Take a chance on me! Jessica Long in profile
Sweden’s southernmost region Skåne is the home of Jessica Long, one of the most prominent trainers—and breeders—in Scandinavia. We met with Jessica Long to learn about her set-up in Sweden and her views on the future. We also found out about her connection to world-famous composer and musician Benny Andersson—and why Swedish horses are so rarely seen racing abroad.
Racehorses have been part of Jessica Long’s life for as long as she can remember. She grew up on the family farm surrounded by horses, and her parents devoted their lives to the racing and breeding industry. As a keen rider, Jessica was involved in the family business from an early age, and you would assume that her career choice was an easy one. However, her mind was initially not set on becoming a racehorse trainer.
“I actually never planned on taking over my parents’ business. Instead, I went to university in Lund and studied molecular biology. To be honest, I found it very boring, and I wanted to change direction; but I didn’t know what to do. Around the same time, one of the members of staff at the farm left, and I decided to fill the vacancy until I had made my mind up. It went well for us that year. My mum became the champion trainer in Denmark, and I got a taste for more. So, I never left,” Jessica says with a smile.
Well, it is not entirely true that she never left the farm again. Jessica made sure to gain valuable experience abroad, and in total she has spent almost five years in Britain and Ireland. “Initially I worked for the eventer Eric Duvander—he is now the coach of the US eventing team. I also completed the National Stud Diploma Course in Newmarket and later spent three seasons at Coolmore Stud.”
In Ireland, Jessica met Padraig Long, now her husband and the co-manager of the family business. But despite the strong Irish connection, Sweden was the obvious choice when the couple decided to settle down. “We never hesitated. Racing in Sweden was doing very well at the time. There seemed to be a bright future for the industry, and we had a nice farm at home. It was an easy choice to head back to Sweden and try to establish ourselves over here.”
In 2008, at the age of 29, Jessica took over the business from her parents and became a racehorse trainer in her own right. With multiple years of experience between them, Jessica and Padraig decided to focus on both the racing and the breeding side of the industry, and to run a small stud farm and consignment alongside the racing yard. “It so happens that the farm works quite well for both training and breeding. It is well planned and fits well for both parts—with large fields for turn-out and a small track for exercise,” Jessica says.
The setup worked very well for quite a few years. But as the number of horses grew, the training facilities at the farm became limited, and for the last three years, the horses in training are now based at Jägersro—a 20-minute drive from the farm.
Set on the outskirts of Malmö, Jägersro is the oldest thoroughbred racetrack in Sweden and the home of almost 250 racehorses, roughly one quarter of the total number of racehorses in Sweden.
The racecourse hosts a handful of Listed events as well as the prestigious Swedish Derby—a race that has been run since 1918. The facility features an oval dirt track for racing and three gallops for training as well as a track for harness racing.
The location in the very south of Sweden is ideal for travelling abroad. Klampenborg, the racecourse in the Danish capital, is within easy reach. Jessica Long does not hesitate to venture further than that, and her four-year-old filly Victoria Placa has made several appearances in Germany during this summer and autumn. “We are aiming for a Listed win in Germany. If everything goes her way, she is good enough to win, which would give her international breeding value.”
Despite the proximity to mainland Europe, Swedish trainers are rarely seen bringing horses to race outside of Scandinavia—with the exception of the occasional Dubai World Cup Carnival participant. “I’m confident that we are good enough and that we have horses that are good enough; but the purses are surprisingly large in Scandinavia, and there is a bonus system for Swedish-bred horses. That is a good thing, of course, but it also means that we tend to stay at home.”
Swedish-bred horses racing in Sweden will receive a bonus on earned prize money in most races, varying from 40% for two-year-olds to 30% for four-year-olds.
“On top of that, quite often our big races coincide with suitable races internationally. You must choose if you want one or the other, and of course it is easier to stay in Sweden. It makes a lot of sense to stay at home for prize money reasons. But at the same time, I think it is part of racing to try to match your horses abroad and see how far you can go against international competition. I am very grateful that we have horse owners who let us try our wings abroad—to see how good the horses are.”
“Then, of course, you also need a good horse to venture abroad. When you only have a limited number of horses, a good one does not show up so often…”
It must be taken into consideration that most professional trainers in Sweden only have about 20 horses in training, with a few exceptions that would have upwards of 40 horses in the stable. Jessica Long currently has 24 horses in the barn at Jägersro. However, she was lucky that a good horse showed up early in her career. That was Volatile—a homebred gelding who took Jessica, Padraig and the owners to Newmarket, Hamburg, Meydan, Maisons-Laffitte and Royal Ascot. With a Listed win in Dubai and Group placings in England and France, Volatile is one of the most successful horses to ever come out of Sweden. “Volatile meant a lot to my career as a trainer. It went incredibly fast. We found ourselves in Newmarket only a few weeks after his debut race at Jägersro. He took us on a journey that few of us could have dreamt of or ever will experience again.
Volatile with his entourage of owners
Wherever Volatile raced, he would come with an entourage of owners. “He was owned by a syndicate made up of 20 shares, and many of the part owners were new to racing. It was such a great group; they really embraced the success and travelled with us to most countries where he raced. It was just a wonderful experience. Volatile is retired now, but most of the part owners have shares in other horses.”
Among the owners in the stable, you will find those who own 5% or 10% of a horse in a syndicate as well as some of the most high-profile owners in Scandinavia. Jessica has received the backing of prominent owner-breeders such as Chess Racing, Stall Perlen, Buck Racing and Light Valley Stud.
ABBA member Benny Andersson, whose horses race in the name of Chess Racing, may be best known for his British-trained horses including recent Gp. 2 winner Lavender’s Blue. However, he also has horses in training with Jessica and regularly makes the headlines in Scandinavia. Jessica recalls the story of how Benny Andersson came to be a racehorse owner. “Benny’s wife Mona was previously married to my father, and they have a son together. When Benny was to meet the extended family for the first time, he realised that if he would have something in common with this family, he needed to buy a horse….”
