two common hoof capsule distortions that include low or underrun heels and the upright or clubfoot, respectively.
A broken-back hoof-pastern axis occurs when the angle of the dorsal hoof wall is lower than the angle of the dorsal pastern. This presentation is commonly caused by low or underrun heel foot conformation accompanied with a long toe. This foot imbalance is common and often thought to be normal with one study finding it present in 52% of the horse population. With a low hoof angle, there is an extension of the coffin and pastern joints resulting in a delayed breakover and the heels bearing more of the horse's weight, which ultimately leads to excess stress in the deep digital flexor tendon as well as the structures around the navicular region including the bone itself.
This leads to caudal foot pain so the horse lands toe first causing subsolar bruising. In addition, this foot imbalance can contribute to chronic heel pain (bruising), quarter and heel cracks, coffin joint inflammation and caudal foot pain (navicular syndrome). The cause of underrun heels is multifactorial with a possibility of a genetic predisposition where they may have or may acquire the same foot conformation as the parents. There are also environmental factors such as excessive dryness or moisture that may lead to the imbalance.
A broken-forward hoof-pastern axis occurs at a high hoof angle with the angle of the dorsal hoof wall being higher than the dorsal pastern angle. One can distinguish between a broken-forward HPA and a clubfoot with the use of radiographs. With this foot imbalance, the heels grow long, which causes the bypassing of the soft tissue structures in the palmar/plantar area of the foot and leads to greater concussional forces on the bone. This foot imbalance promotes the landing of the toe first and leads to coffin joint flexion as well as increases heel pressure. The resulting pathologies that may occur are solar bruising, increased strain of the suspensory ligaments near the navicular bone and coffin joint inflammation.
Center of articulation
When the limb is viewed laterally, the centre of articulation is determined with a vertical line drawn from the centre of the lateral condyle of the short pastern to the ground. This line should bisect the middle of the foot at the widest part of the foot and demonstrates the centre of articulation of the coffin joint. The widest part of the foot (colloquially known as “Ducketts Bridge”) is the one point on the sole that remains constant despite the shape and size of the foot. The distance and force on either side of the line drawn through the widest part of the foot should be equal, which provides biomechanical efficiency.
Heels extending to the base of the frog
With respect to hoof balance, another component of the foot to assess is that the heels of the hoof capsule extend to the base of the frog. The hoof capsule consists of the pedal bone occupying two-thirds of the space and one-third of the space is soft tissue structures. This area is involved in dissipating the concussional and loading forces and in order to ensure biomechanical efficiency both the bone and soft-tissue structures need to be enclosed in the hoof capsule in the same plane.
To achieve this goal the hoof wall at the heels must extend to the base of the frog. If the heels are allowed to migrate toward the centre of the foot or left too long then the function of the soft tissue structures have been transferred to the bones, which is undesirable. If there is a limited amount to trim in the heels or a small amount of soft tissue mass is present in the palmar foot then some form of farriery is needed to extend the base of the frog (such as an extension of the branch of a shoe).
Medio-lateral or latero-medial balance
The medio-lateral balance is assessed by viewing the foot from the front and behind as well as from above with the foot raised. To determine if the foot has medio-lateral balance, the hoof should be bisected or a line is drawn down the middle of the pastern down to the point of the toe.
You should be able to visualise the same amount of hoof on both the left and right of that midline. In addition, one should observe the same angle to the side of the hoof wall. It is important to pick up the foot and look at the bottom. Draw a line from the middle quarter (widest part of foot) on one side to the other then draw a line from the middle of the toe to the middle sulcus of the frog.
This provides four quadrants with all quadrants being relatively the same in size (Proportions between 40/60 to 60/40 have been described as acceptable for the barefoot and are dependent on the hoof slope). The frog width should be 50-60% of its length with a wide and shallow central sulcus. The frog should be thick enough to be a part of the bearing surface of the foot. The bars should be straight and not fold to the mid frog. The sole should be concave and the intersection point of both lines should be the area of optimal biomechanical efficiency.
The less concavity means the bone is nearer to the ground, thus, bearing greater concussional force. Finally, assess the lateral and medial heel length. Look down at the heel to determine the balance in the length of both heel bulbs. Each heel bulb should be the same size and height. If there are any irregularities with the heel bulbs then sheared heels may result, which is a painful condition. Medio-lateral foot imbalance results in the uneven loading of the foot that leads to an accumulation of damage to the structures of the foot ultimately causing inflammation, pain, injury and lameness. Soles vary in thickness but a uniform sole depth of 15mm is believed to be the minimum necessary for protection.
Dorso-palmar/plantar (front to back – DP) balance
Refers to the overall hoof angle and the alignment of the hoof angle with the pastern angle when the cannon bone is perpendicular to the ground surface. When assessing the foot from the side, the dorsal hoof wall should be aligned with the pastern. The optimal angle of the dorsal hoof wall is often cited as being 50-54°. The length of the dorsal hoof wall is variable but guidelines have been suggested according to the weight of the horse.
The heel and toe angle should be within 5 degrees of each other. An underrun heel has been defined as the angle of the heel being 5 degrees less than the toe angle. The heel wall length should be roughly 1/3 of the dorsal wall.
A line dropped from the first third of the coronet should bisect the base. A vertical line that bisects the 3rd metacarpal bone should intersect the ground at the palmar aspect of the heels.
Radiographs
A useful way to assess trimming and foot balance is by having foot x-rays performed. Radiography is the only thorough and conclusive method that allows one to determine if the foot is not balanced and the bony column (HPA) is aligned.
Shoes should be removed and the foot cleaned before radiographs are executed. The horse is often placed on foot blocks to elevate the feet off the ground so that the foot can be centred in the cassette and x-ray beam.
Latero-medial view – The side view of the foot allows one to assess the dorsal and palmar aspects of the pedal bone as well as the navicular bone. The horse should be standing squarely on a flat, level surface. This projection is useful in determining the point of breakover and the hoof pastern axis should be parallel with the hoof wall. The lateral view will demonstrate the length of the toe and the alignment of the dorsal surface of the pedal bone with the hoof wall, which should be parallel. This view also allows one to determine the depth of the sole and inadequate solar depth is usually accompanied with excessive toe length (broken-back HPA). One may observe a clubfoot, broken forward.
One can distinguish between a clubfoot and a broken-forward HPA with radiographs. The broken-forward HPA the hoof angle of the heel is greater than the angle of the dorsal hoof wall. The clubfoot also demonstrates these steep/high hoof angles but additionally the alignment of the coffin, short and long pastern bones are broken forward.
Dorsopalmar/plantar views - this “front to back” view is also performed with the horse standing squarely on 2 positioning blocks. This projection allows the evaluation of medial to lateral balance and conformation of the foot with observation and measurement of the medial and lateral wall length and angle. Horses with satisfactory conformation present with a parallel joint surface of the pedal bone to the ground. The coffin joint should be even across its width. In addition, the lateral and medial coronet and the lateral and medial walls are of equal thickness and the distance from the lateral and medial solar margins to the ground are similar.
With foot imbalance, this author has observed that fore feet may have a higher lateral hoof wall, whereas, the hind feet may have a higher medial hoof wall. It is worth noting that the pelvis, stifle and hocks are adapted to move laterally allowing a slight rotating action as it moves. This action may cause uneven wear or poor trimming and shoeing may cause this limb movement to be out of line.
Trimming
Often, trimming and shoeing are based on empirical experience that includes theoretical assumptions and aesthetic decisions. The goals of trimming and shoeing are to facilitate breakover, ensure solar protection and provide heel support. Trimming is the most important aspect of farriery because it creates the base to which a shoe is fitted. Hoof conformation takes into account the function and shape of the foot in relation to the ground and lower limb both at rest and exercise. Each individual foot should have a conformation that provides protection and strength while maximising biomechanical efficiency often viewed as foot balance.
An important question that initially needs to be addressed is whether the horse requires shoes or not. The answer does depend on what type of work the horse performs, what is the amount of workload, the conformation of the horse (especially the limbs and foot) and are there any previous or current injuries. It must be stressed that the most important aspect, whether the horse is shod or not, is that the trim ensures an appropriately balanced foot for the horse. If there is poor trimming then this may lead to uneven and increased workload on the limb leading to an increased strain of the hoof and soft tissues (i.e. ligaments, tendons) that increase the risk of injury and developing acute and chronic lameness.
The foot can be evaluated, trimmed and/or shod in a consistent, reproducible manner that considers:
Hoof-pastern axis (HPA)
The centre of articulation
Heels extending to the base of the frog
Appropriate trimming and shoeing to ensure the base of the foot is under the lateral cartilage; therefore, maximising the use of the digital cushion, can help in creating a highly effective haemodynamic mechanism. Shoeing must be done that allows full functionality of the foot so that load and concessional forces are dissipated effectively.
To implement appropriate farriery, initially observe the horse standing square on a hard service to confirm that the HPA is parallel. If The HPA is broken forward or backward then these balances should be part of the trimming plan. To determine the location of the centre of rotation, palpate the dorsal and palmar aspect of the short pastern just above the coronary band and a line dropped vertically from the centre of that line should correlate with the widest part of the foot.
Shoeing
When the shoe is placed on the horse, the horse is no longer standing on its feet but on the shoe; therefore, shoeing is an extension of the trim. The shoe must complement the trim and must have the same biomechanical landmarks to ensure good foot balance. It is this author’s view that the shoe should be the lightest and simplest possible. The shoe must be placed central to the widest part of the foot and the distance from the breakover point to the widest part of the foot should be equal to the distance between the widest part of the foot and the heel.
It has been shown that the use of shoes that lift the sole, frog and bars can reduce the efficient workings of the caudal foot and may lead to the prevalence of weak feet. A study by Roepstorff demonstrated there was a reduced expansion and contraction of the shod foot but improved functionality of solar and frog support. With this information, appropriate shoeing should allow increased functionality of the digital cushion, frog and bars of the foot, which improves the morphology and health of the hoof and reduces the risk of exceeding the hoof elasticity.
Disease associated with hoof imbalance
Foot imbalance can lead to multiple ailments and pathologies in the horse. It must be noted that the pathologies that may result are not necessarily exclusive for the foot but may expand to other components to the horse’s musculoskeletal system. In addition, not one but multiple pathologies may result. Diseases that may result from hoof imbalance are:
Conclusion
Foot balance is essential for your horse to lead a healthy and sound life and career. With a strong understanding of the horse anatomy and how foot imbalance can lead to lameness as well as other musculoskeletal ailments, one can work to assess and alter foot balance in order to ensure optimal performance and wellbeing of the horse. It is essential that there is a team approach involving all stakeholders as well as the veterinarian and farrier in order to achieve foot balance. With focus on foot balance, one can make a good horse into a great horse.
Stem Cell Therapy - the improved diagnostics available to treat lameness
Article by Jackie Zions (interviewing Dr. Koenig)
Prevention is the ideal when it comes to lameness, but practically everyone who has owned horses has dealt with a lay-up due to an unforeseen injury at some point. The following article will provide tools to sharpen your eye for detecting lameness, review prevention tips and discuss the importance of early intervention. It will also begin with a glimpse into current research endeavouring to heal tendon injuries faster, which has obvious horse welfare benefits and supports horse owners eager to return to their training programs. Dr. Judith Koenig of Ontario Veterinary College (OVC) spends half of her time as a surgeon and teacher with a strong interest in equine sports medicine and rehabilitation, and the other half as a researcher at the OVC.
Lameness is a huge focus for Koenig, whose main interest is in tissue healing. “I think over the past 20 or 30 years we have become very, very good at diagnosing the cause of lameness,” says Koenig. “In the past, we had only radiographs and ultrasound as a diagnostic tool, but by now most referral centres also have MRI available; and that allows us to diagnose joint disease or tendon disease even more. We are much better now [at] finding causes that previously may have been missed with ultrasound.”
Improvements in diagnostics have resulted in increased ability to target treatment plans. With all the different biologics on the market today, Koenig sees a shift in the management of joint disease with more people getting away from steroids as a treatment.
The following list is excerpted from Equine Guelph’s short course on lameness offered on TheHorsePortal.ca. It outlines the different diagnostics available:
When asked for the latest news on research she has been involved in, Koenig proclaims, “I'm most excited about the fact that horses are responding well to stem cell treatment—better than I have seen any response to any other drug we have tried so far!”
Koenig has investigated the use of many different modalities to see if they accelerate tissue healing and has studied which cellular pathways are affected. Two recent collaborative studies have produced very exciting findings, revealing future promise for treating equine osteoarthritis with stem cell therapy.
In a safety study, Koenig and her team at the Ontario Veterinary College have shown equine pooled cryopreserved umbilical cord blood, (eCB) MSC, to be safe and effective in treatment of osteoarthritis.
“These cells are the ones harvested from umbilical cord blood at the time of foaling and then that blood is taken to the lab and the stem cells are isolated out of it,” explains Koenig. The stem cells are then put through a variety of tests to make sure they are free of infectious diseases. Once given a clean bill of health, they are expanded and frozen.
The stem cells harvested from multiple donors of equine umbilical cord blood [eCB, (kindly provided by eQcell), MSC] were compared to saline injections in research horses. “This type of cells is much more practical if you have a cell bank,” says Koenig. “You can treat more horses with it, and it’s off the shelf.” There were no systemic reactions in the safety study. Research has also shown no different reactions from sourcing from one donor or multiple donors.
In the second study, 10 million stem cells per vial were frozen for use in healing OA from fetlock chips in horses that were previously conditioned to be fit. After the fetlock chip was created, exercise commenced for six more weeks, and then osteoarthritis was evaluated by MRI for a baseline. Half the horses were treated with the pooled MSC stem cells, and the control group received saline before another month of exercise. Then MRI and lameness exams were repeated, and arthroscopy was repeated to score the cartilage and remove the chip.
Lameness was decreased and cartilage scores were improved in the group that received stem cell therapy at the time of the second look with arthroscopy.
Many diagnostics were utilised during this study. MRIs, X-rays, ultrasounds and weekly lameness evaluations all revealed signs of osteoarthritis in fetlock joints improved in the group treated with (eCB) MSCs. After six weeks of treatment, the arthroscopic score was significantly lower (better cartilage) in the MSC group compared to the control group.
“Using the MRI, we can also see a difference that the horses treated with stem cells had less progression of osteoarthritis, which I think is awesome,” says Koenig. “They were less lame when exercised after the stem cell therapy than the horses that received saline.”
This research group also just completed a clinical trial in client-owned horses diagnosed with fetlock injuries with mild to moderate osteoarthritis changes. The horses were given either 10 million or 20 million stem cells and rechecked three weeks and six weeks after the treatment. Upon re-evaluation, the grade of lameness improved in all the horses by at least one. Only two horses presented a mild transient reaction, which dissipated after 48 hours without any need for antibiotics. The horse’s joints looked normal, with any filling in the joint reduced.
There was no difference in the 18 horses, with nine given 10 million stem cells and the other nine 20 million stem cells; so in the next clinical trial, 10 million stem cells will be used.
The research team is very happy with the results of this first-of-its-kind trial, proving that umbilical cord blood stem cells stopped the progression of osteoarthritis and that the cartilage looked better in the horses that received treatment. The future of stem cell therapy is quite promising!
