TopSpec Trainer of the Quarter - George Scott
Article by Lissa Oliver
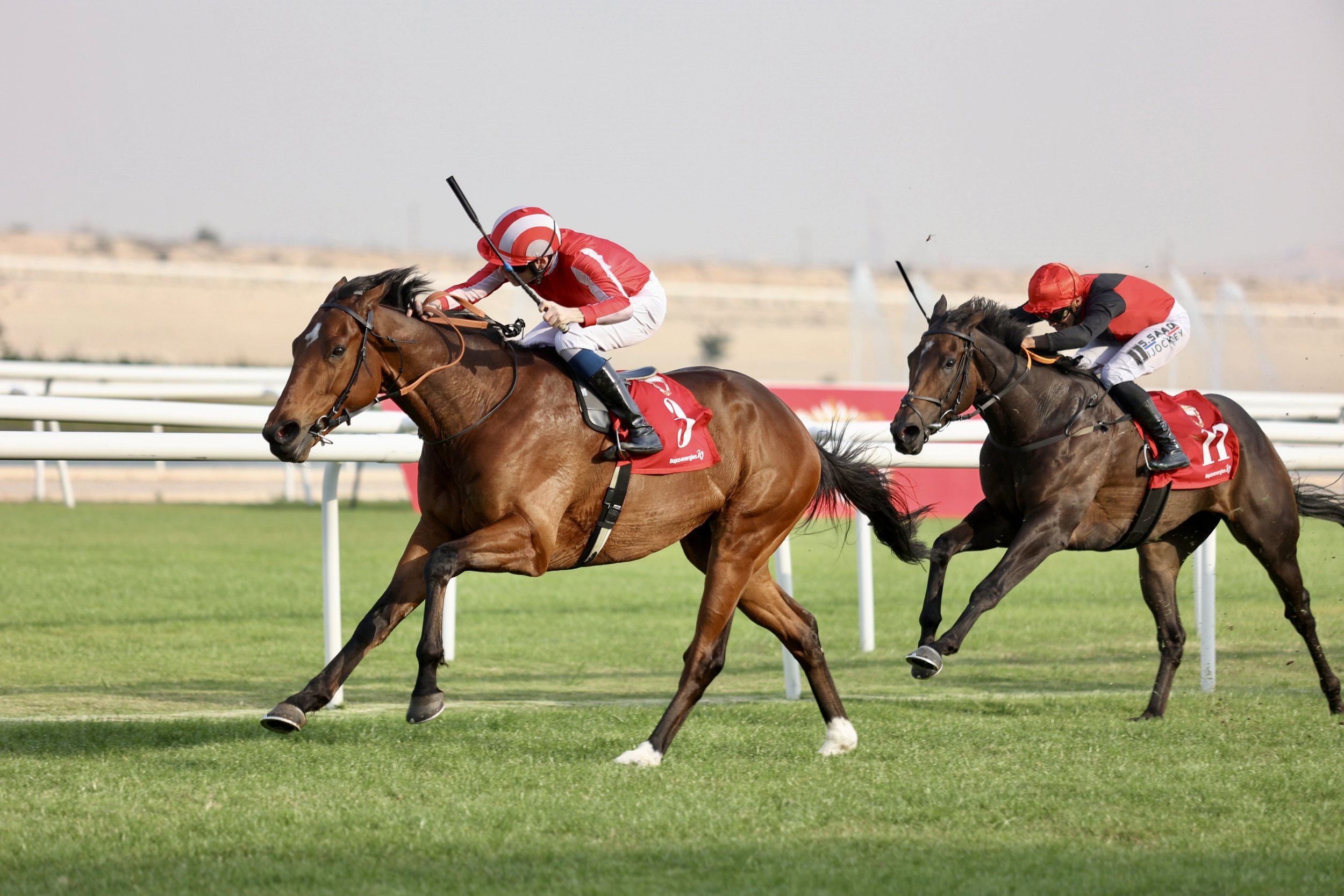
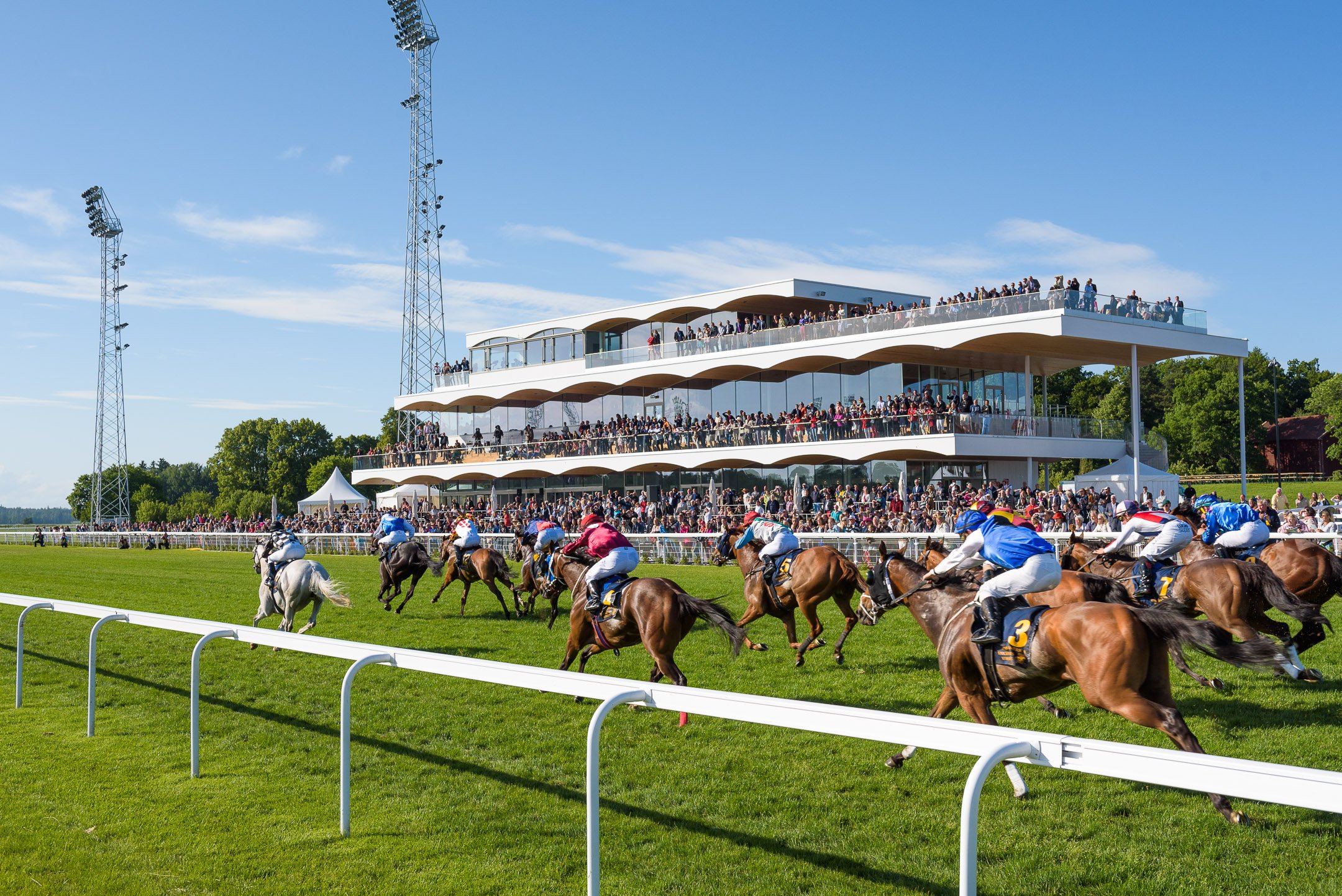
Sending out a Triple Crown winner anywhere in the world is a rare achievement, but for trainer George Scott it was all the more impressive, as he’d plotted a long-distance raid with a horse bought for the purpose.
More to the point, his Newmarket-trained Isle Of Jura became the first horse to complete the Bahrain Triple Crown, much to the delight of his Bahraini owner, HH Shaikh Nasser Bin Hamad Al Khalifa. Triple Crowns are designed to be difficult to win and the Bahrain version is no different. The first two legs, the Listed Crown Prince’s Cup (2200m) and the Al Khalifa Cup (2300m) are run in February, with the final leg the Listed King Hamad Bin Isa Al Khalifa Cup (2400m) in early March.
Bought last March as a once-raced maiden from the Godolphin draft at the final Tattersalls Ascot sale, Isle of Jura quickly climbed the handicap for Scott with two wins from five starts, before travelling to Bahrain in December off a rating of 97.
“We originally bought him with Bahrain in mind,” explains Scott. “HH Shaikh Nasser felt he would suit Bahrain further down the line, his pedigree suggested he would handle the fast ground there and his handicap mark also fitted very well with the Turf series. I was adamant he could step up in trip and I know he can handle a couple of races on the bounce, so I hoped he could win several turf races. Primarily, we targeted Bahrain because his owner loves racing there.”
Acknowledging he loves it when a plan comes together, Scott puts it all down to careful preparation in advance. “When travelling horses, I am lucky in that I have a very good assistant, Alex Mant, she plans the trips meticulously. The settling in process is vital, there’s a very small window of getting them there and settled with the least stress to them as possible. It’s important to keep them well hydrated, we like to keep their food consistent, and don’t stress them. The people you surround the horses with are very important. Isle of Jura did most of his work at home before he left and just ran off the plane. It’s all down to planning.” Scott also speaks highly of Bahrain and the facilities for horses and staff. “They do a fantastic job, they really want to help you and all the team loved being there.”
He is naturally pleased with the positive start to the season, having won the Listed Spring Cup at Lingfield with Watch My Tracer only 24 hours prior to Isle of Jura’s historic win. “Isle of Jura is back here now and after five quick runs we’ll give him a break. The plan is to bring him back for the Hardwicke Stakes at Royal Ascot, where hopefully he’ll get nice ground, I’m optimistic.”
A Greek Racing Tragedy
Article by Paull Khan
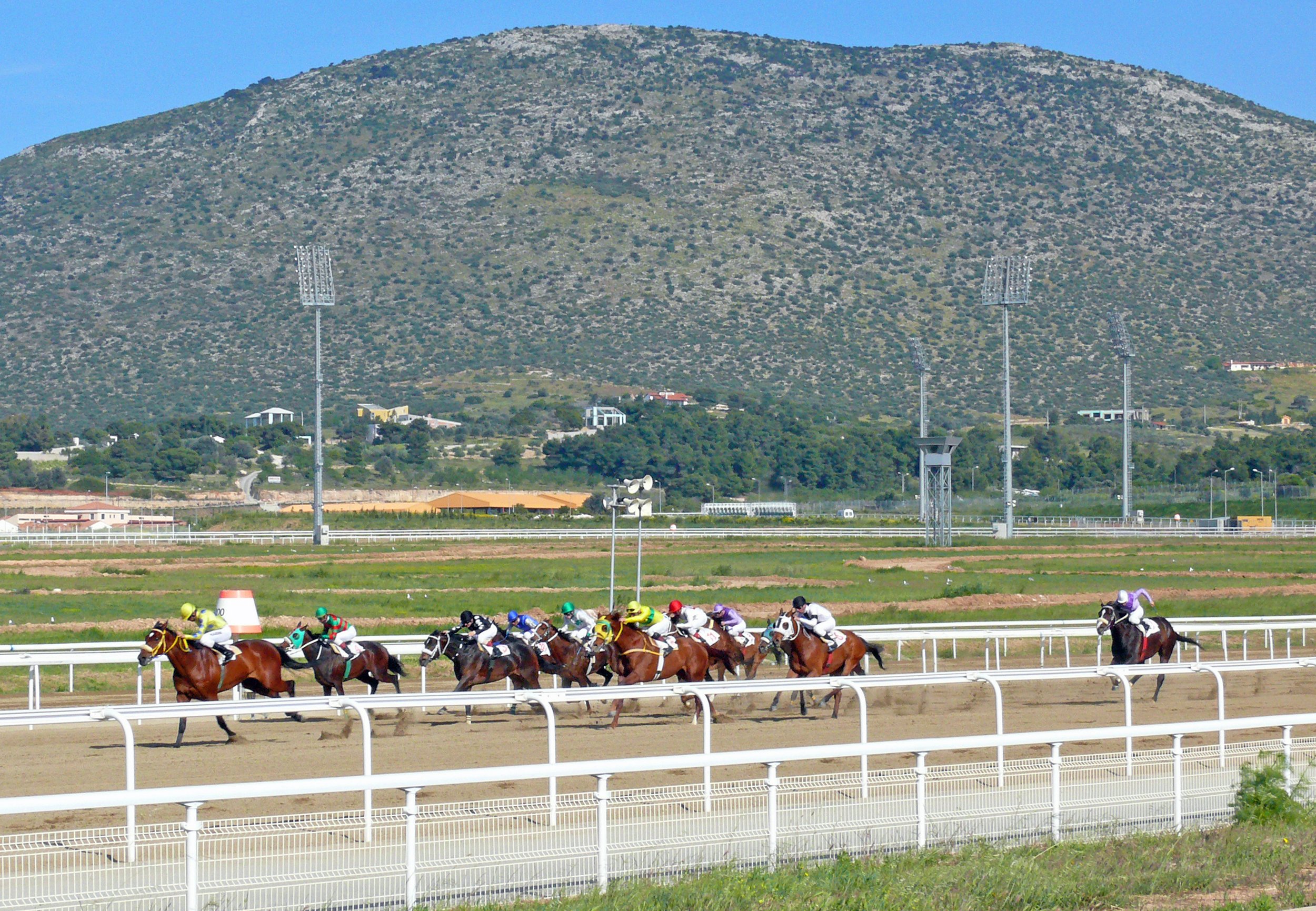
It was a bitter blow when, on January 31st, 2024, Horse Races SA, the Company which had been running racing at Greece’s sole racetrack for the past eight years, announced its immediate closure. The news followed hot on the heels of similar events in Singapore and Macau and underlined the fragility of our sport in many parts of the world.
The announcement referred to the Concession Agreement, between the Greek Government and Horse Racing SA’s parent Company, the Czech-owned O.P.A.P., under which Horse Races SA leased the site of Athens’ Markopoulo Racecourse and was given the exclusive right to stage races there. But, if the numbers of horses in training fell below 300, it was able to terminate the arrangement. At the time of the announcement, the number had dwindled to 172. According to the press release, this was despite investment of over €32 million by the Company, whose losses over the period of operation were given as €103 million.
The agreement also gave OPAP the concession to offer pari-mutuel betting, not only on Greek races, but on horseracing world-wide, and the Company clarified that they would continue to offer betting on foreign racing.
By the time of publication, it is understood that the racecourse will have been handed back to the liquidators. OPAP has offered subsidies on the costs of travelling the horses from their previous home in the racecourse stables to other Greek destinations. An appeal to neighbouring Cyprus, to absorb many of them, is understood to have fallen foul of Cypriot racing’s policy only to accept unraced animals. Some have already moved to Poland and Romania, but the future for many is unclear. The EMHF has written to the Greek Government, seeking comfort that due consideration is given to Greek racing’s participants, both equine and human.
The EMHF has also offered to assist in matching jockeys, work-riders and others, who find themselves suddenly without employment, with member Racing Authorities who report difficulties in sourcing experienced and competent staff.
The fortunes of Greek racing have yo-yoed through the course of this century. The previous track, Faliron, was situated at a coastal site, within easy range of Athens centre. It was vibrant, housing over 1,700 horses and attracted crowds of 15,000. After the Athens Olympics, the venue for the equestrian events – some 37 kms distant – became Markopoulo Racecourse. While its grandstand was, and remains, impressive, attracting crowds to Markopoulo has always been an uphill struggle. The economic crisis of 2008 came as a hammer blow, and by 2015, when the globe-trotting Australian administrator, Fin Powrie, was appointed as Horse Races SA’s Director of Racing, numbers of horses in training had dwindled to below the key figure of 300. By the time of Powrie’s departure – for Malaysia – those numbers had climbed again, exceeding 500.
“I was given a pretty free hand when it came to the racing product”, recalls Powrie. “We introduced a number of initiatives, including the supplemented purchase of good quality young horses from Tattersalls, ratings-based handicapping, inclusion on the International Cataloguing Standards ‘Blue Book’ and membership of the EMHF, all of which helped to raise the profile of the sport”.
So where, in his view, did things go wrong? “The decline in horses really set in around 2020. In 2019, the then Government allowed Horse Races SA to merge with its parent Company, OPAP. This, in turn, would have allowed the offsetting of the racecourse’s losses and significant rental commitments against the overall business’s tax. However, shortly after that the Government changed, and the new Government revoked that law. Development plans for diversifying the usage of the racecourse’s land also fell by the wayside.
“It was then a downward spiral – field sizes dropped, as did prize money, news and media coverage, which was never grand, simply ceased. People probably thought, ‘it’s a great big grandstand, it’s cold, it’s ordinary, there’s nothing else there for the kids’. And COVID didn’t help at all, of course”.
The concession only granted the exclusive right to stage racing at Markpolulo. It was, and still is, perfectly possible for others to start up racing at another Greek venue. However, this may be a big ask given the current climate of public opinion. The view has been expressed that public reaction to this closure has been very different from that which would have been the case a generation ago, with many taking the view: ‘maybe that’s just as well’. Powrie concludes “Personally, I doubt whether we will see the resuscitation of professional racing at some other track in the country”.