He did, and it didn’t take long until Benny Andersson was bitten by the racing bug. “He thought it was fun and soon figured that he would like to be involved in breeding his own horses. It is fascinating to be part of choosing the stallion and to see the horses grow up. He has also bought some horses at the sales, but the homebreds are closer to his heart. He is committed and very active with stallion selections, but he would not have a lot of opinions about the training and how we match the horses and so on. With that said, when I have two similar options, I will always ask him what he prefers. We have known each other for so long that rarely does anything come as a surprise; we have similar goals and plans for the horses.”
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Have you considered the stress on your horses legs?
Click here to learn more
Published in association with Medivet.it
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
TopSpec Trainer of the Quarter – Henk Grewe
The choice for Trainer of the Quarter was no easy one, with many notable successes, but it is Henk Grewe who takes the honours. Scooping both the colts’ and fillies’ BBAG auction races for two-year-olds in September, as well as adding his name to the roll of honour for the Deutsches Derby in July with Sisfahan, Grewe most recently won the Gr. 3 Premio Elena E Sergio Cumani in Rome with Flamingo Girl.
Mister Applebee was an impressive runaway winner of the BBAG auction race at Düsseldorf, and Atomic Blonde fought bravely for her win in the BBAG Johanna and Hugo Memorial; both appear to have a bright future. “Mister Applebee looked very good and is now going to the Ferdinand Leisten Memorial,” Grewe says, hoping to replicate the success of his Horse of the Year, Rubaiyat.
Grewe has 100 boxes at his base in Weidenpescher Park in Cologne. His first notable success came in 2015 with the Austrian Derby, but in the short time since, he has built up a team that has seen him crowned Champion Trainer in 2019 and 2020.
“It has been a good season, especially because of the Deutsches Derby, even though we haven’t had as many winners as last year,” Grewe says. “Winning the Derby was really special for me because I was under so much pressure. Everyone was expecting me to win it for the last three years and now that I have won it, that pressure is gone; it makes everything easier.”
Sisfahan made it look very easy indeed in Hamburg and was having his first start at Group level. “It's nice that Andrasch was on the horse, my parents are here, my brother is here with my niece, who is having a birthday today. He's a great horse and it's just a dream today,” Grewe said on the day. With Sisfahan’s win, Grewe not only enjoyed the greatest success of his career so far but also topped the meeting as leading trainer.
It hasn’t been all joy for Grewe during this time, and he recently lost the promising Preis der Diana runner-up Isfahani—a Gr. 3 winner at two. “It's incredibly sad; when I got the message from the clinic, I was absolutely shocked. Unfortunately, she never had the chance to show her true colours, and I am still convinced that she was the best horse that I have ever trained,” he says of the tragic filly.
“We have a lot of late horses who we hope will be very good for next year,” he says, looking ahead. “COVID has made everything much more difficult. There has been a lot more paperwork and travelling has been much harder, but my team have really handled it well. For me, our team is the most important thing; they work so hard and without them, none of this would be possible.”
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Sales Incentives - added value
Author - Nancy Sexton
The issue of prize money is not going to be resolved soon, with the average horse running for levels far removed from their contemporaries abroad. But that’s not to say ownership is a guaranteed black hole. British and Irish bloodstock remain highly prized commodities overseas, making it the subject of a frenzied export market. And for the domestic horse population, the opportunities are there to win extra money for those looking to work the system.
It is to the credit of the sales companies that many of these opportunities emanate from their various initiatives, whether it be in the form of sales races or bonus series.
At the higher end of the market, Tattersalls has paid out approximately £6.5 million in bonuses against Book 1 of its October Sale, while this year’s Goffs Orby Sale will be staged alongside a new million euro sales race.
For those value seekers, sales races are also attached to Books 3 and 4 of the Tattersalls October Sale as well as the company’s Somerville Yearling Sale. Anyone shopping at the recent Goffs UK Premier Sale also did so with the incentive of a sales race at York, which comes with its own bonus of a free horse to the winning connections.
Such incentives currently run in tandem with various bonus schemes. The Great British Bonus Scheme (GBB), in which payments of up to £20,000 are awarded to the connections of British-bred and/or sired fillies, has paid out over £3 million since its launch in June 2020.
New for this season is the IRE Incentive Scheme, which awards a sales voucher of €10,000 to owners of Irish-bred winners from 150 selected races across the British and Irish Flat and National Hunt programmes in 2021. Winning owners then have until the end of the following year to spend their voucher on an Irish-bred at any Irish sale.
It works across the spectrum
Every lot catalogued to Book 1 of the Tattersalls October Sale is eligible for the £20,000 October Book 1 bonus. Owners make a one-off payment to qualify—in 2021, £1,700 paid by March 1—and receive a £20,000 bonus should their Book 1 purchase win an eligible race run during the British and Irish turf Flat seasons.
The scheme was launched for the 2016 season and within no time at all had gained appreciation within the industry. At the time of writing, Tattersalls has paid out 251 bonuses of over £6.5 million, 24 of them in 2021.
Unsurprisingly, it has proven to be a hit with various syndicates. A number of trainers have also latched on to it, among them Andrew Balding, who sent out Coventry Stakes winner Berkshire Shadow to land a bonus first time out at Newbury and Hoo Ya Mal to win Britain’s most valuable two-year-old maiden, the Convivial at York. Between them, the pair cost 80,000gns out of last year’s sale.
“We have paid out £6.5 million since it was launched,” says Jimmy George, marketing director of Tattersalls. “It’s a huge sum, and owners and trainers who have embraced it have been rewarded. It’s changed buyer behaviour. You have trainers like Ger Lyons, for example, who would have been in the Book 2 camp, but he embraced this scheme and has been successful with horses in that 20,000gns–100,000gns range.
“The beauty of it is the fact that it doesn’t matter if you get beaten in your maiden; you can go again and then again. So it works across the spectrum, allowing it to suit every type of horse.”
The likes of Berkshire Shadow and Hoo Ya Mal prove that while the sale average may hover around 220,000gns, value can be found; in which case, a £20,000 bonus can go a long way.
That much is also evident in the case of Acomb Stakes winner Royal Patronage, who picked up a bonus for Highclere Thoroughbred Racing when successful at Epsom in July. He was bought by John and Jake Warren for 62,000gns out of last year’s sale.