Rehabilitation
Research has shown adhering to a veterinary-prescribed rehabilitation protocol results in a far better outcome than paddock turn out alone. It is beneficial for tendon healing to have a certain amount of controlled stimulation. “These horses have a much better outcome than the horses that are treated with just being turned out in a paddock for half a year,” emphasises Koenig. “They do much better if they follow an exercise program. Of course, it is important not to overdo it.”
For example, Koenig cautions against skipping hand-walking if it has been advised. It can be so integral to stimulating healing, as proven in recent clinical trials. “The people that followed the rehab instructions together with the stem cell treatment in our last study—those horses all returned to racing,” said Koenig.
“It is super important to follow the rehab instructions when it comes to how long to rest and not to start back too early.”
Another concern when rehabilitating an injured horse would be administering any home remedies that you haven't discussed with your veterinarian. Examples included blistering an area that is actively healing or applying shockwave to mask pain and then commence exercise.
Prevention and Training Tips
While stating there are many methods and opinions when it comes to training horses, Koenig offered a few common subjects backed by research. The first being the importance of daily turnout for young developing horses.
Turnout and exercise
Many studies have looked at the quality of cartilage in young horses with ample access to turn out versus those without. It has been determined that young horses that lack exercise and are kept in a stall have very poor quality cartilage.
Horses that are started early with light exercise (like trotting short distances and a bit of hill work) and that have access to daily paddock turnout, had much better quality of cartilage. Koenig cited research from Dr. Pieter Brama and similar research groups.
Another study shows that muscle and tendon development depend greatly on low grade exercise in young horses. Evaluations at 18 months of age found that the group that had paddock turnout and a little bit of exercise such as running up and down hills had better quality cartilage, tendon and muscle.
Koenig provides a human comparison, with the example of people that recover quicker from injury when they have been active as teenagers and undergone some beneficial conditioning. The inference can be made that horses developing cardiovascular fitness at a young age stand to benefit their whole lives from the early muscle development.
Koenig says it takes six weeks to regain muscle strength after injury, but anywhere from four to six months for bone to develop strength. It needs to be repeatedly loaded, but one should not do anything too crazy! Gradual introduction of exercise is the rule of thumb.
Rest and Recovery
“Ideally they have two rest days a week, but one rest day a week as a minimum,” says Koenig. “I cannot stress enough the importance of periods of rest after strenuous work, and if you notice any type of filling in the joints after workout, you should definitely rest the horse for a couple of days and apply ice to any structures that are filled or tendons or muscles that are hard.”
Not purporting to be a trainer, Koenig does state that two speed workouts a week would be a maximum to allow for proper recovery. You will also want to make sure they have enough access to salt/electrolytes and water after training.
During a post-Covid interview, Koenig imparted important advice for bringing horses back into work methodically when they have experienced significant time off.
“You need to allow at least a six-week training period for the athletes to be slowly brought back and build up muscle mass and cardiovascular fitness,” says Koenig. “Both stamina and muscle mass need to be retrained.”
Watch video: “Lameness research - What precautions do you take to start training after time off?” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zNHba_nXi2k
The importance was stressed to check the horse’s legs for heat and swelling before and after every ride and to always pick out the feet. A good period of walking is required in the warmup and cool down; and riders need to pay attention to soundness in the walk before commencing their work out.
Footing and Cross Training
With a European background, Koenig is no stranger to the varying track surfaces used in their training programs. Statistics suggest fewer injuries with horses that are running on turf.
Working on hard track surfaces has been known to increase the chance of injury, but delving into footing is beyond the scope of this article.
“Cross training is very important,” says Koenig. “It is critical for the mental and proper musculoskeletal development of the athlete to have for every three training days a day off, or even better provide cross-training like trail riding on these days."
Cross-training can mitigate overtraining, giving the body and mind a mental break from intense training. It can increase motivation and also musculoskeletal strength. Varied loading from training on different terrain at different gaits means bone and muscle will be loaded differently, therefore reducing repetitive strain that can cause lameness.
Hoof care
Whether it is a horse coming back from injury, or a young horse beginning training, a proficient farrier is indispensable to ensure proper balance when trimming the feet. In fact, balancing the hoof right from the start is paramount because if they have some conformational abnormalities, like abnormal angles, they tend to load one side of their joint or bone more than the other. This predisposes them to potentially losing bone elasticity on the side they load more because the bone will lay down more calcium on that side, trying to make it stronger; but it actually makes the bone plate under the cartilage brittle.
Koenig could not overstate the importance of excellent hoof care when it comes to joint health and advises strongly to invest in a good blacksmith. Many conformational issues can be averted by having a skilled farrier right from the time they are foals. Of course, it would be remiss not to mention that prevention truly begins with nutrition. “It starts with how the broodmare is fed to prevent development of orthopaedic disease,” says Koenig. Consulting with an equine nutritionist certainly plays a role in healthy bone development and keeping horses sound.
Noel George and Amanda Zetterholm - The anglo-swedish duo taking French racing by storm
Article by Katherine Ford
Training partnerships are now firmly established in racing. Father and son (or daughter), husband and wife, or experienced trainer and long-standing assistant; these entities are now regularly seen in Europe and beyond. The association of George & Zetterholm Racing, one of the newest names in the French jumps trainers’ column, doesn’t fit in any of the usual categories but has already proven its efficiency in less than a year of operation.
Twenty-four-year-old Noel George, who found his way to France during Covid, is a former amateur rider and the son of Gr. 1 winning British trainer Tom George; whereas dynamic Swedish-born Amanda Zetterholm boasts a wealth of experience in a variety of capacities in racing and bloodstock around the world. The pair have no background together, and a chance remark has seen them launch as one of France’s most exciting training operations.
“We knew each other, but that was all; and it was (fellow Chantilly trainer) Tim Donworth who suggested we set up together,” explains Amanda. “Noel wanted to train in France, but of course it is complicated to set up here, so it was a good opportunity to do it in partnership. I told Noel I’d found this yard I love, so we went to visit it together, and he said he’d love to train here. I bought the yard exactly a year ago, in September 2022”.
Creating a masterpiece
Amanda and Noel each bring their own talents to the partnership, “I’m the Louvre, and he’s Thomas Gainsborough”! Amanda’s marketing background shines through with her metaphor illustrating that she provides the solid base for Noel to fulfil his role as “the artist” with the horses.
Growing up in Sweden, Amanda Zetterholm enjoyed riding and show jumping but didn’t have any involvement in racing until studies took her to Australia, where she spent time with David Hayes and Matthew Ellerton. “My first job in racing was with agent Damon Gabbedy, who taught me a lot about the breeding side. Then I went to South Africa and spent three years with Mike de Kock, which was a great experience—between Dubai, England and South Africa. He is very avant-garde”.
In 2013, Amanda was recruited by the Aga Khan Studs as commercial executive and has fulfilled a variety of roles for the famous operation. She currently balances the burgeoning training career with work for the Aga Khan Studs but is soon set to devote herself fully to George & Zetterholm Racing. “I’ve spent 10 wonderful years with the Aga Khan Studs, but I will finish at the end of the year; I can’t do both. They’re very proud of what I’ve achieved”.
Add to these achievements a successful amateur riding career on the flat, a stint as Goffs French representative and an instrumental part in the setting up of the stable of former partner David Cottin, with whom she has two young sons, Winston and Clovis, plus success in buying young jumping stock to sell on, which has set her up financially to be able to buy the Chantilly yard; it is clear that Amanda is not shy of a challenge or a busy schedule.
Well-defined roles
“We passed the trainers’ licence together, and the idea was always that Noel wanted to do his training regime. He’s on the track every morning with the horses. I’m out here maybe three times a week currently, but that will change once I finish with the Aga Khan Studs. We both discuss and do the entries. We’re on the same wavelength, and I would say I am a very easy partner. I have a lot of experience, and I don’t feel I have anything to prove.
“In France, there is so much paperwork. I deal with the business side, the staff and the logistics; and I do the communication with the owners, which I love. I don’t feel the stress that Noel feels with the owners as he is the one who has directly prepared the horse, so I can be more relaxed. I am there to reassure them and make sure that they have a good day out. We are very complementary. Noel is a very confident person. You need to be confident to be a good trainer because the horses feel the confidence, and the owners too. He passes that confidence on to everyone”.
Living the dream in France
Noel George displays a confidence which belies his years, and in France he has found an opportunity to fulfil a dream that he had not imagined possible. “Since I left school, I aimed to train flat horses because I didn’t see economically and business-wise how it could work training jumpers in the UK”. After a year with Graham Motion in the USA and summer holidays with Sir Mark Prescott and Joseph O’Brien, Noel George has learnt from some of the best on the flat.
The French connection came about by coincidence, although there is family history across in Chantilly as father Tom George spent time with the pioneering François Doumen in the days of The Fellow, whetting his appetite for cross-Channel raids. “I remember when Dad always used to come over with runners and then Halley won the Gp. 1 Maurice Gillois. I wasn’t there that day but I remember it—Dad built his new kitchen because of it! That stuck in my mind, that the French prize money is amazing… I was meant to be going to Australia as an assistant, but then Covid happened and French racing started before anywhere else; so I moved over to work for Fabrice Chappet”.
Noel didn’t speak French when he arrived but learnt quickly—thanks to language apps, Chappet’s former assistant, and now young trainer Xavier Blanchet, as well as being motivated to communicate when chasing a few French girls!
During the period with Classic-winning Chappet, Noel oversaw a string of horses running under a provisional licence for his father Tom. “I was giving orders to Dad’s horses on the same gallops, and it was a help that I knew the farrier, the feed suppliers etc”.
Provisional training operations in France are restricted to three months, but the experience served to reiterate the financial sense of racing in France but also the accompanying bureaucracy.
“I eventually passed the trainers exams, which aren’t easy! It’s not just knowing the language, it’s knowing all the anatomy of the horse, in French, the employment laws, how to write a payslip—all the different taxes… For that, having Amanda is a huge asset because I can focus on training the horses and she does all that complicated stuff”.
Noel is also full of praise for his father Tom. “He’s a great source of advice for me; I ring him whenever I have a question. We couldn’t do it without him. He’s put his neck on the chopping block by pushing a lot of the horses over here, and it seems to be paying off”.
Top-class training grounds
Another huge advantage for George & Zetterholm Racing is their stable and accompanying facilities. The yard, on the outskirts of the village of Avilly-St-Léonard, has already sent out three winners of France’s feature Grand Steeple-Chase de Paris as former owner Christophe Aubert was responsible for Line Marine (2003) and Mid Dancer (2011 & 2012).
This is part of France Galop’s huge Chantilly training domain, but being slightly out on a peaceful limb compared with the more famous locations of Chantilly, Gouvieux, Lamorlaye and Coye-la-Forêt, it has all the benefits of a private establishment. “We can’t praise France Galop enough for all they do for us,” says Amanda. “When the English owners come over, they just can’t believe it, and even Noel’s dad has his own amazing facilities; but he has to run it all himself. This area of Avilly has been almost dormant for several years and so the France Galop teams are very keen to revive it and make improvements”.
In concrete terms, this means that Noel and Amanda, having the only active stable in the vicinity, have exclusive use of extensive schooling facilities and gallops. “We’ve got cross-country, steeplechase fences and hurdles. They are a little bit smaller than the racecourse ones, but I don’t think you have to jump big in the mornings. It’s better if they’re a bit smaller as they give the horses confidence. We tell the France Galop staff the days when we will be schooling and they make sure everything is prepared”.
Noel adds, “The training centre is incredible, and we are so well looked after by France Galop who really want to help us. They give the horses the best chance possible. We have a 2000m sand gallop through the forest, which we use daily; then there’s a big 2000m sand circle which isn’t watered but in the winter it’s very good for the youngsters—it’s like a racecourse! We have to go to Chantilly to use the grass, but I think it does the horses good to go on the lorry”.
Schooling is an integral part of training jumpers in France; and Noel admits, “I’ve watched videos of how Macaire and Nicolle do all the French schooling and we’ve mixed it with the English way; and it seems to be working”.
The French policy of regular schooling has been adopted, and here again, the French system offers benefits. “The likes of James Reveley, Felix de Giles, Nicolas Gauffenic, and Kevin Nabet will be in nearly every Wednesday. It’s not like in England where the jockeys might be riding up north or down south and are less available for schooling. The horses, especially the older ones over from England, love it. It gives them a change, especially with the different steeplechase obstacles like the bullfinch the bank, the white wall… And as we don’t have the hills they have in England, it is good for fitness”.
“The horses jump more in races here. In a two-mile hurdle in England, they jump eight small hurdles; whereas round Auteuil over two miles, they jump 12 mini-English fences. If you lose two lengths at a hurdle here, it makes such a big difference as the next hurdle comes much quicker than in England. Jumping is very important”.
Making financial sense
Jumping is important, but prize money is even moreso; and in less than a year of operation, the stable has already earnt plenty. “We’ve had 100 runners for 800,000€ in prize money, so that’s 8000€ per runner which is a great statistic. French racing is very lucrative,” says Amanda, while Noel emphasises the point further: “The very fact that a horse can be in training and not cost money is a huge benefit. The number of horses that pay for their training fees in England is very few; whereas if your horse isn’t paying your training fees here, you probably need to think about moving it on. It’s an incredible way to be and a massive advert for French racing. It just takes the pressure off everything”.
Capacity is maybe the only source of pressure currently for George & Zetterholm Racing. The yard has 25 boxes and 14 turn-out paddocks, with a further 15 boxes rented nearby and a barn with 16 more stables under construction at the yard. “We are limited in space, and we want to focus on quality rather than quantity,” says Amanda; although Noel’s ambitions have no limits.
“The dream eventually would be to compete with the top trainers in the championship, but we want to race on both sides of the channel. I’m English. I’ve grown up in England, and we’ve got English owners; so our dream is to win big races in England too. I can’t see why we can’t do that training here. We have amazing grass gallops; we can do racecourse gallops at tracks like Compiègne, so we can get them as ready as anyone in England. Cheltenham is quicker to access for us on the lorry than it is for Gordon Elliot and Willie Mullins; and Kempton is closer to us than Pau”!
Again, the support from Tom George will be key, as horses will spend a few days at his Down Farm in Slad near Cheltenham to acclimatise and school over British obstacles.
“I can understand why Britain is not a priority for many French trainers, as there is so much money to be won here; but we have owners that are buying horses to win on big days and they want to win at the big meetings. When we do get on the boat, hopefully we will bring a few winners back for France, with English owners and English and Swedish trainers”!
Lower limb anatomy and how it can be conditioned for racing
Article by Adam Jackson MRCVS
Better understanding the appropriate levels of exercise and training while the horse’s body grows and develops has been a topic of research for many years. Although it has been shown that young, growing horses are well-suited to adapt to conditioning, it is vital that continued research is performed in order to develop thoughtful and strategic training methods to promote healthy, fit and sound horses with long careers and lives.