The international racing community must hope that this is not the case and that, somehow, somewhere, the sport’s flame can flicker once again in Greece.
The Norwegian Trainer, Silja Støren, with her raft of promising recruits for the season ahead
Article by Xander Brett
Oslo isn’t the North Pole. Polar bears don’t roam the streets. Reaching the Arctic Circle, indeed, requires a 14-hour drive from the city centre. But snow can coat the Norwegian capital for months at a time. Training horses in this country is no easy accomplishment. That said, it’s a feat achieved by some 37 trainers, 14 of whom call it their profession. Among the full-time contingent, Silja Støren is based at Øvrevoll, Norway’s only racecourse, which sits in the Oslo suburbs. Øvrevoll’s surroundings are home to around 200 of the nation’s 250-odd horses in training. Støren, like each of her Øvrevoll colleagues, enjoys use of the course’s turf and dirt oval. She competes at her home track, and has easy access to a myriad of venues in Sweden and Denmark.
Now in her 30s, Støren has always called Oslo home. Her Norwegian father was a surgeon and her Icelandic mother a nurse. She describes it as a “medical family”, and says there were no horses around while she was growing up. That, perhaps, was wise, given young Silja was allergic to the animals. As her equine enthusiasm developed, Støren’s immune system had to keep pace. “To begin with,” she explains, “I could only spend ten minutes inside a stable. As I got better, that grew to 15 minutes. Before long, I was spending time with horses without the allergy bothering me. It had more or less gone by the time I was ten. That was when I started riding lessons.” Støren’s first ‘pony’, Aberfeldy, was a four-year-old retired racehorse. He arrived when Støren was 12. “My father didn’t know much about horses,” Støren laughs, “so he didn’t know that a 12-year-old girl should probably have a pony, not a thoroughbred. I saw Aberfeldy as a big pony, though. He was the kindest horse ever, and probably kinder than most ponies. Ponies, of course, aren’t always gentle.”
Just three years after Aberfeldy’s arrival, Støren took out an amateur jockey’s licence. She threw herself into the Fegentri amateur riders’ series, and spent two winters working in Spain, at the yards of José Lopera and Guillermo Arizkoretta. Another stint saw her based at the Royal Stables in Bahrain. “I wanted to travel the world and gather experience,” Støren explains, adding that Fegentri adventures took her as far afield as Abu Dhabi and the United States, where she even rode a bunch of winners. “I was 15 when I took out my amateur licence,” she continues. “That’s as young as you’re allowed. Fegentri was a fantastic opportunity to explore the racing lifestyles of other countries. I rode out wherever I was, so I made connections with various trainers and learnt their different ways of working.”
Back home, Støren picked up Norway’s Champion Amateur title in 2014 and 2015. She’s adamant, however, that a professional riding career wasn’t for her. “In Norway,” Støren explains, “female apprentices are usually light. That means they get most of their rides from male jockeys who can’t make that weight. I didn’t really have that advantage, though I could make 56 kilos on a good day.” Støren served her apprenticeship under Oslo-based Isidro Vergara. By 2020, she had hung up her boots and joined him in the training ranks. “I always wanted to train,” Støren makes clear. “I just needed to arrive at a point where I thought I could bring in the owners. I was told early on that training horses is easy; it’s finding owners that’s difficult.”
Støren says years of riding experience has provided valuable lessons for her training career. It helps, too, that she can count on advice from her partner, Manuel Martinez, who is currently serving as Norway’s Champion Jockey. “Having Manuel has been so helpful,” Støren muses. “He knows the horses so well. He has played a big part in building up the success of the stable. I don’t think I could’ve done it without him.” Martinez has racked up over 3,000 victories around the world. He was Støren’s ready-made retainer and only form of assistance when she took out a trainer’s licence. Four years on, the yard’s ranks have swelled. The couple are now joined by a steady stream of work riders each morning. “I’m always trying to bring new people into the sport,” Støren states, saying she even welcomes prospective employees whose first equine experience is getting the leg-up on a racehorse.
“My main focus,” Støren explains, “is to keep the horses happy and sound. I try to train and feed them individually. The aim is to keep them fit, but not so as they get injured or lose interest. If a horse isn’t moving like it should, or if I want to change equipment, I’ve an advantage in that I can get on and see how it feels for myself. If I’m in doubt, I can put Manuel onboard. Together, we usually figure it out.” Støren says she knows each of her horses well, and she’d like to think she can spot if one isn’t themselves. She says her stable is assisted by a good team of farriers and vets, and she ensures the horses spend time in the paddocks. “We like to bring our horses to the forest in winter,” Støren adds. “They canter uphill in the snow, building a strong ground condition for the season.”
Norway has exported William Buick and French-based jockey Frida Valle Skar. Martinez and Støren’s former boss, Isidro Vergara, meanwhile, are among many South Americans propping up the Scandinavian racing world. Elione Chaves, Annike Bye Hansen’s newly signed first jockey, hails from Brazil. Chaves flew the Norwegian flag at Royal Ascot last year. He was aboard the Cathrine Erichsen-trained Duca Di Como when the now nine-year-old recorded a disappointing second-last in the Wokingham. Duca Di Como did, however, take a fifth success in Sweden’s Listed Nickes Minneslöpning later in the year.
Carlos Lopez, who acts as stable jockey for Niels Petersen – Norway’s Champion Trainer – is a Chilean arrival. “There are lots of South Americans,” Støren confirms, despite the paperwork required for arrivals outside the European Union or European Economic Area. “They have to apply to work here,” says Støren, “then wait two or three months for a response.” Støren is on a drive to recruit more native-born Norwegians. “The problem is,” she admits, “compared to other work in Norway, this isn’t lucrative. We work long hours, and it doesn’t pay well. The South Americans, however, are earning more than they would back home. They can send money to their families, even if Norway’s living costs are high.”
With new horses filling empty boxes, Støren needs the staff. She is, though, covered for the season, with enough employees to look after her operation. Last year, Støren had a battalion of just over 20 horses. A marked increase, certainly, from the 12 or so she looked after during her first few years with a licence.
The current line-up is headlined by five-year-old Hotline Bling. The son of Cotai Glory ended last season behind Kevin Ryan’s Washington Heights in the Listed Bro Park Sprint Championship. That came three months after he stormed clear to land Bro Park’s Listed Challenge Stakes, delivering Støren her first Black-Type success.
Now the property of Valstad Stable, Hotline Bling transferred from Amo Racing ownership, and the yard of Richard Hannon, midway through his two-year-old campaign. Running three times in Dubai at the start of 2022, he took the Norwegian 2,000 Guineas later that year. A trip to Glorious Goodwood followed, where he came home fifth of seven in the Group 3 Thoroughbred Stakes.
Støren says she’s delighted to have a horse who can compete with foreign raiders. “Hotline Bling particularly loves Bro Park,” she continues. “He raced twice in Norway last year, but the course didn’t suit him. When he gets to a flat track like Bro Park, he’s super good. It has been great to show people that we can train a horse like him.”
Støren says she gets on well with her owners, and they feel they can ring her anytime. “They all support us,” she explains, “and we spend time with them outside work.” Hans Christian Axel Melbye and Miriam Top are among her newest patrons. Together, the couple form Bling Enterprise, an operation that keeps a sizable string at Støren’s yard.
This includes All Star Bling, a €120,000 purchase at last year’s Tattersalls Ireland Goresbridge Breeze-Up Sale. “Bling Enterprise have been a super addition to our team,” Støren explains. “They have invested in us, and they have trusted us with so many nicely bred horses.” Støren says it all started when Hans Christian Valstad (of Valstad Stable, who own Hotline Bling) came to install an alarm at Melbye’s house. “He mentioned he had a racehorse,” Støren explains. Melbye then came to her open day. “I told him we had a 50 per cent share in a Norwegian-bred horse,” she continues. “He bought the share. Later, he wanted something for himself, so he secured two horses at the Tattersalls Craven Breeze-Up Sale. He bought a couple more last summer.”
Støren says she likes to support Norwegian-breds, but she’s equally excited to see how British and Irish imports get on in Scandinavia. Breeders of Norwegian horses receive 20 per cent of what the horse earns, and there are races dedicated to Norwegian or Scandinavian-breds. Owners can also receive a bonus for taking on imported runners, with 30,000 NOK (c. £2,240) available to cover import costs.
Alongside Hotline Bling, Sid Game was among a handful of Støren stable stars last year. The now four-year-old won six of his seven starts in 2023, signing off the season with victory in Øvrevoll’s Breeders Prize Sprint. Thanks to generous prize money in races for Norwegian and Scandinavian-breds, Sid Game was second only to Wido Neuroth’s Norwegian Derby-winning Ami De Vega as the track’s highest earning three-year-old. “He went out and did exactly what he was supposed to do,” says Støren. “I also had Buckyboss. He had two wins and was second to Sid Game in the Breeders Prize Sprint. Those horses have been great advertisements. But helping any horse achieve its best is what I enjoy most about this job.”
Eleven Støren charges won at least once last year, and the trainer says she hopes to run more horses outside Scandinavia shortly. She and Martinez had planned to send a batch of runners to Dubai this winter, but decided to hold off until next year. A return to Goodwood, she says, was also on the cards in 2023. This, however, was skirted to avoid missing key contests at home.
Annike Bye Hansen-trained Hard One To Please represented Norwegian interests at the Sussex track instead. Jim Crowley guided the son of Fast Company to a Group 3 sixth on Glorious Goodwood Friday.
Støren has made six entries for the 2024 Norwegian Derby, and the Bling Enterprise arrivals help form a raft of promising recruits for the season ahead. “I know it’s a big thing for a new trainer to dream about winning a Derby,” she admits, “but you can always try. We’ve had some nice recruits coming in, and that has been a great help. It shows that I can improve and maintain the horses in my care.”
When asked if she can switch off from training, Støren is swift in response. “No,” she laughs. “I don’t stop working.” Støren admits spending every minute with her partner can be challenging, given they not only work in the same industry but in the same yard. “It’s part of being a trainer,” she clarifies. “Even when you try to think about something else, in the back of your mind you’re always planning the next race. Owners call, or you spend time looking at horses for sale. I love horses, so I like life that way. We have good owners, and the future looks bright. There are many young horses who haven’t been out yet. I hope we can accomplish great things with them later this year.”
Trust your gut - the importance of feeding the gut microbiome for health, performance & longevity
Article by Dr. Richard McCormick, M.V.B., Dip. Eq.Sc., M.R.C.V.S.
The science of equine nutrition is really quite simple – The horse is a flight animal and in the wild, needs to be able to escape from predators using a short burst of energy. Nutrition and subsequent ‘energy’ for survival is all provided by grass which has the required balance of vitamins, minerals, immune supportive nutrients and fibre to maintain a healthy gut microbiota and keep the horse in adequate health for reproduction. Proper functioning of the gastro-intestinal tract (GIT) in horses is dependent on a broad range of micro-organisms and more than half of the energy requirement for their survival comes from the microbial fermentation occurring in their enlarged caecum and colon (Chaucheyras-Durand et al 2022). The bacterial populations resident in the various compartments of the horses intestinal tract vary greatly (Costa et al 2015) and there is more DNA in the bacteria located in the gastro-intestinal tract than there is in the entire body. Because of this, having a healthy gut flora is critical to having a healthy immune system.
In modern times, our demands of horses for performance for our pleasure rather than their survival has led to their need for increased energy that cannot be provided from grass alone. Because of this, the intricacies of diet (in particular the consumption of starch, fibre and fat) has come under scrutiny. Equine feed manufacturers have looked for additional sources of starch, a carbohydrate and a natural component of grass that is ‘essential to provide energy, fibre and a sense of fullness’ (Seitz 2022). Today, most horses and rapidly growing foals are commonly fed diets with >50% of total ration by weight in the form of grain ‘concentrates’ and carbohydrates from oats, maize, soya, barley and wheat. These grain based feeds contain high concentrations of soluble, easily fermentable starches but can be deficient in certain minerals and vitamins so getting an optimally balanced feed ‘right’ is difficult.
Too much of a good thing
With advances in scientific knowledge, we now know that when a horse is exposed to surplus starch, the hydrogen ion concentration of their gut increases promoting the production and absorption of lactic acid, acetate and propionate through the activity of fermentation (Ralston 1994). The process is quick, with lactic acid entering the bloodstream within 3 hours of feeding and calcium subsequently being excreted in the urine. In order to combat this nutrient loss, the horses’ hormone system triggers the release of parathyroid hormone into the bloodstream, activating the release of stored calcium (to maintain optimal blood levels) but unfortunately causing bone demineralisation. Clinically, the horse experiences health consequences of varying degrees including digestive diseases (eg: gastric ulcers, diarrhoea, colic or colitis), muscle dysfunction (eg: rhabdomyolysis (known as ‘tying up’), defective bone mineralization (expressed as increased incidence of stress fractures and developmental orthopaedic diseases), systemic diseases (such as laminitis, equine metabolic syndrome and obesity (Chaucheyras-Durand et al 2022) as well as potential causes of fatigue.
The ideal equine diet
There is little equine focused research available on the benefits of individual nutrients (due to limited numbers in trials and their subsequent evaluation) of grain ‘concentrates’. But we do know that ingredient availability and quality is regularly influenced by market pressures.
The table (fig 1) below outlines the sugar, starch and fibre components of the various ingredients commonly found in horse feeds. The optimal grain for equine nutrition with its efficient energy source through lower starch content (relative to other grains) and its high level of soluble fibre (relative to other grains) are oats.
Oats are highly digestible and do not require heat treatment or processing prior to feeding (unlike all other grains). They are the only grain that is easily digested raw and the least likely to cause insulin spikes and blood sugar fluctuations. Unfortunately, oats are not a ‘complete’ nutrient source as they are high in phosphorous and low in calcium. For adequate bone and muscle development as well as proper blood formation, oats must be balanced with additional vitamins and minerals.
The healing power of omegas and short chain fatty acids
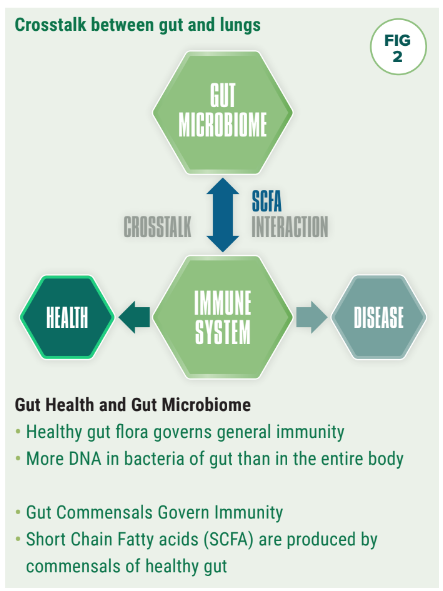
While grass provides optimal equine nutrition in its own right, the ‘curing process’ when making hay depletes the valuable omegas 3 and 6 intrinsic in grass. These ‘healing’ nutrients naturally protect the lining of the gastro-intestinal tract by increasing mucous production and alleviating ‘auto digestion’ (via hydrochloric acid). For horses, bacterial fermentation in the hind gut also results in the production of Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs), namely acetic, proprionic and butyric acids. These SCFAs ‘cross talk’ with the gut immune system providing local immunity in the gut as well as protection of the respiratory system, the brain and other tissues against disease. In human medicine, it has been repeatedly established that a dysfunctional gut microbiome is associated with respiratory problems. This is evidenced by the fact that when gut disorders such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBD) or Coeliac disease exist in humans, they are commonly associated with a higher incidence of respiratory infections and related asthmatic like conditions. Barragry (2024) explores the relationship (Fig 2) between gut microbiome and the immune system's ability to support health and combat disease in cattle. A scenario mirrored in the equine.
The stabled horse should be provided with SCFAs daily to support proper functioning gut microbiome. This critical dietary consideration should ideally be provided in the form of flaxseed which has the highest ratio of omegas 3 and 6 (in the ideal ratio 4:1) in the plant world and is most suitable for the equine herbivore.
The health benefits of flaxseed for both humans and equines has been recognised as early as 3,000 BC. Flaxseed was used for various medicinal purposes such as the treatment of gastric disorders, as a soothing balm for inflammation and as a laxative (Judd, 1995). Horsemen (who relied heavily on their equines) and trainers (who sought optimal performance from their charges through natural means) also used flaxseed as a way to supplement the diet with omega-3’s and fibre to produce high quality proteins. Now, thirteen centuries later, we have research to substantiate the knowledge of our ancestors. The renowned German researcher of ‘fats’ and pioneer in human nutrition, Dr. Joanna Budwig, as early as the 1950’s reported that “the absence of highly unsaturated fatty acids causes many vital functions to weaken". Dr. Budwig’s life’s work focused on the dietary ‘imbalance’ between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in humans has been a cornerstone to the exploration of the role of inflammation and the development of many diseases of the coronary, respiratory, metabolic and immune system.
The small seed of the flax plant is also an excellent source of high-quality protein (exceeding that of soybeans and fish oils) and potassium (a mineral that’s important for cell and muscle function). But, the true power of flaxseed lies in three key components:
Omega-3 essential fatty acids – Also known as "good" fats, omegas enhance the oxygen usage of cells and in combination with alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) are anti-inflammatory in their effect within the body.