“The bonus has certainly become part of the mindset when attending Book 1,” says Jake Warren. “It’s a meaningful prize that feels obtainable for each horse we buy at the sale, and it's that aspect that encourages us to make sure we cover the sale entirely as despite what some people might think. There is plenty of value there if you're prepared to look for it.
“Royal Patronage, for example, was a beautiful yearling. He had an imposing physique with a noticeably deep front and a quality head—very much in the mould of the best sons of Wootton Bassett I've seen.”
If you find the crumbs, you need rewarding
Tattersalls also takes pride in its £150,000 Tattersalls Autumn Race while its sister company, Tattersalls Ireland, stages the €300,000 Super Auction Sales Stakes for graduates of its September Yearling Sale. Both are two of the company’s longer-standing events and remain extremely popular with owners and trainers.
Traditionally run for graduates of Books 3 and 4, the £150,000 Tattersalls Autumn Race will incorporate those from the Somerville Yearling Sale for the first time this year. This year’s Somerville yearlings also have their own race: a 6f event scheduled to be run next August on Newmarket’s July course.
“The £150,000 Tattersalls Autumn Race is one of our well-established events,” says George. “It’s something that is easy for trainers to sell for their owners.”
The race has a firm supporter in trainer Johnny Portman. The Lambourn trainer excels at sourcing value—a fine illustration being the Requinto filly Mild Illusion, who won over £66,000 having been bought for just 1,000gns as a Book 3 yearling.
Mild Illusion didn’t win the Tattersalls October Auction Stakes, but she came very close in 2019 when falling just a head short of Under The Stars. She won approximately £33,000 that day for her enthusiastic owners, the Old Stoic Racing Club, and went on to win the Listed Bosra Sham Stakes. She later sold for 160,000gns to Tally-Ho Stud.
“Every sale needs buyers at every level of the market and if you are one of the pigeons that finds the crumbs, you also need rewarding,” says Portman. “And the rewards are those races, such as the Tattersalls race, for cheaply purchased horses.
“Mild Illusion was offered for sale. Anyone could have bid on her and I was the only one. She was a lovely type and watching her walk round the ring, there was nothing to fault her. Not everyone was a fan of Requinto, but there was no reason not to buy her, especially at that money. And she nearly went on to win a sales race.
“I’m a great believer in them. I don’t enjoy the sales so much, but I do love scratching around and looking for value.” He adds: “We’d like to find a Mild Illusion every year. They’re very hard to find and we were very lucky, but we’ll keep trying. She was wonderfully straightforward to train and was leased to some wonderful individuals. And her sale to Tally-Ho was an utter joy for some of my creditors!”
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Feeding from the sales ring to racecourse
Author - Cath Dunnett
Horseracing’s international sales rings can perhaps be regarded or compared with the professional show circuit. To achieve optimum interest and price, youngsters not only need to be genetically well endowed but must be appealing to the buyers eye. Youngsters need to be in good body condition, ideally fit but not fat with good muscle tone, sufficient topline and a gleaming healthy coat. However the overall ‘picture’ desirable for the sales ring may not be the most appropriate for full training and competitive racing, and so trainers may find themselves needing to resculpture horses in their early days of training.
Yearling Prep
Yearlings are prepared (‘prepped’) intensively for the sales ring. Whilst most yearling prep regimes will incorporate some exercise, this tends to be mostly walking; and yearlings may lack the established and better developed musculature needed for racing. There is also a high reliance on feeding to deliver the ‘sales ring look’.
Prep regimes are often short lived and designed to increase weight and condition relatively quickly, and to produce gleaming coat condition and topline—the latter of which can therefore be based on deposition of adipose tissue or fat, rather than muscle development or hypertrophy.
A prep period typically involves feeding a large amount of high energy, starch-rich feed over a relatively short period of time, typically 6-8 weeks. Research tells us that this prep period is likely to be one of the high risk times for non-glandular gastric ulcers to develop. Large starch-rich feeds, confinement, increased periods of stress and restricted access to pasture or forage are all significant risk factors for gastric ulcers.
Some yearlings will inevitably arrive at the trainer or pre-trainers yard with pre-existing non glandular ulcers, which may require veterinary treatment, or at the very least a sympathetic high forage, low-starch and sugar-based ration for early training. It may be controversial to suggest, but a longer slower period of prep for sales would perhaps allow for a greater contribution from exercise to build muscle, combined with a less intense feeding regime. However, time and economics probably contain too much deviation from the existing model.
Bone Density
Yearlings that move through from studs to sales prep and then into a training yard undergo a very big change in their feed and management that is worthy of consideration. A stud regime and diet are very different to both sales prep and pre-training, in terms of composition and environment. At stud, these young animals spend a large portion of their day at pasture, with a generally small amount of top up feed or balancers to complement the grazing.
A diet, which is typically high in pasture and forage and low in cereals, allows minerals such as calcium to be firmly sequestered in bone, maintaining bone density. In horses on good pasture, this is aided by the high vitamin K1 content of pasture, which is needed to activate osteocalcin involved in the sequestration of calcium in bone. In contrast, with a high-cereal, low-forage prep or pre-training diet—as a result of quite complicated homeostatic mechanisms involving hormones such as parathyroid hormone—calcium can become relatively more mobilised from bone. The characteristic drop in bone density commonly seen in racehorses in the first 60-90 days of training can be the physical result of this phenomenon.
Forage First
Yearlings may come into training on the larger side of perfect for racing; and so it may, at first glance, seem counterintuitive to feed plenty of forage at this time. However, in early training it is a worthwhile exercise, as it establishes good eating habits.
Horses in training often self limit their forage intake, as training progresses and appetite is reduced, which can contribute to problems including inability to maintain condition, gastric ulcers and tying up if the forage intake drops too low. Better to start from a slightly higher intake early on, than to find a horse on a forage knife edge later in training.
Forage, whether hay or haylage, contributes significantly to energy and electrolyte intake and is a particularly rich source of potassium—an important electrolyte for overall metabolism and muscle function. Leguminous forage such as alfalfa/lucerne is highly digestible and so has a reduced effect on gut fill (hay belly). Alfalfa is equally rich in calcium to help buffer the natural mobilisation and loss of calcium from bone during early training.
