EMHF - The state of jump racing around the world
Words - Paull Khan
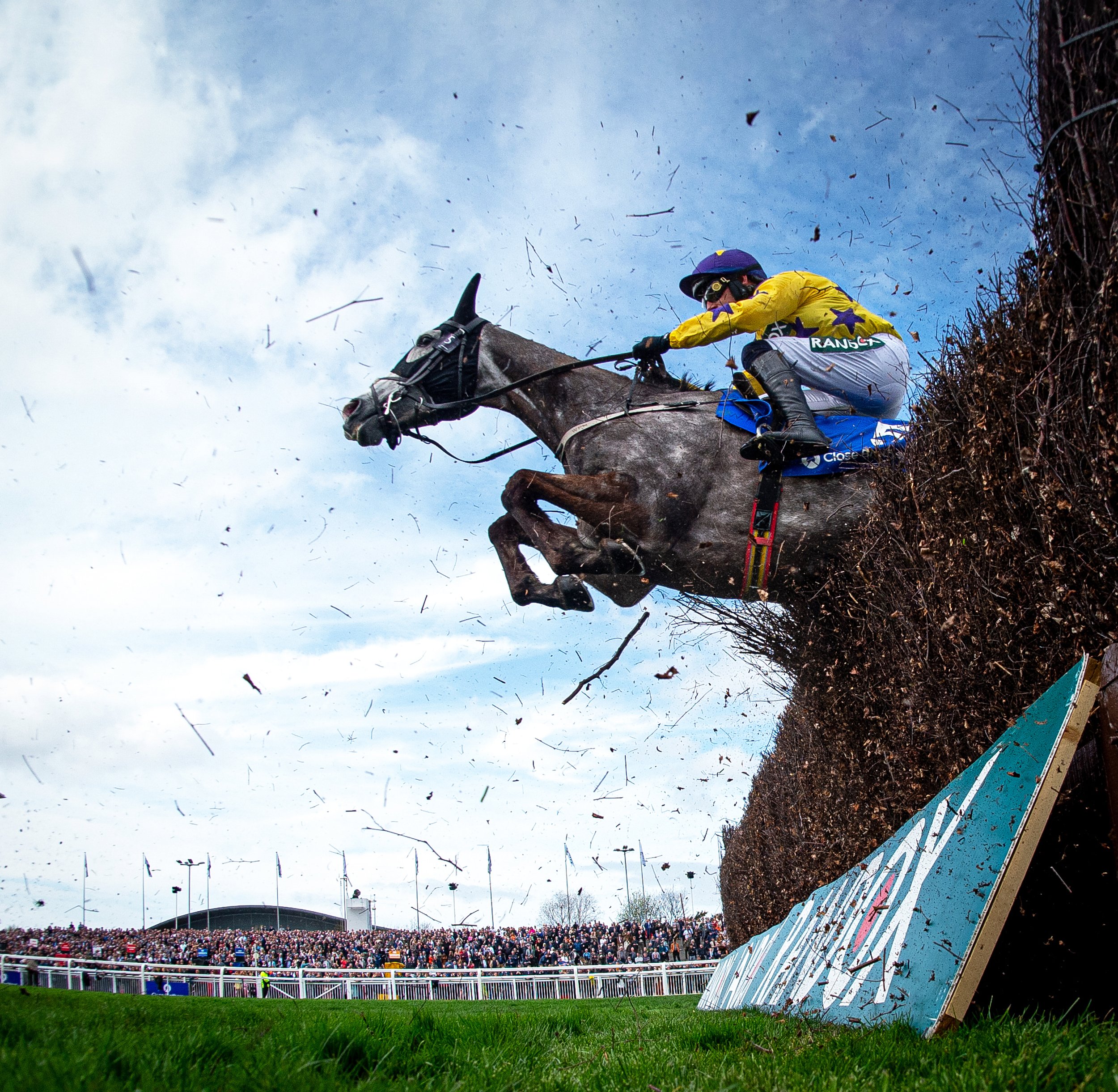
What state of health is jump racing really in? For someone living in Britain, for example, the picture is a little confusing. On the plus side, interest levels in the sport relative to the flat seem never to have been higher – of the top British races by betting turnover, almost all are over obstacles. And no festival, Royal Ascot included, generates more anticipation and excitement than does Cheltenham. Then one considers Ireland and the merciless pummelling, which the Brits have become accustomed to, of the home team by Irish-trained horses at that very Festival. And France: you won’t find a topflight jumps card where the commentator’s mastery of French pronunciation will not be put to the test – such is the prevalence of French-bred imports.
But then, on the darker side of the coin, one cannot fail to register increasing societal unease. A growing unwillingness to accept the unavoidable reality of injuries and fatalities, however rare their occurrence. And views being expressed that these headwinds are not only serious – they may be terminal, with venerable trainers opining that jump racing in Britain will not outlive them. And we are aware of the swingeing contraction of jump racing in Australia, which gives those existential fears more weight.
So, your columnist set out on a journey of discovery – to try to find out the true state of health of jump racing globally.
The first thing I was struck by is how rare a bird jump racing is, globally speaking. There are vast tracts of this planet on which the sport simply does not exist. More troubling yet, in several parts of the world there are memories of a sport that once existed but that has now perished.
Take Canada. Ross McKague of the Canadian Graded Stakes Committee sets out the picture starkly. “We have never had, do not currently have, nor are there any plans for, any organized jump races in Canada.”
Similarly in South Africa. “Apart from one or two amateur jump races on the inside of the race course in the Eastern Cape at the now defunct Arlington Race course”, Arnold Hyde, Racing Control Executive at the National Horseracing Authority there explains, “I am not aware of jump races in an official capacity taking place here. I guess that there has not been a culture for jump racing in South Africa and with our dwindling horse population (hopefully with the latest import/export developments the trend is reversed), I cannot see this changing anytime soon”.
How about South America, then? Ignacio Pavlovsky, IFHA Technical Advisor for that continent, recalls there having been racing in Chile once upon a distant time. His research reveals that the last steeplechase was held there in 1986.
So where, outside Europe, is this elusive creature to be found? The green in the background maps gives the answer. The USA for one – but restricted to a ribbon of States in the East of the nation. We have mentioned Australia, where, within recent years, the sport has ceased in both Tasmania and South Australia and is only now to be found in Victoria. Then there’s New Zealand and Japan. And that, unless anyone corrects me, is just about it.
What is the scale of jump racing in these non-European countries, and how has it shifted in recent decades? Taking as our simple metric the number of jump races staged, we can see that Japan has virtually flat-lined over the past 20 years. USA, meanwhile, has seen a 20% decline, while New Zealand’s programme has all but halved and Australia’s has worse than halved.
Over that period, there has been a remarkable consistency in what has happened to average field sizes. In America, they have reduced by 13%, in New Zealand by 14% and in Australia by 15%, indicating that the pool of jump horses is contracting at a faster rate than the number of contests on offer. The average jump race in Australia attracts 8.2 runners; that in New Zealand 7.8 and that in the States just 6.5. Reducing field sizes is, in fact, a scourge of jump racing affecting virtually all of the world’s jumping nations.
And what of the future? Hearteningly, two recent reviews, the first in New Zealand and the second in Australia, have come down in favour of the continuation of the sport. The latter took place against the backdrop of calls from the local RSPCA for the closure of the sport in Victoria, following the deaths of three horses at the August meet in Ballarat.
September’s announcement from RV stated that “Due to the increase in fatal incidents across the 2024 jumps racing season, this year’s review will go beyond the standard process. A broader, whole-of-business approach will be adopted to analyse a broad range of metrics….The report and recommendations will consider the future viability of jumps racing in Victoria, and/or what further changes can be made to improve the safety record of the sport”.
RV’s Chaiman, Tim Eddy added: “The safety record across the 2024 jumps racing season was unacceptable and the events of the final meeting at Ballarat were heartbreaking for all involved in the Victorian jumps racing community”.
Last month’s report linked jumping’s reprieve to a raft of safety measures, including the cessation of jumps racing at certain tracks, a contraction of the season in the quest for safe ground and increased oversight on safety compliance.
Meanwhile, just over the Tasman Sea, a very similar exercise has recently concluded. And if one needed any more evidence of the existential nature of these deliberations, consider this early sentence from the review’s executive summary:
“The scope of the review is to evaluate the future of jumps racing by examining scenarios in which it either continues or is discontinued”.
Again, the review came down in favour of continuation and prompted this joyous headline to an article by respected journalist Michael Guerin: ‘Jumps racing saved in New Zealand with bold new changes ahead’.
Noteworthy was the difference in tone and apparent motivation for the two studies. Whereas, in Victoria’s, horse welfare was front and centre, in New Zealand the focus was more on such aspects as revenue, employment and jump racing’s role as a second career for flat racers. Its approach to the welfare issue was muted: “It is well documented that jumps racing carries higher risks than flat racing, to both horses and jockeys. The figures however did not suggest to the Panel that jumps racing should be discontinued, but the Panel did agree that any additional safety measures should be identified and implemented”. The report gave a nod to “avoiding firm track conditions early in the jumps season” and noted that “even those who supported the continuation of jumps identified a concern about use of the whip during the races, especially at the end of the races after the last jump…when horses are tired”. Its main recommendations, however, centred on programming changes, promotional initiatives to raise the profile of jockeys, and various measures for their sourcing, (including, intriguingly, “a recruitment and licensing program to streamline the readiness of UK riders for racing in New Zealand”).
For Guerin, this emphasis is reflective of broader public attitudes in New Zealand where, he observes “many have farm ties and most city people probably don’t watch jumps racing as it is no longer in Auckland”.