Horses’ limbs consist of dozens of muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and joints that allow the horse to move as well as support its body weight. The limbs function to provide thrust and movement while absorbing impact and bearing weight. Most of the horse’s weight is supported by the fore limbs, while the propulsion of the horse is provided by the hind limbs. In addition, the horse has two apparatuses referred to as the stay apparatus and suspensory apparatus. The stay apparatus allows major joints in the limbs to lock so that the horse may rest and relax while standing. The suspensory apparatus is designed to absorb shock, carry the horse’s weight, and prevent the overextension of joints. Finally, the hooves are important structures that maintain support and traction as well as provide additional shock absorption.
Since the cardiovascular system provides blood supply throughout the body, by responding to various stimuli, it can control the velocity and amount of blood carried through the vessels, thus, delivering oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other important substances to cells and organs in the body. It plays a very important role in meeting the body’s demands during exercise, stress, and activity.
Exercise is used to increase the body’s ability to withstand repeated bouts of similar exercise with less impact. With a strong and healthy cardiovascular system, there is an improved ability of the musculoskeletal system receiving oxygen, thus, allowing muscles to better their capacity to use oxygen and energy. However, the adaptation period for each of these physiological systems do differ as the cardiovascular system adapts faster compared to the musculoskeletal system. This is often an overlooked consideration when developing training programmes for horses.
It is important to understand the various functions, structures, and adaptive processes of the horse’s musculoskeletal system such as bone, articular cartilage, tendons, and ligaments in order to develop appropriate training regimens.
Bone has many important roles that involve locomotion, the storage of minerals (especially calcium and phosphate), soft tissue and vital organ protection, and the support and containment of bone marrow. Bone is a specialised connective tissue, and together with cartilage forms the strong and rigid endoskeleton. The bone is continuously altering through two processes called bone modelling and bone remodelling, involving four cells referred to as osteoclasts, osteoblasts, osteocytes and bone lining cells.
Osteoblasts secrete bone matrix in the form of non-mineralised osteoid, which is then mineralised over a few weeks to form a bone matrix. Osteoclasts are involved in resorption of bone as this process occurs faster than the formation of bone. When the bone surfaces are not in the development or resorption phase, the bone surface is completely lined by a layer of flattened and elongated cells termed bone-lining cells. Osteocytes are derived from osteoblasts and are highly specialised to maintain the bone matrix. They are designed to survive hypoxic conditions and maintain biomineralisation of the bone matrix. Osteocytes also control osteoblastic and osteoclastic activities allowing bone remodelling.
The function of bone modelling is to alter and maintain shape during growth. As the horse grows and develops, bone modelling occurs with the acquisition and removal of bone. While the young horse grows and develops, bone modelling allows the bone to endure strains from everyday work and exercise. The adult skeleton undergoes a minimal amount of bone modelling. Due to the presence of the high frequency of bone modelling in young horses, their skeletal strength is highly influenced by strains to their bones during exercise and daily use. With this knowledge, it has been concluded and confirmed that short-term dynamic exercise of an adolescent can lead to beneficial changes to its bone morphology.
Bone remodelling is a different process, in which old and damaged bone is renewed, which enables the bone to respond and adapt to changing functional situations. Bone remodelling is usually a coordinated relationship between bone resorption and bone formation. This process occurs throughout the horse’s life with the renewal of primary, damaged or old bone. Osteoclasts absorb old and damaged bone, and the osteoblasts form new bone and lay down new bone matrix until the earlier absorbed bone is replaced. In those animals with musculoskeletal disease or damage, there is an imbalance of osteoblast and osteoclast activity. With the knowledge that osteoblast activity to make new bone takes months whilst osteoclast activity of removing old and damaged bone only takes a few days to two weeks, bone that is being repaired is at a high risk of further injury as bone removed has not been completely replaced. Multiple studies have shown that exercise while growing can provide lifelong benefits; however, it must be done with care and knowledge.
In addition, many studies have shown that exercise of a dynamic nature in moderate distances, such as that achieved in the pasture or prescribed short-distance high-speed work is beneficial to musculoskeletal development and may prevent injuries when entering race training. It has also been observed that long slow work does not increase bone strength. Below is a summary of the young horse response of the various types of exercise.
Articular cartilage is a highly specialised connective tissue found in joints with the role of providing a smooth, lubricated surface of articulation and to help transmit loads with a low amount of friction. The articular cartilage is a hyaline cartilage (flexible and strong tissue providing a smooth, slippery surface) with a dense “ExtraCellular Matrix” (ECM) consisting of specialised cells called chondrocytes, collagen and proteoglycans. These components help to retain water in the ECM that is required for the joints mechanical properties. As age increases, hydration of the matrix does decrease, resulting in stiffness. Chondrocytes are residential cells in articular cartilage that play a role in the development, maintenance, and repair of the ECM. They do respond to a variety of stimuli, including mechanical loads, growth factors, hydrostatic pressures, piezoelectric forces (formation of electric charge with force). Because of the lack of blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves as well as being a harsh biomechanical environment, there is a limited capacity to heal and repair. In addition, chondrocytes have limited potential for replication, thus, have limited healing capacity; and chondrocytes survival depends on an optimal chemical and mechanical environment.
Maintaining joint health is vital, which requires the preservation of healthy cartilage tissue. Inactivity of joints is detrimental to articular cartilage; thus, regular movement of joints and dynamic loads is needed to provide a normal articular cartilage structure and function. Biochemical responses of the cartilage to exercise are not nearly as well known compared to bone. While the confinement of young horses stunts joint development, excessive straining of cartilage can also reduce joint development. It has been observed that pasture access was optimal for the development of joints and the confinement or excessive sprint exercise (12–32 sprints of 40 metres for 6 days a week for 5 months) causes detrimental effects on the joint and may be deemed as unnatural exercise. It is also thought that exercise is needed well before two years of age to allow cartilage thickening as well as the avoidance of confinement. It can be concluded that further studies are required with respect to level of exercise and type of exercise in order to achieve healthy cartilage tissue as there is clearly a fine line between frequency and intensity of exercise.
Tendons and ligaments are distinct but closely related tissues that have unique and important roles in musculoskeletal function and musculoskeletal disease. Tendons and ligaments are dense, fibrous connective tissues that connect muscle to bone or bone to bone, respectively. These tissues transmit mechanical forces to stabilise the skeleton and allow body movement. Tendons and ligaments consist mainly of collagen type I as well as small amounts of collagen III, IV, V, and VI. There are also various proteoglycans in tendons and ligaments that both organise and lubricate collagen fibre bundles. The elasticity of tendons and ligaments is due to the large amount of type I collagen. During locomotion, the tendon decreases energy cost to the horse by acting as a spring to store and release energy while stretching and recoiling in the stance and swing phases of each stride. Tendons and ligaments have blood vessels and nerves that allow the homeostasis and response to injury.
Tenocytes are tightly regulated by a series of growth factors and transcription factors that allow the synthesis, maintenance, and the degradation of the tendon extracellular matrix. Tendons are elastic, but tearing may occur if there is excessive loading on the tendon and the repair of collagen is a slow process. In addition, tendons have crimp morphology where the tendons buckle in a state of relaxation and act as shock absorbers. Unbuckling of the tendon occurs during loading. This crimp morphology may be disturbed if an injury occurs and also is reduced in older horses.
Due to the variation of activity of tenocytes in foals and young horses, it has been observed that both a lack of exercise and excess of exercise can impair tendon make-up and subsequent functionality. With the current data and research that has been gathered, it can be concluded that if horses take advantage of spontaneous exercise when in the paddocks (which they often do), the developing tendons may benefit and be at a lower risk of injury when racing training starts.
Conclusion
It is clear that further research is needed in order to ascertain the optimal amount and type of exercise that is needed in order to provide a strong musculoskeletal system and functional performance. However, it has been shown that prescribed exercise during the growth of the horse can increase the longevity of the horse’s health and performance. It has been observed that confinement and the lack of loading can result in weaker tissues and the loss of function of none, tendons, ligaments and articular cartilage. However, it must also be recognised that medical attempts to alleviate pain so that a horse can continue to train through an injury can greatly increase tissue damage which is detrimental to the horse’s health and career. It is far more beneficial to provide an adequate amount of time for the injury to heal, thus, putting the horse’s health and wellbeing as a top priority.
Nutritional Perspective
Bone development in yearlings from the sales ring to racing
Article by Des Cronin B.Ag.Sc, MBA
Maintaining the equine skeleton is vital to ensure optimal development of the young growing horse, minimise risk of injury in the performance horse, and promote longevity and soundness.
The skeletal development and health of a young horse begins in utero and ensuring the broodmare receives the correct intake of key nutrients will be critical to the growth of the unborn foal. Producing high-quality milk places a significant drain on the mineral reserves of the mare. Maintaining mineral intakes during peak lactation is vital to ensure the foal receives the best nutrition to support the rapid skeletal development in the early weeks and months of growth. During this time, bone formation, body size, and muscle mass greatly increase. Risk of defective bone and related tissue formation increases with one of more of the following:
Poor diet with the incorrect balance of energy and nutrients in the daily ration
Inadequate amounts of calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P)
A reversed Ca:P ratio
Low zinc (Zn) or copper (Cu) in the diet
Low Vitamin D
Feeding a young horse for a maximum growth rate is undesirable because bone hardening lags greatly behind bone lengthening. At 12 months old, the young horse could reach about 90 to 95 per cent of its mature height but only about 75 per cent of its mature bone mineral content.
Ideally, young horses should gain weight at a rate that their developing bones can easily support. Growing bones and connective tissues don’t have the strength to support rapid weight gain from overfeeding, especially energy. Rapid weight gain can also make other skeletal anomalies worse. In these cases the risk of developmental orthopaedic disorders (DOD) and unsoundness increases.
DOD and unsoundness can also occur during uneven growth. For example, switching an underfed, slow-growing horse to a good diet that allows quick growth (compensatory growth), increases the risk of DOD. Foals between the ages of 3 and 9 months of age are at greatest risk of DOD.
Fresh forages, for example grazed grass, usually provide enough major minerals such as calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P) for the growing horse. However, there can be significant variation in calcium and phosphorus levels in all forages but particularly preserved forages (hay and haylage). Forage analysis should always be undertaken to determine mineral composition.
For young fast-growing horses, the diet must supply the quantities of calcium and phosphorus needed for normal bone formation. In terms of Ca:P ratio, the ratio must be positive in favour of calcium. Horses are much more tolerant of high-dietary calcium than other species. For practical purposes, a good guideline would be to keep the ratio Ca:P between 1.5 to 1 and 2.5 to 1. Grains (e.g., oats) contain 10 per cent of the calcium level found in typical forages. Grains are poor sources of calcium, both in terms of the amount of calcium supplied and their effect on Ca:P ratio in the diet. Where grains are fed, supplementation will be necessary to balance the diet.
While some forages may contain adequate calcium and phosphorus, they will typically supply less than 20 per cent of the daily requirements for trace elements. Supplementation of trace elements will generally be necessary to support normal bone development.
Where concentrates are fed (especially low levels), supplementation may still be necessary to balance the overall mineral and trace element intake. Nutritional advice should be sought to ensure the horse's diet is correctly balanced.
To meet the carefully balanced requirements of key minerals, it is advisable to supplement the daily rations of growing horses and young horses entering training with an appropriate nutritional product.
Make sure that the supplement used contains the correct ratio of calcium and phosphorus, as well as other key nutrients such as vitamin D and chelated trace elements (copper, manganese, and zinc) to support normal bone development.
Supplementing branch chain amino acids in the diet ensures that growth is maintained. Lysine plays a key role when protein concentrations in the body are low. Vitamin A supports collagen formation, which is a key component of the supportive structures of joints (tendons and ligaments). Vitamin D3 is added to enhance calcium absorption.
Although growth rates slow after the age of two, they are still juvenile in their skeletal development with some growth plates, such as the shoulder and stifles, yet to completely close. Although they may look like fully grown adults, it is still important to meet nutritional requirements especially if starting training and work. With the addition of exercise and training, a young horse's nutritional needs change. The added forces from groundwork on the long bones and increased requirements of other nutrients like electrolytes need to be considered.
Finally, horses all grow and develop at different rates because of factors such as genetics. Some youngsters will need more support for longer periods of time than others, so it is important to manage accordingly.
Who should be dictating the Rules of Racing - the racing industry or government?
Article by Lissa Oliver
Regular readers of this publication will already be well aware of racing’s social licence and the efforts required to ensure the sport’s popularity with the public and, essentially, the wellbeing of our participants. EU legislation is increasing in strength in addressing equine welfare in general, but in Germany in particular, laws coming down from the government are impacting many racing yards.
The law introduced last year regarding minimum paddock time for all horses is one such notable problem. As Belgian trainer Guy Heymans points out, “Turnout for horses every day is not the same as the requirement for horses to remain in paddocks. If I understand correctly, the demand is not just turnout; they mean that the horses are in a paddock for a certain period of time every day. It’s OK for me, but a trainer with 20 horses or plus in training will probably not have enough paddocks, and it is difficult to keep such a horse in shape. Of course it is a plus for horses to spend a short time in the paddock, but when they demand horses stay permanently in paddocks, it is impossible to bring a horse to top form.”
Not every trainer may agree with that, and some have enjoyed great success ‘training from the field’, but it is a matter of personal choice and methods, as well as having the luxury of such choice. It isn’t so much about making our own decisions on equine welfare in particular, which we would all prefer to embrace as much as we can; but it’s more about the practical ability to do so and the apparent gulf between those setting the rules, and now laws, and those who have to apply them in daily practise.
“There are some countries lagging a bit behind in welfare, and I would be happy to see more legislation coming in,” says Irish trainer Amanda Mooney. “We just have to learn to adapt and work with it. Sweden has a very high standard of welfare and a very good aftercare service. Horses aren’t just sold on and rehomed; they’re put out on loan—the same as the Godolphin Lifetime Care programme. I think more could be done for aftercare.”
Germany has the strictest animal welfare legislation worldwide and is the only country in the EU to have integrated animal welfare into its constitution. German law could be the crystal ball into the rest of European racing’s future. In 2018, horses were no longer allowed to run in a tongue-tie, as a result of animal welfare concerns. Rüdiger Schmanns, director of racing for German Racing, said at the time, "In all other equestrian sports in Germany the use of tongue-ties is banned—racing was the last equine sport which allowed tongue-ties. With growing animal welfare activities, especially in Germany, there was no possibility of allowing the use of tongue-ties to continue."
This year, stricter whip rules were adopted; and any jockey who uses the whip six times in a German horse race could expect an 84-day ban under the new penalty system. The number of strokes of the whip allowed per race has been cut from five down to three, and the length of bans for going more than one over the limit can now be measured in weeks and months, rather than days.
“This looks extreme but will hopefully not occur,” said Rüdiger Schmanns. “The animal health pressure is high in Germany. We would like to have harmonised rules regarding the whip at least in the whole of Europe, but that seems to be a long way off as the differences in England and Ireland compared to France and Germany are still quite big.”
At least those rules are coming down from racing’s governing bodies, assisted by Boards of selected professionals representing all industry stakeholders. In theory, the Rules of Racing should be a suitable compromise agreed by all for the betterment and progression of the sport. But what happens when Rule changes have not involved industry stakeholders? When changes come from government level they may not always be the desired result of consultation with racing’s professionals.