Lignans – Flaxseed contains 750 - 800 times more lignans than other plant foods (McCann 2007, Yan 2014). Lignans are a group of compounds with antioxidant properties which also contain plant oestrogen. Lignans are linked to a reduced risk of developing osteoporosis, heart disease and cancer.
Fibre - Flaxseed contains both the soluble and insoluble types of fibre essential for maintaining ‘gut’ health.
In equines, adding flaxseed to the diet has the immediate benefits of a shiny, healthy coat and fewer skin allergies. Consistent use of flaxseed has multiple long term benefits including strong hoof quality, improved joint health, reduced muscle soreness, faster healing of ulcers (Sonali et al 2008) and significantly impacts inflammation associated with chronic skin conditions (commonly known as ‘sweet itch’). In breeding stock, increased Omega-3 levels in mares’ milk leads to boosted immunity in foals with higher stallion fertility and improved conception rates in broodmares documented (Holmes, 2015).
How diet can influence performance
It is easy to think that ‘providing more is better’ when it comes to using nutrition to support performance. But having excess levels of essential vitamins and minerals being processed by the horses’ sensitive gut has a direct impact on their behaviour and willingness to perform. Today, we have greater ‘choice’ at the feed store with a broad range of commercial feeding offerings available including mixes, mashes and supplements but the discerning horse owner can be forgiven for being overwhelmed by the range of diet options for every ailment and stage of life.
In modern times, despite advances in nutrition offerings, we have seen a falloff in performance (Fig 3). During the late 1960s, the U.S. Jockey Club stats noted that racehorses averaged 12 starts per year – a far cry from today's horses racing in the U.S. where the average of 3 ‘starts’ was highlighted by leading US Trainers in 2020 (www.ownerview.com). Unfortunately, this is not just a U.S. based problem, but a phenomenon noted worldwide.
The first equine pelleted feed was formulated in the US by the Cistercian monks in Gethsemani, Kentucky in 1957. Prior to this, all horses were fed ‘straights’ (primarily oats as their energy source and flaxseed as their protein source). My own understanding of the link between modern feeding practices and compromised performance since the 1960s has been curated off an understanding of “what was different” then, as well as a career of observations, clinical practice and scientific review. Fact is, the equine diet of the 1960s was lower in starch and high in fibre. It consisted of oats, minerals, and flaxseed as the “norm”. Hay was the preferred forage (Fig 4).
Today, soya (with one fifth of the omega 3 content of flaxseed) has practically replaced flaxseed as the protein source in equine nutrition. This small change has seen a significant drop in omega-3 and 6 (needed for prostaglandins) in the diet with consequential gastro-intestinal and joint issues. Other dietary changes include those recommended by the National Research Council (NRC) in 1978, who suggested doubling the recommended calcium levels for horses with a subsequent increase in levels of Osteochondrosis (OCD) and Osteopetrosis in the equine population (Krook and Maylin, 1989). Additional moisture in the diet too has led to excess mould formation in convenience feeds and with severe exposure causes liver damage (Buckley et al 2007). Stabled racehorses today mostly lack the nutritional protection afforded a previous generation of horses. The impact has been noted clinically in the widespread increase in equine gastric issues and as stated by J.E. Anthony “Racing fans are missing about half of what they once enjoyed in racing.”
The role of the gut bacteria in the prevention of disease
The gut microbiome begins populating and diversifying from the moment of birth. Though ‘sterile’ in utero, gut derived DNA immediately drives immune health with exposure to nutrition. Recent research suggests that the gut microbiome can be stimulated by using proven probiotics with a track record in enhancing gut health (Barragry 2024). But it is the protective power of SCFAs to allow ‘cross talk’ between the lungs and the gut microbiome that is critical to supporting horses through their lifespan.
Nutrition using grain ‘concentrates’ is currently at approximately 99% saturation in today’s equine population so a return to feeding ‘straights’ is a swim against the tide of modernity. But, knowing the influence of nutrition on health, performance and longevity it falls on horse owners to be mindful of the consequential impacts such convenience feeds have on the gut microbiome and immune system. Random supplementation and high starch feeds are leading to dietary health issues such as gastric ulcers, hyperinsulinemia and hyperlipaemia (obesity) as well as increased risk of laminitis . So trust your gut and keep it simple – a diet of oats, flaxseed, a multi-vitamin balancer and ad lib hay will not only meet your horses’ energy needs but will keep them happy and healthy too.
REFERENCES
Barragry. TB (2024) WEB https://www.veterinaryirelandjournal.com/focus/254-alternatives-to-antibiotics-probiotics-the-gut-microbiome-and-immunity
Buckley T, Creighton A, Fogarty (2007) U. Analysis of Canadian and Irish forage, oats and commercially available equine concentrate feed for pathogenic fungi and mycotoxins. Ir Vet J. 2007 Apr 1;60(4):231-6. doi: 10.1186/2046-0481-60-4-231. PMID: 21851693; PMCID: PMC3113828.
Budwig, Dr. J (1903-2008) WEB https://www.budwig-stiftung.de/en/dr-johanna-budwig/her-research.html
Chaucheyras-Durand F, Sacy A, Karges K, Apper E (2022). Gastro-Intestinal Microbiota in Equines and Its Role in Health and Disease: The Black Box Opens. Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 19;10(12):2517. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122517. PMID: 36557769; PMCID: PMC9783266. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9783266/
Holmes, R (2015) Feeding for stallion fertility. WEB
https://www.theirishfield.ie/feeding-for-stallion-fertility-172113/
Judd A (1995) Flax - Some historical considerations. Flaxseed and Human Nutrition, S C Cunnane, L U Thompson. AOCS Press, Champaign, IL 1995; 1–10 [Google Scholar]
Martinac, P (2018) What are the benefits of flaxseed lignans? WEB https://healthyeating.sfgate.com/benefits-flaxseed-lignans-8277.html
National Research Council. 1989. Nutrient Requirements of Horses. Washington D.C.: National Academy Press.
Ralston, S VMD, PhD, ACVN (1994) The effect of diet on acid-base status and mineral excretion in horses in the Journal of Equine Practice. Vol 16 No. 7. Dept of Animal Science, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ 08903
Seitz, A (2022) What to know about starch_Medically reviewed by Seitz, A - MS, RD, LDN, Nutrition — WEB https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/what-is-starch#benefits
Sonali Joshi, Sagar Mandawgade, Vinam Mehta and Sadhana Sathaye (2008) Antiulcer Effect of Mammalian Lignan Precursors from Flaxseed, Pharmaceutical Biology, 46:5, 329-332, DOI: 10.1080/13880200801887732
The different incentives available across Europe this summer for those in search of prize money and black type success
Article by Lissa Oliver
In February, the European Pattern Committee (EPC) announced changes to the 2024 European programme of Flat Black-Type races. The EPC sanctioned a total of 826 Black-Type races (838 in 2023), comprising 416 Group races (418 in 2023) and 410 Listed races (420 in 2023). Five Pattern races have been downgraded in 2024, with a further 11 Listed races losing that status.
Jason Morris, Chair of the EPC, explained, “This year will see another contraction in the number of Pattern and Listed races to be staged throughout Europe, with the total number having declined from 852 races in 2022 to 826 in 2024. The European Pattern Committee continues to enforce the most stringent international quality control measures so that the racing and breeding industries can have the utmost confidence in the quality of European Black Type.”
This leaves trainers rethinking traditional routes to Black Type, but at the same time adding new avenues, some of which could lead to some interesting destinations. The EPC approved an application from Denmark to stage a new Black Type race in 2024, with the Golden Mile at Klampenborg over 1600m (8f) for three-years-olds and upwards in May being upgraded to Listed status and carrying a purse of €46,749 (£40,000).
In Ireland, the Salsabil Stakes, a 2000m (10f) race for three-year-old fillies at Navan in April, has been upgraded from Listed to Group 3. Ireland will also stage a new Listed race for three-year-olds over 2400m (12f) at Gowran Park 27th July, the Marble City Stakes worth €46,749 (£40,000).
Flagship races in Poland and Spain
Although no new Listed race applications have been received from emerging racing nations, the EPC noted the strong first Listed edition of the Wielka Warszawska in Poland in 2023. Run over 2600m (13f) at Sluzewiec Racecourse 6th October, for three-year-olds up, it carries a prize of €111,138 (£95,092).
The €85,000 (£72,728) Gran Premio de Madrid in Spain also continues to perform well after being allocated Listed status by the EPC in 2022. It’s run at Madrid over 2500m (12.5f) 22nd June for three-year-olds up.
These were created through the recent Flagship Race scheme by the European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation (EMHF) and EPC, allowing countries with no Black Type races to apply for a single Flagship race which qualifies for Black Type at a lower rating level. This provides horses with a slightly easier Black Type opportunity, by 2.2kg (5lbs). It also opens up new and often interesting destinations for owners and team.
Morocco
Dr Paull Khan, Secretary-General of the EMHF, explains, “The quality control that is applied to European Black Type is the most stringent in the world. This is good, of course, because everyone recognises the strength of European Group and Listed races. But, on the other hand, countries with less-rich racing industries have long found it hard to establish races which attract the necessary quality of runners to qualify for Black Type. Essentially, for most race types, the average ratings of the first four finishers must be at least 100. Two years ago, the EMHF and EPC devised the Flagship Race scheme, under which countries with no Black Type races can apply for a single Flagship race to be given Black Type based on average ratings of the first four finishers being 5lbs lower than would normally be the case. In simple terms, this means that trainers with horses up to 5lbs shy of normal Listed Race standard stand a reasonable chance of attaining black type when targeted at these races.
“There is a ripple effect which is of benefit to trainers,” Dr Khan points out. ”Other countries are looking to join the party, and in order to attract the necessary quality of entries - particularly from abroad – are ploughing money into their candidate races, and are often offering attractive travel incentives, too. Even if these races have not yet attained their Black Type status, they can still be immensely attractive propositions.”
Top of the list in this respect is Morocco’s Grand Prix de la Sorec. The 10th renewal of the Morocco International meeting will be held on the weekend of 16th and 17th November 2024 at the Casablanca-Anfa racecourse, a dirt track. This prestigious 14-race meeting plays a major role in promoting the Moroccan horseracing industry internationally and includes eight international races worth €1m in total. Sunday is devoted to Purebred Arabians, with over €500,000 in prize money for the four Black Type races.
Saturday is an all-thoroughbred card and of interest here is the feature €123,000 Grand Prix de la Sorec, 2400m (12f) for three-year-olds up. Entry is €600 by 31st October, free to declare. Also on the card is the €71,600 Grand Prix des Eleveurs for three-year-old fillies, over 1750m (8.75f) and the €61,600 Grand Prix des Proprietaires for three-year-old colts, over 1900m (9.5f). Casablanca-Anfa racecourse provides a children's area, entertainment and excellent facilities for visiting owners and trainers. The Cité du Cheval is the 87-hectare training centre on the outskirts of Casablanca, 15 minutes from Casablanca airport and 30 minutes from the racecourse, with 400 boxes, several training tracks, a farriery centre, two restaurants and a housing and catering area for staff.
International runners will have their flights, via the BBA, paid for, or up to €3,000 toward overland transport. Flights, hotel accommodation and all transfers are provided for two owners, the trainer and guest, and the jockey. Hospitality includes lunch at the racecourse on both days and dinner at the Gala Evening on Saturday.
As Dr Khan points out, “Another factor here is the ‘racing tourism’ element. The exotic location of these races provides an additional appeal for owners and trainers who want to soak up the fantastic experience of racing in different cultures.”
Turkey
Turkey and its International festival on the first weekend of September at Veliefendi Racetrack, Istanbul, has for long been a popular destination, particularly for British trainers. Since Brexit, however, the issues involving a Third Country have deterred British runners, leaving the races more open for other European runners. What is instead happening is that two valuable €240,000 (£208,000) Group races have been wholly contested by locally-trained horses, the 2023 Bosphorus Cup attracting just five runners.
The International Bosphorus Cup has this year been downgraded to Group 3, but remains an attractive proposition. Run on turf over 2400m (12f), the €240,000 (£208,000) race is open to three-year-olds up. With the same prize money, the 1600m (8f) International Topkapi Trophy is another Group 3 for three-year-olds up that last year attracted no foreign runners. And the same applies to the fillies only Group 3 International Istanbul Trophy over 1600m (8f), worth €127,000 (£108,645).
Entry for the International meeting is by 2nd August, and a very generous travel subsidy is available to foreign runners, including $18,000 to horses arriving from the continents of America (North and South), Oceania, Africa and Far East countries. Up to €12,000 is available to European and UAE runners.
Sweden and Norway
Sweden’s 500-acre Bro Park has permanent stabling and training facilities, just over 30 minutes from the centre of Stockholm by car and a similar distance from Arlanda Airport. The two main international days are the Stockholm Cup day 15th September and the Stockholm Stora day 9th June, both branded as Super Sunday, during which the local 1000 and 2000 Guineas are also run. Run on turf at Bro Park, the Group 3 Stockholm Stora Pris is run over 1750m (8.75f) and worth €88,817 (£75,992), with a strong supporting card of the €29,309 (£25,000) Listed Bro Park Varsprint over 1200m (6f) and Listed Bloomers’ Vase 1600m (8f) for fillies, carrying the same value.
The Group 3 Stockholm Cup International over 2400m (12f) on turf carries prize money of €124,343 (£106,380) and the three supporting races each offer €58,619 (£50,151); the Listed Tattersalls Nickes Minneslöpning 1600m (8f) run on dirt, the Listed Bro Park Sprint Championship 1200m (6f) on turf, and the Listed Lanwades Stud Stakes 1600m (8f) on turf for fillies. Lanwades Stud also generously offers a free nomination to one of its stallions to the winner. The card also includes a 1400m (7f) two-year-old race on turf worth €36,859 (£31,534), the Svealandlopning. The other mentioned races are for three-year-olds up.
There are also interesting opportunities in Norway on Norsk Derby day 25th August at Oslo, as Director of Racing Liv Kristiansen tells us. ”Oslo offers a great range of both historic and modern hotels and restaurants and makes for a great long weekend with the Derby Day as a finale. The racecourse is just a 15-minute drive from the city centre and is home to most of the racehorses in Norway. On the day, there will be many runners from Denmark and Sweden as well.”
Kristiansen reminds us that it is prohibited to use the whip throughout all of Scandinavia, and in Norway jockeys are not allowed to carry a whip in races for three-year olds and older.
Germany
As an accompaniment to the familiar Pattern races in Germany, Deutscher Galopp Director of Racing Rüdiger Schmanns tells us, ”in general all races are open for foreign trained horses, even handicaps if the horses have a rating in the home country. We have good prize money options in handicaps on the so-called Premium Race Meetings, which are meetings on Sundays or Bank Holidays with at least a Group race on offer on that day. Handicaps of the best category are in total value of €20,000 (£17,103), the second best of €15,000 (£12,827), the third best of €10,000 (£8,551), and the lowest category of €8,000 (£6,841). At the Baden-Baden meetings there is usually one handicap of the day with higher prize money and in Bad Harzburg we have the so-called Super-Handicaps with exceptional prize money in the different categories, but they have an early closing stage at the beginning of April. Average prize money is the highest ever on offer in Germany at €14,200 (£12,143).”
France
Handicaps should also be on the radar in France, where France Galop is contributing heavily in the relaunch of the Quinté+ bet. As a result, the 13 Major Handicaps programme has been remodelled to restore appeal. Four Super Handicaps are now worth €100,000 (£85,519) and eight more have increased in value to €75,000 (£64139), with maximum runners raised to 20. The four €100,000 Super Handicaps cannot be on a Group 1 card and will be run on 7th April at ParisLongchamp 1400m (7f) four-year-olds up; 5th May ParisLongchamp 2000m (10f) four-year-olds up; 4th August Deauville 1600m (8f) three-year-olds up; and 8th September ParisLongchamp 1850m (9f) three-year-olds up.
The dates of the €75,000 Grands Handicaps, with a maximum of 18 runners, are 2nd June Chantilly 2400m (12f) four-year-olds up; 16th June Chantilly 1800m (9f) four-year-olds up; 15th August Deauville 1200m (6f) three-year-olds up; 18th August Deauville 1900m (9.5f) three-year-olds up; 5 October ParisLongchamp 1600m (8f) three-year-olds up; 5th October ParisLongchamp 2500m 12.5f) three-year-olds up; 6th October ParisLongchamp 1300m (6.5f) three-year-olds up; 6th October ParisLongchamp 2000m (10f) three-year-olds up.
Another shake-up comes in the reduction of entry fees for Group 1 races to revitalise entries, introducing a uniform entry price of 0.65% of prize value, with the exception of the Qatar Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe and the Classic races. This lowers the entry fees for 15 Group 1 races, out of a total of 21. Trainers should note that entries have also been brought forward to earlier dates, now four weeks prior to the race.
Ireland
Horse Racing Ireland confirmed a record 395 fixtures for 2024, with an increase of €1.3m (£1.1m) in prize money, creating additional opportunities for horses at all levels. In addition, the final €1.4m (£1.2m) in capital schemes will be paid out for stableyard expansions (€0.3m) and racetrack and industry facility improvements (€1.1m), making it a more attractive proposal for visiting horses and team.