Japanese jump racing is battling twin concerns of declining betting revenue and dwindling jockey numbers. The Japan Racing Association’s Takahiro Uno, Chair of the Asian Pattern Committee notes that its jump races were recently moved, as a result, from the major tracks to smaller venues. But there is a desire to protect the rich history of jumping – Japan’s premier jump race, the Nakayama Daishogai, is not far away from its centenary. Already, an apprentice system which is agnostic as to the age of the apprentice has been introduced, to incentivise flat riders to make the transition and a return of some jump races to the big metropolitan venues is under consideration.
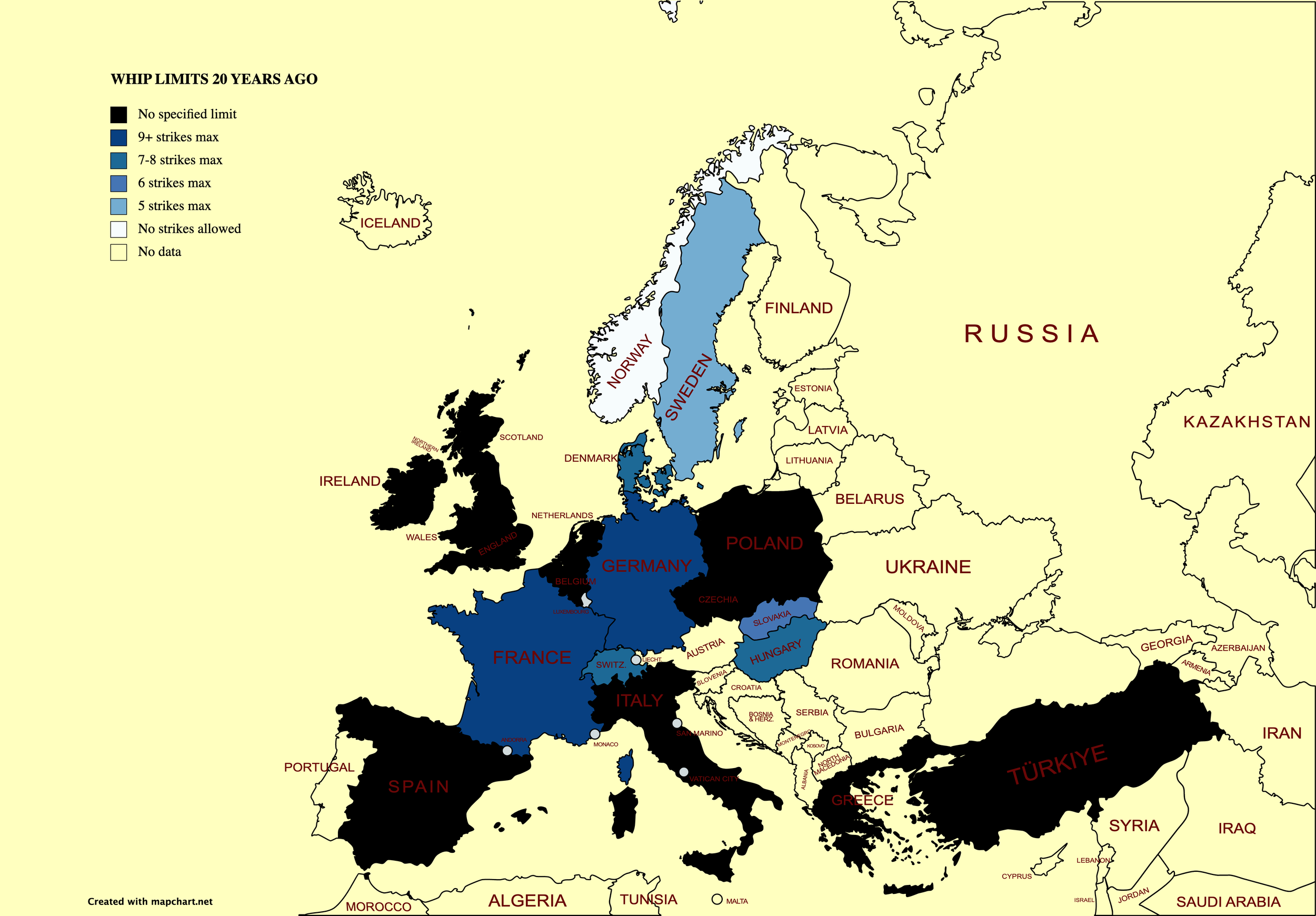
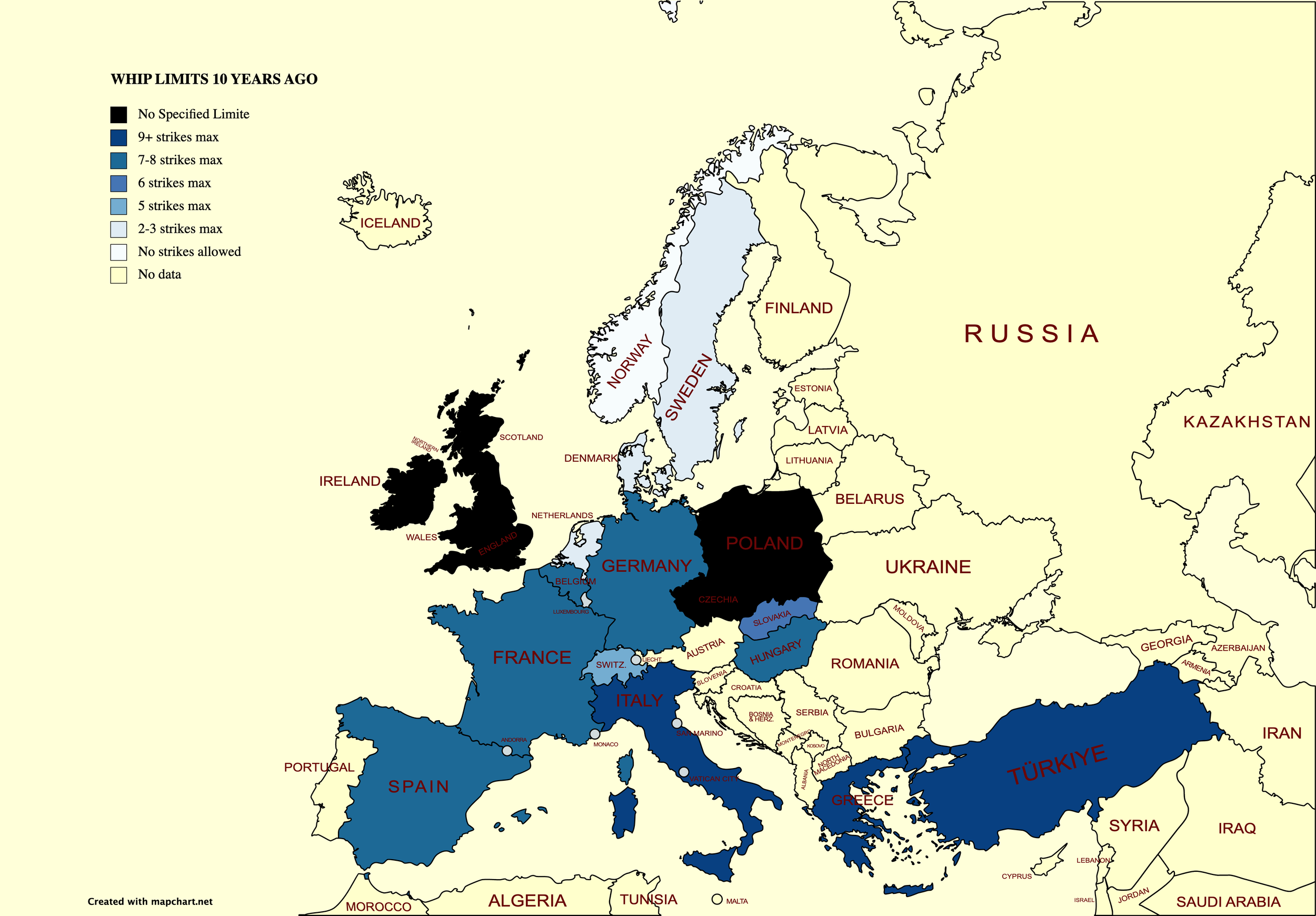
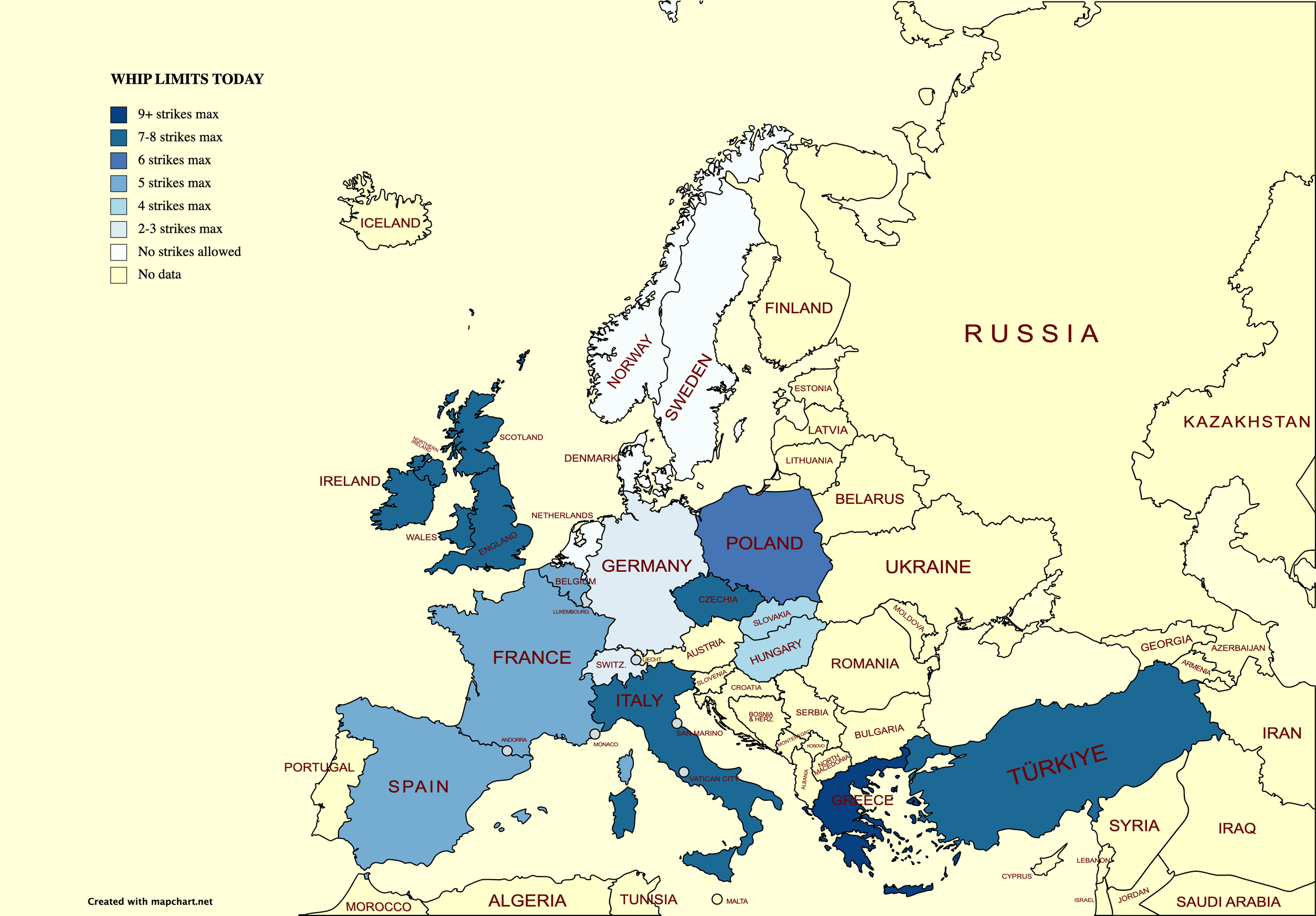
Let us return home, to Europe. A survey of EMHF members revealed that jump racing can be found in no fewer than 13 of them. That’s the good news. The less good news is that decline and contraction is evident virtually across the board, and in two countries - Austria and Norway - jump racing has died out within the last 20 years.