The Rules of Racing have historically been set down by industry participants to govern the sport in a fair manner. The earliest known example is quite literally set in stone and dates to the earliest part of the first century, some 2,000 years old. Professor Hasan Bahar’s 2016 discovery at an ancient Roman racecourse in Turkey—the oldest existing tablet describing the rules of horseracing—illustrates a keen sense of fairness in the sport. Prof. Bahar points out, “It says that if a horse comes in first place in a race, it cannot participate in other races.” A winning owner was also forbidden from entering any other horses into an event’s subsequent races, presumably to give others a chance at glory, Prof Bahar suggests. “This was a beautiful rule, showing that races back then were based on gentlemanly conduct.”
It also highlights the origins of the sport’s governance, replicated in Britain by the next earliest-known Rules of Racing set by The Jockey Club in 1750. The Rules were dictated by racehorse owners to preserve and progress their racing and breeding interests. Even prior to a rule book, in 1664, it was King Charles II who personally wrote The Rules of the Newmarket Town Plate. According to Whyte's History of the English Turf (1840), King Henry VIII passed a number of laws relating to the breeding of horses. Racing was a self-governing institution, more to the point, one governed by racehorse owners.
Nevertheless, governments haven’t always been keen for that arrangement to continue. The British Jockey Club was formed in 1750, specifically to create and apply the Rules of Racing in the wake of a decade of Parliamentary opposition to the sport. There are few racing nations left where the original governance of a Turf Club or Jockey Club hasn’t transitioned into a State-funded corporate body.
Parliamentary opposition to the growth of horse racing in the 1740s focused on the damaging effect of gambling. Three hundred years on, no other sport has entangled itself so constrictively with gambling. Racing’s economy is no longer based on the revenue of racehorse owners, and the sport is answerable to the holders of the purse strings.
While researching a quote from former Member of Parliament Sir Clement Freud, who claimed that “horse racing is organised purely to generate taxes,” the transcript of an interesting House of Lords debate surfaced. Though dated February 1976, the facts, figures, and sentiments quoted could as easily place it in 2023, which makes for a sorry commentary on British racing.
The establishment of a Royal Commission on Gambling led to Sir Clement Freud remarking on the “large number of otherwise non-viable racecourses kept open to ensure sufficient races being run, even as the financial rewards to the owners and trainers declined to the point where most could barely cover their expenses.”
During the House of Lords’ debate on the matter, Lord Newall observed, “The income from betting is believed to reach the optimum level with two meetings every day with staggered starting times. After this, the same money apparently chases after more horses.” And perhaps initiating an argument that continues to this day, Lord Gisborough pointed out, “There has been, and often is, criticism of the value of the Pattern race prizes, but these few races at the top of the pyramid of racing are the necessary incentives to encourage breeding of the best animals, the very capital of the industry. It would not help racing in the long run if the value of the Pattern prizes were to be spread over the rest of racing. They provide the vital opportunity for the best horses of the world to be matched together, without which the best British horses would have to race more abroad to prove their value for breeding purposes.”
Perhaps we digress here, but the relevant points of 40 years ago, 300 years ago and, indeed, 2,000 years ago are summed up by The Lord Trevethin Oaksey, who explained, “What you need is honourable, fair-minded, unbiased men who are answerable to nobody but themselves, and who have as much experience as possible of the problems involved.”
And therein lies the modern problem, with racing dependent upon gambling revenue and accountable to the betting operators and the taxpayer. Self-governance is fast becoming a thing of the past, but the bigger problem is being given the necessary time and finances to adapt.
In our 2021 winter issue, German trainer Dominik Moser warned, “We have so many new rules and many more rules being introduced for next year. All horses must spend a number of hours out in the paddock each day, and they must be assessed by a vet before going into training. I have paddocks for my horses, but I don’t currently have enough for all of them to be out every day, so I have to build more paddocks. My aim is that all of my horses will be able to go out from after they have finished training at 1pm until the evening. The training centres, such as Cologne, will have a big problem, because there is not enough space for the number of paddocks needed.
“These rules are coming directly from government, not from Deutscher Galopp. I like that we think more about the horses; we have recently been thinking more about the people, the jockeys and staff. The horse had stopped being our number one concern. This is the right way, but the rule is not easy to adapt to; we haven’t been given time to prepare.”
Christian von der Recke agrees wholeheartedly with the reasoning behind the legislation and tells us, “From day one, our horses go to the paddock; and I am sure that is part of the success. They enjoy more variety and have less stomach ulcers. More exercise is the key to success.” However, von der Recke has a large private facility at his disposal, with ample paddock space, denied to those trainers based at training centres.
One such centre is Newmarket, where John Berry reasons, “It's clearly preferable to turn one's horses out for part of the day rather than have them confined in their boxes for 23 hours a day or more; but some people prefer not to do so, often because of not having either the time nor the space to do so. Just common sense says it's better for them mentally, and physically too; but each to his own.
“I'd actually regard not gelding horses as a far bigger concern as regards horses' mental well-being than lack of freedom, but that's by the by. Obviously, some colts have to remain colts to ensure the survival of the species, but only a tiny percentage are required for stud duties; and keeping the others as colts rather than gelding them is just nuts. Sexual frustration must be at least as great a cause of anguish for horses as frustration at lack of liberty.
“I'd have thought if a government wanted to do something to increase the sum of equine happiness, addressing this issue might be more appropriate, but obviously it would be hard to frame the laws satisfactorily.
“Obviously in utopia every horse would have access to freedom and to companionship (although the latter isn't always a good idea with colts), but life isn't utopian. Similarly, it would clearly be a good idea if every dog could have a life where he can have a run off the lead every day, every school would have good sports facilities, and every community would have good recreation and leisure facilities. But we can't even manage to achieve that with humans, so I'd be surprised if the government thought that this was a worthwhile way to direct its energies.”
British government’s current distraction is reforming gambling legislation, which is creating anxiety and even panic among the racing community. Once again, it’s social licence and a need to enforce ‘protection’ that attracts government attention, with affordability checks upsetting punters and threatening horse racing's revenue.
In Ireland, that same focus is the driving force behind the Gambling Regulation Bill, which proposes a ban on televised gambling advertising between 5.30am and 9pm, which of course affects a large portion of advertising on live horse racing coverage. As a result, Racing TV and Sky Sports Racing have threatened to pull their racing coverage in Ireland, stating that their service will become "economically unviable.”
This no longer comes down to welfare or integrity within the sport. Do we protect the vulnerable or protect our own interests, even in the knowledge our interests conflict? We may try to excuse our decision, but further down the line, as more attention is put on the sport, will we really be able to defend our corner?
Ryan McElligott, CEO Irish Racehorse Trainers Association, announced in reaction to the bill, "If Racing TV determined it was no longer viable to broadcast in Ireland, then Irish racing disappears off our screens. That would be detrimental to the whole industry.
"There are plenty of owners who don't get to go racing as much as they would like, but it's very easy to watch their horses run should they not make it. If you take that away, I think that would put a huge dent in the sport's appeal and also demand from an owner's point of view. It would put us at a huge disadvantage when compared to other jurisdictions.
"We're talking about subscription channels, and it is a requirement that you are over the age of 18 to buy a subscription to a package like Racing TV. These dedicated racing channels exist behind a paywall, so there is already a safeguard there.
“Every facet of the industry is wholly supportive of gambling regulation which protects vulnerable people. This is not a deliberate move to damage the sport; this would be an unintended consequence. It is hugely concerning for the industry."
In Britain, owners have already very publicly left the game as a result of the Gambling Act Review White Paper financial risk checks. All betting operators have a social responsibility to create a safe environment, and how much money a client can afford to spend on gambling is a key part of the safe environment.
Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport, Lucy Frazer KC, described the White Paper as “consumer freedom and choice on the one hand, and protection from harm on the other” while stating in the House of Commons in April: “With the advent of the smartphone, gambling has been transformed: it is positively unrecognisable today, in 2023, from when the Gambling Act was introduced in 2005. Temptation to gamble is now everywhere in society, and while the overwhelming majority is done safely and within people’s means, for some, the ever-present temptation can lead them to a dangerous path. When gambling becomes addiction, it can wreck lives: shattered families; lost jobs; foreclosed homes; jail time; suicide. These are all the most extreme scenarios, but it is important to acknowledge that, for some families, those worst fears for their loved ones have materialised. Today we are bringing our pre-smartphone regulations into the present day with a gambling White Paper for the digital age.”
More and more, we can expect legislation to encroach on the racing industry and force us to face moral dilemmas. Racing jurisdictions are doing their best to be seen by the public to be doing their best for equine welfare. Currently, Ireland has a very basic 28-page “Our Industry, Our Standards” guide to equine welfare; France has a very comprehensive 139-page “Charter for Equine Welfare,” based upon the official EU Paper; Germany has a 44-page “Animal Welfare in Equestrian Sport Guideline”; and Britain has “A Life Well Lived,”—a 130-page welfare strategy. Sweden, renowned throughout other racing nations for its top-class welfare, relies on a website to provide current guidelines and information.
The EU Discussion Paper on Equine Care, adopted so well by France Galop in its charter, has multiple language versions and informative images, making it a simple solution for those countries lagging behind. It is also of visual appeal to those outside of the sport seeking reassurance. We may not consider them to be relevant, but they are proving to be the most important players in rulemaking.
TopSpec Trainer of the Quarter – Stuart Williams
Article by Lissa Oliver
“A conjurer of a trainer. One who can transform an apparently moderate animal into a frequent winner.” Thus quoted Timeform, and we can only concur as we award our TopSpec Trainer of the Quarter to Newmarket-based Stuart Williams for a truly remarkable upgrade of the Godolphin cast-off, Quinault.
Joining Williams from Charlie Appleby in February this year, the three-year-old gelding had only one previous run to his name, when finishing last in a 2022 novice race. Quinault’s first run for Williams saw him place third and earn an official rating of 47. His record for 2023 now reads an impressive seven wins from 10 starts to date, including a straight run of six wins in handicap company, which took him to the brink of an historic record, hardly disappointing when breaking the run with a third in the Shergar Cup Sprint at Ascot. However, it was back at Ascot that Quinault did manage his seventh win in the bet365 Handicap in September, taking his official rating to 97.
“I’m pleased to say he has come out of the race in good form. He’s a very tough horse, and he’s got loads of talent as well,” says Williams, singling out apprentice jockey Luke Catton as instrumental in his development. “Luke has done a fantastic job settling him. The horse was just a runaway when he arrived—he would just bolt.
“We trained him on a treadmill for the first two months—so he never left the yard—before we slowly started to introduce him to Newmarket Heath. There’s a lot of work gone into him.
"He’s always had talent; it’s just been a case of letting the horse know it and letting him use it. He’s always been fast, and he’s bred to get further; so as long as we can keep him settled in his races, that’s a route we’ll look to go with him. He's fairly straightforward to ride—he just jumps and goes.”
Williams, who took out his licence in 1993, is based on Hamilton Road in Newmarket, conveniently backing onto the racecourse side training grounds. Diomed Stables has 72 boxes, including 60 newly refurbished American barn-style boxes with climate control and six grass turnout paddocks. Williams also has a sand ride for light exercise of his horses, as well as an equine solarium.
He is a great believer in the benefits of swimming, and his horses use the nearby equine swimming pool on a regular basis to help improve fitness without putting excessive strain on their legs.
Williams has been involved in racing since he was a child—his father having been a jockey, and in his formative years worked for Bill O’Gorman, Ron Sheather and Alex Scott, as well as Bart Cummings in Australia. He also spent time working in France and Norway before taking out his own licence. In 2011, he received what he acknowledges as ‘the highest recognition’ from his peers when he was voted president of the National Trainers Federation.
Williams feels it might now be time to step Quinault up to stakes company after his latest win; and the once 47 to now 97 rated gelding certainly gives the impression there’s plenty more to come.
Dangers of inbreeding and the necessity to preserve sire lines in the thoroughbred breed
Inbreeding is the proportion of the genome identically inherited from both parents.
Inbreeding coefficients can be estimated from pedigrees, but pedigree underestimates the true level of inbreeding. Genomics can measure the true level of inbreeding by examining the extent of homozygosity (identical state) in the DNA of a horse. A mechanism to examine genomic inbreeding for breeding purposes has yet to be developed to be used by all breeders but once available, it must be considered as a tool for breeders.
Breeding of potential champion racehorses is a global multi-billion sterling or dollar business, but there is no systematic industry-mediated genetic population management.
Inbreeding in the modern thoroughbred
The thoroughbred horse has low genetic diversity relative to most other horse breeds, with a small effective population size and a trend of increasing inbreeding.
A trend in increased inbreeding in the global thoroughbred population has been reported during the last five decades, which is unlikely to be halted due to current breeding practices.
Ninety-seven percent of pedigrees of the horses included in a recent study feature the ancestral sire, Northern Dancer (1961); and 35% and 55% of pedigrees in EUR and ANZ contain Sadler’s Wells (1981) and Danehill (1986), respectively.
Inbreeding can expose harmful recessive mutations that are otherwise masked by ‘normal’ versions of the gene. This results in mutational load in populations that may negatively impact on population viability.
Genomics measured inbreeding is negatively associated with racing in Europe and Australia. The science indicates that increasing inbreeding in the population could further reduce viability to race.
In North America, it has been demonstrated that higher inbreeding is associated with lower number of races. In the North American thoroughbred, horses with higher levels of inbreeding are less durable than animals with lower levels of inbreeding. Considering the rising trend of inbreeding in the population, these results indicate that there may also be a parallel trajectory towards breeding less robust animals.
Note that breeding practices that promote inbreeding have not resulted in a population of faster horses. The results of studies, generated for the first time using a large cohort of globally representative genotypes, corroborate this.1,3
Health and disease genes
It is both interesting and worrisome to consider also that many of the performance-limiting genetic diseases in the thoroughbred do not generally negatively impact on suitability for breeding; some diseases, with known heritable components, are successfully managed by surgery (osteochondrosis dessicans, recurrent laryngeal neuropathy, for example), nutritional and exercise management (recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis), and medication (exercise induced pulmonary haemorrhage). This unfortunately facilitates retention of risk alleles in the population and enhances the potential for rapid proliferation of risk alleles if they are carried by successful stallions.
Types of inbreeding
Not all inbreeding is bad. Breeders have made selections for beneficial genes/traits over the generations, resulting in some inbreeding signals being favoured as they likely contain beneficial genes for racing. Importantly, examination of a pedigree cannot determine precisely the extent of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ inbreeding. This can only be determined from DNA analysis.
Historic inbreeding (arising from distant pedigree duplicates) results in short stretches of DNA identically inherited from sire and dam.
This may be considered ‘good’ inbreeding.
It has no negative effect on racing.
The horse may be carrying beneficial mutations that have been maintained from distant ancestors through breeders’ selection.
Recent inbreeding (arising from close pedigree duplicates) results in long stretches of DNA identically inherited from sire and dam.
This may be considered ‘bad’ inbreeding.
It is negatively associated with racing.
The horse may be carrying harmful mutations that have not yet been ‘purged’ from the population.
Obviously, in terms of breeding, it’s always possible to find examples and counterexamples of remarkable individuals; but the science of genetics is based on statistics and not on individual cases.