A couple of kilograms of alfalfa per day complements a more traditional less digestible hay such as Timothy. The added advantage of feeding a decent amount of forage is that the level of concentrate feed needed will also be reduced. Forage provides energy mainly from fibre and so is not generally associated with excitability, with the energy provided being colloquially known as slow-release energy.
A decent amount of forage for a horse in training is about 1.5% of bodyweight; so for a 500kg horse, that’s about 7-8kg or 4 typical slices. For haylage, this needs to be slightly higher to account for its higher water content.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Orthopaedic problems in young Thoroughbreds
Helping these future athletes achieve a protective conformation is vital with respect to their welfare, athletic career and sales potential: Orthopaedic conditions have the potential to blight a promising athletic career and prevent young horses reach their full potential. Early diagnosis and management are critical if horses are to be given the best chances of a successful and long career. And this, of course, depends on horsemen being able to pick up on problems as early as possible so they can be dealt with effectively. The Beaufort Cottage Educational Trust is a charity that aims to help disseminate knowledge in the Thoroughbred breeding and racing communities with the ultimate goal of improving horse welfare.
Each year, the charity organises the Gerald Leigh Memorial lectures which are fantastic resources for horsemen. The lecture series is supported by the Gerald Leigh Trust in honour of Mr. Leigh's passion for the Thoroughbred horse and its health and welfare. Most years, the lectures are presented in person in an event at the UK’s National Horseracing Museum in Newmarket; but for 2021, an in-person gathering was not possible and instead, the lectures are available online. For 2021, the charity chose the theme of orthopaedic problems, which are such a common challenge in young Thoroughbreds.
Angular Limb Deformities: Evaluation and treatment in foals and yearlings
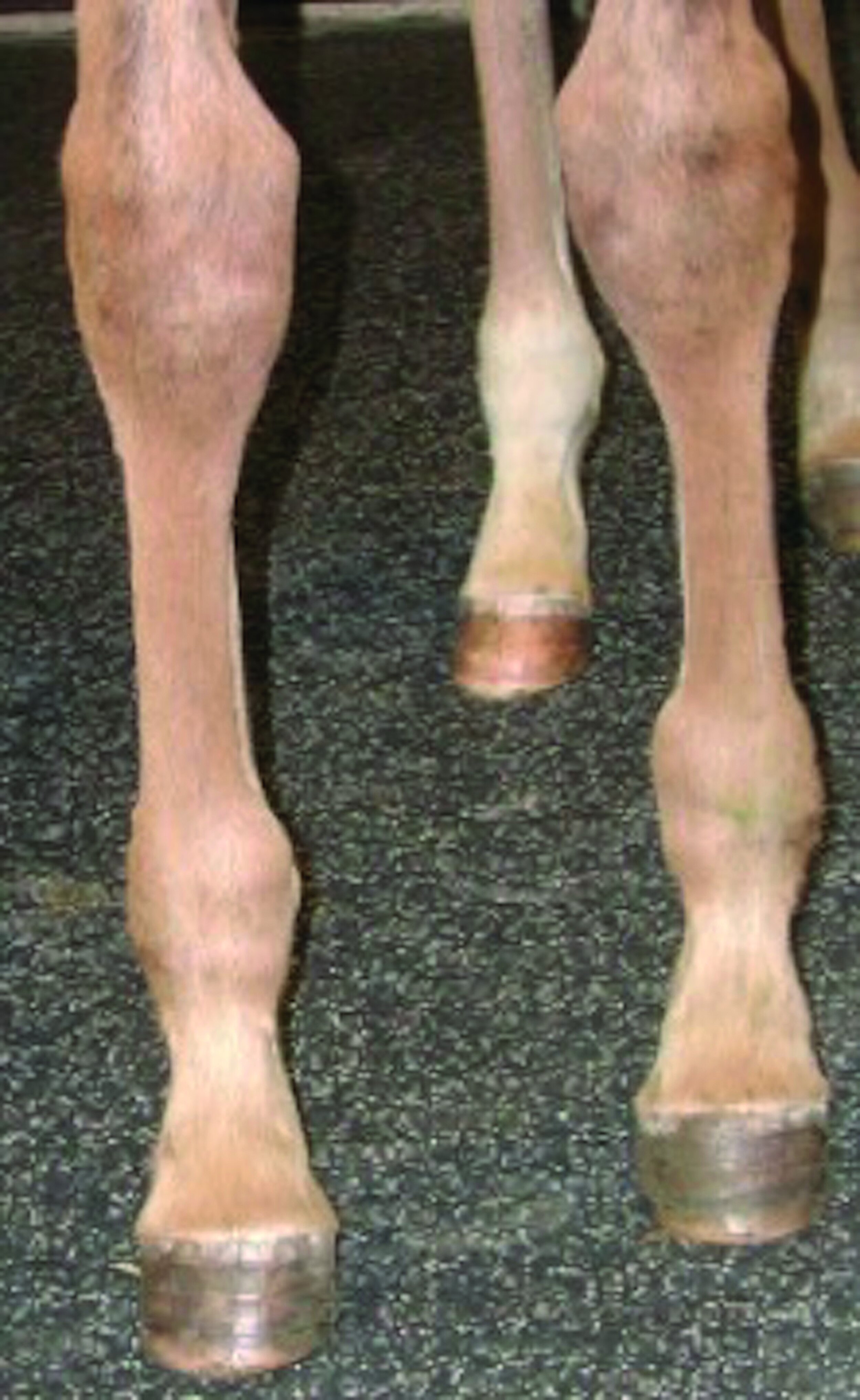
Recognising, diagnosing and understanding angular limb deviations in young Thoroughbreds are critical skills for horsemen and an important part of both stud management and veterinary care. Angular limb deformities (ALD) refer to deviation of the limb in its frontal plane, or side to side when evaluating the individual from the front or back. A varus deformity is a medial deviation of the limb below the location of the problem (e.g., toeing in), whereas a valgus deformity is a lateral deviation of the limb below the location of the deformity (e.g., toeing out). Angular limb deformities must be distinguished from a flexural limb deformity, which is in the sagittal plane, i.e., from front to back when evaluating the individual from the side.