HRI, the Irish EBF and Gowran Park Racecourse have announced a significant boost to the three-year-old programme for middle-distance horses with a new Spring Series of median sires races, culminating in the €200,000 (£170,980) Irish Stallion Farms EBF Gowran Classic, 2000m (10f), the richest race ever held at the County Kilkenny course, on Bank Holiday Monday 3rd June. The race is designed to attract three-year-old middle-distance horses with a median price of no more than €75,000 (£64,121). The winner will receive an automatic free entry into the Dubai Duty Free Irish Derby at the Curragh on 30th June.
The series, with total prize money of €330,000 (£282,125), will consist of six races with a minimum prize-fund of €25,000 (£21,373) per race. The Curragh, Navan and Cork will host four maiden races between them, two for fillies only, and each of these races will be restricted to runners whose sires achieved a median price of not more than €50,000 (£42,747) in 2022.
A median price of €75,000 (£64,121) will apply to runners in The Irish Stallions Farms EBF three-year-old Spring Series Race, with a value of €30,000 (£25,647) at Roscommon on 13 May. The same median price restriction will apply to runners in the €200,000 series Finale.
Racecourse Manager Eddie Scally says, “Gowran Park are really excited to host the inaugural €200,000 Irish Stallion Farms EBF Gowran Classic, the region’s richest Flat race. This race will form part of an action-packed day both on and off the track with live music and a massive family fun day. We hope the Gowran Classic will attract all the top trainers and riders from both Ireland and abroad and see for themselves the warm Kilkenny welcome.”
Irish Stallion Farms EBF already sponsor two successful series for two-year-olds, the auction and median series with 27 races in each and a combined value of nearly €850,000 (£726,712). ”We felt it important to develop a similar series for later developing middle-distance three-year-olds,” says Irish EBF Chairman Joe Foley, ”hence the Spring Series was initiated with the Gowran Classic as its centrepiece. We look forward to seeing this three-year-old series grow and develop and are delighted to support Gowran Park racecourse in particular, who are investing heavily in their facilities.”
Curragh-based trainer Willie McCreery points out, “These races are designed to be linked to the median price of the stallion, which allows everyone to participate. It offers great opportunities for middle-distance horses that needed a bit of time to mature and gives them a big target to aim at. The prize money along with the ‘win and you’re in’ to the Dubai Duty Free Irish Derby is a super incentive.”
The new series consists of the 2000m (10f) €25,000 3yo Median Auction Maiden (Fillies) at the Curragh 6th April; 2000m (10f) €25,000 3yo Median Auction Maiden at Navan 9th April; the 2000m (10f) €25,000 3yo Median Auction Maiden at Navan 27th April; the 2000m (10f) €25,000 3yo Median Auction Maiden (Fillies) at Cork 10th May; the 2000m (10f) €30,000 3yo Median Auction Winners of 1 at Roscommon 30th May; and the Gowran Classic.
If tourism is the agenda, don’t forget Ireland’s only beach race meeting at Laytown, a small seaside resort just 46km (29 miles) from Dublin. The six-race card at Laytown races is held Monday 16th September 2024 with an average of €7,000 (£6,000) to the winner.
Britain
Last year saw the introduction of high value developmental races in Britain, a scheme the BHA has expanded for 2024. From 63, there are now 84 developmental races for the Flat season worth over €3.5m (£3m) in total prize money. The initiative has been made possible by British Stallion Studs (EBF), Juddmonte, Darley and Tattersalls, as well as the BHA Development Fund and is aimed at supporting the domestic breeding industry and encouraging the purchase of young talent in Britain. The races offer enhanced prize money to horses embarking on the early stages of their racing careers.
Richard Wayman, Chief Operating Officer of the BHA, explains, “These races play a hugely important role within the race programme and yet, historically, it is an area where prize money has been behind our international competitors. It is essential that steps are taken to retain quality horses on our shores and with over 80 of these races scheduled for the coming season, this is one initiative that we believe will support this broader aim.”
The 2024 programme began with the Brocklesby Stakes at Doncaster on the opening day of the 2024 Turf season, one of 60 such races for two-year-olds. It comprises 32 Open Novice/Maiden races for two-year-olds, worth a minimum of €46,789 (£40,000); 29 Restricted Novice/Maiden races for two-year-olds, worth a minimum of €35,091 (£30,000); and 23 Open Novice/Maiden races for three-year-olds up, worth a minimum of €46,789 (£40,000).
“British Stallion Studs (EBF) are delighted to be a leading sponsor of the 2024 High Value Developmental Race programme, with a contribution of over €380,172 (£325,000), covering more than 30 races,” says Simon Sweeting, Chairman of British Stallion Studs (EBF). “One of the unique features of our prize money contributions is to encourage racecourses to ‘match-fund’; it is wonderful to see the model we pioneered and embedded, replicated by our fellow sponsors in these races.”
The EBF remains the leading sponsor of European racing and Kerry Murphy, European Breeders Fund CEO, points out, ”The EBF was set up over 40 years ago primarily to tackle the threat of less prize money in two-year-old maidens. With £3.5m total prize money and over 80 high value two-year-old and three-year-old races worth at least £30,000 from the end of March to October, there will be opportunities for all types. It is a great credit to all involved and, of course, all the British stallion farms that contribute to the EBF, and I hope will give owners and purchasers at the yearling sales plenty of incentives.”
The full race list can be seen at:
https://ebfstallions.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/2024-Development-Race-List-public.pdf
A 20-minute drive from Stansted Airport, Chelmsford City offers some tempting opportunities for runners from abroad. Not least is the Cardinal Condition Stakes on Saturday 6th April, a Class 2 race that is the last stop of the European Road to The Kentucky Derby, a “win and you’re in”. Run over a mile (1600m) and restricted to three-year-olds, the race is worth £100,000 (€116,953), with the winning horse receiving 30 points, ensuring a place at Churchill Downs. Second through to fifth place receive 12, 9, 6 and 3 points respectively.
“Last year Bold Act won for Charlie Appleby and he has since won a Grade 3 at Keeneland. The runner-up was the Archie Watson-trained Brave Emperor, who had won twice here as a two-year-old and he followed up with a Group 3 win in Germany next time out. Brave Emperor has since added three more Group wins and has just won the Irish Thoroughbred Marketing Cup, a local Group 2, at Doha. We are hopeful of seeing the Cardinal Condition Stakes upgraded to Listed status for next year, given the strength of the race,” says Neil Graham, Chelmsford City Racing Director.
Another imminent upgrade to hope for is the currently Listed Queen Charlotte Stakes over 7f (1400m) for fillies four-year-olds and up, run on Sunday 7th July, with prize money of £100,000 (€116,953). Graham points out, “Past winners include One Thousand Guineas heroine Billesdon Brook, Group 1 winner Highfield Princess and Soft Whisper, a subsequent Group 2 winner in Meydan. It comes a month before the Oak Tree Stakes at Goodwood and is good stepping stone, as Billesdon Brook showed. It is also Britain’s second-most valuable Listed race, behind only the Chesham Stakes at Royal Ascot.”
The third of Chelmsford City’s feature races is the £80,000 (€93,595) Listed Chelmer Fillies Stakes over 6f (1200m) for three-year-old fillies, run Thursday 2nd May. “It’s a good option for the non-stayers and it’s a race that builds on quality year on year. Last year it was won by George Boughey’s Believing, who won a Group 3 at Chantilly on her next start,” says Graham.
“We work hard on promoting our feature races, which includes ensuring a high level of prize money, and we work closely with Adrian Beaumont at the International Racing Bureau to attract foreign runners. We look to offer travel incentives to runners from abroad and we consistently offer Class 6 prize money of £7,650 (€8,949) and £9,650 (€11,288) for Class 5 races, considerably more than any other All-Weather track in Britain.
“We have 125 boxes built to the highest standard located in a quiet and secure yard, with ample room for parking and a fantastic team on hand. Paper or shavings are available.”
“We are in the process of developing a Turf track for 2025 to open up further opportunities,” adds Graham, “and a month ago we were voted one of the Top 10 racecourses in Britain, which is a nice accolade to receive and a reflection of the excellent customer experience we offer.”
Overlooking the parade ring, the exclusive Owners and Trainers Bar provides a complimentary welcome drink and light refreshments. An additional facility for Owners and Trainers adjacent to the parade ring has a fully accessible glass-walled marquee and lawn, and there is also a dedicated viewing area in the main Grandstand, fully wheelchair accessible, for owners with runners on the day.
If it’s culture and tourism of most interest, a day at Ascot is always a highlight. This season, Ascot’s total prize money has risen to €20.4m (£17.5m) including Royal Ascot at €11.6m (£10m), with no Royal meeting race run for less than €128,688 (£110,000). Entry for Royal Ascot Group 1s is 30th April and for the King George VI and Queen Elizabeth Stakes 4th June.
Conditions for the Chesham Stakes (7f 2yo’s), traditionally run on the last day of the fixture, have been altered for 2024 - with horses no longer eligible to qualify via their dam’s performance. The race will return to a stallion only qualification as the race was prior to 2019 (sire must have won over 10f+).
Hannah Parlett, Owners and Trainers Manager, tells us, ”We have received an ROA Gold Standard again for our outstanding owners’ and trainers’ facilities here at Ascot, which include dining rooms overlooking the pre-parade ring in addition to a dedicated bar in the same area, along with a superb track facing facility. There are also two dedicated viewing areas.”
Another ROA Gold Standard winner is Newbury, recognising Newbury’s continued efforts to enhance the on-course experience for owners. The OLBG Owners Club is close to the pre-parade ring beside the owners and trainers entrance. It is exclusively reserved for owners, with a private terrace.
*Euro/Sterling rates Xe.com 07/03/2024
Assessing the approaches to diagnosing and treating proximal suspensory desmitis
Article by Connor Parsons DipWCF
Diagnosing proximal suspensory desmitis in the hind limb can be difficult. However, the modern diagnostic modalities available to the industry today makes it possible to isolate injuries, allowing both veterinarians and farriers to work together to achieve the best diagnosis and prognosis possible for the equine in question.
In this article, Connor Parsons reviews the anatomy and function of the suspensory ligament, causes and signs of proximal suspensory desmitis and whether there is an ideal procedure for diagnosing, treating and formulating a prognosis for the horse as part of his DipHE Farriery studies.
ANATOMY
The equine limb is complex yet effective. The suspensory ligament is made up of dense white fibrous connective tissue which suspends the fetlock and prevents hyperextension.
Originating at the proximal, plantar aspect of the third metatarsal/carpal attaching to two palmar depressions distal to the carpometacarpal and tarsometatarsal joints descending the channel formed by the 2nd, 3rd and 4th metatarsal/carpal, bifurcating two thirds of the way down the 3rd metatarsal/carpal, making a firm attachment to the palmar aspect of the proximal sesamoids, pulling the sesamoids proximally, then travelling dorsally and distally at an oblique angle to merge with the common digital extensor tendon. This forms a sling to support the fetlock joint. The ligament and its branches are strong but only slightly elastic (Devereux, 2006).
The suspensory ligament also forms a part of the hindlimb stay apparatus which is a system of ligaments, tendons and muscles that work together to allow the horse to stand and doze with minimal muscular effort. Also known as the fright and flight mechanism (Colles & Ware, 2020).
DAMAGE TO THE SUSPENSORY LIGAMENT
Suspensory ligament damage can affect horses of all breeds and ages. However, it is most common in competition horses. Proximal suspensory desmitis (PSD) is inflammation or damage of the main body at the origin of the ligament at the proximal end of the third metacarpal/metatarsal.
The suspensory ligament can be inflamed or there can be changes to the fibre pattern of the ligament. These cases will present with lack of performance, being worse on soft surfaces. In more severe cases a core lesion (hole) can be seen on an ultrasound scan, where a number of fibres have ruptured. This type of injury will have a more sudden onset of lameness (Dyson, 1994). Injury can be solely within the ligament, involve tearing of the fibres of the ligament or be connected to avulsion fractures at the origin, involving the proximal 3rd metacarpal/tarsal (Baxter, 2020). Complete rupture is possible, however, very rare. The prognosis for a complete rupture is not favourable (Dyson, 1994).
Although the suspensory ligament has a slight elasticity to its make-up, if it is stretched it tends to heal with a loss of elasticity making it susceptible to recurrent damage (Colles & Ware, 2020).
SIGNS OF PROXIMAL SUSPENSORY DESMITIS
Proximal suspensory desmitis is a difficult condition to diagnose as the hind limb is complex and many of the functioning structures work in unison. A horse suffering with inflammation or damage to the main body of its hind suspensory can present one of three ways. It may have a unilateral lameness, a bilateral lameness or just a general decrease in performance (Dyson,1994).
CAUSES OF PROXIMAL SUSPENSORY DESMITIS OF THE HINDLIMB
Although there has been extensive research into proximal suspensory desmitis, there is no primary cause in all cases.
Proximal suspensory desmitis is a common injury in both front and hind limbs of the equine athlete. Usually bilateral in the hind limb (Dyson, 2016). All types and breeds of horses are susceptible to this type of injury. Poor conformation is a contributing factor to proximal suspensory desmitis.
Conformational defects such as straight hocks, sloping pasterns and long-toe, low-heel conformations would be at higher risk to injury. These conformational defects will all apply unnecessary pressure to the suspensory ligament. Horses that have suffered with this condition will be predisposed to a repetitive strain injury of this ligament (Devereux, 2006). Overextension of the tarsus as a result of overextension of the fetlock has been linked to proximal lesions. The higher the severity of trauma, the higher the severity of ligamentous lesion. Working horses on deep, soft surfaces will increase the risk of this injury (Baxter, 2020).
The hindlimbs are more frequently affected with this condition than the forelimbs with a much lower success rate of the horse returning back to performance prior to rest (69% hind vs 80% forelimb) (Colles & Ware, 2020).
DISCUSSION
In a study of six horses, this is an extremely small cohort of horses to be able to state an average age a horse is likely to present with this condition. This study also shows that all of the horses studied were of varying fitness levels, therefore stating that this does not affect the likelihood of injuring the hind suspensory ligament. There was only one horse in this study that was unfit and overweight. The rest were all competition fit with good muscle mass, showing that fitness doesn’t necessarily decrease the risk of this injury happening. The case history of the six horses studied did not include which discipline or level the horse was working at. This would be an interesting factor to consider when looking at which horses would be more susceptible to proximal suspensory desmitis.
Each individual case was being looked after by different veterinarians, giving a clear picture of different approaches on how to diagnose and treat this condition. Although for the purpose of a study the varying opinions will make the comparison more difficult. All horses presented with a reduction in performance prior to veterinary contact. Only one horse was reported with a bilateral lameness behind. Flexion testing appeared to aggravate the lameness making it more prominent to see. Local analgesia has been shown to be effective in isolating the area to be investigated. Also, showing lameness on the other hind once the worse limb has been blocked out.
Using digital diagnostic modalities such as ultrasonography to diagnose this condition allows the veterinarian to study the changes in the fibre pattern of the suspensory ligament. This will allow the veterinarian to see the severity of damage caused and allow them to provide the best treatment plan possible. In this study only one horse had a lesion while the other five horses had thickening and slight changes to the fibre pattern. Horse 2 had lesions on both hind limbs however the veterinarian didn’t medicate, box rest was recommended. His prognosis was guarded.
Although radiographs of the feet don’t directly help with the diagnosis of proximal suspensory desmitis, they do allow the farrier to trim accordingly to restore the hoof back to correct hoof pastern axis and mediolateral foot balance. This will reduce lever arm forces thus reducing any unnecessary pressures on the plantar aspect of the limb.
Horses were radiographed for foot balance to aid with remedial trimming and shoeing. This will increase the equines prognosis allowing the farrier to have a clear picture of what is being dealt with. All of the horses that were radiographed presented with a negative sole plane and weak heels.
The question is whether this foot conformation is because the horses are wanting to apply more pressure to the caudal aspect of the hoof in the landing phase, reducing the movement of the metacarpophalangeal articulation. This is an attempt to reduce the loading forces applied to the suspensory ligament. However, it will also cause the heels to become weak. Or, if this conformational defect has caused the suspensory ligament to become inflamed or damaged, thus causing proximal suspensory desmitis.
Proximal suspensory desmitis can be secondary to other conditions such as hock conditions or sacroiliac problems which cause the horse to adopt a different gate. Therefore causing unnecessary loading on the suspensory ligament. It is important that the primary cause is diagnosed and treated when treating proximal suspensory desmitis. This is where scintigraphy can be a useful tool to get a clear picture of the cause involved in individual cases. Scintigraphy is an expensive diagnostic modality which carries significant health and safety risks, this must be taken into consideration when dealing with cases.
All horses studied were worse on a soft surface where it is harder for the horse to guard itself from soft tissue injuries. Horses that are worse on soft surfaces generally are suffering from soft tissue pain. However, nerve blocks will help the veterinarian pinpoint the structures involved when diagnosing lameness.
Although it is possible to have a unilateral lameness with proximal suspensory desmitis in the hind limb it is most common for the lameness to be bilateral. All of the horses in this study had a bilateral lameness, generally worse on one limb than the other. Although presenting prior to veterinary contact as lack of power or struggling to strike off on the correct canter lead.