In Germany, the downswing is precipitous.
Despite a 93% reduction in jump races since 2004, field sizes have plummeted to less than 4.5 runners. To Rudiger Schmanns, Racing Direktor at Deutscher Galopp the sport is in its last throes. What does he envisage in the next 10 years? “No races. No, riders, no horses and further animal welfare pressure”.
The picture in Italy is brighter – but not much.
In 2004, 728 individual horses started over the jumps; today that number is 212. Twenty years ago, one could enjoy jumping at 15 Italian tracks. Now, there is just Pisa, Trevisa and Merano left. The last-named remains a gem amongst European jumps courses, but is heavily propped up by incoming foreign-trained runners, mainly from the Czech Republic. Around half of Merano’s prize money goes abroad, and around half of that to the powerful Czech stable of Scuderia Aichner and Josef Vana jnr.
And, turning to Czech Republic on our European round-up, we detect the first green shoots of optimism.
While a reduction in scale is still apparent, it is far less pronounced than in the earlier countries. And the above tells but half the story, since, as has been noted, Czech-trained runners ply their trade in neighbouring countries with great success. Martina Krejci, General Secretary of the Czech Jockey Club observes: “Very many Czech trainers and owners start in jump races abroad. For example, this weekend in Wroclav (Poland), the Crystal Cup runners were almost all Czech”. Krejci anticipates a bounce-back will take place starting next year, with race numbers returning to their levels of 10 and 20 years ago. One of the biggest impediments to growth, though, is the dearth of jockeys.
It is as well to consider the Central European countries as a region, as well as individual territories, such is the level of international traffic of runners.
Polish statistics are distorted somewhat by the fact that, in the early part of this century, a number of jump races for half-breds were additionally run. These then ceased, and were supplanted with thoroughbred races, which drew liberally for their runners from neighbouring countries, such as Czech Republic. Notwithstanding this quirk, Polish jump racing, if not in rude health, is certainly faring better than most.
Sweden now flies the Scandinavian jump racing flag alone. The jumps are a distant memory in Denmark and the last hurdle race in Norway took place in 2022. Swedish jumping’s future is itself under intense scrutiny, explains Dennis Madsen, Racing Director of the Swedish Horseracing Authority, following the betting operator’s devastating decision no longer to take bets on this code of racing. For Madsen, though, jump racing’s problems are very largely replicated on the flat in Sweden, and he detects a frightening decline in horseracing the world over which he feels is both inexorable and inevitable. “Yes”, he concedes, “Cheltenham and Ascot and the Melbourne Cup still sell out, but these are merely the biggest icebergs, which will melt the slowest. The smaller countries will be erased before the bigger countries – but the bigger countries are melting as well”.
One can find jumping in Belgium, Channel Isles, Hungary, Slovakia and Switzerland, in some of which it is hanging on doggedly, but the scale of activity in these countries is even tinier – none runs more than 20 jump races annually.
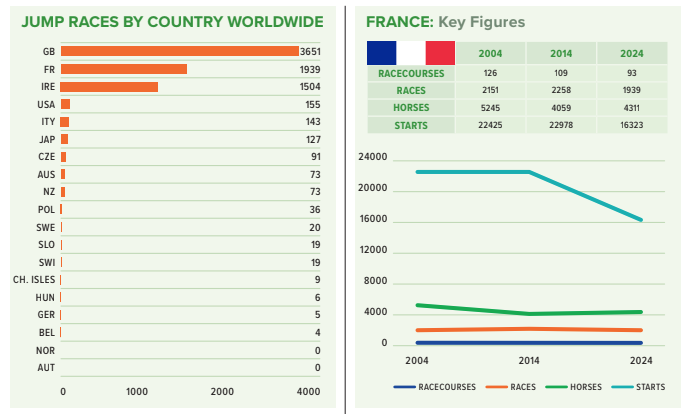
Which leaves Britain, Ireland bigger countries and France. The sheer scale of the dominance of the ‘big three’, and particularly of Britain, is vividly apparent from this chart. Between them, they account for over 90% of the world’s jump races. Nearly 8,000 jump races are run each year around the world and nearly half of these take place in Britain.
So, when considering the overall health of the jumps, most of our attention must be paid to this triumvirate.
France has seen just a modest 10% reduction in its jump races since 2004, where it is staged on 93 tracks today, compared with 123 tracks then. But the number of starts has fallen far faster, by more than one quarter, meaning that field sizes have gone from 10.4 down to 8.4.
Among the causes of this decline, Henri Pouret, Chief Operating Officer at France Galop cites the rise in French-breds being exported, a reduction in racecourses on security grounds due to a lack of volunteer staff and a shortage of jump jockeys, especially amateurs. However, the code remains an important part of the French racing product: “Jump racing and breeding are key in the horse racing landscape in France”, says Pouret. “t still represents one third of the races organised in France and of our different runners. There is a plan to restore Auteuil Racecourse which is the flagship of jump racing in France”.
“The main factor likely to influence the scale of jump racing in your country over the coming years, will be public perception and social license to operate regarding falls and fatalities”.
To invigorate the sport, Pouret would welcome the development of pony racing over jumps.
Ireland’s jumps industry is showing considerable resilience. The number of races has actually increased, but individual horses competing in those races and the aggregate number of starts are both down by over 10%, leading to average fields of a still healthy 11.5, compared with a whopping 13.8 twenty years ago. However, the metrics have improved in the most recent decade.
Jason Morris, Director of Strategy at Horse Racing Ireland, provides the context: “Ireland is in a more positive position than many jurisdictions as jump racing has grown over the past 10 years in line with HRI's strategic objective to become the global leader. The number of races and runners has increased while we have been able to maintain a very competitive average field size of 11.5 runners per race. Irish runners are consistently winning the majority of races at the Cheltenham Festival and an Irish trainer Willie Mullins was crowned British champion trainer for the 2023/24 jumps season. An attractive race programme, strong prize money, well attended race meetings and the continued success of Irish-trained runners are incentivising many international owners to have their jumps horses based in Ireland, while the Irish point-to-point sector continues to provide an invaluable nursery for developing young horses”.
“Our intention is that jumps racing will continue to grow in Ireland over the next 10 and indeed 20 years”.
“The biggest influencing factor and threat to Irish jumps racing is the potential decline of jumps racing in Britain given its importance as an export market for Irish horses and the symbiotic racing and breeding relationship between the two countries. A strong British jumps sector is vital for Irish racing”.
“In terms of invigorating jumps racing, there are concerns about the availability of sufficient horses going forwards and HRI is working on initiatives with the Irish Thoroughbred Breeders Association to ensure the continuing production of quality Irish-breds, including earlier participation on the racecourse for jumps-bred horses. The concentration of success in a shrinking number of very powerful yards is another area for focus. While we celebrate the success of our top trainers, we want to ensure that the grass roots continue to grow as well and that there is a strong pyramid supporting the upper echelons. We will therefore be looking at race planning measures to provide more opportunities for smaller trainers and owners to be competitive. Finally, equine welfare is very much at the forefront of everything HRI does, and we work very closely with the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board to ensure the highest standards of veterinary care and injury risk prevention”.
And a not dissimilar picture is apparent in the world’s jump racing capital, Britain. Again, there are more races today – 10% more over two decades. But, as we have seen in so many countries, the jump horse population and its preparedness to compete has fallen, by some 12%. The pressure on field sizes is more acute in Britain than in Ireland, having fallen from 10.2 (2004) to 8.2 today.