Examples of Valgus (left) and Varus (right) ALDs: A Valgus deformity is a lateral deviation of the limb below the location of the deformity (e.g. Toeing out) whereas a Varus deformity is a medial deviation of the limb below the location of the problem (e.g. Toeing in).
How do ALD occur?
ALD can be both congenital and acquired. Congenital means the condition has been present from birth and causes include incomplete ossification or immaturity of the small cuboidal bones, which make up the hocks and knees as well as weakness of the ligaments supporting the joints and periarticular laxity. These issues tend to result in valgus knees and hocks. We also know that ALD can be inherited and that as a breed, Thoroughbreds tend to be varus (toe in).
Acquired ALD develop after birth and come about through overloading of the physis (growth plate), which is usually caused either from hard ground, an over-conditioned foal or a combination of the two. The biomechanics of equine limb lead horses to bear more weight through the inside of the leg; therefore, the inside of the growth plate, which is inhibited more than the outside and when there is overloading the net effect is that the foal will toe in.
How do ALD impact a foal’s future career?
Carpal and fetlock injuries in racing Thoroughbreds account for a large majority of the reasons racehorses spend time out of training. Intervening while foals are growing and developing to help them achieve a protective conformation gives them the best chance of maximising their potential and enjoying their racing career.
Diagnosis of ALD
Evaluating young stock is certainly best achieved using a team approach involving owners/managers, farriers and veterinarians. Regular evaluation from a young age is key, as is examination of the foal while static and while walking. Severe deviations should also be evaluated radiographically.
Treatment of ALD
Conservative treatment options can include exercise restriction, corrective farriery and nutritional management. Hoof correction and toe extensions can be extremely helpful in managing foals and yearlings with minor deviations; and farriery can often correct such issues without needing to resort to surgical treatment options.
The surgical treatment of choice for correcting ALD is the transphyseal screw. In general, it achieves the most effective and cosmetic outcome of the surgical options. The procedure involves placing a screw across the growth plate on the side of the leg that is growing too fast. For example, for a foal that is toeing in, the screw is placed on the outside of the leg. This allows the inside of the growth plate to grow faster and so correct the deviation. The screws are placed under a short general anesthetic. The screw does need to be removed to avoid over-correction, but often they can be removed with the horse standing using a mild sedative once the desired correction is achieved.
Radiograph of a foal’s fetlock post surgery; a transphyseal screw was placed on the outside of a front fetlock to correct a varus (teoing in) deviation.
Osteochondrosis – recent advances and diagnosis
Osteochondrosis is one of the most important developmental diseases in young athletic horses. It occurs in young, large-breed horses, including Thoroughbreds, and can cause a variety of clinical signs. The age at which the disease starts to cause clinical signs varies from a young foal to horses over 10 years old. This is because lesions can remain silent and only cause clinical signs later on in life. But even in the absence of any clinical signs, the pathological lesions will have been present since the horses reached skeletal maturity.
How does osteochondrosis affect athletes?
Osteochondrosis often starts to cause problems when the horse is put into training—when they are athletically challenged. This age will differ for different populations, starting earlier in Thoroughbred racehorses than in Warmbloods destined for sports horse disciplines. Often the horse will be sound, or can experience different degrees of lameness and may present with joint effusion. This disease affects more than one joint in an individual in over 50% of cases, and it usually occurs in the same joint on the contralateral limb; but it can also affect multiple different joints.
How does osteochondrosis develop?
In foals, areas of growth cartilage within the joints will continue to ossify (become bone) after birth. When this process is complete and the animal is skeletally mature, a thin layer of normal articular cartilage will remain supported by subchondral bone. Osteochondrosis is caused by a “failure of endochondral ossification,” which simply means the growth cartilage fails to become healthy bone. A defect, with or without a fragment, is then created in the articular surface of the bone. This dynamically changing area is susceptible to trauma or high biomechanical loads. Recent advances in research, carried out in Norway by Dr. Olstad, suggest that failure of endochondral ossification is likely caused by loss of blood supply to these areas of growth cartilage, which prevents it from ossifying. This has been linked to a heritable predisposition, among other factors such as rapid growth, dietary imbalance, exercise, environment and prior joint sepsis.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
Thorough clinical examination and radiography remain at the forefront of osteochondrosis diagnosis. This disease occurs at joint-specific predilection sites as a result of site-specific biomechanical forces and differences in the age at which that site becomes skeletally mature. For example, in the femoropatellar joint (pictured), the most common site of osteochondrosis is the lateral trochlear ridge of the femur. This is predilected by the thick cartilage surface, later age of maturation/ossification, and by the shear forces the patella exerts on the ridge as the stifle flexes and extends. Ultrasonography can also be very sensitive in detecting osteochondrosis in the stifle. Research performed by Dr. Martel in Canada suggests early detection of subclinical lesions in the stifle have been found in foals aged 27-166 days old.
The photograph on the left shows femoropatellar joint effusion of the left stifle. The radiograph on the right shows a large osteochondrosis lesion of the lateral trochlear ridge of the femur within the femoropatellar joint.
Management of osteochondrosis
Lesions can spontaneously resolve, and the majority will have done so by 12 months old. Otherwise, management recommendations to limit lesion development include keeping horses exclusively at pasture up to 1 year old, not using rough terrain, in large group sizes (>3 brood mares) or in a large pasture size (large pasture size > 1 hectare before 2 weeks old and > 6 hectare before 2 months old). Strict box rest is discouraged, and a convalescence paddock of 33ft x 56ft (10m x 17m) for 60-90 days may help stabilise lesions.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Focus on two-year-olds – is the programme working?
Author - Lissa Oliver
We are living in an age of consumerism and disposable products, instant gratification the main aim for many. Now it seems that mentality is spilling over into horse racing. The two-year-old thoroughbred is fighting more than one battle—the balance of precocity over physical development, tough opposition on the racetrack, even tougher opposition in the marketplace competing against the ready-made horse in training, and the ultimate challenge of the limitation of the two-year-old racing programme.