When a veterinarian is deciding on a treatment plan, the horse is looked at carefully including its previous history as some treatments come with higher risks, although can be extremely effective for reducing inflammation. Shockwave treatment comes with minimal risks involved and is effective; however, many racing authorities require a mandatory 5 day Stand-Down period from racing following the administration of extra-corporeal shockwave therapy. Findings from this study show that the horses with the best prognosis of getting back to competitive work have undergone surgery. Understandably this is the last resort treatment as it is invasive and expensive for the client.
Only one horse from this study did not have any medical intervention and this horse had the least favourable prognosis. This would suggest that box rest alone is not generally enough if the horse is expected to get back to full athletic fitness. The most common veterinary treatment is steroidal injections into the area of interest and shockwave therapy with rest. However, the use of corticosteroids in horses in training often adopt a clear 14-day exclusion on the use of intra-articular (joint) injections before racing in line with different racing authority regulations.
Water based therapy can also be considered as part of the recovery process when bringing the horse back into work. It’s known to reduce limb oedema, stimulate nerves, and improve circulation, which speeds the healing process and provides pain relief. It also aids in joint stability, providing all-around support to the limbs.
Cold water therapy is typically prescribed when the goal is to reduce heat and inflammation. Applying cold water or ice reduces the amount of accumulating fluid to an injured area and can somewhat numb the area, causing a topical analgesic effect.
Underwater treadmills are often used for horses with tendon and ligament injuries to provide a gradual transition back into exercise and regain the range of motion. Swimming is also used to condition the horse without putting a load on the skeletal system. It is often used in the early stages of tendon and suspensory injuries due to no pressure being placed on the lower limb. Trainers who use swimming as part of their routine often find that, in addition to the cardiovascular workout, it also helps the horse relax and settle its mind.
This is not always successful and horses are then admitted for surgery. While the surgery for this condition is successful, there must be consideration taken into the fact that it is not legal to compete at certain levels once this surgery has taken place.
The study shows that the farriery treatment involved when dealing with this condition is varied, depending on which veterinarian the horse is being looked after by. However, the author has had positive results from many different shoeing styles. The main importance of trimming and shoeing for this condition has been shown to restore the best possible hoof pastern axis through trimming, supporting the entire limb and fitting a shoe with an early breakover. This will reduce the lever arm on the metacarpophalangeal articulation, thus minimising unnecessary pressure on the suspensory ligament.
CONCLUSION
Having such a small cohort of horses in a study makes it difficult to finish with a conclusive result. This small study however, has given a positive result in the diagnosis stages of dealing with this condition. At this stage nerve blocks are invaluable along with ultrasonography. In less obvious cases MRI is useful to gain a diagnosis and occasionally scintigraphy will be used to locate the problem. Radiography is a useful tool when dealing with PSD and checking the origin area for avulsion fractures.
This study has also shown that there is a link between a negative solar angle and proximal suspensory desmitis. However, this would need to be studied further and on a greater scale to determine why there is a link between this conformational defect and this condition.
It is paramount that correct foot balance is achieved by the farrier. To achieve this foot balance radiographs are required. This study has shown that there is no definitive way to shoe for this condition, however it has shown a positive result from an early breakover shoe, allowing the horse relieve pressures on the caudal aspect of its hoof. Horses that had the best prognosis underwent surgery, allowing them to get back to competitive fitness.
REFERENCES
Baxter, G. M., 2020. Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses. 7th Edition ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Colles, C. & Ware, R., 2020. The Principles of Farriery. 2nd edition ed. Marlborough: J.A.Allen.
Devereux, S., 2006. The Veterinary Care Of The Horse. 2nd Edition ed. London: J.A.Allen. Dyson, S., 1994. Proximal suspensory desmitis in the hindlimb: 42 cases. British Veterinary Journal, 150(3), pp. 279-291.
Dyson, S., 2016. American Association of Equine Practitioners. [Online] Available at: https://aaep.org/horsehealth/lowdown-high-suspensory-disease-proximal-Suspensory-desmitis [Accessed 19 11 2022].
Smith, M., 2022. Newmarket Equine Hospital. [Online] Available at: https://www.newmarketequinehospital.com/media/pm1beabc/hah349-Vet_susp_desmitis-final.pdf [Accessed 9 April 2023].
How trainers promote best welfare practice across Europe
"Mens sana in corpore sano" - is a well known Italian phrase which translates to “a healthy mind in a healthy body" is a fundamental principle for every athlete, and racehorses are true athletes of the sporting arena. Just like their human counterparts, the performance of a racehorse depends not only on their physical condition but also on their mental well-being. The issue of animal welfare in horse racing is not just a matter of ethics or sensitivity, but the foundation upon which the integrity of the entire sport rests.
The concept of equine welfare extends beyond the mere absence of disease or injury. It concerns the quality of life of the horses, including their daily treatment, living conditions, access to open spaces, appropriate nutrition, and the ability to express natural behaviours. Moreover, it includes ethical training practices that respect the animal's physical limits, avoiding bad training and stress.
In the context of racing, equine welfare is scrutinised not only by industry insiders but also by the public and animal rights activists. Our focus in this section of the article is on the evolution of welfare practices in the leading countries of European horse racing: Great Britain, France, Ireland and Germany.
The goal is to understand not only the current state in terms of equine welfare but also to identify trends and areas for improvement, reflecting on the importance of an ethical and responsible approach to these extraordinary athletes.
GREAT BRITAIN - HORSE WELFARE BOARD (BHA)
The Horse Welfare Board, inclusive of representatives from the BHA, racecourses, and horsemen, unveiled a five-year welfare plan in 2020 to elevate horse welfare in British racing. This plan is dedicated to ensuring a "life well-lived" for racehorses, with a focus on traceability, safety, well-being, alongside initiating the industry's most extensive data project. It targets enhancing health care practices, ensuring lifelong responsibility, reducing injuries, and fostering public trust through transparency and ethical practices. Additionally, the strategy commits to developing a Code of Ethics and advancing veterinary care and injury prevention. Importantly, the implementation team is collaborating with the industry on 26 strategic projects, backed by funding from the Horserace Betting Levy Board (HBLB) since 2019 and a recent £3 million grant from the Racing Foundation, to realise these goals.
In the array of projects undertaken by the Welfare Board to bolster safety and uphold equine welfare standards, there are a few that stand out as being exceptionally cutting-edge, such as the: Thoroughbred Census, Equine Vision Project, Data Partnership.
Thoroughbred Census
The project aims to enhance the traceability of retired thoroughbreds, enabling better support for owners and the adaptation of welfare initiatives by British Racing and Retraining of Racehorses (RoR). It involves a six-month census, in partnership with RoR, collecting detailed information on retired racehorses to improve aftercare and respond quickly to equine disease outbreaks.
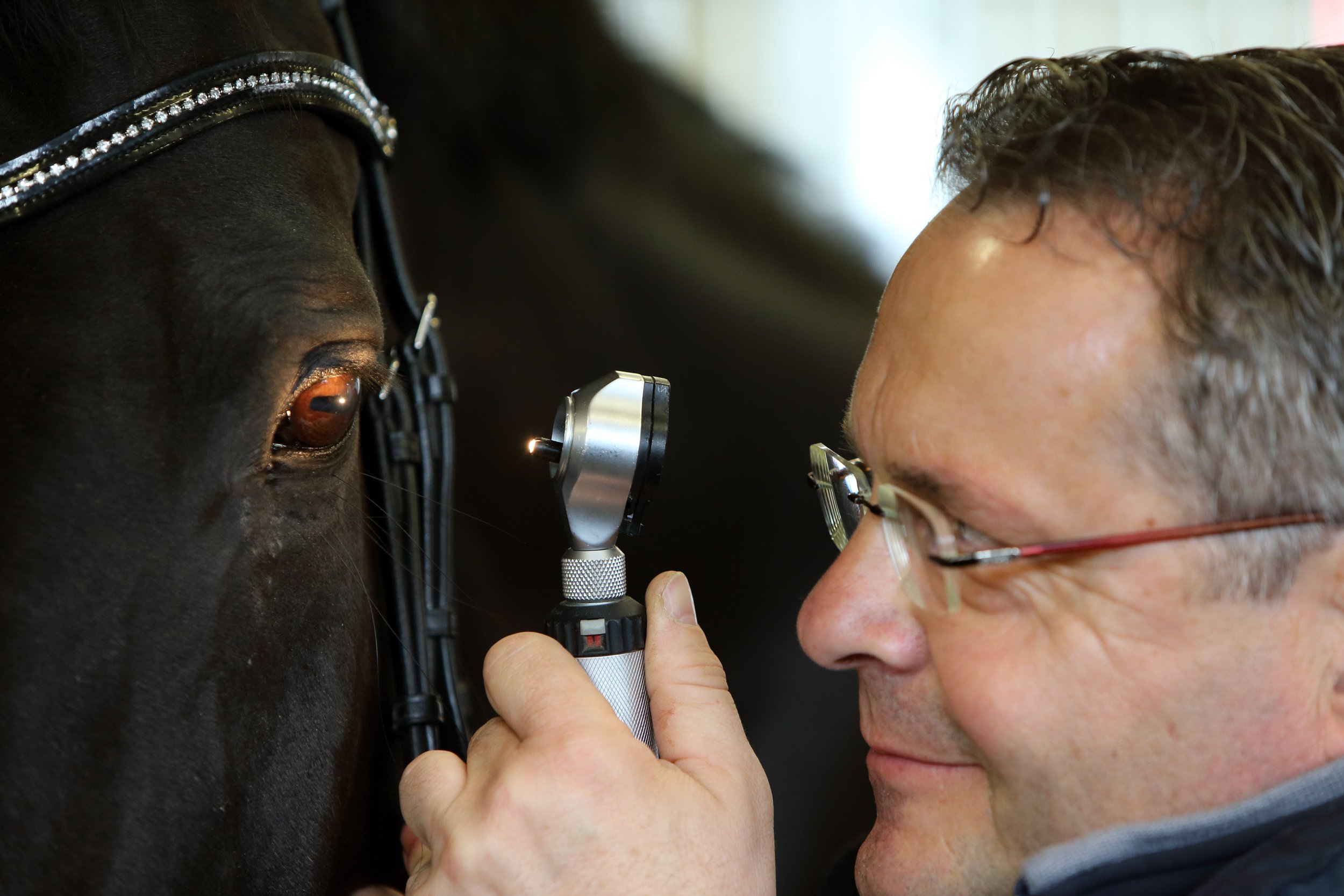
Equine Vision Project
“We try to look through the horses’ eyes” - Mike Etherington-Simth
In 2017, the BHA and Racing Foundation funded research into equine vision to enhance hurdle and fence safety. Horses, seeing fewer colours than humans, struggle to distinguish between hues like red, orange, and green. The study assessed the visibility of orange markers on racecourse obstacles against alternative colours, considering how weather conditions affect perception.
Data Partnership
This project seeks to enhance racehorse safety and welfare by analysing risks and factors leading to injuries and fatalities on racecourses and during training in Great Britain. It utilises extensive data on races and training practices, employing advanced statistical models to identify risk factors. The initiative, in collaboration with industry stakeholders, aims to provide evidence that informs decisions and measures to minimise risks, directly contributing to the betterment of racehorse welfare.
FRANCE - FRANCE GALOP
France Galop is deeply committed to promoting high standards of horse welfare, aligning with the 8 principles outlined in the "Charte Pour le Bien-Être Équin". This commitment is evidenced through various initiatives, including the inspection of facilities by France Galop veterinarians for new trainers who have acquired their flat racing licences. These checks, part of the certification process, aim to ensure that the infrastructure is suitable for housing horses. In 2021, a total of 410 training centres were inspected by the veterinarians of the Fédération Nationale des Courses Hippiques. The vets also check for prescribed medications and substances on site, adhering to a “zero tolerance” policy.
IRELAND - THOROUGHBRED WELFARE COUNCIL (HRI)
“They have horse welfare right at the forefront of everything they do and I would say they are doing a very good job” Joseph O’Brien
In 2021, the Irish Thoroughbred Welfare Council was assembled to act as an advisor to the Board of HRI and assist in devising policies on welfare matters. HRI gathered 60 industry participants in a co-design project to create a manual called “Our Industry, Our Standards,” aiming to establish a system where welfare standards are verified and measured. These standards include good feeding, good housing, good health and good well-being. Additionally, the Thoroughbred Council is collaborating with IHRB, Weatherby’s, and the Department of Agriculture to create a traceability system that will ensure every horse always has a known link to the responsible person.
Best-Turned-Out League
To promote and encourage the implementation of good animal care and welfare practices, HRI has introduced the “Best-Turned-Out League,” which aggregates these prizes from across the country into a league table with substantial prizes from six different categories, highlighting the impressive standards maintained across the industry. The primary caregivers, who are often lifelong careerists, are our industry employees.
GERMANY - DEUTSCHER GALOPP
Deutscher Galopp, has notably advanced equine welfare within racing in recent years. Not only has it raised the quality standards of horse care within stables, monitored through surprise veterinary checks, but it has also started to develop an intriguing project that monitors the physical development of racehorses.
Physical Maturity Check for 2-Year-Olds Before Training
Deutscher Galopp has implemented regulations requiring that every horse must pass specific veterinary checks. These checks are designed to ascertain sufficient physical maturity before a horse enters into training. A second assessment is conducted shortly before the horse can start in a race, to confirm its physical fitness for competition.
For this section of the article, we canvassed opinion from a selection of industry professionals for their perspectives on issues related to equine welfare.
Q: What role does horse welfare play in your training practices and what specific measures do you implement to safeguard the physical and mental well-being of the horses?
"The welfare of my horses is central to me; it is the most crucial element for the success of my business” asserts Seamus Mullins, a sentiment unanimously echoed by all interviewees who have long regarded animal welfare as a key factor from the outset of their careers in the racing sector. When delving into the practicalities of ensuring each horse's welfare is honoured, Joseph O'Brien highlights the significance of tailoring care to individual needs. "It's crucial not to generalise, as what satisfies one horse might not suit another," he explains. This underlines the necessity of adapting training and rest schedules to cater to their unique preferences and inclinations, guaranteeing their well-being and happiness.
Luca Cumani, who since retiring from training has remained active within the industry, including a term as a director of the BHA and as a pre-eminent breeder emphasises the importance of observation to understand each horse's psychological capabilities and preferences.
Seamus Mullins discusses the regular turnout of horses in individual paddocks while ensuring they are always in association with other horses. The stables are varied to suit different preferences, emphasising the need for regular updates to training methods and facilities to keep the horses in the best condition possible.
Peter Schiergen, Nastasja Volz-Degel, and Alessandro Botti all share this commitment to horse welfare, implementing daily routines, wellness programs, and training methods tailored to the individual needs and physical aptitudes of each horse. They focus on creating a comfortable environment for the horses, using modern facilities such as solariums, water treadmills, and magnetic blankets for massage, highlighting a collective effort to maintain high welfare standards in the racing industry.
Q: How do you educate your staff or team members about the importance of animal welfare?
"I always said to the riders: the relationship with the horse you ride should be viewed as a partnership, akin to that with your wife or daughter, and should be treated with the same respect and care" Cumani explains with a touch of warmth. The stable staff plays a pivotal role in the implementation of animal welfare, which is why, as the interviewees emphasise, it's crucial to focus on their education and enhance their knowledge to the fullest. "We want our staff to become better horsemen," states Schiergen.
Beyond the training provided internally within their stables, some trainers, like Alessandro Botti, with the support of AFASEC (the Association de Formation et d'Action Sociale des Ecuries de Courses - which roughly translates to Association for Training and Social Action of Racing Stables), have decided to offer courses in equine ethology led by experts brought in from outside. This initiative not only sparked significant interest among their staff but also led to an improved approach to working with horses.
Q: The risk of injuries is an inherent component in all sports, including horse racing. What is your opinion on this statement, and what specific actions do you take to minimise the risks?
"Risks are everywhere, especially in competitive activities, whether involving humans or animals, there's a significant element of risk," are the words of Cumani, which also resonated with others we interviewed.
The consensus is that, unfortunately, injuries are inevitable despite efforts to minimise them through practices and care that respect the physical state of the horse. "We try to minimise the risks by checking every horse before a race and during training, we never push the limit of a horse if he isn't ready enough” underlines Schiergen, “we have to get the message across that we are doing all our best to minimise the risks at all accounts”, adds Mullins.
Q: What role do you believe transparency plays in communicating to the public the importance placed on the welfare of racing horses in daily activities, and how do you ensure that this information is effectively shared with the general public?
“There are fewer and fewer people growing up with animals and in farming, and as a result, this is why we need to show through platforms what we do because things we take for granted, someone who has never been to a racing yard may not realise what happens,” says O'Brien. He adds, “It is important to give people access to behind the scenes, and this is why we try to be quite active on social media and encourage people to come to our yard, so that they realise the amount of passion that staff puts in their daily work.”
Public involvement, to make them part of the daily practices of stable life, is crucial, as our interviewees from various parts of Europe maintain. Thanks to numerous activities promoted by the racing authorities of the interviewees' respective countries, Open Day events allow the public to participate in stable life.
Many trainers, like Seamus Mullins, have noticed a significant increase in participation in recent years, “Ten years ago, participation in the UK was about 100, while in 2023 it was more than 500. Moreover, people who participate often express surprise at how well race horses are treated.” However, all the trainers, like Alessandro Botti affirms, it is necessary to increase content on social media, to give the possibility to everyone, every day and in every part of the world, to participate in the daily life of horses in various stables.