Sire lines
Analysis of the Y chromosome is the best-established way to reconstruct paternal family history in humans and animal species. The paternally inherited Y chromosome displays the population genetic history of males. While modern domestic horses (Equus caballus) exhibit abundant diversity within maternally inherited mitochondrial DNA, until recently, only limited Y-chromosomal sequence diversity has been detected.
Early studies in the horse indicated that the nucleotide variability of the modern horse Y chromosome is extremely low, resulting in six haplotypes (HT). However, this view has changed with the identification of new genetic markers, showing that there is considerably more genetic diversity on the horse Y chromosome than originally thought. Unfortunately, in thoroughbreds, the male gene pool is restricted, with only three paternal lines remaining.
The Institute of Animal breeding and genetics of the Veterinary Medicine School at Vienna applied fine-scaled Y-chromosomal haplotyping in horses and demonstrated the potential of this approach to address the ancestry of sire lines. They were able to show the microcosmos of the Tb-clade in the thoroughbred sire lines.
It is interesting to note that more than half of the domestic horses in the dataset (76 of 130) have a Y chromosome with a thoroughbred ‘signature’. These includes thoroughbreds, standardbreds, many thoroughbred-influenced breeds (warmbloods, American quarter horses, Franches-Montagnes, a Lipizzan stallion and the Akhal-Tekes).
The General Stud Book shows that thoroughbred sire lines trace back to three founding stallions that were imported to England at the end of the 17th century. 5 Now, the heritage of the thoroughbred sire lines can be better understood using Y chromosome information. It is now possible to clearly distinguish sublines of Darley Arabian, born in 1700 (Tb-d) and Godolphin Arabian, born in 1724 (formerly Tb-g, now Tb-oB3b). The third founder, Byerley Turk, born in 1680, was characterised by the Tb-oB1 clade. According to pedigree information, only few of the tested males trace back paternally to Byerley Turk, which are nearly extinct.
There are now 10 different Y chromosome sub-types known in the thoroughbred. Two come from the Godolphin Arabian, five come from Byerley Turk, and three come from Darley Arabian.
Even if genetic analysis shows that there was an error in the stud book recording of St Simon’s parentage and that horses descending from St Simon should be attributed to the Byerley Turk lineage, probably 90% of the current stallions are from the Darley Arabian male line. So, there is a true risk that we could lose a major part of the Y chromosome diversity.
Conclusions and solutions
We should do everything we can to ensure that thoroughbreds are being sustainably bred and managed for future generations. With the breeding goal to produce viable racehorses, we need to ask ourselves, are we on track as breeders?
If inbreeding is negatively affecting the chances of racing and resulting in less durable racehorses, will this continue to affect foal crops in the future? How can we avert the threat of breeding horses that are less able to race? If the ability to race is in jeopardy, then is the existence of the thoroughbred breed at risk?
International breeding authorities are studying the situation and thinking about general measures allowing the sustainability of the breed.
Breeders
What can individual breeders do to produce attractive foals that are safe from genetic threats? How do you avoid the risk of breeding horses that are less fit to race?
There is no miracle recipe, and each breeder legitimately has his preferences.
An increasingly important criteria for the choice of a stallion is his physical resistance and his vitality, as well as those of his family. It is often preferable to avoid using individuals who have shown constitutive weaknesses, or who seem to transmit them.
The use of stallions from different male lines can make it possible to sublimate a strain and better manage the following generations. The study of pedigrees must exceed the three generations of catalogue pages.
In the future, genomics—the science that studies all the genetic material of an individual or a species, encoded in its DNA—will certainly be able to provide predictive tools to breeders. This is a track to follow.
Trainers
Trainers should be aware of the danger of ‘diminishing returns,’ where excessive inbreeding occurs. Today, when animal welfare and the fight against doping are essential parameters, it is obvious that trainers must be aware of the genetic risks incurred by horses possibly carrying genetic defects.
Together with bloodstock agents, trainers are the advisers for the owners when buying a horse. Trainers already know some special traits of different families or stallions, but genomic tools might become essential for them too.
Sources
1. Genomic inbreeding trends, influential sire lines and selection in the global Thoroughbred horse population Beatrice A. McGivney 1, Haige Han1,2, Leanne R. Corduff1, Lisa M. Katz3, Teruaki Tozaki 4, David E. MacHugh2,5 & Emmeline W. Hill ; 2020. Scientific Reports | (2020) 10:466 | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57389-5
2. Inbreeding depression and durability in the North American Thoroughbred horse Emmeline W. Hill, Beatrice A. McGivney, David E. MacHugh; 2022. Animal Genetics. 2023;00:1–4. _wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/age
3. Founder-specific inbreeding depression affects racing performance in Thoroughbred Horses. Evelyn T. Todd, Simon Y. W. Ho, Peter C. Thomson, Rachel A. Ang, Brandon D. Velie & Natasha A. Hamilton; 2017. Scientific Reports | (2018) 8:6167 | DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-24663-x
4. The horse Y chromosome as an informative marker for tracing sire lines Sabine Felkel, Claus Vogl , Doris Rigler, Viktoria Dobretsberger, Bhanu P. Chowdhary, Ottmar Distl , Ruedi Fries , Vidhya Jagannathan, Jan E. Janečka, Tosso Leeb , Gabriella Lindgren, Molly McCue, Julia Metzger , Markus Neuditschko, Thomas Rattei , Terje Raudsepp, Stefan Rieder, Carl-Johan Rubin, Robert Schaefer, Christian Schlötterer, Georg Thaller, Jens Tetens, Brandon Velie, Gottfried Brem & Barbara Wallner; 2018. Scientific Reports | (2019) 9:6095 | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42640-w
5. Identification of Genetic Variation on the Horse Y Chromosome and the Tracing of Male Founder Lineages in Modern Breeds Barbara Wallner, Claus Vogl, Priyank Shukla, Joerg P. Burgstaller, Thomas Druml, Gottfried Brem Institute of Animal Breeding and Genetics, Depart. 2012. PLOS ONE | www.plosone.org April 2013, Volume 8, Issue 4, e60015
6. New genetic evidence proves that the recorded pedigrees of the influential leading sires Bend Or and St. Simon were incorrect. Alan Porter; ITB 2021
7. Eight Belle’s breakdown: a predictable tragedy William Nack; ESPN.com 2008
8. Suzi Prichard-Jones: Founder of "The Byerley Turk & Godolphin Arabian Conservation Project"
Special thanks to Emmeline Hill for her help in the completion of this article
Air Quality and Air Pollution’s Impact on Your Horse’s Lungs
There’s nothing like hearing a horse cough to set people scurrying around the barn to identify the culprit. After all, that cough could mean choke, or a respiratory virus has found its way into the barn. It could also indicate equine asthma. Yes, even those “everyday coughs” that we sometimes dismiss as "summer cough" or "hay cough" are a wake-up call to the potential for severe equine asthma.
Formerly known as heaves, broken wind, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or recurrent airway obstruction (RAO), this respiratory condition is now called severe equine asthma (sEA). These names reflect how our scientific and medical understanding of this debilitating disease has changed over the years. We now consider heaves to be most comparable to severe asthma in people.
But what if your horse only coughs during or after exercise? This type of cough can mean that they have upper airway irritation (think throat and windpipe) or lower airway inflammation (think lungs) meaning inflammatory airway disease (IAD), which is now known as mild-to-moderate equine asthma (mEA). This airway disease is similar to childhood asthma, meaning that it can go away on its own. However, it is still very important to call your veterinarian out to diagnose mEA. This disease causes reduced athletic performance, and there are different subtypes of mEA that benefit from specific medical therapies. In some cases, mEA progresses to sEA.
Equine Asthma and Air Quality
What does equine asthma have to do with air quality? A lot, it turns out. Poor air quality, or air pollution, includes the barn dusts—the allergens and moulds in hay and the ground-up bacteria in manure, as well as arena dusts and ammonia from urine. Also, very importantly for both people and horses, air pollution can be from gas and diesel-powered equipment. This includes equipment being driven through the barn, the truck left idling by a stall window, or the smog from even a small city that drifts nearly invisibly over the surrounding farmland. Recently, forest-fire smoke has been another serious contributor to air pollution.
Smog causes the lung inflammation associated with mEA. Therefore, it is also likely that air pollution from engines and forest fires will also trigger asthma attacks in horses with sEA. Smog and smoke contain many harmful particulates and gases, but very importantly they also contain fine particulate matter known as PM2.5. The 2.5 refers to the diameter of the particle being 2.5 microns. That’s roughly 30 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair. Because it is so small, this fine particulate is inhaled deeply into the lungs where it crosses over into the bloodstream. So, not only does PM2.5 cause lung disease, but it also causes inflammation elsewhere in the body including the heart. Worldwide, even short-term exposure is associated with an increased risk of premature death from heart disease, stroke, and lung cancer. This PM2.5 stuff is not trivial!
In horses, we know that PM2.5 causes mEA, so it’s logical that smog and forest-fire smoke exposure could exacerbate asthma in horses, but we don’t know about heart disease or risk of premature death.
Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests and Treatments
Equine asthma manifests with a spectrum of symptoms that vary in severity and the degree of debilitation they cause. Just like in people with asthma, the airways of horses with mEA and sEA are “hyperreactive.” This means that the asthmatic horse’s airways are extra sensitive to barn dusts that another horse’s lungs would just “ignore.” The asthmatic horse’s airways constrict, or become narrower, in response to these dusts. This narrowing makes it harder to get air in and out of the lungs. Think about drinking through a straw. You can drink faster with a wider straw than a skinnier one. It’s the same with air and the airways. In horses with mEA, the narrowing is mild. In horses with sEA, the constriction is extreme and is the reason why they develop the “heaves line”; they have to use their abdominal muscles to help squeeze their lungs to force the air back out of their narrow airways. They also develop flaring of their nostrils at rest to make their upper airway wider to get more air in. Horses with mEA do not develop a heaves line, but the airway narrowing and inflammation do cause reduced athletic ability.
The major signs of mEA are coughing during or just after exercise that has been going on for at least a month and decreased athletic performance. In some cases, there may also be white or watery nasal discharge particularly after exercise. Often, the signs of mEA are subtle and require a very astute owner, trainer, groom, or rider to recognise them.
Another very obvious feature of horses with sEA is their persistent hacking cough, which worsens in dusty conditions. “Hello dusty hay, arena, and track!” The cough develops because of airway hyperreactivity and because of inflammation and excess mucus in the airways. Mucus is the normal response of the lung to the presence of inhaled tiny particles or other irritants. Mucus traps these noxious substances so they can be coughed out, which protects the lung. But if an asthma-prone horse is constantly exposed to a dusty environment, it leads to chronic inflammation and mucus accumulation, and the development or worsening of asthma along with that characteristic cough.
Accurately Diagnosing Equine Asthma
Veterinarians use a combination of the information you tell them, their observation of the horse and the barn, and a careful physical and respiratory examination that often involves “rebreathing.” This is a technique where a bag is briefly placed over the horse’s nose, causing them to breathe more frequently and more deeply to make their lungs sound louder. This helps your veterinarian hear subtle changes in air movement through the lungs and amplifies the wheezes and crackles that characterise a horse experiencing a severe asthma attack. Wheezes indicate air “whistling” through constricted airways, and crackles mean airway fluid buildup. The fluid accumulation is caused by airway inflammation and contributes to the challenge of getting air into the lung.
Other tests your veterinarian might use are endoscopy, bronchoalveolar lavage, and in the specialist setting, pulmonary function testing. They will also perform a complete blood count and biochemical profile assay to help rule out the presence of an infectious disease.
Endoscopy allows your veterinarian to see the mucus in the trachea and large airways of the lung. It also lets them see whether there are physical changes to the shape of the airways, which can be seen in horses with sEA.
Bronchoalveolar lavage, or “lung wash” is how your veterinarian assesses whether there is an accumulation of mucus and inflammatory cells in the smallest airways that are too deep in the lung to be seen using the endoscope. Examining lung wash fluid is a very important way to differentiate between the different types of mEA, between sEA in remission and an active asthma attack, and conditions like pneumonia or a viral lung infection.
Finally, if your veterinarian is from a specialty practice or a veterinary teaching hospital, they might also perform pulmonary function testing. This allows your veterinarian to determine if your horse’s lungs have hyperreactive airways (the hallmark of asthma), lung stiffening, and a reduced ability to breathe properly.
Results from these tests are crucial to understanding the severity and prognosis of the condition. As noted earlier, mEA can go away on its own; but medical intervention may speed healing and the return to athletic performance. With sEA, remission from an asthmatic flare is the best we can achieve. As the disease gets worse over time, eventually the affected horse may need to be euthanised.
Management, Treatment and Most Importantly—Prevention
Successful treatment of mEA and sEA flares, as well as long-term management, requires a multi-pronged approach and strict adherence to your veterinarian’s recommendations.
Rest is important because forcing your horse to exercise when they are in an asthma attack further damages the lung and impedes healing. To help avoid lung damage when smog or forest-fire smoke is high, a very useful tool is your local, online, air quality index (just search on the name of your closest city or town and “AQI”). Available worldwide, the AQI gives advice on how much activity is appropriate for people with lung and heart conditions, which are easily applied to your horse. For example, if your horse has sEA and if the AQI guidelines say that asthmatic people should limit their activity, then do the same for your horse. If the AQI says that the air quality is bad enough that even healthy people should avoid physical activity, then do the same for you AND your horse. During times of poor air quality, it is recommended to monitor the AQI forecast and plan to bring horses into the barn when the AQI is high and to turn them out once the AQI has improved.
Prevent dusty air. Think of running your finger along your tack box – whatever comes away on your finger is what your horse is breathing in. Reducing dust is critical to preventing the development of mEA and sEA, and for managing the horse in an asthmatic flare.
Logical daily practices to help reduce dust exposure:
Turn out all horses before stall cleaning
Wet down the aisle prior to sweeping
Never sweep debris into your horse’s stall
Use low-dust bedding like wood shavings or dust-extracted straw products, which should also be dampened down with water
Reduce arena, paddock, and track dust with watering and maintenance
Consider low-dust materials when selecting a footing substrate
Steam (per the machine’s instructions) or soaking hay (15–30 minutes and then draining, but never store steamed or soaked hay!)
Feed hay from the ground
Feed other low-dust feeds
Avoid hay feeding systems that allow the horse to put their nose into the middle of dry hay—this creates a “nosebag” of dust
Other critical factors include ensuring that the temperature, humidity and ventilation of your barn are seasonally optimised. Horses prefer a temperature between 10–24 ºC (50–75 ºF), ideal barn humidity is between 60–70%. Optimal air exchange in summer is 142 L/s (300 cubic feet/minute). For those regions that experience winter, air exchange of 12–19 L/s (25–40 cubic feet/minute) is ideal. In winter, needing to strip down to a single layer to do chores implies that your barn is not adequately ventilated for your horse’s optimal health. Comfortable for people is often too hot and too musty for your horse!