If the trainer had more say in the programme, there would appear to be a consensus of agreement on how the juvenile programme might look. Whether French, German, British or Irish, there are similar needs to assist the average two-year-old to progress and go forward at three. But as Dominik Moser highlights, the programme and framing of races may not be the only contentious issue.
“I think we are beginning to lose the point of why we do this—why we breed and race horses,” Moser says. “In Germany, still, we have a big family line; the pedigree is why we race. My father was a jockey, and I come from the breeding side. I see how much time and luck it takes to bring a horse to the racetrack, and our breeders understand that. We breed for more than one season of racing.
“I want every horse to be a good broodmare or stallion, and this is my job; but the new generation focuses more on a fast return of investment rather than achieving black type performance with a horse. We have auction races with big prize money for two-year-olds, so the new generation of owners can get their money back quickly and buy a new horse and a future career is not important. It doesn’t matter to them if the horse breaks down; they can just buy a new one.”
Breeding for precocity—or as some would say, for the sales ring—is not a new problem and has been an increasing concern in recent years. But surprisingly, the two-year-old programme doesn’t seem to be catering to the young speedsters either. By mid-summer, the two-year-old sprinter is beginning to run out of opportunities, and this seems to be an issue across the board throughout Europe.
“I would say we’re reasonably happy with the two-year-old programme in Ireland, although the more you get into the season, the fewer the opportunities at 5f (1000m) and 6f (1200m), which is something we keep a careful eye on,” says Michael Grassick, CEO of the IRTA. “Where those races are staged, they attract fewer runners, so it’s hard to argue a stronger need for them.”
Willie McCreery takes that further, arguing, “In Ireland, they don’t cater for sprinters at all. I would love our two-year-olds to have more sprint options at the end of the year. We cater a lot for the top-quality horses—the ones with the big pedigrees who cost big money and will make up into Derby types.”
There is a similar situation in France, Gina Rarick pointing out, “The whole programme is geared to precocious youngsters and speed, but then there are not enough races to place them in. The two-year-olds from Britain and Ireland come over and win all the top two-year-old races because France Galop is not giving us a programme. The early horse has got enough options at the start of the season, but some that are only starting now have no races at their optimum distance.
“The biggest problem for two-year-olds is if they can’t run over 7f (1400m) by September, then basically they’re screwed. There is almost nothing for them at 5f (1000m)—maybe a few 6f (1200m) races for horses that have not run before. It’s really hard to find a race for them over a shorter distance, especially within a reasonable travel distance from the yard.”
Gavin Hernon agrees, pointing out, “There are races there for the sprinter, but from 1 September to the end of November, there are only two conditions races on a straight track and only five races under 1400m (7f). I think there will be more focus put on those opportunities in the future—it’s part of the France Galop plan. The programme is good for the mile to 2400m (12f) two-year-old, but people don’t buy those horses. Even in August, we’re already having 1800m (9f) maidens, and in September we have 2000m (10f) races.”
In Germany, the later spring and later foals dictate the programme to an extent, with two-year-olds not starting until May, and many of them the middle-distance three-year-old in the making, around which the programme is designed. However, the programme is not the biggest difficulty German trainers are facing.
“We can’t start our two-year-olds earlier than May, and nearly 20% of our two-year-olds in training start,” explains Dominik Moser. “I don’t mind this. I like to protect them, and I’m not under pressure from my owners. They’re not thinking about a two-year-old career; they prefer to wait for the big races for three- and four-year-olds.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Building a stronger racehorse with DYNAMIC MOBILISATION EXERCISES
Author - Kimberley Marrss
Yoga, Pilates, cross training, pre-habilitation—whatever you prefer to call it—are strength- training exercises also known as dynamic mobilisation exercises, which can greatly benefit your racehorses. You can perform these exercises on your horses to help with correcting posture, gaining strength, flexibility and core stability. All of these positive gains will help a racehorse be more balanced in his movements. Incorporating these exercises daily will of course help alleviate tensions in the body that could potentially turn into problems or pathologies down the road, while reducing the risk of repetitive use injuries.
The concept is the same as cross training in human athletic training. A horse also needs several types of exercises to help keep the body balanced and able to handle the intensity of competition, reduce performance issues and aid in the body's recovery after competition. As human athletes have known this, one size—one exercise—does not fit all. The body's systems all need to be challenged to produce an all-around balanced athlete. This logic needs to be addressed with training racehorses as well. Regular sessions of these types of exercises will result in the improvement of the horse's posture and ability to carry a rider in a balanced way. A horse with good posture will allow for optimal performance for a longer period with less exhaustion and muscle fatigue.
Muscles at work
A dynamic mobilisation stretch is mostly done using a bait and are referred to sometimes as carrot stretches. While performing a stretch, certain muscles are activated so that they move, and stabilise the intervertebral joints.
Then the activated abdominal muscles help to bend and round the back. This is especially important for a racehorse unlike horses who are trained to carry a long low frame, which will help them engage their body’s core. Racehorses will tend to train with their head high and with a hollowed back. Over time, this can predispose a horse to back pain, kissing spines, lumbosacral issues—all which can then lead to compensatory issues.
If you take a series of two-year-old thoroughbred racehorses, a high proportion of them will have radiological evidence of kissing spines, and quite a lot will have associated back pain.
So joint stabilization is particularly important to help with improving performance and the prevention of injuries. Research has also shown that with regular performance of these exercises, the equine back becomes enlarged. Subsequently, this will strengthen the back muscles and enable the horse to carry the rider more efficiently with a lessening of back stress. To demonstrate this, I have a person put a 11 to 22 kg sack of feed over their shoulder. Next, I have them walk between 7 to 9 metres as they would normally walk. Then I have the person stand up straight, hold in their core (abdominals) with correct posture and walk back 7 to 9 metres. The difference is usually substantial, and the person can feel less stress on the limbs with a straighter and more balanced way of moving. Now they get why the horse's core strength is so important!
Get started on a routine
I have been doing these for some time and have seen amazing results in my horses' overall posture, toplines, reduction of back pain and suppleness in their musculature. To get started with your dynamic mobilisation routine, keep in mind that performing these exercises are safe. Do take care though: If your horse has a musculoskeletal or neurological issue, clear it with the vet first before starting dynamic mobilisation exercises. Also keep in mind that many of these exercises are also utilised in rehabilitation from injuries.