Q: What do you think will be the future trends in horse welfare in Racing in the coming years?
All the trainers interviewed are convinced that the standards of equine welfare in racing are already very high. However, they unanimously believe that social pressure from activists will continue to grow, making it necessary to increase transparency and public engagement. Joseph O'Brien emphasised the importance of education: "What I think really has to be put to the forefront is educating people who are not involved in racing; this will be the biggest challenge."
Given the insights on how Racing Authorities operate in terms of Horse Welfare and the daily interest and commitment of trainers, the trend seems to be very positive and reflects very high standards. It is essential, however, that countries collaborate with each other to inspire one another, further improving equine welfare practices, as Helena Flynn, the British Horse Welfare Board Programme Director emphasises "We love these animals and do our best to ensure they are protected, and thus it would be beneficial if the results of various state projects could contribute to inspiring everyone internationally." Therefore, the issue of equine welfare in racing is a complex mosaic of care, respect, and dedication towards the thoroughbred racehorse. Recognising and acting for their welfare is not just a moral duty but the foundation on which to build a fair, sustainable, and most importantly, animal-respectful racing industry.
There's more to it than meets the eye!
Article by Adam Jackson MRCVS
The horse’s eyesight has evolved to scan its environment rather than picking up sharp details, in order to survive from predators. As a prey animal, the horse’s eyes are eight times larger than a human’s eye; however, this makes them more vulnerable to injury and disease that may be catastrophic. Horses develop many of the same eye problems as humans such as glaucoma, corneal ulcers, cataracts and other issues.
The working of the eye
Vision is provided by light entering the eye, which is made into an image by the brain through various complex biomechanical and physical processes.
As light enters the eye, it is targeted to the retina by the cornea and the lens bending the light. This light reaches the sensory tissue at the back of the eye. In fact, the retina or nervous tunic is made of cells that are extensions of the brain coming off the optic nerve. The retina consists of 2 types of photoreceptors called rods and cones. The rod cells are more light-sensitive, thus providing night vision, whereas the cones are less light sensitive but provide visual acuity and the ability to see colour. The optic disc in the retina does not contain photoreceptors and is the location the optic nerve leaves the eye to transmit the visual information to the visual cortex of the brain.
Visual field of the horse
Because the horse’s eyes are positioned on the side of the head, the range of vision is roughly 350 degrees, thus, allowing the horse to spot potential predators. Due to the positioning of the eyes, the horse has two blind spots that include in front of the face and behind its head extending over its back and behind the tail.
The horse has both binocular and monocular vision. Monocular vision means vision in one eye only and binocular vision means seeing with two eyes. 65 degrees of the 350 degree vision consists of binocular vision while the remaining 285 degrees is monocular vision. As a result, the horse has a smaller field of depth perception compared to a human. The horse must raise or lower its head in order to increase its range of binocular vision. By introducing a bit and making the horse hold its head perpendicular to the ground, the binocular vision becomes less focused on distant objects and more focused on what is immediately in front of the horse. Show jumpers and jump jockeys allow the horse to raise its head a few strides before a jump so that the horse can properly assess the jumps to allow appropriate take-off.
Sensitivity to light
Horses’ eyes have evolved to allow them to have good vision in dim light and due to this evolution they have better vision on slightly cloudy days compared to sunny, bright days. There are two particular structures that allow them to have superior night vision, which include a high proportion of rods to cones (20:1) and the presence of the tapetum lucid.
The horse’s large pupils allow a large amount of light to enter and the size of the retina allows a high number of cells to be involved in the capturing of light. In addition to the rods and cones, the horse's tapetum lucidum is a reflective structure in the back of the eye that bounces light back to the photoreceptors for a second time, thus further increasing the ability to capture more light. Ultimately, this structure allows greater night vision.
Interestingly, horses have also evolved structures to protect their eyes from photic damage during bright sunny days. The pupil has the ability to significantly constrict in order to reduce the amount of light entering the eye. In addition, there is a structure referred to as the corpora nigra, which is a bulbous structure extending from the iris into the space of the pupil that acts as a shade.
Colour Vision
Horses have dichromatic vision; therefore, they are not colour blind but they have a smaller spectrum than humans typically do. Horse’s dichromatic vision means they see in the green-blue spectrum and the ocular variations based upon them. They cannot distinguish red and are often thought to have a red-green colour blindness. The horse’s colour vision must be taken into account when designing obstacles for horses to jump.
Eyelids
There are three layers to the eyelids that include a thin layer of skin covered in hair, a layer of muscles that allow the opening and closing of the eyelid and the palpebral conjunctiva, which lies against the eyeball. The horse also has a third eyelid, also known as the nictitating membrane which has the function of protecting the cornea.
Non-pigmented third eyelids are more susceptible both to solar-induced inflammation and to squamous cell carcinoma. Therefore, careful scrutiny of this structure is important. Prominence of the third eyelid may be a result of inflammation caused by solar-induced inflammation or conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva). Inflammation and neoplasia should be differentiated on the basis of clinical appearance. For example, squamous cell carcinoma has a plaque-like appearance and erosion. Conjunctivitis is the inflammation with thickening and reddening of the transparent membrane that lines the eyelid and eyeball. Any suspected tumour should be excised and undergo histopathology to determine if it is indeed neoplasia or a type of inflammation. Other neoplasia that may occur in the eyelids are melanomas or periocular sarcoids.
Entropion is the inversion of the eyelid margin and lashes. Often seen in foals as a consequence of either anatomical imperfection or of dehydration and debility, it is the inward rotation of the eyelid that leads to the rubbing of hair in the cornea leading to keratitis. Later onset entropic is usually a consequence of a traumatic injury and can result if primary repair of an eyelid laceration has not been performed.
Trauma to the eyelids may result in bruising or a laceration. If bruising has occurred, a warm compress may be helpful if the horse will tolerate it. If a laceration has occurred it should always be repaired.
Lacrimal system
The horse has a pair of nasolacrimal ducts that carry lacrimal secretions, commonly known as tears, from the eye to the nasal cavity.
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca is a deficiency in the acqueous portion of the tear film and is relatively rare. If it occurs, it is a result of damage to the facial nerves or direct damage to the lacrimal gland or duct. With the lack of tears the cornea appears dull and lacklustre and may lead to corneal ulceration. It is often associated with a mucopurulent eye discharge as well as pain and inflammation. This condition can be managed with regular cleaning and the application of a tear replacement solution.
Acquired stenosis/occlusion of the lacrimal drainage system may be a consequence of infectious, trauma, neoplastic or inflammatory disease within the drainage system or external to it. It is often presented with epiphora (tear overflow) or a mucopurulent discharge if infection is involved. Following treatment of the underlying cause, the goal is to re-establish the drainage system with flushing of the duct with saline solution, or a combination of steroid, antibiotic (if required) and saline solution.
Conjunctiva/Sclera
The sclera is the white of the eye which is the relatively tough outer layer of the eye and is covered by a thin mucous membrane, referred to as the conjunctiva, and runs from the edge of the cornea and covers the inside of the eyelid.
Conjunctivitis is the inflammation and swelling of the conjunctiva and includes a primary conjunctivitis or a secondary conjunctivitis. Primary conjunctivitis is inflammation caused directly by irritants, chemicals, toxins and bacteria. However, conjunctivitis may be secondary to another ocular disease such as disorders of the lacrimal system, eyelid problems, and keratitis. In addition, conjunctivitis may be a non-specific symptom of other systemic diseases such as a respiratory viral infection. Conjunctivitis presents with a reddened inflamed conjunctiva with mould, purulent, serous or a combination of these discharges. The horse will have discomfort of the eye with this ailment.
Conjunctival foreign bodies are often acute and unilateral and caused by organic material resulting in excessive tearing, inflammation of the conjunctiva and ocular discomfort.
Conjunctival neoplasia is most often a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) as this tumour usually affects areas of epithelial transition such as the mucocutaneous junction of the eyelids. The extent and appearance of the lesion is variable but SCC should always be considered especially in those horses lacking pigment in those areas. The symptoms range from mild ocular discomfort with discharge to plaque-like and cauliflower-like masses without ulceration.
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil and anterior chamber. It is a domed-shaped structure that acts as the eye’s windshield protecting the eye from insult such as an infection. Along with the tear film, it provides a proper anterior refractive surface for the eye, in fact, it contributes two-thirds of the refractive power of the eye. Congenital problems of clinical significance are rare in horses but acquired corneal problems as a result of trauma are common in horses.
Traumatic keratitis due to lacerations or penetrating injuries are common and in most cases involve full thickness penetration, acqueous loss and iris prolapse. This condition presents with sudden and severe pain accompanied with excess tearing and blepharospasm (involuntary tight closure of the eyelids). The extent of the damage to the cornea can be determined by the use of fluorescein dye. If the wound is not repaired quickly then the iris may become incarcerated and the restoration of the normal eye anatomy is difficult.
Abrasions to the surface of the cornea is a common condition seen by equine practitioners. Some simple scratches heal quickly while others may become more complex, involving fungal or bacterial infections resulting in a protracted recovery.
Corneal ulcers are a defect in the surface of the epithelium of the cornea that involves the underlying stroma. They are often described as sores on the cornea. It is important that they are diagnosed and treated promptly as there is potential that the horse’s vision may be affected. The clinical symptoms are often ocular discomfort with excessive tearing, squinting or blepharospasms. Discolouration and swelling of the cornea and the eventual development of blood vessels around the ulcer and an irregularity of the cornea. The depth of the ulcer must be established and it may range from superficial to deep.
Liquefactive stromal necrosis (melting ulcers) are not an uncommon condition in the horse and may present acutely or as a progression from a corneal ulcer. It should be deemed as an emergency because corneal perforation may result. This disease may be accompanied by uveitis.
Corneal foreign bodies are usually organic material and present with blepharospasm, excess tearing and pain. Various illuminations, magnifications as ophthalmic stains may be used to identify it and aid in removal.
Bacterial keratitis is often seen after a corneal injury especially if an ulcer is present. The horse will demonstrate acute eye pain with serous discharge that quickly becomes mucopurulent or purulent. The clinical appearance is not usually diagnostic and cultures and scrapings should be taken from the edge of the ulcer. This procedure ensures the correct selection of treatment and pain relief.
Mycotic keratitis is uncommon in the UK but with the changing climate it may become more prominent. This type of keratitis is a result of fungal growth so tends to occur in climates supportive of this type of growth. Diagnosis is based on the history, clinical appearance and the demonstration of fungal hyphae and positive fungal culture. This disease may be a consequence of inappropriate drug therapy (such as corticosteroids) or from previous corneal trauma. Following the identification of the fungus, topical treatments can be used but may take weeks to months.
Uveal Tract
The uveal tract consists of three parts that include; The choroid which is the tissue layer filled with blood vessels; The ciliary body that is the ring of tissue containing muscles that change the shape of the lens as well as producing the clear fluid that fills the space between the cornea and the iris; The iris which is the coloured part of the eye.
Persistent pupillary membranes are vascular arcades and developing tissue of the eye that fail to atrophy as the eye matures. These are very common in horses and usually have no consequence and no treatment is needed.
Cysts may arise in various parts of the uveal tract and are not uncommon in the horse. Irrespective of their origin, they may vary between pigmented to unpigmented and are smooth, round and do not invade neighbouring tissue. No treatment is required except on rare occasions when they interfere with the horse’s vision.
Neoplasia of the uvea is not common but may arise and are often melanomas that are locally invasive but without cellular malignancy.
Trauma of the iris may result from direct trauma, or a secondary consequence of corneal perforation or a whiplash injury. Any uveitis that is caused by trauma can be treated medically. If there is an iris prolapse, then the iris is placed back into the anterior chamber provided they are not contaminated. Any foreign bodies must be removed and any hyphaema (bleeding in the anterior chamber between the cornea and iris) is usually left to be resorbed naturally.
Uveitis is inflammation of the uveal tract and can cause eye pain and alterations in vision. There are many causes of uveitis that include trauma, lens-associated uveitis, general viral infections (such as equine viral arteritis) and bacterial disease (such as Rhodococcus equi in foals). However, many situations of uveitis are an immune-mediated uveitis often referred to as equine recurrent uveitis (also known as moon blindness). Uveitis may present as an acute or a chronic condition.
This disease can be treated medically often with the use of a sub-palpebral or nasolacrimal lavage system. In addition, the patient should be placed in a quiet fly-free and dust-free environment.
Lens
The lens is a clear curved disk that sits behind the iris and in front of the vitreous of the eye, which bends light as it enters the eye to develop an image. The horse’s lens is large and minor opacities associated with embryonic remnants are common.
Cataracts are the most common lens abnormality to be encountered causing an opacity of the lens. Cataracts may be acquired from trauma or post-inflammation situations. However, cataracts may be congenital commonly seen in Arab and thoroughbred foals. These opacities can be classified in various ways:
Age of onset – juvenile, senile or congenital
Cause - post inflammation (uveitis) or trauma
Location – cortical, capsular, nuclear, polar, equatorial
Stage of development – immature, mature, hypermature
Most cataracts cause no obvious visual deficits unless they are dense and obstruct the visual axis. in which cataract surgery may be considered.
Acqueous drainage
The acqueous humor is a transparent water-like fluid similar to blood plasma but containing low protein levels. It is secreted from the ciliary body (a supporting structure of the lens) and fills both the anterior and posterior chamber of the eye.
Glaucoma is a pathological elevation of the intraocular pressure resulting in the optic nerve becoming damaged . Primary glaucoma in horses is exceptionally rare while secondary glaucoma is uncommon but may occur after anterior segmental inflammation. Often there is little to no pain but an enlarged globe and raised intraocular pressure with the lack of pupillary light reflex may be seen. Treatment may be attempted if the vision is present with various medications to reduce the intraocular pressure. If the horse is blind it may be left without treatment.
Conclusion
Good eye care is vital as the horse relies on its site to receive a great deal of information on its surrounding environment. Even with the horse holding its head forward it has remarkable peripheral vision but the horse’s vision is a little blurrier and less colourful compared to humans. In addition, both the strengths and weaknesses of the visual abilities of the horse must be seriously considered when looking at various techniques for training.
Point-to-Point racing and its role in developing jumpers
Article by Daragh Ó Conchúir
There has always been something special about a well organised point-to-point.
It is social, in the truest sense. A communal gathering of like-minded people, with a love of rural pursuits and lifestyle.
It is racing at its purest too, founded on the genesis of steeplechasing in the Irish county of Cork in 1752. That was when Edmund Blake and Cornelius O’Callaghan chose to resolve which of them possessed the best steed by racing the four and a half miles from Buttevant Church to its Doneraile counterpart. Steeple to steeple, taking whatever route they saw fit and clearing whatever obstacle was in the way. Naturally, the money was down to increase the stakes.
Good horses often emerged from this sphere, with Tom Costello a legendary source of Gold Cup winners, but that wasn’t the raison d’être. Pointing was a leisurely pursuit. There was no competition for National Hunt trainers when it came to the acquisition of stores or younger jumping stock.
The landscape began to change with the introduction of an autumn point-to-point season by Irish authorities to make up for the fixtures lost by the outbreak of Foot And Mouth in 2001 but the last decade has seen an increasing commercialism that has altered the face not just of point-to-pointing, but of racing under Rules.
This has only accelerated by the reduction in availability of the good Flat handicappers, now flowing to jurisdictions such as Hong Kong and Australia with mammoth prize money justifying the eye-watering sums that National Hunt people could not justify.
There is always a risk with buying thoroughbreds but for end users, that is alleviated somewhat when there is form with proven depth. Of course there is a premium on that.
The results speak for themselves when it comes to the question of whether or not the sector is developing jumpers to a requisite level. Just look at the recently concluded Cheltenham Festival, where of the 27 races, nine were won by graduates of the point-to-point circuit – eight from Ireland and one from Britain. That latter success was in the point-to-point feature, the Foxhunter Chase, as Sine Nomine repelled the strong raiding challenge for Fiona Needham, her father Robin Tate and jockey John Dawson.
What is notable though is the high level of achievement. Of the other eight graduates from the point scene to score, five did so in Grade 1s: Slade Steel (Supreme Novices’ Hurdle), Ballyburn (Gallagher Novices’ Hurdle), Fact To File (Brown Advisory Novices’ Chase), Jasmin De Vaux (Champion Bumper) and Stellar Story (Albert Bartlett Novices’ Hurdle). There was a clean sweep of placings by ex-pointers in the Brown Advisory and Albert Bartlett.
This is not anything like a one-off, of course. When Colin McKeever’s Loughanmore winner, Ballyburn, sauntered to a 13-length triumph in the Gallagher, he was the fourth alumnus of the sphere to land the spoils in that particular Grade 1 in five seasons. Slade Steel was the fourth to bag the Supreme in the same period. That’s Constitution Hill, Shishkin, Envoi Allen and Bob Olinger we’re talking about between the two.
There is depth in terms of the handlers producing these talents also. Donnchadh Doyle, whose brothers Seán and Cormac are established providers with the likes of Monkfish, Holywell and Bravemansgame included on the roll of honour, was the only provider to have multiple winners, having guided Fact To File and Stellar Story to successes at Bellharbour and Castlelands.
Apart from the aforementioned McKeever, Pierce Power, Colin Bowe, Euguene O’Sullivan, Stuart Crawford and Warren Ewing had the satisfaction of seeing former charges deliver on the biggest stage.