Medical interventions for controlling asthma are numerous. If your veterinarian chooses to perform a lung wash, they will tailor the drug therapy of your asthmatic horse to the results of the wash fluid examination. Most veterinarians will prescribe bronchodilators to alleviate airway constriction. They will also recommend aerosolised, nebulised or systemic drugs (usually a corticosteroid, an immunomodulatory drug like interferon-α, or a mast cell stabilisers like cromolyn sodium) to manage the underlying inflammation. They may also suggest nebulising with sterile saline to help loosen airway mucus and may suggest feed additives like omega 3 fatty acids, which may have beneficial effects on airway inflammation.
New Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is paramount to expanding our knowledge of what causes equine asthma and exploring innovative medical solutions. Scientists are actively investigating the effects of smog and barn dusts on the lungs of horses. They are also working to identify new targeted therapies, immunotherapies and other treatment modalities to improve outcomes for affected horses.
Conclusion
Both mild and severe equine asthma are caused and triggered by the same air pollutants, highlighting the need for careful barn management. The alarming rise in air pollution levels poses an additional threat to equine respiratory health. Recognising everyday coughs as potential warning signs and implementing proper diagnostic tests, day-to-day management practices and medical therapies are crucial in combating equine asthma. By prioritising the protection of our horse’s respiratory health and staying informed about the latest research, we can ensure the well-being of our equine companions for years to come.
Gastric ulcers in racehorses – what trainers should know
Article by Dr Michael Hewetson
Why are gastric ulcers so important in racehorses?
Gastric ulcers are very prevalent in racehorses, with between 52% and 93% of horses in active training affected. This is significant, because gastric ulcers can impact both the horse's performance and its overall health and welfare, which in turn can have financial and competitive implications for their owners, trainers, and the racing industry as a whole.
Gastric ulcers can affect a horse's performance by causing abdominal discomfort and reduced appetite. This can lead to changes in stride length and decreased energy levels that may impact their racing performance. Horses with gastric ulcers may also exhibit changes in behaviour, such as nervousness, aggression, or reluctance to train or race, which again, can affect their overall performance and temperament. If left untreated, gastric ulcers can lead to more serious health concerns such as colic, potentially requiring costly medical intervention and downtime for the horse. But most importantly, gastric ulcers are a welfare issue for the Thoroughbred racing industry, and with growing public scrutiny on the industry, ensuring the well-being of racehorses is a priority, and addressing gastric ulcers promptly should be considered part of responsible horse management. This requires a close working relationship with your vet, who will be able to give you expert advice about diagnosis, treatment, and management of this frustrating disease.
Understanding gastric ulcers
FIGURE 1
Equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS) is a general term used to describe erosions and ulcers of the horse’s stomach and is similar to the term peptic ulcer disease in people. Unlike people however, the horse is unique in that the stomach lining (mucosa) is divided into an upper squamous and a lower glandular portion (figure 1); and it is important to realise that there are differences between these two regions with respect to how these lesions develop, their prevalence, associated risk factors and response to treatment. Therefore, when referring to EGUS, your vet may use the terms Equine Squamous Gastric Disease (ESGD) and Equine Glandular Gastric Disease (EGGD) to clearly distinguish the anatomical region of the stomach affected.
FIGURE 2
There does not appear to be a clear relationship between the presence of squamous disease and glandular disease, and the fact that both conditions may occur concurrently in the same horse does not indicate that they are associated. In the case of squamous disease, the cause of the ulcers is well understood, with a variety of managemental risk factors (e.g. increase in exercise intensity, low roughage/high starch diet, stall confinement) contributing to an increase in the exposure of the squamous mucosa to acid. The squamous mucosa is not normally exposed to acid. As such it is inherently susceptible to acid injury, and with prolonged acid exposure, ulcers may develop (figure 2).
FIGURE 3
In contrast to squamous disease, the cause of glandular disease is poorly understood. The glandular mucosa is fundamentally different from the squamous mucosa in that it is exposed to a highly acidic environment under normal physiological conditions. As such, it is only when there is a breakdown of the normal defence mechanisms that protect the glandular mucosa from acidic gastric contents that glandular disease occurs. While ulcers are most commonly seen with squamous disease, horses with glandular disease rarely present with ulcers. Rather, the lesions are more consistent with an erosive inflammatory gastritis and can vary widely in their appearance (figure 3). There is a now evidence to suggest that stress, both psychological (e.g. multiple riders or caretakers; confinement; stress associated with transport and competition) and physiological (e.g. increases in the total amount and frequency of exercise without adequate rest periods) may increase the risk of glandular disease in horses. This may be due to a variety of mechanisms including a reduction in the mucus coating and blood supply to the glandular mucosa; both of which compromise the gastric barrier, resulting in acid injury.
The prevalence of gastric ulcers appears to vary with age, use, stage of training, as well as the region of the stomach affected. The prevalence of squamous disease is consistently highest in performance horses, with 52-93% of Thoroughbred racehorses found to be affected. The prevalence of glandular disease is less well reported, however up to 47% of Thoroughbred racehorses may be affected.
Why are racehorses so susceptible to gastric ulcers?
It is most likely because of their unique management when compared to most other horse populations; and the intensity of exercise that is inherent of racing competition. For example, it has been shown that the risk of squamous disease increases with an increase in the intensity of exercise and the duration of time at work. Strenuous exercise causes an increase in intra abdominal pressure associated with contraction of the abdominal muscles1. This results in compression of the stomach, and exposure of the sensitive squamous mucosa to acidic gastric content (acid splash). Strenuous exercise has also been shown to cause an increase in a hormone called gastrin, which stimulates acid production in the stomach.
Several factors associated with management have also been shown to increase the risk of squamous disease, many of which are imposed on racehorses at the commencement of training or during racing competition. These include a high starch/low roughage diet, intermittent fasting, stall confinement, transport, intermittent access to water and administration of hypertonic solutions of electrolytes. In fact, exposure to a combination of a high starch diet, stall confinement and strenuous exercise has been shown to induce ulcers in as little as 7 days; and intermittent fasting is so effective at inducing ulcers that it is used as a model for squamous disease in experimental studies. Thoroughbred racehorses are also exposed to many of the risk factors for glandular disease, most notably, multiple riders or caretakers; confinement; and stress associated with transport and competition.
How do you know if your horse has gastric ulcers and how might they affect performance?
A variety of clinical signs may suggest that a horse has gastric ulcers, however there is currently very little evidence to support a direct association between any of these signs and the presence or absence of ulcers seen on gastroscopy. This is likely because most of the clinical signs are non-specific and are often very subjective. This is complicated further by the fact that horses with gastric ulcers may not demonstrate clinical signs and if they do, the signs do not necessarily correlate with the severity of the lesions seen on gastroscopy. Clinical signs suggestive of gastric ulcers should therefore always be interpreted with caution, and most importantly, gastroscopy should always be performed to confirm the disease (figure 4).
In racehorses, gastric ulcers have been associated with poor appetite, poor body condition, changes in behaviour (including an aggressive or nervous attitude), post prandial colic, stereotypic behaviour and resentment of girthing. Any one of these clinical signs can potentially have an indirect effect on performance (for example, through reduced appetite or interruption in training), but the big question is if gastric ulcers themselves, in the absence of other clinical signs, have an effect on performance. Despite the fact that it is a well entrenched ’fact’ amongst trainers that gastric ulcers have a direct effect on poor performance or reluctance to train, there is surprisingly little evidence in the literature to back this up. This may be in part due to the difficulties in excluding the many confounding factors that might influence poor performance (e.g. lameness, respiratory disease etc.).
The mechanism by which gastric ulcers may affect performance has not been identified but is likely to be related to epigastric pain. In people, epigastric pain is defined as pain localised to an area below the sternum and above the umbilicus and is common in athletes with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Acid reflux onto the sensitive squamous mucosa of the oesophagus during exercise causes a “burning sensation” that gets worse with increasing exercise intensity and has been shown to affect performance. Horses with squamous gastric disease have similar lesions to those causing GERD in human athletes, and the problem is likely to be exacerbated by the fact that the squamous mucosa extends from the oesophagus into the upper one-third of the stomach and is not protected by an oesophageal sphincter. Interestingly, a recent study in human athletes suggested that GERD may be associated with increased abdominal pressure during exercise, a mechanism that I have already alluded to in the equine athlete. How exactly epigastric pain impacts on athletic performance in the horse is a matter of ongoing speculation. One theory is that it may affect stride length. It has been shown that horses with gastric ulcers have a reduced stride length when galloping, likely due to abdominal discomfort. Stride length and lung ventilation are mechanically coupled in the galloping horse, and therefore, reduced stride length will result in decreased oxygen uptake, thus limiting aerobic capacity during peak exercise.
How are gastric ulcers treated and what can you do to prevent them?
Let’s turn our attention now to the treatment of gastric ulcers. Because there is currently little evidence to suggest an association between clinical signs and the presence or severity of gastric ulcers, treatment should always be based on gastroscopic evidence of ulcers. Some trainers may still choose to commence treatment based entirely on clinic signs without gastroscopy and assess for a clinical response. I would caution against this approach, as it can be costly if the horse does not have ulcers, and gastroscopy is still going to be necessary to conclusively rule out gastric ulcers if clinical improvement is not seen with treatment.
Treatment of gastric ulcers will vary depending upon the severity and the location of the ulcers and your vet will be able to give you advice on the best approach. In most cases treatment consists of management and dietary modification in conjunction with the use of proton pump inhibitors which suppress acid production. Oral omeprazole is the drug of choice and is currently the only licensed drug for the treatment and prevention of gastric ulcers in horses in the UK and Ireland.
Administering oral omeprazole on an empty stomach can improve the bioavailability of the drug. This can be achieved practically by administering it first thing in the morning at least 1 hour prior to feeding. This ensures the stomach will be empty as horses eat very little during the night even if they have access to forage.
The duration of treatment will depend on the location of the lesions, with squamous disease tending to heal faster than glandular disease. In most cases, your vet will prescribe oral omeprazole for 3-4 weeks and then the requirement for additional medication will be determined following a repeat gastroscopy. In the case of glandular disease, oral omeprazole is often combined with sucralfate, which adheres to the damaged mucosa, providing a physical barrier while also stimulating mucus secretion, both of which reduce potential exposure to acid. Omeprazole is a controlled drug, and therefore needs to be withdrawn prior to competition. The BHA published detection time for oral omeprazole is ≤ 48hrs, so withdrawal of the drug 3-5 days before competition would be prudent. There is, however, some concern that the requirement for withdrawal times might influence the efficacy of oral omeprazole treatment in racehorses. Many vets report reoccurrence of squamous disease following discontinuation of treatment with omeprazole, often within as little as 3 days, and this was demonstrated in a recent study comparing withholding periods for oral omeprazole treatments in racing Thoroughbreds6. The authors reported a squamous disease prevalence of 83% in horses after a “2 clear days'' recommended withholding period for oral omeprazole, which was an increase from 25% of horses with squamous disease before the recommended withholding period, and they theorised that ‘rebound acid secretion’ may be implicated. This phenomenon occurs following the discontinuation of proton pump inhibitor drugs such as oral omeprazole, and is linked to a loss of negative feedback from gastric acid during treatment that causes an increased secretion of the hormone gastrin that can persist for up to 2-4 days after the last dose of omeprazole has been administered. This results in a short period of increased gastric acid production when treatment is stopped. Whilst nothing can currently be done about the required withdrawal periods during racing, strict management practices should be implemented for the 2-4 days following cessation of omeprazole treatment to mitigate against development of squamous gastric disease. This could include ensuring provision of adequate roughage during this time, avoiding fasting or withholding water, and perhaps limiting exercise or transport if possible.
Additional management and dietary adaptations which may help prevent gastric ulcers and can be implemented longer term in a racing yard include free choice access to roughage (and if not, ensuring that roughage is provided at intervals of no more than 4-6 hours); turn out into a paddock with good quality grazing where possible; a low starch/high fat diet (or alternatively, smaller concentrate meals more frequently); reduction/avoidance of any potential stressors; and provision of regular rest days. Where possible, training schedules should be adjusted so that they occur later in the day when enough roughage has been consumed to ensure that there is a mat of roughage in the stomach to buffer acid in the upper squamous portion and to reduce acid splash during exercise. Alternatively, a handful of palatable chaff should be fed 20 minutes prior to exercise.
Numerous supplements are marketed for prevention of gastric ulcers, however there is currently very limited evidence to support their use.
References
Lorenzo-Figueras M, Merritt AM. Effects of exercise on gastric volume and pH in the proximal portion of the stomach of horses. Am J Vet Res. 2002;63(11):1481–1487.
Vatistas NJ, Sifferman RL, Holste J, et al. Induction and maintenance of gastric ulceration in horses in simulated race training. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999;29:40–44.
Murray MJ, Eichorn ES. Effects of intermittent feed deprivation, intermittent feed deprivation with ranitidine administration, and stall confinement with ad libitum access to hay on gastric ulceration in horses. Am J Vet Res. 1996;57(11):1599–1603.
Herregods TV, van Hoeij FB, Oors JM, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. Effect of running on gastroesophageal reflux and reflux mechanisms. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(7):940–946. doi:10.1038/ajg.2016.122
Nieto JE, Snyder JR, Vatistas NJ, Jones JH. Effect of gastric ulceration on physiologic responses to exercise in horses. Am J Vet Res. 2009;70(6):787–795.
Shan R, Steel CM, Sykes B. The Impact of Two Recommended Withholding Periods for Omeprazole and the Use of a Nutraceutical Supplement on Recurrence of Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome in Thoroughbred Racehorses. Animals. 2023; 13(11):1823.
Clark B, Steel C, Vokes J, Shan JR, Gedye K, Lovett A, Sykes BW. Evaluation of the effects of medium-term (57-day) omeprazole administration and of omeprazole discontinuation on serum gastrin and serum chromogranin A concentrations in the horse. J Vet Intern Med. 2023 Jul-Aug;37(4):1537-1543.
The Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures 2023
The Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures, is an annual gathering devoted to the racing industry and the health and wellbeing of the horses involved.
This year, equine veterinarians, researchers, students and industry professionals from around the world attended the event, held June 8, 2023, at the historic Tattersalls Sales in Newmarket, England.
There were insightful and informative lectures that educated the attendants but also instigated a healthy, lively debate on the health and welfare of the training and competing of horses. The underlying theme that was present during the whole event was all members of the conference had a deep passion and commitment to continuously progress and improve on managing the welfare and wellbeing of the horses in the industry, both on and off of the track.
Two very special guest speakers, Sir Mark Prescott and Luca Cumani, wonderfully illustrated these sentiments as they described their reflections on the improvement and enhancement of horse safety.
Horse racing may be regarded as an elite sport, and all activities involving horses have an element of risk. All stakeholders in the racing industry must continuously work to ensure that the risks are minimised in order to reduce the number of injuries and fatalities that may occur in training and on the racecourse. There are now well-publicised concerns regarding the acceptability of exposing horses to risk in racing. These lectures and all of the attendees embraced the values of the public will so that there can be continued acceptance of horse sports.
Reducing the incidence of fractures in racing
Christopher Riggs of The Hong Kong Jockey Club clearly outlined the various strategies to reduce the risk of fractures in racehorses. There are two principal strategies that may used to reduce the incidence of severe fractures in horses while racing and training:
Identifying extrinsic factors that increase risk and take action to minimise them.