When implementing these exercises, ensure the horse follows the bait in a nice smooth manner, and get the horse to hold the stretch. This can sometimes be easier said than done. Some horses will try to snatch and then snap their head back forward. So be patient; there is a learning curve with each individual horse. The more you perform these moves, the better you’ll get, and the smoother the stretches will become.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Stable standards - are racecourses forgetting the horse?
The thoroughbred industry is fairly diverse, with factions arguing their own importance.
Without breeders, we have no horse. Without owners, we have no racing. And without the racehorse, we have no need of racecourses. Racecourse Manager Bill Farnsworth identifies this basic point when he speaks of the stabling facilities at Musselburgh. But sadly, many racecourses in Britain and Ireland are missing the point altogether, and the horse—as Farnsworth refers to an athlete—is the least of their priorities.
The image of half a bale of shavings in a box at Killarney racecourse is a stark one. It is physically awkward to cut a bag and to carry an open bag.
How many of us would bother to go to such penny- pinching lengths at home? Indeed, one Irish trainer pointed out that the provision of just half a bale of shavings per box in a racing yard would certainly incur penalties from any IHRB (Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board) stable inspection. Although the IHRB does not include racecourse stabling standards within its Rules, its veterinary department accepts that half a bale is adequate for race day use. Yet in England, there has been at least one withdrawal due to the minor injuries sustained by a horse rolling in a box with inadequate shavings.
With multiple complaints from British and Irish trainers, a naming and shaming of offending racecourses would have made for a very long and already well-known list. Instead, we might look at those countries who have got it right throughout their tracks, and the racecourse in Britain consistently mentioned as setting the gold standard.
In Germany, trainers seem surprised to be asked about the quality of racecourse stables. Dominik Moser is typical when he explains, “We don’t have a problem with racecourse stabling—90% are on straw, 10% shavings; and where we have shavings, we have three bales per box. The cost of straw has increased this year due to the heavy rains and slight shortage, but it isn’t a problem. I like to see good- sized boxes. I don’t like to see a horse lying down if it doesn’t have enough room.”
Similarly, it isn’t lack of bedding that’s an issue in France but sometimes in the province’s lack of stabling. “We have no problem with hygiene or bedding at racecourse stables,” Gavin Hernon says, “but the problem we have is at smaller tracks when there might be no stable available or we could be sharing with an earlier runner. To be fair, I’ve never had a complaint.”
In recent years, in cases of positive post-race tests in France, the most common cause has been cited as contamination of racecourse stabling, which has led to much more stringent hygiene. “I suppose you could say that one good thing, as a result of that, is that now when you come to the racecourse stables, each box has a plastic seal and you have to break it to enter,” reveals Gina Rarick. “So we can be sure that every box has been disinfected and has clean straw.
“Most of our bedding in France is straw, and there is always enough at the races. If you want to have shavings instead, you have to book in advance and it’s quite expensive. You’ll pay €50-€60, and for that you’ll only be given two bales.
“The worst case I found was in Lyon—there was so much straw in the box and such a lot of dust, the horse started coughing immediately. Deauville always has plenty of bedding, and they use good quality straw. It’s really nicely done, and I find they are really accommodating. Other racecourses can be hit and miss; there is no rule on any set standard.”
Like Hernon, Rarick finds it is the lack of boxes that can be an issue at smaller tracks, particularly after a long journey to get there. Bear in mind that some tracks can be more than eight hours from the main training centres. “The biggest problem I find is that sometimes there are not enough boxes; and at some racecourses out in the country, there are none at all. You are working from the truck,” she says. “When there are too many runners and not enough boxes, the later runners use the same boxes as the earlier runners, which is not really great if you have a later runner. And then in contrast, you might get Chantilly, for example, (who uses) the number of available boxes as an excuse not to have a race; while at other racecourses, they are happy to double up.”
And Rarick raises another point when she notes, “I think it’s unique to France, but there is also a security issue. It seems as though anyone can just wander into the racecourse stables with very few questions asked. So if you’re concerned about that and your horse’s safety, you have to take it upon yourself to be looking after your horse for the whole time it’s there. But really, I think as trainers we kind of like that—not having to be constantly showing the right passes at every gate. It’s very relaxed.”
So that, at least, is how ‘the other half ’ live with the complaint of too much straw, no doubt breaking many Irish hearts. Like in France and Germany, the standard of stabling at Irish racecourses is not written into the Rules.
Michael Grassick, CEO of the IRTA (Irish Racehorse Trainers Association) explains, “It’s at the discretion of the racecourse, but half a bale of shavings is standard, with paper available as an alternative on request. I know a lot comes down to the cost, but the reason behind the half bale is that if there were a deeper bed, it would encourage the horse to roll. We don’t have overnight stays here in Ireland, and horses don’t have so far to travel to the races; so it’s not the issue it is in the UK or some other countries. I would say 99% of trainers find the stabling at Irish racecourses reasonable.”
However, several trainers, including those based in Northern Ireland who still come under the IHRB jurisdiction, are far from happy. With so much media attention on equine welfare, the argument is that half a bale of shavings is totally insufficient for a horse, which might arrive at the races four hours early.
Amanda Mooney
Amanda Mooney tells us, “I am a small trainer in County Meath, and horses are everything to me. All are treated as individuals in my yard and all their needs met to a high standard. I am at a loss when I go racing and feel it’s so wrong that a top athlete—who needs a good thick bed underneath them to pee or feel relaxed—is then asked to deliver what they are trained for, but it is not made comfortable by racecourses.
“As instructed by the IHRB veterinarian, they only need half a bag of shavings in the stable at the racecourse even though they could be stood in the stable for a good few hours before and after their race. If I were to leave a racehorse in a stable at home with just half a bag of shavings on concrete, would this be acceptable to a vet?”
Most trainers raised the issue of the horse’s reluctance to urinate where lack of bedding caused splashing. A comparison to eventing was made, where temporary boxes are made up to match the comfort the horse would be used to at home.