It is significant too that the octet won their maidens at eight different venues, illustrating the calibre of the tracks.
The growth in the sector and the unarguable evidence that this system is working is seen in figures provided by Irish point-to-point website, p2p.ie. If we take the past 15 completed jumps season from 2008/09 to 2022/2023, we see a progression from when graduates won 725 track races, eight of which were at Grade 1 level, to a stunning 1570 winners and 27 elite successes. The total number of black-type winners increases from 39 to 98.
Since 2015/16, the number of winners has only dropped below 1400 once, and that was in the Covid-impacted 2019/2020 term.
While the number of winners has largely been consistent – 1718 in 2020/21 was a high-water mark – the quality continues on an upward climb, with 27 Grade 1s secured by Irish point products in two of the last three seasons with completed figures.
And that is why the prices continue to rise. The record for the most expensive point-to-pointer was set in November 2020, when JP McManus shelled out £570,000 for Jonbon at the Goffs UK Sale in Yorton after the full-brother to multiple Grade 1 winner Douvan had cantered to a 15-length triumph for Ellmarie Holden, Paul Holden and Michael Shefflin.
At the Punchestown Festival Sale 12 months ago, it was a mare that attracted the biggest bonanza, as Mags O’Toole spent €500,000 on behalf of Brian Acheson’s Robcour ownership banner for Qualimita, who had dotted up in a Fairyhouse maiden by 30 lengths for Walter Connors and Bowe.
A highest price for a British filly pointer was set last May, when Saunton Surf was sold in May for £175,000 by Brad Gibbs to Warren Greatrex at the Goffs Spring Sale in Doncaster.
That was matched last December, as Just A Rose was bought by Tom Malone, for British champion trainer Paul Nicholls, from Tom Ellis and breeders Sarah and Nigel Faulks. The same buying combination snapped up Will Biddick’s facile Badbury Rings victor, No Drama This End for £160,000 at the Cheltenham Festival Sale in March.
Meanwhile, Eddie O’Leary signed a chit for €265,000 at the Tattersalls Ireland Derby Sale last June for a store that was heading in Gordon Elliott’s direction and in all, 33 horses sold for €100,000 or more at that auction, making it the third best result in Derby Sale history.
And remember, a Camelot half-brother to Altior realised a staggering €155,000 at the Tattersalls National Hunt Sale in November 2019, purchased by former Republic of Ireland soccer international Kevin Doyle from Coole House Farm on behalf of Paddy Behan Jnr. It was the highest price paid for a foal at the sale for 12 years and the third highest in its history.
While the most recent auctions might finally be suggesting a slight correction, Irish producer and trainer, Liz Doyle wasn’t far wrong when she described the point-to-point sector as ‘pandemic and recession-proof’.
Jerry McGrath is relatively new to the scene as a bloodstock agent, a role he took up upon his injury-enforced retirement at the beginning of 2022. But the Cork native had long been tasked by his boss Nicky Henderson with keeping an eye on the Irish point-to-point circuit during his time at Seven Barrows, during which he rode two Cheltenham Festival winners.
Love Envoi provided him with his first Cheltenham triumph as a buyer. Jango Baie is a Grade 1-winning novice hurdler this year and Jingko Blue is another youngster acquired from racing through the flags that has made a good transition to the track.
“It’s been well documented; it’s harder to get hold of these highly rated, staying flat horses now because there’s such a market for them abroad,” says McGrath. “Because that has happened it has narrowed where you get your jump horses from and I think that’s why maybe the point-to-point thing has come so strong.
“Of course, it has been massively influenced by the point-to-point handlers themselves. I have the utmost respect for those lads. They go out there, they put their money on the line, they invest in horses that they like at the store sales. We’ve seen in the last three or four years, they’ve been outbidding plenty of trainers.
“When you look at it like that, it sounds a bit bonkers that the point-to-point men are outbidding the end users, bearing in mind they have to prove the horse’s ability, with the hope that the end user comes back and buys it as a winning point-to-pointer.”
This is why not every trainer is a fan, as they are now priced out of the market at both potential entry points –sales for stores and pointers. But in an open market, those willing to risk the most, make the most. The vital element to it all is the emergence of talented animals on a consistent basis.
The handlers are clearly discerning in their sourcing too. While there are fashionable stallions, the point graduates that delivered at Cheltenham came from a variety of sires: Flemensfirth (Ballyburn), Shantou (Stellar Story), Poliglote (Fact To File), Telescope (Slade Steel) and Tirwanako (Jasmin De Vaux) were the Grade 1 performers, while Gamut (Corbetts Cross), Milan (Better Days Ahead) and Saint Des Saints, whose three winners at the festival included Sine Nomine, completed the crop.
This is why McGrath’s priority is the model rather than the page, although pedigree has to be taken into account.
“You can have a potential superstar but if he’s a terrible mover, his longevity is going to be very short. It’s a bit like cheap speed, the two-year-old that’s going out very early. You might win a two-year-old maiden at the start of the year but will you be there at the end of the season competing in group races? Probably not. So you do have to have an athletic horse.
“Temperament definitely comes into it but at the same time, these are young horses, and their temperament can be managed, especially if they go into the right hands. If you’ve got a hot and buzzy horse, it doesn’t mean they’ll be hot and buzzy in two years’ time.
“Athleticism and movement is the big thing for me. And you have to have a bit of pedigree. If they’re not bred to be a good racehorse, why would you be surprised they’re not a good racehorse?”
Pat Doyle is one of the enduring characters of the Irish point-to-point sector, having been among the pioneers for using it to sell four and five-year-olds with form before the likes of the Wexford crew of Bowe, Denis Murphy and the unrelated Doyle brothers raised the bar. He kept up with the evolution though and had at least ten graduates running at Cheltenham. The majority of them were trained by Mullins, which is no mean imprimatur.
It is 50 years this year since Doyle broke future dual Champion Hurdle winner Monksfield as a two-year-old. Later on, he pre-trained Minnehoma for his good friend Roddy O’Byrne to sell. Minnehoma followed Cheltenham success with a famous Grand National victory in 1994.
Bob Olinger, Appreciate It, First Lieutenant, Shattered Love, Colreevy, Readin Tommy Wrong, Bacardys, Commander Of Fleet, Champ Kiely and Brindisi Breeze are just some of the other Grade 1 and Cheltenham winners to have emerged from his academy.
The very latest off the production line, Ballycahane winner In The Age, sold at the Cheltenham Festival Sale for £100,000 to Ryan Mahon for the leading British trainer at the festival, Dan Skelton. The headline act at this boutique offering was the purchase of Echoing Silence by Peter Molony from Sam Curling and Correna Bowe for £410,000, to be trained by Henry de Bromhead.
This sale has produced the last two Gold Cup runners-up, Bravemansgame and Gerri Colombe, while three of its graduates from the 2023 sale participated in the Champion Bumper this March, including the runner-up Romeo Coolio and third-placed Jalon D’Oudairies.
“The biggest trick is selling them to good trainers,” Doyle relates. “I’ve been very, very lucky with Willie Mullins, Henry de Bromhead and fellas like that buying horses off me that turned out to be successful. I’m an open market for anyone to buy horses off but Willie Mullins (had) seven or eight horses I sold him running at Cheltenham.”
For a long time, Doyle and his fellow Irish handlers had this niche to themselves. The likes of Sophie and Tom Lacey were trading but the point-to-point arena remained Corinthian in spirit and action.
The old traditions are gradually being cast off with the likes of Gold Cup runner-up Santini (Ed and Polly Walker) and Ahoy Senor (Melanie and Philip Rowley) having emerged and with handlers of the calibre of Tom Ellis and Gina Andrews, Bradley Gibbs, Fran and Charlie Poste, Josh Newman and Kayley Woollacott and Will Biddick in the vanguard of those guiding young talent.
Tom Lacey is now training under Rules, but having produced dual Champion Chase winner Energumene, Sebastapol (this pair won two divisions of the same open maiden at Larkhill in January 2018), Blackbow, Kimberlite Candy and the most expensive British pointer ever Interconnected (sold for £220,000 after winning at Larkhill in a month after Energumene and Sebastapol), remains an ardent advocate of the division on his native shore.
“I think it’s irreplaceable. I don’t believe there’s any better grounding for jumps horses than point-to-points,” Lacey states definitively.
“Ten years ago you could send a well-educated horse 80 per cent fit to an English point-to-point and you’d win it stylishly. Now you need to be well educated and be a 100% fit. There’s plenty of depth there now. There’s more and more people doing it and you’ve got plenty of good, sharp lads doing it.
“I think there’s still an element where the British point-to-point programme needs to be tweaked… For example, this is the time where your four-year-olds start coming to fruition. You know where you are with them, you’re ready to run and this weekend they’ve got a five-year-old and over maiden point-to-point. Well that’s just stupid.
“They have also introduced these point-to-point Flat races. The issue I have with those is they have diluted the maidens. They have taken away a lot of the young horses which would traditionally have run in a point-to-point. And now the people that don’t want to be commercial fiddle around for a season running around in these point-to-point Flat races and to be quite honest with you, they’re dirt. You won’t sell a horse out of one of them. They should never have been allowed to come in.”
Does it damage the reputation of the product?
“Yes it does. All of the boys operating on a commercial basis won’t entertain them. If you want to sell a horse, it needs to be able to jump 16 or 18 fences and do it nicely.”
McGrath has plenty of praise for the British scene.
“There is talent emerging and we’d love for it to be stronger again but sometimes, people struggle to get a grasp on the English form, whereas a lot of people know the Irish point-to-point handlers better, they know the tracks better and can get a better handle on the form but at the same time, it doesn’t mean that there’s not lots of good horses come out of English point-to-points.
“I think sometimes there can be a bit of value and when you are buying pointers, it is important to remember that it is budget driven and you don’t always have to shell out the big numbers to buy a good horse.”
Lacey and Doyle are in agreement about the importance of producing a racehorse over a sales horse. It is the only way to ensure longevity as a commercial entity.
“There’s no point trying to sell a mediocre horse for a lot of money ‘cos you’ll only ever do it once,” Lacey declares. “We had a horse won at Dingley Point-To-Point (by 16 lengths) called Space Safari. Bryan Drew was there that day and rang me up that evening and said, ‘What do you want for that horse?’ I said, ‘Bryan, I can’t sell him to you. Don’t ask me any more questions but I can’t sell him to you.’ And that was because I wanted him to come back and buy another one.”
“I don’t want to sell a bad horse,” is the Doyle mantra. “I had a few horses in Cheltenham at the (February) sale. They made good store prices, but I explained to the guys that bought them, ‘This is what these horses are capable of doing. They’re good horses. Are they Saturday horses? Maybe not, but they’ll win races.’”
When a vendor is known for this sort of honesty, buyers take note when he vouches for a horse. Doyle’s word was enough for Willie Mullins to acquire Appreciate It, Champ Kiely and Readin Tommy Wrong despite them failing to win their maidens but they are all Grade 1 victors now.
And of course, Nicky Henderson bought Constitution Hill because of his respect for Warren Ewing and his former No 1 jockey Barry Geraghty, who had sold him future Gold Cup winner, Bobs Worth. Constitution Hill finished second in his point at Tipperary, after making a terrible mistake at the last. What’s more, the physical exertions left a toll. It was only the word of men he knew and trusted that maintained Henderson’s interest. As we know, the Blue Bresil seven-year-old has yet to lose a race on the track and sauntered to a Champion Hurdle success last year before illness ruled him out this time around.
Some horses are just slower developers. Grand National winner Corach Rambler, who ran a stormer to be third in the Gold Cup and is a short price to back up his Aintree heroics, took five attempts to win a point for John Walsh, finally getting his head in front in a six-year-old’s and older maiden at Monksgrange in September 2020. So a relationship and trust with the vendor is critical.
“A very good example was Love Envoi,” McGrath explains. “She didn’t show herself very well on the day and there was a minor vetting issue but Seán (Doyle) assured me it had not stopped her and it would have surprised him if it ever did cause an issue. We paid thirty-eight grand for her and she turned out to be a Cheltenham Festival winner, a multiple black-type filly and a Grade 1-placed filly. That was a perfect example of trust.”
It is noteworthy how often Mullins’ name crops up in the course of these discussions, reflective perhaps of his dominance. What is interesting is how often he gets his business done privately, via his agent, Harold Kirk, with Pierre Boulard his man on the ground in France when it comes to acquiring the talent emerging from French three and four-year-old hurdles. Lacey is adamant that this, more than anything else, is why he is the leviathan of jump racing.
“People say, ‘What’s Willie Mullins doing that allows him to get all these best horses?’”, the Cottage Field Stables conditioner begins.
“If you’ve got a good horse and you genuinely believe it’s a graded horse, if you ring Harold Kirk and say, ‘Harold, I’ve got one for you,’ he will say, ‘What do you want for it?’ You’ll name your price and he will say, ‘I’ll have it.’
“That is what Willie Mullins does differently. He doesn’t say, ‘I’ll come back to you in a week’s time.’ The vet’s there within the week and they just get the business done. They do not sit on the fence and allow horses to be sold from underneath them. That is one of the things he does that no one else does. They are so straightforward.
“He’s got Harold Kirk working from November onwards with all the point-to-point handlers working in Ireland, with the point-to-point handlers in England. He used to come over and see all mine before Christmas, see which ones he liked, asked me which ones I liked and if they did what I expected them to do, I rang him up and said, ‘Harold, you should buy that horse.’
“‘I’ll have it.’
“That’s what Willie Mullins does that no one else does.”
Horse Racing Ireland has intimated a willingness to develop a programme of bumpers and hurdles for three-year-old store horses, while there is a programme of junior NH hurdles in Britain, though for paltry prize money.
This comes on the back of the success of the French programme of three-year-old hurdles that is backed with significant prize money by France Galop and is producing major talent. The first of the year was held at Compiegne on March 5, with the connections of Willie De Houelle landing €27,140 for a four-length triumph, the total prize fund amounting to €59,000.
The Beaumec De Houellle gelding is trained by Arnaud Chaille-Chaille, who also was responsible for the sire winning at Grade 1 level. His best graduate, however, is Galopin Des Champs, who won a four-year-old hurdle at Auteuil on debut before relocating to Ireland and becoming a two-time Gold Cup hero.
McGrath has a number of Gallic contacts and sourced the highly promising juvenile, Sir Gino for Henderson from an April maiden at Auteuil. He is a huge fan of a system that also produced the new Champion Hurdler, State Man.
Doyle has reservations about racing moving in this direction though concedes that he would get involved in two-year-old sales if they were to come on stream.
For his part, Lacey believes that this method, while suitable to French-breds, is not necessarily transferable.
“I’d be very old school,” says Lacey. “I think we are all expecting too much too soon from a lot of these young horses. The powers that be want us to follow the French model with Irish pedigrees. We’re breaking a lot of horses at two, turning them away, bringing them back at three and turning them away. They’re still not ready. I don’t know if it’s the breed or the way we produce them or the way we train them or what, but our horses just don’t come to hand like they do in France.”
And you have to do right by the horse.
“Course you have. But when Energumene was here, the ease with which he did everything was astonishing. The gulf between a good horse and a Grade 1 horse is vast. You see it on the gallops, it just floats everywhere. Everything is so effortless.”
He jokes that he had to buy a lot of stores to find that Grade 1 winner – to be fair, Energumene is a six-time Grade 1 winner – but that is the role the handlers play, taking on risk, filtering the wheat from the chaff.
“They go out, they put their own money on the line, they buy these horses as three-year-olds, they take all the risk. They break them. They canter, they school, they gallop the horses, they run the horses in a short space of time. Ideally they like to sell them as four-year-olds, sometimes they carry over till they’re five-year-olds. The good ones go on and make a lot of money and a profit, but there’s an awful lot of horses don’t even see the track, they don’t make the grade. And there’s plenty ones aren’t as good as they want them to be and if they’re lucky, they wipe their faces with them. That’s why they need the big priced ones because they’re covering the cost of the ones we don’t see or hear about.”
High risk, high reward, providing the ultimate quality control service.
Still special.
Gut issue biomarkers and their use in signalling dysbiosis
Article by Jackie Zions
Gastrointestinal issues (GI) are the number one cause of morbidity in horses other than old age. An unhealthy digestive system can cause poor performance, pain, discomfort, diarrhoea, and a whole host of issues that can sideline your horse. It’s no wonder researchers are paying close attention to the ‘second brain’ and its billions of inhabitants. Ontario Veterinary College (OVC) researcher, Dr. Luis Arroyo has been studying the equine gastrointestinal systems for many years with several research projects receiving funding from Equine Guelph. Arroyo discusses what we know about equine gut health, causes of GI disorders and the extensive continuing research to understand what unstable and stable gut populations look like.
Starting with some basic anatomy Arroyo says, “The gastrointestinal tract of a horse is extremely large, and there are many things that can cause disturbances to the normal functioning or health of the gut.” A healthy gut microbiome is essential for the horse’s entire body to function optimally.
Signs of GI issues
Common signs of disorders could include abdominal pain, bloating, changes in faecal consistency (including diarrhoea or constipation), excessive drooling, decrease in water consumption, lack of or poor appetite, weight loss and low body condition score.
“Some cases are more obvious to owners,” says Arroyo, “like poor performance, or acute or chronic diarrhoea.”