Let us turn to Richard Wayman, the British Horseracing Authority’s Director of Racing and Betting, for a perspective on these bald statistics.
“Although our numbers have remained relatively stable in more recent years, since 2004 there has been a 6.5% decline in the number of horses running at least once over Jumps during the course of the year.
There are many factors that will have contributed to that downward trend, not least the expansion and improvement of the all-weather programme on the Flat through the winter. It is only since 2006 that we have had floodlit meetings routinely staged throughout the core Jumps season and we believe that this change has had an impact on the number of horses running over obstacles.
We’ve also seen an increase in the number of Flat horses being sold to continue their careers overseas and that too has also meant fewer horses switching codes. The days of Jump trainers buying large numbers of horses off the Flat at the Horses in Training Sales in the autumn has become an increasingly distant memory as more and more horses are purchased to continue their Flat racing career elsewhere.
There have been some changes in the make-up of racehorse owners that, in all likelihood, have worked against Jumping. The number of sole owners has declined, with there being an increase in syndicates and racing clubs. Whilst some of those groups, of course, own horses over Jumps, the lower risk of injuries, the prospect of the horses being able to run more often and the potential to pick up more prize money has almost certainly worked in favour of the Flat. Indeed, it is interesting to see an increasing number of Jumps trainers evolving their own business models to include training Flat horses.
More generally, the difficult economic climate will have had a downward impact on racehorse ownership, as will the increasing urbanisation of society meaning that fewer people are involved with horses generally, again something that will have particularly worked against Jump racing”.
How would Wayman anticipate these numbers will look in 10 and 20 years' time?
“Although some of our numbers have been under pressure over the past decade or two, Jump racing remains incredibly popular with fans of the sport. The top 15 races in Britain for generating betting turnover all take place over Jumps. In addition, 37 of the top 50 betting races are also over obstacles.
Of the three race meetings that cut through into mainstream media in Britain – namely the Cheltenham Festival, the Grand National meeting, and Royal Ascot – two take place over Jumps. Our terrestrial broadcaster reports that their viewing figures are at their highest through the Jumps season.
Jump racing remains a hugely popular and much-loved sport that can thrive in the years ahead. That doesn’t mean that it will return to the levels of 20 years ago as we have to accept that the world has changed. However, with help from a mix of short- and longer-term measures, we believe that Jump racing can grow, and indeed thrive, over the course of the next decade and beyond”.
What would he like to see happen to invigorate Jump racing?
“A variety of measures, rather than one silver bullet, will all need to play a part in supporting our participants and racecourses to ensure that we collectively deliver a robust and vibrant sport in the years to come.
This will involve supporting the supply chain of Jump horses, continuing to invest in the mares’ programme and providing financial incentives to support the breeding of quality Jumping stock. It will require learning lessons about what has worked elsewhere and understanding whether those could be successfully applied in Britain, for example the earlier development of Jump horses such as in France, or the Novice Chase programme in Ireland.
We must make the ownership of Jump horses as attractive as possible. As well as investing in the overall experience, at a time of rising costs, making the financial equation more enticing for owners will be key to supporting the quality and quantity of our Jump horses. We have some brilliant Jumps trainers and, again, introducing steps that will assist them in attracting investment from owners, in particular building upon our increased investment that is being made into the Novice programme for both hurdlers and chasers, will be vital.
The race programme also has a role to play in ensuring that we can deliver an effective development pathway which provides promising young horses with the opportunities to help them fulfil their potential and provide the sport with its future stars.
And, of course, the development of exciting equine stars is critical to ensuring that Jump racing remains an attractive proposition for fans and customers, both new and existing. As a broad, overarching and final point, it obviously remains vital to maintain a strong and constant focus on all possible measures to improve the welfare and safety of our horses and riders, together with ensuring we provide a sport that is consistently more competitive and compelling at all levels”.
What, then, might we say in answer to our opening question? Well, first, it must be conceded that we have simply taken jump racing’s pulse – a full medical examination would be necessary to make secure pronouncements. But it might be safe to conclude the following.
Jump racing, while present in fewer locations than in the past, is still to be found in seventeen jurisdictions spread across four continents, and staged at over 200 racetracks.
Nearly half of all jump races are run in Britain, with over 90% in Britain, Ireland or France.
In the past 20 years, the number of jump races has fallen, but only by 3.5%, from a little over 8,000 races to a little under that figure.
The pool of horses taking part has shrunk significantly, by around 18%, from over 23,000 to around 19,000.
Further, these horses are tending to run less slightly frequently, with aggregate starts in jump races falling by over 20%. The average jumper now makes 3.55 starts per season, rather than 3.7.
Field sizes have come under pressure world-wide, as a consequence. There are, on average, two fewer horses in each jumps race – 8.6 compared with 10.6 in 2004.
EMHF Update
Article by Paull Khan
This summer, to coincide with the Italian Derby, Italy’s Ministry of Agriculture (MASAF) and its Institute of Culture organised an event in Rome celebrating the role of the thoroughbred in culture. EMHF Secretary-General, Paull Khan was asked to speak on ‘the role of the thoroughbred in the development of human society.’ The text of his talk is repeated here.
I would like to start by commending MASAF and the Institute of Culture for conceiving of and delivering this event today. Because, in many ways, these are troubled times for our sport globally: the number of thoroughbreds foaled has fallen significantly over recent years, from over 123,000 20 years ago to around 86,000 today; just this year, racing will cease in Singapore, Macau and Greece, and our very social licence to operate – alongside that of other sports and pastimes that make use of animals – is being brought increasingly into question.
So there is no better time to shine a spotlight, for a change, on the enormous benefits that the thoroughbred has brought to human society in the relatively short time since its creation in England in the late-1700’s.
I could look at the big picture – for example, the overall economic impact of racing (which we have calculated at no less than 21 billion Euros per annum across Europe alone) – but instead, in an attempt to convey the very varied contribution that thoroughbreds can make to society, and with the ten minutes I have available to me, I am going to take three examples: of thoroughbred racing, first as a symbol of renewal and normalcy after conflict, secondly as a focus for unity and peace and finally as an economic and charitable powerhouse.
For my first example, I look to Libya. You will all remember how Libya descended into turmoil and civil war after Col. Gaddafi’s overthrow in 2011. War was raging in Tripoli as recently as July 2021. However, despite the chaos and conflict that has wracked the country, horseracing has staged a remarkable recovery. Seemingly at the very first races were being organised again. I liken it sometimes to those desert flowers which, after years of inactivity, at the first opportunity, bloom again. Today, there are several tracks that have not only been re-opened, but are being renovated and modernised, and one brand new track is under construction. Government has supported the sport’s funding generously, and racegoers have turned out in high numbers. Despite there being no betting, horseracing is second only to football in terms of attendances, (as in Britain, where I live). I firmly believe the reason for all this is that racing is a symbol of normalcy, and is seen to be by enlightened administrations. The Libyan Horseracing Authority is adopting a particularly socially enlightened approach – it has established the Social Solidarity Cup, which might be the first race meeting in the world designed especially around those with disabilities, special needs and autism spectrum disorders.
Secondly, I turn to Lebanon. Lebanon is a country of great religious diversity - however, for 15 years, from 1975 to 1990, some of you will remember, it was wracked by civil war. A ‘green line’ developed in Beirut, separating the Christian East from the Muslim West. And smack, bang on that green line was the racecourse. Two years into the war, it was decided to re-establish racing. And when they did, at the first race meeting, 12,000 people defied the dangers and went to the races. From then, rather than the racecourse becoming a no-go area, it actually became the only place where, for several years, people from opposite sides of the green line could meet each other, united in their love of the sport of racing. It became a symbol of the hope of national unity and of peaceful Christian/Muslim coexistence.
There’s a wonderful short film, a German-made film, on Youtube, which describes it very well. It’s called ‘Stories from No Man’s Land’ and I urge you to watch it. At one point, there’s the story of a former fighter who was ordered by his boss, near the start of the war, to plant a bomb in the racecourse buildings. He went to check the place out – ‘do a reccy’. He’d never been racing before, never seen how people react at the finish of a race. And he says: “suddenly everyone got up, Muslims and Christians together, and started waving their arms around, and then sat down”.
“I was troubled” he says, “all I saw were simple people, Muslims and Christians joined together”. He refused to carry out his mission – no bomb was ever planted on the course.
For several years, racing continued for most of the time. At the President’s request, race meetings took place during the worst of the civil war fighting – when the racing was on, the shooting would subside – only to start again once the spectators had gone home.
Extraordinarily, there was never any trouble at the racetrack, and the course was even used as the venue for peace talks.
In 1982 the Israeli invasion completely destroyed the stands. But, after the war was over, they were quickly rebuilt in the 90’s and racing started up again – much like in my first example of Libya.
Just because the war was over, it didn’t mean the threats to the racecourse were over. The civil authorities wanted to capitalise on its prime location – right in the centre of Beirut - and use it for a new presidential palace. But there was a concerted and spirited campaign to save the track, which attracted great public support, I dare say because it had become part of the fabric of society, symbolic of humanity’s better nature.
And finally, to Hong Kong.
The richest Racing Authority on earth is the Hong Kong Jockey Club. It is a quite remarkable organisation. As you know, Hong Kong is tiny – you could fit five Hong Kongs into Rome. It has only two racecourses. But its Jockey Club employs nearly 20,000 people and is in the top ten charity donors, not only in Hong Kong itself, not only in Asia – but in the world. The Jockey Club is Hong Kong’s biggest taxpayer.
In round terms, there are 37bn Euros bet with the Hong Kong Jockey Club. They take a little under 15% of that and, of their cut, they then give three-quarters to the state. And that amounts to 3.3bn Euros in tax and nearly a further billion Euros in charitable donations.