The provision of a safe, non-slip area for trotting up for veterinary inspections was another common appeal. Amanda Mooney points out, “I have a horse who has a very slightly enlarged fetlock, which has never given him any problems and was like this when purchased from Godolphin. I, like all trainers in Ireland when getting our licence, have undertaken to look after all the horses in my care to a top standard, which includes not running a horse if lame or sore. Every time he runs, he is subjected to rigorous joint movement and then required to trot up, which I’ve refused on the grounds of unsuitable surfaces. I have even given a full vet report on the horse for all vets to read at the course.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Looking after our jockeys - Q&A with Denis Egan
Author - Dr. Paull Khan
In this issue, we conclude our series of Question and Answer sessions with the chairs of the various committees that operate in the EMHF region.
Following our features on the Pattern and doping control, we turn our attention to the well-being of our human athletes, the jockeys.
Denis Egan, who until recently was CEO of the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board, has also been the driving force within the International Federation of Horseracing Authorities (IFHA) when it comes to the welfare of riders. Not only does he chair the European Racing Medical Officers Group, but he has also been at the helm of the global International Conference for the Health, Safety and Welfare of Jockeys (ICHSWJ) since its inception some 15 years ago.
This time, our questions have been posed by various jockeys’ associations.
Q: What is the ICHSWJ?
DE: The ICHSWJ is a biennial conference for racing administrators, racecourse doctors, researchers and jockeys’ associations. The first conference was held in Tokyo (Japan) in 2006, and the ICHSWJ was officially recognised as one of the sub-committees of the IFHA in 2009. There have been eight conferences to date, which were held in Tokyo, Japan (2006), Antalya, Turkey (2008), Monmouth Park, USA (2012 & 2013), Hong Kong (2015) and Dubai, UAE (2010, 2017 and 2019).
The conference features presentations from the world’s leading racing administrators, racecourse doctors and researchers who work closely with jockeys both on the racecourse and through research studies. We are hoping to hold the next conference in Dubai in 2022, subject to COVID-19 restrictions being lifted.
Q: What is the charter of the ICHSWJ?
DE: The mission of the ICHSWJ is to provide a forum to discuss and implement strategies to raise the standards of safety and the standards of care provided to jockeys and to create a safer and healthier everyday life for jockeys when they participate in the sport.
The ICHSWJ has seven strategic objectives, namely to:
• RAISE awareness of jockeys’ health, safety and welfare issues
• HARMONISE standards and procedures throughout the world
• HARMONISE the collection of injury data
• PROVIDE a forum for the sharing of information
• SHARE research findings and foster collaboration
• PROPOSE strategies to deal with issues on a global basis
• SET UP a more effective communication mechanism between countries
Q: What do you see as the main focus by the attendees and presenters re jockeys’ health, safety and welfare?Is it bone health, making weight in a healthy manner (e.g., saunas, nutrition and fluid intake), concussion, injuries and falls, psychological/mental health issues, PPE (e.g., helmets and vests), or all of the above?
DE: It is all of the above with an increasing focus on mental health, concussion and making weight safely.If you look back at the agendas for the eight conferences that have taken place, the focus of the initial conferences was on what could be described as ‘traditional’ jockey issues such as weights, injuries and safety equipment, with little or no research having been carried out in any of the areas. Now everything has changed, and the focus is on the increasing amount of research that has been carried out in jockey health and safety-related issues. In Ireland we have been funding research since 2003, and many other countries have now developed their own research programmes. There is now much greater research collaboration between countries than there would have been in the past, and this has contributed to better results.
The one thing that has surprised me most is the huge focus that is now on mental health. The first time it appeared on a conference agenda was in 2017, and it has now become such a major issue everywhere. There have been numerous studies carried out that have found there are significant levels of depression amongst jockeys; and the industry is now addressing this with most countries putting better support in place for jockeys.
Studies have found that the life of a jockey has major highs and lows, and while success is a high, there are far more lows such as wasting, injuries, failing, travelling and social media abuse, which can be very hard to take. Studies have also found that there is a complex interplay between physical and psychological challenges: weight, dehydration, making weight and mood.
Q: What do you think is the number one issue facing jockeys at the moment?
DE: There is no doubt that the number one issue facing jockeys at the moment is mental health; and the fallout from this is being addressed by both the governing bodies in collaboration with the jockeys, which is the way to go. Many countries make sports psychologists available for jockeys if they want to use their services. We have been doing this in Ireland for many years, and while some jockeys may have been reluctant to use these services in the past, more and more have come to realise the benefit of the service.
Q: There has been a lot of research into mental health and wellbeing issues in jockeys, especially in Ireland and the UK. What can governing bodies do to either proactively improve jockeys’ mental wellbeing or support those with issues?
DE: Practically every governing body is now aware of the importance of jockeys’ mental health and wellbeing. The best way of helping jockeys is to be aware of the issues they are facing and to work with the jockeys’ associations to address these issues. The recent collaboration between the Professional Jockeys Association in Great Britain and the BHA is testament to what can be achieved by working together where an outcome was delivered that benefited everyone.
The other way governing bodies can assist is through education and the provision of support services to jockeys, which are easily accessible. Jockeys sometimes need to be educated in the sense of making them aware of what is available and how the services can be accessed. It is sometimes difficult to encourage jockeys to use mental health support services as some see it as a sign of weakness that they need to access these services; and they don’t want their weighing room colleagues to know that they perceive themselves as having issues. In reality, it is a sign of mental strength that they (are) able to make the decision that they need the service.
Q: The issue of burnout is one that is increasing across all sports. How do you feel governing bodies deal with or recognise this as an issue?
DE: It is now being dealt with far better than it was in the past. Great Britain recently announced that jockeys will be restricted to riding at one meeting per day in 2022. This is the second year that this has occurred, and this was agreed in cooperation with the jockeys’ association there. In Ireland there was a holiday for the professional jump riders for a three-week period in early June this year. This worked very well as it gave the jockeys an opportunity for some down time to recharge and take a holiday.
Burnout may not be as big an issue for riders in countries where there are a small number of racecourses or where there is a restricted racing season, but nevertheless, all governing bodies need to be aware of it.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.