Changes of behaviour such as becoming cranky or moody can be tell-tale signs there is unrest in the GI system. Biting at the flanks can signal abdominal pain as well as reactivity to being saddled. When the horse stops wanting to perform and athletic abilities suddenly decline, if there is no obvious lameness, GI issues are high among the considerations.
“Horses are herbivores, designed to consume a diet of forage, and to break down complex sugars within that forage.” says Arroyo. “The gut microbiota does this job and is very important for healthy digestion.” Recent research is connecting the changes in diversity of microbial communities to conditions like colic, colitis, and gastric ulcers.
Causes of GI Issues
Colic is the number one clinical condition occurring in horses. It is well-known that sudden dietary changes can be a major contributor as well as diets that are high in grain. This can create changes in the volatile fatty acids produced in the GI system, which in turn can lead to the development of gas colic. Arroyo provides the example of switching from dry hay fed in the winter, to rich, lush, spring grass as a big cause of rapid fermentation that can cause colic.
Any abrupt change, even if it’s a good quality feed to a different good quality feed, can be a source of colic. Then there is the more obvious consumption of mouldy, poor quality hay. So not only the quality but the transition/adaptation period needs to be considered when making feed changes and this goes for both changes to forage or concentrates.
A table of feed transition periods on the Equine Guelph website states an adaptation period of at least 10 – 14 days is recommended. Transition periods under seven days can increase colic risk over 22 times! (https://www.equineguelph.ca/pdf/tools/How%20to%20Transition%20Feedstuff.pdf)
“Decrease in water consumption can be an issue, especially in countries with seasons,” says Arroyo. When water gets really cold, horses often drink less, and if it freezes, they don’t drink at all, which can lead to impaction colic. Parasite burden can also cause colic. If your horse lives in a sandy environment, like California, ingesting sand can cause impaction colic.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) can cause colic or ulcers. NSAIDS can interfere with blood supply to the GI tract causing ulceration, for example in the mucosa of the stomach. Prolonged use can cause quite severe ulceration.
NSAIDS are not the only drugs that can contribute to GI issues. “Antibiotics - as the name says - kill many kinds of bacteria,” says Arroyo. “They are designed for that! Invariably they deplete some bacterial populations including in the intestine, and that is a problem because that may allow some other bacteria, potentially pathogenic or harmful, to overgrow, and that can cause dysbiosis.”
In a recent study, by fellow OVC researcher, Dr. Gomez and co-workers, it was determined that damage to the intestinal microbiota could occur after only 5 days of administering antibiotics to horses. Damage to the intestinal microbiota resembled dysbiosis that can potentially result in intestinal inflammation and colitis predisposing the horse to diarrhoea. Judicious use of antibiotics and antimicrobials are advised.
There are infectious and non-infectious causes of colitis. Infectious examples include salmonella and then there is Neorickettsia risticii, which if ingested from contaminated sources, can cause Salmonellosis or Potomac horse fever, respectively.
“Any stress factors such as transportation, fasting or intense exercise like racing, can be a factor for developing stomach ulcers,” says Arroyo.
Current Diagnostics
Putting together a picture of the horse’s health status includes gathering clinical history from the horse owner and performing a physical examination for motility and hydration status. A biochemistry profile and complete set count can be gathered from blood testing.
Gastric ultrasound allows veterinarians to view the wall of the intestine, noting if it has thickened or distended, which could occur in cases when there is colic. They can assess appearance and find out if the intestine is displaced or if there is a twist. Gastroscopy is commonly used to find ulcers in the stomach and can reach as far as the first part of the duodenum.
GI Research
“DNA sequencing has been a breakthrough in science in terms of understanding the communities of different microorganisms living in many different niches from the skin to the lungs to the upper airways to the intestine,” says Arroyo.
It has allowed in-depth study of the population of microorganisms, providing a big picture of the different inhabitants in various areas of the GI tract, such as the lumen of the small intestine and the small and large colon. “The microorganisms vary, and they have different functions in each compartment,” says Arroyo.
DNA sequencing has allowed researchers to study microbial populations and gather information on what happens to bacterial communities when impacted by diseases like colitis. “We can see who is down, and who is up,” explains Arroyo, “and determine what populations have been depleted.” It has led to a better knowledge of which of the billions of factors are harmful to the system and which can compromise the health of the horse.
Robo-gut is one example of a fantastic system where bacterial communities are being replicated in the lab to mimic what would be found in a natural environment.
Researchers at the University of Guelph have measured metabolic profiles of the bacterial population after the addition of supplements like probiotics and prebiotics. They found they can dramatically change the metabolites that are being produced, according to what is being added to the system.
Exciting new research that could impact the future of diagnostics includes screening for biomarkers as indicators of intestinal health among equine microbiota. Dr. Arroyo is currently working with research partner, Dr. Marcio Costa, from the University of Montreal, looking for biomarkers that indicate changes in the inhabitants of the equine gut that take place during the early onset of illness.
“A biomarker is a biological molecule that you can find in different places,” explains Arroyo. “For example, you might find them in tissue, blood, urine, or different body fluids. They can signal normal or abnormal processes or could reveal a marker of a disease. For example, a biomarker can be used to see how well the body might respond to a treatment or to a disease condition.”
“The objective of a dysbiosis index is quantifying ‘X’ number of certain bacteria that are important to us,” says Arroyo. In this case, the dysbiosis derives from sequencing of the bacterial population in faecal samples.
Changes in the intestinal microbiota (dysbiosis) are present before and during the outset of diseases and after treatment with antibiotics. Arroyo cites the example of decreased Lachnospiraceae commonly observed when there is intestinal inflammation.
Bacterial biomarkers are currently being used in other species to accurately predict intestinal dysbiosis, for example in cats and dogs. One canine study quantified the number of seven different taxa of importance of the total bacterial populations. This information is entered into a mathematical algorithm that comes up with results explaining which bacteria have increased or decreased. Based on those numbers, one can use a more specific taxa to identify dysbiosis. In a feline study, it was discovered that six bacterial taxa could be accurately used to predict diarrhoea in 83% of cases.
It is hoped the same results could be accomplished for horses. Developing PCR testing to screen for biomarkers could be a game changer that could potentially provide speedy, economical early diagnostics and early treatment.
So far, the most remarkable finding in the preliminary data reveals that in horses with colitis, the whole bacterial population is very depleted.
“At this stage we are in the process of increasing our numbers to find significant differences in which bacterial taxa are more important,” says Arroyo. “Soon we hope to share which bacteria taxa are more promising for predicting dysbiosis in horses with gastrointestinal disease.”
The researchers are delving into a huge biobank of samples to identify potential markers of intestinal dysbiosis in horses, utilising PCR testing as a faster and more economical alternative to the complex DNA sequencing technologies that have been used to characterise changes in microbiota thus far. The goal is to develop simple and reliable testing that veterinarians can take right to the barn that will result in early treatment and allow closer monitoring of horses at the first onset of GI disease.
Top Tips to Protect Digestive Health
Horses are hind gut fermenters who rely on adequate amounts of fibre in the diet to maintain healthy gut function.
Make dietary changes slowly as abrupt changes disrupt the microbiota.
Avoid large grain meals as huge portions of highly fermentable diets can be quite harmful to the microbiota and can also be a source of risk for developing gastric ulcers. Opt to spread out concentrates into several smaller rations.
Prevent long periods of fasting which can also lead to ulcers. Horses are continuous-grazers, and they need to have small amounts of feed working through their digestive system to keep it functioning optimally.
Have a parasite prevention programme.
Provide fresh water 24/7 to maintain good hydration and keep contents moving smoothly through the GI tract.
Keep up to date on dental appointments.
Motion is lotion – turn out and exercise are extremely important to gut function.
In closing, Arroyo states, “These top tips will help keep the horse happy and the gastrointestinal tract functioning properly.”
2023 Champion Trainer profiles - Peter Schiergen (Germany) / Kadir Baltaci (Turkey) / Claudia Erni (Switzerland)
NATIONAL CHAMPION TRAINERS IN FOCUS
In this issue, we take a look at some more of Europe’s champion national trainers, courtesy of the latest data compiled by Dr Marian Surda, doyen of Slovakian racing.
A notable feature of the tables, when comparing the last two years, is the infrequency of trainers retaining their crowns. Only in 7 of the 18 countries that featured in both years did this happen (France, Jean-Claude Rouget; Ireland, Aidan O’Brien; Spain, Guillermo Arizkorreta; Germany, Peter Schiergen; Norway, Niels Petersen and Greece, Charalambos Charalambus). The baton changed in all other countries, including in Great Britain, the country whose trainer earned the most money, for the second year running. This time, that trainer was the father and son combination of John and Thady Gosden, who wrested the title from Charlie Appleby.
Among the jockeys, Maxim Guyon, in France and William Buick, in Britain headed the table once again. But the dominance of the big three countries – France, Britain and Ireland – was interrupted by an extraordinary performance by Turkey’s Champion, 20-year-old Vedat Abis, who clocked up a remarkable 283 wins – far more than any of his fellow champions.
Our featured trainers this year are Peter Schiergen (Germany / 5th in the table), Kadir Baltaci (Turkey / 6th) and Claudia Erni (Switzerland / 11th).
PETER SCHIERGEN
The name of Peter Schiergen is a familiar one across the European racing scene and beyond, with Group wins in France, Britain, Italy and Dubai as well as his native Germany. At time of writing, that Group race tally stands at 199. Champion Trainer in Germany no fewer than eight times (2002, 2005, 2006, 2013, 2015, 2021, 2022 and 2023), with six German Derby wins to his name (Boreal 2001, Schiaparelli 2006, Kamsin 2008, Lucky Speed 2013, Nutan 2015 and Sammarco 2022), his crowning single achievement remains his Arc win with Danedream in 2011.
But before becoming one of the most successful German trainers of recent generations, Peter had been one of his country’s most successful jockeys. His outstanding record in the saddle encompassed five jockeys’ championships – 1992 to 1996 – and nearly 1500 wins, including a record 271 successes in 1995.
I asked Peter about his journey into racing and what had led to his becoming a jockey at the age of 16. “I always wanted to become a show jumper. My plan was just to do my apprenticeship in racing and after that to go back to show jumping. But it turned out differently and I had quite a bit of success as an apprentice and stayed in the game”.
The transition from jockey to trainer (taking over from fellow legend Heinz Jentzsch in 1998) was made at a younger age – just 33 – than is often the case.
“The opportunity came up to take over from Heinz Jentsch. I knew that this was a huge chance and even though it was quite early I decided to take over. I started in 1998 in Köln and still train there today. In 2009 we built a new stable next to the old one so that’s really the main thing that has changed”.
“I had a great time as a jockey and was five consecutive years champion jockey and broke the European record in 1995. But the owners didn’t give me the chance to ride in the big races abroad such as Lando in the Japan Cup. This is something I don’t want to happen to my stable jockeys and therefore I use them both in Germany and abroad.
What does Schiergen consider the pros and cons of training on the track? “The horses are used to the racetrack. A great benefit is that it’s easier to get staff. Furthermore, the racecourse is in charge of preparing the training facilities. A disadvantage would be that we have certain times at which we must be at the track, as there are many trainers who use the facilities. On a private track you have more peace”.
“The team consists of 25 staff. It gets more and more difficult to get good staff and competent work riders. We have a great team and many people have been staff members for many years. There are plenty of Germans working with us. Other than Germans, most of the staff tend to be from the eastern European countries such as Poland, Czech Republic, Bulgaria etc.”.
When asked which trainer he admires the most, Schiergen replies: “I didn’t have a jockey I admired the most when I was a jockey, and now, as a trainer, neither do I have a trainer I would single out as admiring. I look at many others and try to take the best of each”.
“The state of racing in Germany isn’t great, but there are many ambitious people who are trying to bring the sport back to better times. It’s difficult with social change and especially the animal welfare movement. Racing’s lobby sometimes appears to be too weak to work against these forces. Therefore, we need a change. It’s difficult to compare our racing jurisdiction to other countries. We don’t have training facilities such as Newmarket or Chantilly.”
As well as the 200 Group race milestone, Schiergen has another in his sights. Ending last year on 1,907 wins on the flat and 31 over jumps, it is a real possibility that he could send out his 2,000th winner this year. “Certainly is a milestone and a great achievement. But it is more important to win big races.”
KADIR BALTACI
Kadir Baltaci’s 31 wins last year came at the hooves of just 37 individual starters (his stable currently houses just 30 horses in training). His tally included seven domestic Group races, including three at Group 1.
From Baltaci’s base in Turkey’s capital, Ankara, it is a long haul to the tracks where he does most of his racing: a 5-hour drive north-west takes him to the nation’s racing headquarters, Veliefendi in Istanbul, or a lengthier run yet in the opposite direction finds the track in Adana.
“I was born in Adana”, Baltaci begins. “I lived in Adana until 2010. Adana is my city, my place but Ankara is now ‘my city’ and ‘my place’, where I live with my two sons and my wife. Though I train my horses here, when they are ready to race I mostly prefer to run in Istanbul because of the classic and other big races that are run at Veliefendi racecourse”.
“I began as an Assistant Trainer in 2011. After spending seven seasons as an Assistant, I started training in my own right, in 2017.
“When I was at high school, I was best friends with the son of the owner of the famous Turkish-Arabian horse Nurhat. I often went with my friend to (Adana’s) Yesiloba Racecourse to see the horse. As a child, I loved the horses. I used to watch racing on the television, especially the classic and GAZI races.
“Workwise, I started out working at my father's painting company, but it collapsed. I then worked as a driver for one of my now-owners, Mr Fedai Kahraman. When working as his driver, he often used to send me to the races at Ankara, in order to help his trainer out. After a couple of years, he asked me if I would move to the track to assist the trainer. I said ‘yes’ and that’s how my journey started.
“I don’t have a private training centre. Like all trainers in Turkey, I must be based at one of the Jockey Club racecourses. We chose Ankara for the wintertime: because the racetrack is empty then, I can easily prepare my horses.
“I have 20 people working for me. My staff are all Turkish. We did try employees of other nationalities, but I did not like the way they worked. Most of my crew have been with me since I started training. Because we have been working together for so long, it is a great relief to me that they know exactly what I want. It is hard to find new people to take care of horses. Really hard. I have five exercise riders. You can find exercise riders very easily, but most are not proficient. The Jockey Club of Turkey trains exercise riders. One of mine came from there – he graduated last year. But they are young and need time to learn the job properly. We have also got a broader problem with finding stable staff generally. Not only me, other trainers have the same problem”.
To date, Baltaci has ventured abroad to race but once, sending a runner to Meydan to contest the Grade 2 Cape Verdi and Ballanchine Stakes. “I believe my horses will run more often abroad. My big ambition is to run in - and win - a European Classic.
“We are not well educated about training practices in other countries, so I will not make comparisons. All I would say is that many are lucky to have private training facilities. I think our trainers probably spend more time in nursing horses which have suffered minor injuries back into racing”.
Baltaci places much hope for the future in Serdal Adali, Adana-born President of the Turkish Jockey Club. “Mr Serdal Adali is spending time ensuring a better future for us. I believe he will succeed. Then my countrymen will be more interested in racing outside of Turkey.”
Balaci’s strike rate, particularly at the top level, is impressive indeed, but he is modest when asked to explain the secret of his success. “It’s down to the efforts of everyone, from my horse owner to my team. That's why I can't give any specific reasons for my success. I have 30 in training right now. Thirty different horses, which all act differently, and that is why I train each horse differently”.
CLAUDIA ERNI
Over in Switzerland, there has seen a changing of the guard. After several years of domination by Miro Weiss, there is a new woman in town. Step forward, Claudia Erni. Her yard of 20 horses – ranging from 2yo’s to a 10yo sprinter and stayer, ranks fourth by size within the country, but in 2023 punched above its weight to capture the championship.
“I grew up with horses. My father had a riding school. I took part in some national dressage competitions. My father’s girlfriend was in racing, and this was how I found my way into racing. I rode as an amateur, both on the flat and over jumps, and also held an amateur training license before taking out my professional trainer’s licence in 2006”.
“I am also a physical therapist and still devote two afternoons a week to working in this profession”.
Erni trains from Switzerland’s westernmost racetrack, Avenches, south of Lake Neuchatel. This impressive complex (a good idea of which can be gleaned from www.iena.ch), extends to 140 hectares/350 acres and accommodates multiple equine disciplines. It is important to the finances of Swiss racing, many of its race days being taken by the French betting operator, PMU.
“It is really nice to train here. We have a lot of space. We have two tracks of 1600m and 1800m circumference, with paddocks and a horse-walker. And I am almost alone here! At present, I have four employees, from France, Switzerland and Chechia. I do find it difficult to find good riders. For so many, money is more important than passion - sad, but that’s how it is”.
“My owners have been in the business for a long time. It is difficult to find young owners. But I am fortunate, in that mine came to me – I didn’t have to go looking for them!”
“I often race in France, Germany and Italy, when the owners allow it. I love Longchamp. We are very close to France – for example, it takes just three hours to reach Lyon.”
And what of the outlook for the sport in her country? “As in every country, racing in Switzerland is getting harder. It is harder to find sponsors and new owners, and the number of racehorses is reducing. The Swiss racing authority is trying to find ways to increase the popularity of the sport. Maybe, jockeys will be prevented in future from using the whip?”