So when it says on its website: “The Hong Kong Jockey Club is a world-class racing club that acts continuously for the betterment of our society”, you might think that’s just marketing speak. But it is not. In the last month alone, for example, they have been able to make these announcements:
Jockey Club donates HK$ 720 million to help low-income families in transitional housing become self-reliant and Jockey Club Expands to five districts the scheme bridging the poverty divide through holistic support for disadvantaged children and families
And what is at the core, at the heart, of this behemoth? It is the thoroughbred. Hong Kong is, I feel, a great example for the world’s Governments. Governments can choose to establish other ways of raising charitable funds through gambling – such as lotteries. And, more broadly, they can elect to put in place a legislative and taxation framework that favours other modes of gaming – roulette, slot machines, etc. But what none of these arid forms of gambling can do is what the thoroughbred does – support an extensive network of related jobs, which, in most jurisdictions around the globe, are primarily in rural areas; boost those rural economies and bring to society generally a point of cohesion, a sense of shared celebration, a recognition of continuing a great historical tradition. So, I say: “Governments: if you support horseracing with a benign legal and financial framework, our sport will repay you, and repay society, many times over”.
It was Kemal Ataturk, the towering Turkish leader of a century ago - still revered by many in Turkey to this day - who said:
“Horseracing is a social need for modern societies”.
‘A social need for modern societies’….. I believe he was right.
A BUSY SUMMER FOR THE EMHF
This summer saw a succession of EMHF events. Here is a quick summary.
General Assembly – Copenhagen, Denmark
Our General Assembly took place in Copenhagen in June. For the Federation this was a first – and highly successful – visit to Denmark. In recent years, EMHF annual meetings have evolved into mini conferences, rather than traditional general assemblies and delegates were treated to a wide range of presentations.
Horse Racing Ireland CEO, Suzanne Eade, kicked off a discussion on sustainability and what it means for racing authorities by explaining the approach being taken in Ireland, as part of the HRI’s broader strategy.
Di Arbuthnot, (Chair of the International Forum for the Aftercare of Racehorses) outlined IFAR’s new membership-based model, under which interested organisations and individuals can show their support for aftercare by becoming a member or a supporter of IFAR and then and Teodor Sheytanov (Secretary-General of the European Equestrian Federation) discussed ways in which the thoroughbred and equestrian world’s could align in aftercare efforts.
Paull Khan (EMHF Secretary-General) summarised the results of a survey of EMHF members on their experience and awareness of illegal betting, before Brant Dunshea, BHA Chief Regulatory Officer and a member of the Asian Racing Federation’s Council on Anti-Illegal Betting and Related Financial Crime, spelt out the concerning implications of its growth for European racing.
Darragh O’Loughlin (CEO of the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board) gave a case study of collaboration between EMHF members, concerning a range of integrity initiatives.
The European Pony Racing Association had considered what those in charge of mainstream racing might do, in order that pony racing could best provide the stars of tomorrow. Paull Khan, as EPRA Chair, set out this ‘wish-list’.
Cathy McGlynn, (EMHF Political Advisor) summarised progress on the EU’s review of its animal welfare legislation and the continuing efforts of the EMHF’s Political & Legislative Committee in seeking to minimise the adverse unintended consequences of what is currently proposed.
Peter McNeile (Director of EMHF’s Official Ticketing Partner, Future Ticketing) explored recent advances in the ways in which racecourses are making use of customer data.
Finally, Paull Khan presented the results of the EMHF’s National Racing Survey, which were set out in the last issue of this magazine.
This was the third year of an arrangement whereby commercial organisations, relevant to racing in our region, are invited to join in the General Assembly and its social programme and, at their first attendance, make a short presentation to the delegates. What began with just three companies has expanded to 17 delegates from 12 companies. This year’s presentations - from European Horse Services, Steriline, Berlinger, Turftrax, Weatherbys and Cavago – underlined just how multi-faceted our industry is.
As last year, the General Assembly was followed by the EuroMed Stewards Conference, again organised by the British Horseracing Authority. Brant Dunshea chaired the gathering which, in just two years, has become a highly-valued event among the region’s Stewards and regulators.
And so it was that around 50 attendees were invited to the following day’s racing action. Klampenborg, on the northern outskirts of the capital, is one of European racing’s success stories. Bucking the general trend, attendances are buoyant and the demographic vibrant. It is perhaps only to be expected that the experience of racing at Denmark’s premier racecourse would be the very embodiment of its concept of hygge. With its architecturally pleasing stands, treed surroundings and proliferation of comfy chairs, it delivered a garden party atmosphere that will live long in the memory.
European Pony Racing Association Annual Meeting – Ascot, England
Following the first two annual meetings, in Budapest and Chantilly, the EPRA Annual Meeting swung into Ascot in July. Britain’s Pony Racing Authority (PRA) kindly hosted us in Ascot’s Berystede Hotel. As well as representatives from several European countries, we also welcomed - in a nod to the Eurovision Song Contest – Australia! Tracey O’Hara gave a fascinating account of how Pony Racing, under Pony Club Australia, which has only been in existence for little over a year, is developing fast. There are lessons to be learnt by all and we are delighted that Australia has become an Associate Member of the EPRA.
The following day allowed our visitors to see how Pony Racing is conducted in Britain, and what better venue than Ascot to showcase this? For the young riders, their experience is wonderful, from their course walk under the tutelage of dual Grand National-winning jockey coach, Carl Llewellyn, to donning real racing silks and mounting their ponies in the storied paddock, to the race itself and, for the winning rider, an interview in the winner’s enclosure, overlooked by the crowds and the towering stands. If they do not remember that for the rest of their lives, it would be a surprise.
Our party was royally looked after and our thanks go out to Howden Group, who generously made available their box, and to stalwart pony racing supporters, Richard and Dawn Prince, who provided the dinner.
Outgoing PRA Chief Executive, Clarissa Daly was made an Honorary Member of the EPRA - meaning that we will have the pleasure of seeing her at future annual meetings. Speaking of which, next year’s EPRA Meeting will be held at the unique ‘Nationaldagsgaloppen’ racing event that is staged in a park in central Stockholm on Swedish National Day – June 6th – in front of crowds of up to 50,000 people.
European Beach Racing Association – Loredo, Spain
Loredo and Laredo enjoy many similarities. Aside from just their names, both are resorts on Spain’s Cantabrian coast, (separated by less than 40 kilometers) and both have for many years staged official beach race meetings, featuring the Loredo and Laredo Derbies, respectively.
Since COVID, Laredo has, sadly, been unable to stage a meeting, although the signs are good that a return to action in 2025 may be on the cards. So, it has been left to Loredo to fly the Cantabrian Beach Racing flag. We were thrilled when Loredo offered to host our Seventh Annual Meeting. Grateful thanks are due to Antonio Sarabia, lynchpin of Cantabrian racing, from whom we learnt much about the history of beach racing in the region, and to Loredo Neighbourhood Council and Ribamontan al Mar City Council for their kind hospitality.
Sarabia explained that Beach Racing at Loredo would reach its 70th Anniversary in 2026. Initially it involved farmers with the carts they would also have used to transport their produce. It was in 1975 that races for thoroughbreds were first organised and in 1983 when they became Official races. Today, these races constitute a significant draw for local tourism - in 2019 a record crowd to date of 18,500 attended. Races are confined to Amateur Riders and the meetings are important events in the Gentlemen Riders' calendar.
This year's meeting was not without its challenges. Inclement weather forced organisers to amend the configuration of the track. The two thoroughbred races, of 1,500m/7.5f and 2,000m/1m 2f respectively, were to have been run round one and two bends respectively. However, in the event they were run over a straight course.
In addition, two Pony Races (the first for riders aged 8 to 11, the second for those aged 12 to 16) were run, together with a Pony Racing Challenge Match between two 13-year-old girls, considered stars of the future. Cantabrian Pony Racing has produced significant numbers of amateur and professional jockeys, trainers and owners.
European Parliament ‘Mission’ – Brussels, Belgium
This year being an election year for the European Parliament, 2024’s EMHF ‘Brussels Mission’ took on extra significance. To help maintain racing’s profile and influence in Europe’s corridors of power, we stage an annual visit to its Parliament and Commission to talk to the key decision-makers on the burning issues of the moment. Currently, this means the review of European animal welfare legislation and, most topically within that, welfare in transport. While, in the current proposals for the new legislation, vital exemptions from many of the administrative requirements have thankfully been secured for thoroughbreds travelling to race or for training, there is still much to do to convince the legislators of the need to extend those freedoms for breeding and sales travel.
All EMHF EU Member Countries are invited to send appropriate delegates to these ‘missions’, which are led by Paull Khan and arranged by the EMHF’s Political Advisor, Cathy McGlynn.
We were excited to see that, among the rookie MEP’s, is a certain Nina Carberry, the celebrated Irish Grand National-winning jockey – daughter of multiple Irish Champion Jump Jockey, Tommy Carberry and sister-in-law to another great champion, Ruby Walsh - with whom we had a most productive discussion.
Nina Carberry sits on the Transport and Tourism Committee - highly relevant to the current review. Another key Committee for this dossier is that for Agriculture and Rural Development, and we also met with former Irish Agriculture Minister, Barry Cowen, another new MEP.
The Missions allow us not only to meet with new 'movers and shakers', but also to build relations over time and we were delighted to meet up again with former EP First Vice-President, Mairead McGuinness and MEP's Sean Kelly and Billy Kelleher.
The EMHF delegation had a strong Irish flavour this year, with Horse Racing Ireland's Chief Executive Officer, Suzanne Eade, Equine Welfare & Bloodstock Director, John Osborne and Director of Communications & Marketing, Paula Cunniffe making the journey. The team also met with Pat O'Rourke, Advisor to Ciaran Mullooly, MEP and Kevin Foley-Friel, Agricultural Attache with the Irish Permanent Representation to the EU. These national permanent representations are an important group in the next phase of the review’s passage.