An example would be investigating different racing surfaces in order to determine which may provide the safest racing surface. However, studies have provided limited evidence and support for subtle extrinsic factors.
2. Identifying individuals that are at increased risk and prevent them from racing or minimise that risk until the risk has subsided.
There are many research routes that are being undertaken to identify those horses that may be at a higher risk of fractures. There are investigations involving heritability and molecular studies that may provide evidence of genetic predisposition to fracture. However, Dr. Riggs explained that further understanding of the relationship between genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors is required before genetic screening is likely to be of practical use.
Pre-race screening of horses by diligent clinical examination is poor at reducing the incidence of fracture. Dr. Riggs described another strategy that may assist with a clinical examination that is the use of biomarkers in blood and urine.
Unfortunately, the precision to be of practical value has so far remained relatively unrewarding. Wearable technology that records biometric parameters, including stride characteristics, has shown some promise in identifying horses that are at increased risk of fracture; although Dr. Riggs explained that this work requires further development.
Finally, Dr. Riggs described both the use and current limitations of diagnostic imaging in identifying pre-fracture pathology in order to identify a horse at imminent risk of fracture. He conceded that further knowledge of the significance of the range of abnormalities that can be detected by imaging is incomplete.
Dr. Riggs concluded his lecture by expressing that the implementation of diagnostic imaging to screen “high-risk” horses identified through genetic, epidemiology, biomarkers and/or biometrics may be the best hope to reduce the incidence of racing fractures. This field can be advanced with further studies, especially of a longitudinal nature.
Professor Tim Parkin of Bristol Veterinary School discussed the need for further investment in welfare research and education. One avenue of investment that should be seriously considered is the analysis of data related to (fatal) injuries in Thoroughbred racing over the last 25 years.
It was expressed, with the abundance of data that has been collected, that some risk factors would be relatively simple to identify. An encouraging example in the collection and use of data to develop models in predicting and potentially preventing injury has been conducted by the Hong Kong Jockey Club funded by the Hong Kong Jockey Club Equine Welfare Research Foundation. This may provide an opportunity to pilot the use of risk profiling to contribute to decision-making about race entries. In addition, the results of the pilot study combined with other sources of data may encourage race authorities to mandate the collection of veterinary and training data in order to help in risk mitigation.
Horse racing is an international sport, and there are different governing bodies that ensure racing integrity. However, the concept of social licence equestrian sports and Thoroughbred horse racing continues to gain significant public attention. Therefore, racing governing bodies are increasingly aiming to provide societal assurances on equine welfare.
Dr. Ramzan of Rossdales Veterinary Surgeons provided an eloquent and clear message during his lecture that race yard veterinarians and trainers are instrumental in ensuring good horse health and welfare and reducing serious injury of the horse both while training or racing, which will provide sufficient trust and legitimacy from the public and society. This feasible goal can be reached with good awareness of members involved in the care and training of each individual horse and conveying this information and any concerns to their veterinarian. The veterinarian can also contribute by honing their knowledge and skills and working closely with yard staff in order to make appropriate and better targeted veterinary intervention.
In the last two decades, there has been an incredible evolution and exciting developments in diagnostic imaging in the veterinary profession. It is believed that these technologies can provide a significant contribution to helping in mitigating fracture risks to racehorses on the course and in training.
Professor Mathieu Spriet of University of California, Davis, described how these improvements in diagnostic imaging has led to the detection of early lesions as well as allowing the monitoring of the lesions’ evolution.
He continued by explaining the strengths and limitations of different imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). Being one of the leaders in the use of PET in equine veterinary medicine, he presented further insight on how this particular modality provides high-resolution 3-D bone scans while being very sensitive to the identification of bone turn-over prior to the development of structural changes and allowing one to distinguish between active and inactive processes when structural changes are present.
He concluded his impressive lecture by providing evidence with amazing PET images that the role of imaging is not merely for diagnostic purposes to characterise clinical abnormalities, but can also be used as a screening tool in certain horse populations for fracture risk assessment or for the monitoring of lesions to provide clearance for racing.
Fractures, due to bone overloading rather than direct trauma occur commonly in Thoroughbred racehorses and are the leading cause of euthanasia on the racecourse. Despite many changes to race conditions, the number of catastrophic fractures has remained relatively static, with approximately 60 horses a year having a fatal fracture during a race in the UK.
Against this backdrop, there have been great developments in the diagnosis and treatment of fractures in the last 40 years. Prevention of racecourse and training fractures would be ideal so the development of efficacious techniques to screen horses at risk may reduce the incidence and preserve social licensing.
One technique discussed by Dr. Ian Wright of Newmarket Equine Referrals was to help mitigate the impact of racecourse fractures, which would be acute immobilisation of racecourse fractures, thus, reducing associated pain and anxiety while optimising clinical outcome and reducing on course fatality rates. Because of our increased understanding of fracture pathogenesis and their associated biomechanics, effective fracture immobilisation has been made possible. The majority of fractures that occur in flat racing and between obstacles in jump racing, are a result of stress or fatigue failure of the bone and not associated with trauma.
In addition, fractures seen on the racecourse are often found in the same specific sites (i.e., metacarpal/metatarsal condyles and the proximal sesamoid bones of the fetlock) and have repeatable configurations. With this understanding and knowledge, racecourse veterinarians can optimally immobilise a fracture in a logical and pre-planned manner.
As Dr. Wright expressed, this allows the fracture patient to have reduced pain and anxiety and enable the horse to be moved from the course comfortably so that it can be further examined. Ultimately, this allows the veterinarian and all stakeholders to make effective and judicious decisions for the sake of the horse’s welfare and wellbeing. As Dr. Wright concluded, this benefits both horses and racing.
Dr. Debbie Guest of the Royal Veterinary College discussed a different approach in mitigating the risk of fractures during training and racing by developing novel tools to reduce catastrophic fractures Thoroughbreds. Because it has been found that some horses are more inherently predisposed to fractures than other horses, Dr. Guest and her team have developed a genome-wide polygenic risk score so that one can potentially calculate an individual horse’s risk of fracturing during training or racing compared to the population as a whole.
This strategy may contribute in identifying genetically high-risk horses so that additional monitoring of the patients can be exercised during their careers and also leading to fracture risk, which are found to be the cause of approximately half of these incidents.
The system of using DNA testing to identify biological processes that may or may not be present ultimately leading to fracture risk may be a powerful tool in lowering the risk of catastrophic fracture and requires further research and application.
Cardiac events & sudden cardiac death in training and racing
In racehorses, sudden death that is associated with exercise on the racetrack or during training is a serious risk to jockeys and adversely affects horse welfare and the public perception of the sport. It is believed 75% of race day fatalities result from euthanasia following a catastrophic injury. The other 25% of fatalities is due to sudden deaths and cardiac arrhythmias are found to be the cause of approximately half of these incidents. The lectures focused on this area of concern by providing three interesting lectures on cardiac issues in the racehorse industry.
Dr. Laura Nath of the University of Adelaide, explained the difficulties in identifying horses that are at risk of sudden cardiac death. It is believed that part of the solution to this difficult issue is the further development and use of wearable devices including ECG and heart rate monitors.
With the use of these technologies, the goal would be to recognise those horses that are not progressing appropriately through their training and screen these horses for further evaluation. This course of action has been seen in human athletes that develop irregular rhythms that are known to cause sudden cardiac death with the use of computational ECG analysis, even when the ECGs appear normal on initial visual inspection.
Knowing that ECGs and particularly P-waves are used as a non-invasive electrocardiographic marker for atrial remodelling in humans, Dr. Nath recently completed a study on the analysis variations in the P-wave seen on ECGs in athletic horses and found that increases of P-waves in racehorses are associated with structural and electrical remodelling in the heart and may increase the risk of atrial fibrillation (cardiac event).
Dr. Celia Marr of Rossdales Veterinary Surgeons continued the discussion of cardiac disease in both the training and racing of horses. Unfortunately, cardiac disease knowledge does lag compared to musculoskeletal and respiratory diseases when considering the causes of poor performance in racehorses. Due to the fact that cardiac rhythm disturbances are fairly common, occurring in around 5–10% of training sessions in healthy horses in Newmarket and over 50% of horses investigated for poor performance, Dr. Marr expressed the need for further research and investigation in this area.
In addition, this research needs to determine if there is indeed a link between heart rhythm disturbances and repeated episodes of poor performance and sudden cardiac arrest. ECGs and associated technologies are helpful, but there are limitations such as the fact that rhythm disturbances do not always occur every time the horse is exercised. Therefore, it would be of great value that a robust criterion is established when evaluating ECGs in racehorses. The Horserace Betting Levy Board has provided funding for investigation by initially exploring the natural history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (self-correcting form) to understand risk factors and predict outcomes for affected horses.
Continuing the theme of the lectures on irregular heart rhythms and associated sudden cardiac death (SCD) in training and racing, Professor Kamalan Jeevaratnam described his exciting research in using artificial intelligence (AI) to identify horses at increased risk of developing irregular rhythms that may cause SCD.
AI is an exciting and rapidly expanding field of computer science that is beginning to be implemented in veterinary medicine. With funding by the Horserace Betting Levy Board and the Grayson Jockey Club Research Foundation, Professor Jeevaratnam of the University of Surrey, has piloted three novel algorithms that help predict horses with rhythm abnormalities through the analysis of horses’ ECGs.
It was acknowledged that further research is required to develop this technology by using data collected from multiple sources, but the initial results are promising in the development of an useful AI tool to identify horses at risk of SCD and prevent catastrophic events, thus, ensuring the welfare of the horse in racing.
Conclusion
The Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures was a thoroughly successful and enjoyable event attended by a variety of different members of the horse racing industry. Not only did the lecturers provide interesting and valuable information but also excitement for the future of racing. It was very clear that all the lecturers and attendees were passionate and committed to the racehorse welfare and wellbeing as well as retaining the social licence for an exciting sport.
Shared ownership
It has always struck me—as someone with a keen interest in most sports—that the lack of harmonisation around various rules and issues such as interference, jockey’s weights, and doping isn’t helpful as racing remains such a puzzle to most of the world.
This is evident too in the area of shared ownership, of syndicates, racing clubs and the developing area of micro share groups.
Never has it been more important for racing to attract fresh blood, with its core support ageing and the sport barely causing a ripple in mainstream media. Shared ownership is a foolproof mechanism for unearthing new acolytes because emotion and feeling will trump catchy slogans or slick promotional videos every time. If you want converts, having them in the parade ring as part of the inner circle and seeing their horse run and contend or win is your best bet.
Piers Winkworth, racing manager of Kennet Valley Thoroughbreds, summed it up well after Dragon Leader maintained his 100 per cent record from three runs by landing the £147,540 first prize in the Goffs UK Harry Beeby Premier Yearling Stakes at York’s prestigious Ebor meeting in August.
Dragon Leader with Ryan Moore up wins the 2023 Premier Yearling Stakes at York’s prestigious Ebor meeting in August.
“This is what syndicates are all about really—having cracks at these ultra-valuable sales handicaps with modestly bought horses,” Winkworth noted. “Dragon Leader, a £45,000 Donny yearling, goes and wins the big race by some distance under Ryan Moore. It was thrilling for all of our owners. We had about 16 people up at York to see him, and there were great celebrations after the race”.
Johnny Murtagh has participated in many such celebrations, having had a hefty number of syndicates at Fox Covert Stables since he took out a licence to train at the conclusion of a stellar riding career.
The Curragh-based conditioner secured his first Gp. 1 triumph with Fitzwilliam Racing’s Champers Elysees in 2020, and bagged his first Classic the following season when Sonnyboyliston swooped to score in the Comer Group International Irish St Leger for Kildare Racing Club.
This season, Murtagh has had runners for 11 syndicates, saddling winners for six of them. So enamoured is he with shared ownership that he has just launched a new racing club, Racing Revolution, more of which anon.
“There’s nothing better than coming back into the ring and seeing people who never thought they’d ever own a horse so happy”, reports Murtagh.
“We’ve been very lucky with Fitzwilliam. They ended up winning a G.p 1. We now have the likes of the Brunabonne Syndicate—lads from where I grew up. They’ve been so lucky with Mashhoor. He won a couple of big races (including at Gp. 3 level), brought the lads to York and Ascot, and ran on all the big days”.
The idea of the racing club came out of Mashhoor’s Listed triumph on Tattersalls Irish 2000 Guineas day at Curragh Racecourse in May. In particular, it was the reaction of Tommy Dowd, a celebrated former Gaelic footballer who led Meath to All-Ireland glory in 1996, that resonated.
“Tommy Dowd picked up the Sam Maguire as captain of Meath and he said, ‘This is the same feeling as that.’”
Dr Paull Khan, secretary-general of the European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation summarises the overall situation brilliantly.
“In many countries (in and outside our region), racing is struggling to maintain its popularity and relevance, as societal practices and preferences shift,” notes Khan.
“Broadening the base of racehorse ownership may well prove a key weapon in countering this trend. Quite simply, the more people that have an involvement in owning a racehorse, the more our sport becomes embedded in society.
“For racing authorities, the challenge is not limited to promotion. Appropriate Rules of Racing must underpin such activity, which allow for and define co-ownership options.
“But there is also a potential downside, in that the creation of ownership entities which encompass large groups of individuals brings with it increased risks of incompetent or, yet worse, fraudulent management. Any examples of people suffering bad experiences, which are not satisfactorily dealt with, are likely to gain much publicity and have the effect of putting off future owners. So the final aspect to which racing authorities must give thought is the need for effective regulatory oversight, to minimise this risk”.
What follows is something of a potted overview of the situation in Europe, thanks to a number of different stakeholders from governing bodies to trainers and plenty more in between.
BRITAIN
Establishing a new syndicate isn’t laborious in Britain, and only the manager/syndicator must register as an owner. The members do not have to register, but an updated list of members must be provided to the BHA as well as the percentage share held by each one.
Racing clubs are focussed entirely on the experience of ownership but without having any equity in the horse or share in whatever proceeds it accrues while racing. Members pay an annual fee to enjoy most of the other benefits of ownership, on race day and while in training. Once again, only the person setting up or running the club must register.
Micro share groups are becoming more visible and are a very cheap way to become involved in racing as a tiny percentage of a share, normally a fraction of 1 percent , can be acquired for as little as £40. Like racing clubs, they are primarily experiential, though members are owners and are entitled to the equivalent cut of any money accumulated.
All forms of shared ownership in Britain are subject to a code of conduct that includes specific mandatory clauses in each written contract. Transparency and protection are the key tenets of the code. The BHA has committed to auditing a proportion of syndicate/racing club/micro share contracts to ensure compliance.
George Baker’s ‘Have horse, will travel,’ mantra has always made him attractive to shared ownership groups. The Robins Farm trainer has saddled winners all over the world and is as good a host as he is a trainer.
The Surrey-based conditioner has his own racing club, the George Baker Racing Club, which provides all the perks of an involvement in racehorses, including open house visits, parade ring passes, regular communication, picnics at Royal Ascot and Glorious Goodwood, and even a share in a prize money.