Tanguy Courtois, Head of Public Affairs for French racing, represented France and met with Céline Imart (EPP - France), Maria Noichl (S&D - Germany), and Valérie Deloge (Patriots - France), as well as the Permanent Representation of France.
Finally, Paull Khan and Tanguy Courtois joined EMHF Political and Legislative Committee Member and European Horse Network (EHN) Secretary-General, Florence Gras in an EHN planning meeting with MEP Horse Group Chair, Hilda Vautmans, MEP.
All in all, a packed and highly valuable series of meetings.
EMHF Racing Industry Survey
Article by Paull Khan
In this issue, we take a novel perspective on our region’s national racing industries. As well as looking at various measures of their scale, we will – perhaps for the first time – consider these in the context of the overall size, population and wealth of the countries in question.
Let us look at the big numbers first. Our region boasts over 300 racecourses staging thoroughbred racing, between them putting on nearly 5,000 races and running over 30,000 races for prize money of nearly €600M. These races are competed for by nearly 30,000 owners, 4,500 trainers and 4,300 jockeys. The average prize money across all 21 countries is – perhaps surprisingly – as high as circa €19,000 and the average field size a very respectable 9.1 (runners per race). It is also noteworthy that those horses which race average over five starts per year.
We produce over 27,000 thoroughbred foals – representing nearly one in three of the global foal crop.
Before looking at how these figures break down between the 21 countries, let us consider the context within which each racing industry exists: how big, how populous and how rich is each nation?
An early observation is the enormous disparity in their size. Our largest racing nation is not a factor of 9 bigger than our smallest, nor of 90, nor even 900. The Channel Islands could fit into Libya nearly 9000 times!
Turkey and Germany boast the highest human populations, some way ahead of Britain and France.
In terms of overall size of the national economy, Germany is some way ahead of Britain and France. But when we look at how this wealth is spread across the population, a very different picture emerges. The wealthiest average citizen is to be found in Norway, with Switzerland and Ireland filling the places.
With that backdrop, our respondents answered questions on the scale and nature of their racing in the following way.
France boasts twice as many thoroughbred tracks as any other country, and together with Britain, accounts for 60% of the region’s total. Five of our members – Channel Islands, Cyprus, Hungary, Netherlands and Norway have just a single active racecourse.
Many of the French tracks race infrequently and, when looking at the number of individual days’ racing offered, Britain is the clear winner, with nearly four meetings taking place every single day. It is a similar story with the number of races run.
As for total prize money on offer, Britain and France are well clear of the field, accounting between them for nearly 70% of the region’s overall pot.
But when it comes to average prize money per race, Britain (€21,527) drops to third behind both France (€29,098) and Ireland (€23,676).
All nations strive for significant average field sizes, in many cases looking to 8 as the magic number. It is interesting to note that the region as a whole comfortably exceeds that target – the EuroMed average being 9.2 runners. It might be expected that Ireland sits atop this table, but the fact that Morocco shares this lead, with Libya a close third, will surprise many.
The figures confirm Ireland’s numerical breeding dominance, its foal crop almost equating to that of France and Britain put together. A striking feature of these tables is Turkey’s high ranking on many measures. Foal crop is a case in point – Turkey now produces nearly four times as many thoroughbreds as either Germany or Italy. The country also makes a top-four spot in number of race days staged, number of races run and prize money offered. There is an argument to be made that Turkey should now be considered as being part of the ‘big four’ of EuroMed racing.
There has been much discussion in recent years, around the European Pattern Committee table and elsewhere, about the need for Europe to bolster its staying and sprint divisions. Countries were asked how many flat races they ran (a) at distances up to and including 1200m/6f (which is how, for the purpose of this exercise, we have defined ‘sprints’; (b) at distances between 2400m/12f up to 3200m/16f (which we have termed ‘Classic+); and (c) of 3200m/16F or longer (which we have called ‘long-distance’).
Britain stages more than double the sprints of any other country. Before one gets to either France or Ireland, one finds Turkey, Cyprus, Morocco, Italy and Libya.
On average, the region allocates 18% of our races to the sprinters. It is noteworthy – and a complete surprise to the author - that France appears right at the bottom of this particular table, with only 4.8% of its races being sprints.
Italy leads the way in running races in the ‘Classic+’ category. Here, the average allocation is 13.4%. While France (15.1%) is slightly above that, both Ireland (6.6%) and Britain (6.2%) are well below this figure.
But when it comes to true long-distance races, Britain is a clear leader, staging more than half of those in the whole region. Half of our countries do not stage a single long-distance race. Percentage-wise, both Britain and Ireland give the same exposure to long-distance races, at 1.2% of the total.
So, to return to the question of relativity, let us look first at which countries have the highest and lowest density of racecourses. Specifically, we’ve calculated how many tracks each country has for every 100,000sq.km. Norway, with its sole racecourse, has the lowest density, with only one-third of a racetrack in each of its 100,000sq.kms. The figures reveal that Ireland, Britain and France have a remarkably similar racecourse density, posting figures of 24, 26 and 31 tracks/100,000sq.km respectively. But the runaway winner in this category is little Channel Islands. For France to match its racecourse density, it would need to build more than 2,500 new racecourses!
We remarked earlier on Ireland’s preeminent position in the breeding sector. But when one takes the human population into account, the findings are staggering. If one looks at the number of thoroughbreds born annually per million of the population, Britain has 68 foals, France 88 foals, Cyprus is a surprise second with 121 foals, but Ireland is on a different planet, with 1367.
Finally, we ask how each country’s prize money allocation stacks up against its national wealth. In other words, how much of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) does it spend on prize money for races? The figure we’ve chosen is annual prize money in Euros per $bn GDP. France and Britain come out near identical in third and fourth with €72K and €71K respectively. Ireland is comfortably ahead with €120K. But the runaway winner, remarkably, is Cyprus, which boasts £235K in prize money for every $bn of their national GDP.
And so, the answers to the quiz: Q1 You could fit 8,886 Channel Islands into Libya. Q2 Ireland and Morocco boast the highest average field sizes. Q3 France has the lowest percentage of its races that are sprints. Q4 Slovakia has the highest percentage of its races that are 2m/3200m+. Q5 Channel Isles has the most racecourses per square km. Q6 Ireland breeds the most thoroughbreds per million of its population. Q7 Cyprus devotes the highest proportion of its national wealth to prize money. Well done if you got those right!
Sources: Country size data - Nationsonline.org (except Channel Islands, Wikipedia); Population data – worldpopulationreview,com (except Northern Ireland and Channel Islands, Wikipedia); GDP data – worldometers.info (except Northern Ireland, Channel Islands, Wikipedia); Exchange Rates – Xe Currency Converter. All other data – the Racing Authorities themselves.
A Greek Racing Tragedy
Article by Paull Khan
It was a bitter blow when, on January 31st, 2024, Horse Races SA, the Company which had been running racing at Greece’s sole racetrack for the past eight years, announced its immediate closure. The news followed hot on the heels of similar events in Singapore and Macau and underlined the fragility of our sport in many parts of the world.
The announcement referred to the Concession Agreement, between the Greek Government and Horse Racing SA’s parent Company, the Czech-owned O.P.A.P., under which Horse Races SA leased the site of Athens’ Markopoulo Racecourse and was given the exclusive right to stage races there. But, if the numbers of horses in training fell below 300, it was able to terminate the arrangement. At the time of the announcement, the number had dwindled to 172. According to the press release, this was despite investment of over €32 million by the Company, whose losses over the period of operation were given as €103 million.
The agreement also gave OPAP the concession to offer pari-mutuel betting, not only on Greek races, but on horseracing world-wide, and the Company clarified that they would continue to offer betting on foreign racing.
By the time of publication, it is understood that the racecourse will have been handed back to the liquidators. OPAP has offered subsidies on the costs of travelling the horses from their previous home in the racecourse stables to other Greek destinations. An appeal to neighbouring Cyprus, to absorb many of them, is understood to have fallen foul of Cypriot racing’s policy only to accept unraced animals. Some have already moved to Poland and Romania, but the future for many is unclear. The EMHF has written to the Greek Government, seeking comfort that due consideration is given to Greek racing’s participants, both equine and human.
The EMHF has also offered to assist in matching jockeys, work-riders and others, who find themselves suddenly without employment, with member Racing Authorities who report difficulties in sourcing experienced and competent staff.
The fortunes of Greek racing have yo-yoed through the course of this century. The previous track, Faliron, was situated at a coastal site, within easy range of Athens centre. It was vibrant, housing over 1,700 horses and attracted crowds of 15,000. After the Athens Olympics, the venue for the equestrian events – some 37 kms distant – became Markopoulo Racecourse. While its grandstand was, and remains, impressive, attracting crowds to Markopoulo has always been an uphill struggle. The economic crisis of 2008 came as a hammer blow, and by 2015, when the globe-trotting Australian administrator, Fin Powrie, was appointed as Horse Races SA’s Director of Racing, numbers of horses in training had dwindled to below the key figure of 300. By the time of Powrie’s departure – for Malaysia – those numbers had climbed again, exceeding 500.
“I was given a pretty free hand when it came to the racing product”, recalls Powrie. “We introduced a number of initiatives, including the supplemented purchase of good quality young horses from Tattersalls, ratings-based handicapping, inclusion on the International Cataloguing Standards ‘Blue Book’ and membership of the EMHF, all of which helped to raise the profile of the sport”.
So where, in his view, did things go wrong? “The decline in horses really set in around 2020. In 2019, the then Government allowed Horse Races SA to merge with its parent Company, OPAP. This, in turn, would have allowed the offsetting of the racecourse’s losses and significant rental commitments against the overall business’s tax. However, shortly after that the Government changed, and the new Government revoked that law. Development plans for diversifying the usage of the racecourse’s land also fell by the wayside.
“It was then a downward spiral – field sizes dropped, as did prize money, news and media coverage, which was never grand, simply ceased. People probably thought, ‘it’s a great big grandstand, it’s cold, it’s ordinary, there’s nothing else there for the kids’. And COVID didn’t help at all, of course”.
The concession only granted the exclusive right to stage racing at Markpolulo. It was, and still is, perfectly possible for others to start up racing at another Greek venue. However, this may be a big ask given the current climate of public opinion. The view has been expressed that public reaction to this closure has been very different from that which would have been the case a generation ago, with many taking the view: ‘maybe that’s just as well’. Powrie concludes “Personally, I doubt whether we will see the resuscitation of professional racing at some other track in the country”.
The international racing community must hope that this is not the case and that, somehow, somewhere, the sport’s flame can flicker once again in Greece.
2023 Champion Trainer profiles - Peter Schiergen (Germany) / Kadir Baltaci (Turkey) / Claudia Erni (Switzerland)
NATIONAL CHAMPION TRAINERS IN FOCUS
In this issue, we take a look at some more of Europe’s champion national trainers, courtesy of the latest data compiled by Dr Marian Surda, doyen of Slovakian racing.
A notable feature of the tables, when comparing the last two years, is the infrequency of trainers retaining their crowns. Only in 7 of the 18 countries that featured in both years did this happen (France, Jean-Claude Rouget; Ireland, Aidan O’Brien; Spain, Guillermo Arizkorreta; Germany, Peter Schiergen; Norway, Niels Petersen and Greece, Charalambos Charalambus). The baton changed in all other countries, including in Great Britain, the country whose trainer earned the most money, for the second year running. This time, that trainer was the father and son combination of John and Thady Gosden, who wrested the title from Charlie Appleby.
Among the jockeys, Maxim Guyon, in France and William Buick, in Britain headed the table once again. But the dominance of the big three countries – France, Britain and Ireland – was interrupted by an extraordinary performance by Turkey’s Champion, 20-year-old Vedat Abis, who clocked up a remarkable 283 wins – far more than any of his fellow champions.
Our featured trainers this year are Peter Schiergen (Germany / 5th in the table), Kadir Baltaci (Turkey / 6th) and Claudia Erni (Switzerland / 11th).
PETER SCHIERGEN
The name of Peter Schiergen is a familiar one across the European racing scene and beyond, with Group wins in France, Britain, Italy and Dubai as well as his native Germany. At time of writing, that Group race tally stands at 199. Champion Trainer in Germany no fewer than eight times (2002, 2005, 2006, 2013, 2015, 2021, 2022 and 2023), with six German Derby wins to his name (Boreal 2001, Schiaparelli 2006, Kamsin 2008, Lucky Speed 2013, Nutan 2015 and Sammarco 2022), his crowning single achievement remains his Arc win with Danedream in 2011.
But before becoming one of the most successful German trainers of recent generations, Peter had been one of his country’s most successful jockeys. His outstanding record in the saddle encompassed five jockeys’ championships – 1992 to 1996 – and nearly 1500 wins, including a record 271 successes in 1995.
I asked Peter about his journey into racing and what had led to his becoming a jockey at the age of 16. “I always wanted to become a show jumper. My plan was just to do my apprenticeship in racing and after that to go back to show jumping. But it turned out differently and I had quite a bit of success as an apprentice and stayed in the game”.
The transition from jockey to trainer (taking over from fellow legend Heinz Jentzsch in 1998) was made at a younger age – just 33 – than is often the case.
“The opportunity came up to take over from Heinz Jentsch. I knew that this was a huge chance and even though it was quite early I decided to take over. I started in 1998 in Köln and still train there today. In 2009 we built a new stable next to the old one so that’s really the main thing that has changed”.
“I had a great time as a jockey and was five consecutive years champion jockey and broke the European record in 1995. But the owners didn’t give me the chance to ride in the big races abroad such as Lando in the Japan Cup. This is something I don’t want to happen to my stable jockeys and therefore I use them both in Germany and abroad.
What does Schiergen consider the pros and cons of training on the track? “The horses are used to the racetrack. A great benefit is that it’s easier to get staff. Furthermore, the racecourse is in charge of preparing the training facilities. A disadvantage would be that we have certain times at which we must be at the track, as there are many trainers who use the facilities. On a private track you have more peace”.
“The team consists of 25 staff. It gets more and more difficult to get good staff and competent work riders. We have a great team and many people have been staff members for many years. There are plenty of Germans working with us. Other than Germans, most of the staff tend to be from the eastern European countries such as Poland, Czech Republic, Bulgaria etc.”.
When asked which trainer he admires the most, Schiergen replies: “I didn’t have a jockey I admired the most when I was a jockey, and now, as a trainer, neither do I have a trainer I would single out as admiring. I look at many others and try to take the best of each”.
“The state of racing in Germany isn’t great, but there are many ambitious people who are trying to bring the sport back to better times. It’s difficult with social change and especially the animal welfare movement. Racing’s lobby sometimes appears to be too weak to work against these forces. Therefore, we need a change. It’s difficult to compare our racing jurisdiction to other countries. We don’t have training facilities such as Newmarket or Chantilly.”
As well as the 200 Group race milestone, Schiergen has another in his sights. Ending last year on 1,907 wins on the flat and 31 over jumps, it is a real possibility that he could send out his 2,000th winner this year. “Certainly is a milestone and a great achievement. But it is more important to win big races.”
KADIR BALTACI
Kadir Baltaci’s 31 wins last year came at the hooves of just 37 individual starters (his stable currently houses just 30 horses in training). His tally included seven domestic Group races, including three at Group 1.
From Baltaci’s base in Turkey’s capital, Ankara, it is a long haul to the tracks where he does most of his racing: a 5-hour drive north-west takes him to the nation’s racing headquarters, Veliefendi in Istanbul, or a lengthier run yet in the opposite direction finds the track in Adana.
“I was born in Adana”, Baltaci begins. “I lived in Adana until 2010. Adana is my city, my place but Ankara is now ‘my city’ and ‘my place’, where I live with my two sons and my wife. Though I train my horses here, when they are ready to race I mostly prefer to run in Istanbul because of the classic and other big races that are run at Veliefendi racecourse”.
“I began as an Assistant Trainer in 2011. After spending seven seasons as an Assistant, I started training in my own right, in 2017.
“When I was at high school, I was best friends with the son of the owner of the famous Turkish-Arabian horse Nurhat. I often went with my friend to (Adana’s) Yesiloba Racecourse to see the horse. As a child, I loved the horses. I used to watch racing on the television, especially the classic and GAZI races.
“Workwise, I started out working at my father's painting company, but it collapsed. I then worked as a driver for one of my now-owners, Mr Fedai Kahraman. When working as his driver, he often used to send me to the races at Ankara, in order to help his trainer out. After a couple of years, he asked me if I would move to the track to assist the trainer. I said ‘yes’ and that’s how my journey started.
“I don’t have a private training centre. Like all trainers in Turkey, I must be based at one of the Jockey Club racecourses. We chose Ankara for the wintertime: because the racetrack is empty then, I can easily prepare my horses.
“I have 20 people working for me. My staff are all Turkish. We did try employees of other nationalities, but I did not like the way they worked. Most of my crew have been with me since I started training. Because we have been working together for so long, it is a great relief to me that they know exactly what I want. It is hard to find new people to take care of horses. Really hard. I have five exercise riders. You can find exercise riders very easily, but most are not proficient. The Jockey Club of Turkey trains exercise riders. One of mine came from there – he graduated last year. But they are young and need time to learn the job properly. We have also got a broader problem with finding stable staff generally. Not only me, other trainers have the same problem”.
To date, Baltaci has ventured abroad to race but once, sending a runner to Meydan to contest the Grade 2 Cape Verdi and Ballanchine Stakes. “I believe my horses will run more often abroad. My big ambition is to run in - and win - a European Classic.
“We are not well educated about training practices in other countries, so I will not make comparisons. All I would say is that many are lucky to have private training facilities. I think our trainers probably spend more time in nursing horses which have suffered minor injuries back into racing”.
Baltaci places much hope for the future in Serdal Adali, Adana-born President of the Turkish Jockey Club. “Mr Serdal Adali is spending time ensuring a better future for us. I believe he will succeed. Then my countrymen will be more interested in racing outside of Turkey.”
Balaci’s strike rate, particularly at the top level, is impressive indeed, but he is modest when asked to explain the secret of his success. “It’s down to the efforts of everyone, from my horse owner to my team. That's why I can't give any specific reasons for my success. I have 30 in training right now. Thirty different horses, which all act differently, and that is why I train each horse differently”.
CLAUDIA ERNI
Over in Switzerland, there has seen a changing of the guard. After several years of domination by Miro Weiss, there is a new woman in town. Step forward, Claudia Erni. Her yard of 20 horses – ranging from 2yo’s to a 10yo sprinter and stayer, ranks fourth by size within the country, but in 2023 punched above its weight to capture the championship.
“I grew up with horses. My father had a riding school. I took part in some national dressage competitions. My father’s girlfriend was in racing, and this was how I found my way into racing. I rode as an amateur, both on the flat and over jumps, and also held an amateur training license before taking out my professional trainer’s licence in 2006”.
“I am also a physical therapist and still devote two afternoons a week to working in this profession”.
Erni trains from Switzerland’s westernmost racetrack, Avenches, south of Lake Neuchatel. This impressive complex (a good idea of which can be gleaned from www.iena.ch), extends to 140 hectares/350 acres and accommodates multiple equine disciplines. It is important to the finances of Swiss racing, many of its race days being taken by the French betting operator, PMU.
“It is really nice to train here. We have a lot of space. We have two tracks of 1600m and 1800m circumference, with paddocks and a horse-walker. And I am almost alone here! At present, I have four employees, from France, Switzerland and Chechia. I do find it difficult to find good riders. For so many, money is more important than passion - sad, but that’s how it is”.