Baker joins Andrew Balding and Harry Eustace as trainers for the MyRacehorse fractional share group, making a big splash on this side of the Atlantic and having initially enjoyed stupendous success when established in America by Michael Behrens.
The relationship with MyRacehorse began with Get It and Watchya racing in Bahrain; and the ambition was rewarded by the former being awarded a victory after the winner on the day was disqualified due to a positive sample.
“The key point here is making racehorse ownership accessible to absolutely everybody in the way that it has been for a few years now and obviously in Australia, where the big syndicates have had massive success”, Baker declares.
“Like our horse (Get It) at Wolverhampton (on September 7) that won the Racing League race—a share in him was £45. The wonderful thing about a share at whatever level [is] the horse becomes your horse, regardless of whether you’ve paid a million pounds or forty pounds.
“We all know it’s the way forward because we’ve just got to get as many people as we can into this game, and of course you hope that some of them become more heavily involved in the sport and that it evolves to a longer association; but the most important thing is showing racing as a viable means of enjoyment”.
A degree of suspicion has lingered around micro share operations, but Baker is happy to go to bat for MyRacehorse.
“I can’t speak for any of the other micro share entities, though obviously I’ve heard rumours of numbers not quite stacking up or that horses worth ‘x’ have been marketed for ‘x + y + z’; but that’s not something I can be quoted on because I haven’t had intimate involvement or knowledge.
“I know from the MyRacehorse perspective, they are wholly transparent and very keen to be treated as you would treat a security in the stock market. They want to create a secondary market so people can trade in and out of their shares.
“People demand absolute transparency and absolute integrity and from my experience, clearly that’s what MyRacehorse have based their brilliant business on in America and Australia; and they’re trying to bring the same criteria here. And that’s absolutely correct. I don’t want to be involved with any organisation or micro share entity where there’s a level of suspicion around the numbers. And that’s why MyRacehorse is creating a niche and an attractive market”.
Baker returns to Get It and Wolverhampton to ram home his point about the impact feeling a winner can have regardless of financial outlay.
“There was one of the guys in the winner’s enclosure who’d won a share that night in a race card competition that MyRacehorse had organised with the Racing League. And there he is in the winner’s enclosure being photographed with (jockey) Paul Mulrennan and the horse. The guy was almost in a state of shock, but he was absolutely loving it”.
IRELAND
Ireland is among the most proactive European jurisdictions for the promotion and growth of multiple ownership. Figures from 2022 indicate that the number of syndicates increased by 24 per cent to 825, comprising 8,030 people.
The number of racing clubs increased by 6 per cent, comprising 1,683 members.
People can join existing syndicates or racing clubs or establish their own. Syndicates in Ireland comprise 3–100 people, while racing clubs can have an unlimited number of members.
The above figure for syndicates also includes the evolving fractional ownership model, with MyRacehorse having horses in training with Joseph O’Brien and Michael O’Callaghan.
“It is a great way to dip your toe in the water and see if it is the pastime for you,” says HRI’s owner development manager, Amber Byrne of shared ownership, who adds that plenty with the means to indulge in sole ownership prefer syndicates as a means of spreading their risk or because they derive more enjoyment from them.
HRI maintains a register of racehorse owners and can void or suspend owner registrations. The onus falls on the agent to ensure the syndicate/club and its members complies with the rules of racing, HRI directives, owner eligibility policy etc. Unlike the BHA, they do not have a specific code of conduct in place but advise that all syndicates and clubs provide them.
Agents must be registered as full owners and provide necessary ID, bank details etc., while a full list of membership including addresses and contact details and shares held must be supplied and continuously updated. Syndicates/clubs must declare if they are selling shares publicly and declare the maximum number of shares available in a particular horse.
Jack Cantillon, founder of the hugely popular Syndicates.Racing, says HRI has it just right in terms of regulation and oversight.
“We recently registered in France, and it took over a month for our application to be successfully processed; so we should be thankful for how quick it has been for us to do so in Ireland”, Cantillon relates. “We also are registered in New York, and they even wanted my fingerprints before we got over the line! Ireland strikes a balance of enough protections while not over burdening with ridiculous red tape.
“Syndicates are the backbone of building the pipeline of ownership of racehorses throughout the world”, he continues. “We’ve had incidents of people taking a €200 share as their first share in a racehorse and progressing to owning horses worth €100,000 on their own. It’s an amazing journey to see in full sight and something that’s incredibly rewarding”.
Syndicates.Racing has enjoyed spectacular success in a short period in both codes, with runners and winners at a host of major meetings and venues, including graded-winning mares Cabaret Queen and Grangee. Their trainers include Willie Mullins, Joseph O’Brien, Henry de Bromhead, Jessica Harrington, Gavin Cromwell, Peter Fahey, John McConnell, Jack Davison and the aforementioned Johnny Murtagh. They also have horses in training in Britain and America.
Grangee with Jack, John and Tom from Syndicates.Racing.
“We have been blessed with over a thousand owners that have gotten involved in Syndicates.Racing since its inception and bringing so many of them to the winner’s enclosure has been a hugely rewarding thing… If you do have a positive experience, there’s very few more rewarding experiences of intimate involvement that you can get in any sport”.
As mentioned earlier, Murtagh is such a believer in the benefits of shared ownership that he has just launched his own racing club.
“You’d love people to have a good experience of racing. They’re going to be racing, but they’re going to see behind the scenes as well—even things like a horse being shod or going through the stalls; the ins and outs of JP Murtagh on a weekly basis with a horse ready to run. You’ll have a morning on the gallops, a few get-togethers. I think there’s going to be a great take-up and plenty of entertainment.
“There’s a bit more work, but I only speak to the racing manager and they keep everyone else informed. You’re going to have to employ somebody to take videos and keep it updated every day. I want people to see what’s going on and to feel part of it.
“You like to promote the game as best you can and show it in a good light and maybe in a way that people with some bit of interest want to see more and you never know what it leads to. One fella might say, ‘I enjoyed that; can you buy me a horse?’ Rather than jumping into it straight away, they get a good feel.
“I think it’ll work. We’ve a good horse, and we’ve a plan for the horse. We have everything in place, ready to go. I think people will like to be part of it.
While there is “a bit involved” in setting Racing Revolution up, “Murtagh found HRI very helpful. Ireland’s governing body is full square behind shared ownership as a means of growing the sport and industry.
“The promotion of shared ownership is central to our domestic marketing strategy”, Byrne emphasises. “Syndicates and clubs are key in introducing the ownership concept. We see it as an affordable entry stage into ownership and a way for those interested in racing to get closer to the action and behind-the-scenes access.
“For the most part our domestic marketing promotion concentrates on highlighting multiple ownership. There is no other sport that allows the kind of access that ownership offers and allows fans to get fully immersed in a sport that they love”.
Cantillon sees one area of potential improvement.
“I think we as an industry should invest in a comprehensive customer relationship management system for our owners. We should take advantage of affordable technology available to improve owner experience tenfold. Send a special deal to owners on their birthday, invite them back to the anniversary of their winner last year, issue tickets digitally so there’s no mix-ups at the gate. It’s simple stuff but makes a huge difference”.
FRANCE
Syndicates are known as ecurie de groupe in France, which translates directly to racing stables but are generally known as racing clubs. They are not to be confused with the experiential model of racing clubs in Britain and Ireland and which do not exist in France.
Neither are there any micro share companies, though there have been some initial discussions with MyRacehorse.
“It is certainly an interesting model, one which is full of potential in France,” outgoing managing director of France Galop, Olivier Delloye tells us.
There are 44 syndicates in operation in France, and that figure—while low and down on the 72 recorded in 2014—will increase “in the coming months” according to France Galop’s marketing and ownership development manager, Raphaël Naquet. Ecurie Team Spirit, Shamrock Racing, Ecurie Vivaldi, Ecurie Brillantissime, and High Heels Racing Stable are among the flourishing factions; and there are links to several syndicates on the France Galop website.
As Jack Cantillon touched on, the process of registering a syndicate is more arduous in France than elsewhere. Irish native Timmy Love, who is a colleague of Naquet’s in the ownership development wing of France Galop, concedes that point but insists that this is due to the law of the land rather than the racing regulator.
“Setting up a racing club is probably slightly more bureaucratically heavy than what it would be in Ireland or in England, but that’s just the nature of the French system”, Love asserts. “It’s not a reflection on France Galop. It’s just in France (by law); there is quite a rigorous administration system. It’s quite demanding, but it’s to protect the people already within the sport or those trying to come into it.
“It’s by no means rocket science to get set up over here. Once you get all your different documentation together, it’s no more difficult than anywhere else. You just need slightly more documents in the first place”.
The syndicates must be registered as a company, and that means articles of association, declarations of the company, certificates of incorporation are required to establish the company’s eligibility. Once that is done, the usual proof of identification for the agent running the syndicate is required.
Every member of an ecurie de groupe has an owner’s card that entitles them to the exact same benefits as a sole owner. These include being allowed to bring four guests to every meeting at all the France Galop racecourses, with no exclusions. Being able to do that on Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe day is a phenomenally attractive perk as a syndicate member.
The provincial tracks are not bound by general rule as regards to how many people are allowed to attend per owner card or runner, but according to Love, they are generally very hospitable.
“For example, I know Middleham Park (Racing) had a winner in Cagnes-Sur-Mer over the winter (Brave Emperor), and the racecourse was very good to the members of that syndicate that travelled over. That is just to give one example, but there are lots of country tracks that look after their owners extremely well”.
France Galop is considering being more proactive in going out into the marketplace to sell the benefits of syndicates as an ownership option.
“We can see more and more shared ownership is more attractive. It makes the sport more accessible, so it’s certainly something we’re considering; and now we have a good base of racing clubs that are well set up and having a bit of success. It’s becoming an easier product to market”,
French trainers are not as enamoured with shared ownership as their British and Irish counterparts, however, as illustrated by Hélène Hatchiguian of the Association des Entraîneurs de Galop, the French trainers’ association.
“We have more and more owner agreements, but mainly for shared ownership, because having a racehorse is a cost. The consequence is that we have less horses in training,” Hatchiguian observes.
“For a trainer, it is easier and better to have one owner per horse, but now we have less of these owners and more shared ownership. It represents more work for the trainer, and more time (to communicate, for invoicing etc.). If trainers do not have time for it, they need to employ someone to do this job.
“When some shared owners do not pay their training fees, we can appeal to France Galop, the horse cannot run, and it is penalising other owners. In the future, it will be necessary to change the rules: if one or more shared owner does not pay, the horse can still run but the money won by the horse is not paid to the owner but to the trainer’s account”.
GERMANY
Christian von der Recke is cut from the same cloth as George Baker. Land and sea borders are no impediment to the multiple-champion jumps trainer travelling and running horses.
He says running a proper syndicate is difficult in Germany and points us in the direction of Lars-Wilhelm Baumgarten. A former sports agent (with Grand Slam winner Angelique Kerber among his clients), now breeder and board member of Deutscher Galopp, Baumgartner founded Liberty Racing with his wife Nadine and realised a lifetime ambition when Fantastic Moon won the Deutsches Derby in Liberty silks.
Members are glorying in the anticipation of a tilt at the Breeders’ Cup and/or the Japan Cup at present – wherever there is good ground - after the Sarah Steinberg-trained son of Sea The Moon recorded a decisive victory in the Qatar Prix Niel. Some hefty offers came in for the German-bred colt after the romp at ParisLongchamp but they have been rejected by shareholders and he will continue to race for Liberty.
“I worked as a sports agent all over the world and was a lot of times in Australia and saw the syndicates there,” Baumgartner explains. “I decided to sell my company and do what I want—horses, poker, real estate, and coaching. I started breeding and was on the board of German Racing, and I saw the problem: less owners, less breeders.
“I started eight years ago with my partnership ownership, only with two or three friends. We had a lot of success together. Then I decided to make my three- or four-people ownership syndicate bigger and started in 2020, to bring all my owner and breeder know-how to bring more people to horses. That was in my mind, but also in my mind was to win bigger, not just to buy handicap horses for people. We wanted to buy stayers with stamina from good German families for the Classic races, the Derby, the Oaks, and the Leger.
“The idea was that new people can dream and be part of the bigger races. That was the main vision for Liberty Racing. Nadine and I started with 12 shareholders and four horses. The next year, we had 22 shareholders in four horses and then 30 in five horses. This year we will buy 10 to 12 horses with 90 or 100 owners.
“It’s not easy with the German tax situation. We have a lot of law restrictions to bring money together. It’s not like in England and America. They have more share culture, but we did it. We created a good contract, and we have the okay from the government to do it, and so we started”.
Deutscher Galopp is very helpful, Baumgartner tells us, not least than when he brought 50 people to shout on Liberty Racing’s two Derby runners.
There are more racing clubs in Germany than syndicates, but Liberty Racing is a poster child for the latter model with its professionalism and specific departments to cater for acquisitions, financials, social media, and so on.
“German racing was a closed shop. We have to open it. At the moment, we have 1,800 horses in training. That’s not good. We have to find 1,000 new shareholders in horses, and then we find 100, 200 horses more for trainers to train”.
ITALY
Former top trainer and now flourishing bloodstock agent, Valfredo Valiani, is looking forward to attending all the major European sales in the coming weeks and months, but he won’t be buying for Italian syndicates.
“Italian people usually don’t like syndicates, and it’s something that never took off in Italy,” Valiani remarks. “When I used to train, I tried myself with a couple of friends to set up a few syndicates for a few horses. We had results with the horses. We went up to six partners. But Italians are pretty individual. We’re not used to doing syndicates in anything and especially in racehorses.
“It’s not that easy to register a syndicate over here. You’re going to need all the papers for every single partner in the syndicate. So it’s really tough. And then, just the representative is allowed to get to the parade ring.
“We need syndicates because Italian racing is not flying, especially in quality; and when you get a few people together, of course you have more money to spend and more power, and you can look for better horses.
“We do have one syndicate, which is named Equos. It’s very public because it belongs to somebody that runs the only racing paper in Italy. But nobody emulated that, so far at least. Italians are proud to be THE owner, and they don’t feel like being ONE of the owners. There are horses in partnership, but it’s not the norm.”
SCANDINAVIA
Norway does have company-regulated syndicates, but there are some operating on a private level.
“The main reason is that Norwegian rules and regulations do not allow ownership of racehorses to be defined as a business,” says Marianne Ek of the Norwegian Jockey Club. “It has to be taxed as private. This means that there are no incentives for companies to offer this service.
“The industry is constantly working towards our politicians to try to change this, but no luck so far.
“This does not mean that we don’t have syndicates and shared ownerships, but they are set up either by the owners themselves or the trainers.”
In Sweden and Denmark, syndicates are allowed to trade as businesses. Also, there are some companies that specialise in putting syndicates together and running them for a fee.
CONCLUSION
As noted at the start, this is by no means a thorough investigation of shared ownership from the perspective of all stakeholders in all regions—lengthy and all as it is.
It is evident though that while some jurisdictions are more open to shared ownership than others, for a variety of reasons, there is a growing acknowledgement that for trainers, and thus the industry, the model has far more upside than any perceived negative once all stakeholders are protected by watertight regulation and rigorous oversight.
Make it as easy as possible, and make it attractive. After that, the smiles will go miles.