“My owners have been in the business for a long time. It is difficult to find young owners. But I am fortunate, in that mine came to me – I didn’t have to go looking for them!”
“I often race in France, Germany and Italy, when the owners allow it. I love Longchamp. We are very close to France – for example, it takes just three hours to reach Lyon.”
And what of the outlook for the sport in her country? “As in every country, racing in Switzerland is getting harder. It is harder to find sponsors and new owners, and the number of racehorses is reducing. The Swiss racing authority is trying to find ways to increase the popularity of the sport. Maybe, jockeys will be prevented in future from using the whip?”
Updates from the EMHF and we learn about Europe's latest beach racecourse - Zahara de los Atunes
Article by Paull Khan
The European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation first started providing regular articles for European Trainer back in 2016. I thought, after eight years, it was time to have a look ‘under the bonnet’ of the federation, to see how it works.
EXECUTIVE COUNCIL MEETING, MADRID, SPAIN OCTOBER 14th
The Executive Council of the EMHF comprises nine members, elected by our General Assembly from among its members. The ‘ExCo’ sets the policy tone of the federation, agrees its budget and what the membership fees should be, etc. ExCo members elect, from amongst their own number, the EMHF’s Chair and its three Vice-Chairs.
Brian Kavanagh, now CEO of The Curragh Racecourse and formerly CEO of Horse Racing Ireland, has held the position of EMHF Chair since its inception, in 2010. Brian has indicated that he will stand down at the end of his current term, in mid-2025.
Your correspondent has served as the EMHF’s Secretary-General since 2012. There are no employees, although we do receive valuable help from Horse Racing Ireland, which provides resources for invoicing and handling the Federation’s finances.
Our Vice-Chairs are Rudiger Schmanns, Racing Director at Deutsche Galopp, representing EU countries, Julie Harrington, CEO at the British Horseracing Authority, representing non-EU European countries and Omar Skalli, serving for Mediterranean and Other countries. Rudiger and Omar are, like Brian, founding members of the ExCo.
The other members of the ExCo represent France (Henri Pouret), Poland (Jakub Kasprzak), Norway (Liv Kristiansen), Spain (Paulino Ojanguren Saez) and the Channel Islands, whose Jonathan Perree, in May, became the only person to be re-elected back on to the council, having also served between 2016 and 2019. Three countries – France, Great Britain and Ireland, enjoy automatic representation within ExCo. The other six ExCo places are filled by process of election.
ExCo deliberations span the full range of the responsibilities of our member Racing Authorities – governance, regulation, marketing, financial, legal, social, etc. Specific reports are received from the EMHF’s standing Political and Legislative Committee, together with the committees which sit within the EMHF umbrella – the European Pattern Committee (EPC) and European Horserace Scientific Liaison Committee (EHSLC). The EMHF has also created two special interest associations, the European Beach Racing Association and the European Pony Racing Association.
Much of the Political and Legislative Committee’s work concerns keeping alert to forthcoming legislation, whether within the EU or elsewhere, which may have a bearing on racing. Very often, this centres on the potential unintended consequences of changes which are being suggested with the best intentions. For example, animal health and welfare laws which are drafted with farm animals in mind and are not suited to horses. It was in this context that the EMHF led a delegation to Brussels in the summer, to impress upon policy-makers a number of potential pitfalls in the European Commission’s review of Welfare in Transport.
The European Pattern Committee’s work is not limited to deciding which races across Europe qualify as Group 1, 2, 3 or Listed. The EPC is constantly alive to trends, identifying any areas where the quality of European racing may be under threat or in decline – staying races, perhaps - and agreeing race planning policy initiatives designed to address these by influencing, over time, the behaviour of owners, breeders or trainers.
Doping and medication control sit at the core of the EHSLC’s remit, whether in the detection of substances prohibited at all times, or in the regulation of those therapeutic substances which need to be controlled. Alongside this, increasingly being raised are matters relating to horse welfare more widely and on which a pan-European response and approach is sought. The Chief Veterinary Officers of the major European Racing Authorities sit on the EHSLC and therefore steps are being taken to expand its brief to cover such issues.
At our most recent ExCo Meeting, which took place on October 14th in Madrid, we received a presentation on the report recently published by Horse Racing Ireland, in conjunction with Deloitte, ‘Social and Economic Impact on Irish Breeding and Racing, 2023’. As its title implied, this study took a broader view than the previous HRI/Deloitte report had done – not simply looking at economic factors, but also identifying the considerable and varied social benefits that racing brings, especially to those living in rural areas. This message had resonated strongly in Irish political circles and it was felt that this approach could profitably be replicated by other countries.
At each meeting, the ExCo agrees the shape of the EMHF’s educational programme over the coming twelve months. Last year featured two very successful events: an inaugural EuroMed Stewards’ Conference, hosted by the British Horseracing Authority, and a seminar on Racecourse Surface Management hosted by France Galop. It was decided to repeat the former in Copenhagen in June, where we will be holding our 2024 General Assembly, and to hold a seminar on Starting and Judging Procedures, led by the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board.
The ExCo also seeks to identify which of the pressing issues facing racing could most usefully be focused on at our General Assembly. It was agreed that this year there should be sessions devoted to climate change and sustainability in relation to our sector, as well as the growing threat of illegal betting.
After the business was over, ExCo members were treated to a day’s racing at Spain’s premier track. La Zarzuela impressed on many levels. The luxuriant grass of the turf track belied the drought that had afflicted the region in recent months. The architecture of the gleaming white grandstand is striking, with its arched windows and billowing roof. The demographic was family-orientated, with little peacockery on show. Trees are plentiful, and the footprint of the track is such that there is space for a decent-sized crowd to spread out in the varied outdoor areas provided. And the top floor of the grandstand is now home to a series of airy hospitality areas, with comfy seating and a vibe which is less like a typical racecourse box and more akin to a chilled roof-top bar. All in all, a more than agreeable racing experience.
EUROPE’S YOUNGEST BEACH RACECOURSE: ZAHARA DE LOS ATUNES
The ExCo also receives reports from its two special interest associations, the European Pony Racing Association and the European Beach Racing Association (EBRA). But the latter’s annual meeting was held a couple of weeks after the ExCo – hence this separate bulletin.
The clue is in the name – Zahara de los Atunes is a small town dominated by a large fish! On hiring a car at Malaga airport, en route to this year’s annual EBRA meeting, the woman sorting the paperwork exclaimed jealousy: ‘Oh, you’re going to Zahara. You MUST try the red tuna!’.
‘Red tuna’ in this instance refers, somewhat confusingly, to the Atlantic Bluefin tuna – a prized goliath of the sea, averaging around 6.5 feet/2 metres in length and 550lbs / 250kgs in weight, whose lifespan, at 40 years, is greater than that of a racehorse. Born in the Mediterranean, they then venture out into the broad expanses of the Atlantic, before returning to breed. And, just as they sweep, as they must, through the narrow gap between ocean and sea - the Straits of Gibraltar – there, waiting for them, are the good fishermen of Zahara. They still employ the ancient and more eco-friendly ‘almadraba’ fishing technique, involving a complicated sequence of nets, strategically positioned, the gauge of which allows the younger fish to proceed, whilst trapping those of a certain size and maturity.
The influence and importance of the tuna to the town is all-pervasive. But, for one weekend of the year – the last weekend in October – the focus now moves from fish to thoroughbred. Because the vast strand which stretches both to the north and the south of the resort then becomes home to Europe’s newest official Beach Racecourse and to the staging of the Gran Premio de Zahara.
This is still a very young tradition, with nothing like the rich history of Zahara’s celebrated beach racing neighbour, Sanlúcar de Barrameda, which sits just 100 kms north up the Costa de la Luz, the other side of Cadiz. Sanlucar, which stages six days of racing and partying in the high summer, and which hosted the EBRA in 2019, is approaching its 180th anniversary, no less.
That year – 2019 – Zahara dipped its toe into the sea of beach racing, holding some unofficial exhibition races. But then COVID struck and three years passed before the first official races, (for thoroughbreds and held under the auspices of the Spanish Jockey Club), were run at Zahara. So, 2023 was, to all intents and purposes, ‘Year 2’ in an initiative – sponsored in part by Andalucia Tourism - designed to extend the tourist season, from its previous closure in early-October, for a few more precious and profitable weeks.
Progress over just these two years has been remarkable and testimony to its creator and driving force Pio Gonzales. It already has the feel of an embedded community event. Some 4,500 spectators lined the temporary barriers to watch the races, which were both live-streamed and covered by local television. “Beach Racing has been central to our success in keeping Zahara open for business for longer”, explains Gaspar Castro Valencia, Chair of the Zahara Beach Races Association. “We have just 1,300 inhabitants, but this year there were still 12,200 people here for the Gran Premio de Zahara weekend when, previously, the hotels and restaurants would have been closed. It has been an economic engine for the region. The presence of the European Beach Racing Association further helped to position Zahara, and Andalucia more widely, as an international tourist destination.”
The three thoroughbred races were interspersed with exhibition races, including one pony race for children, featuring a staggered starting-point based on the rider’s age. Two of the main races were over 1500m /7.5f, and the Gran Premio itself over 2000m /10f. Zahara is therefore noteworthy, among the world’s racecourses, in boasting - with Newmarket’s Rowley Mile – a straight 2000m / 10 furlongs! Starter numbers were modest, but included participants bred in France, Great Britain, Ireland and USA. The Gran Premio had the distinction of including Legionario (GB), a Listed Race winner in France the previous year, trained by the Duke of Alburquerque and coming to the sands off the back of a run in a €135K race at Meydan. The intention was to use Zahara as a stepping stone to the International races in Morocco the following month but, sadly, Legionario failed to fire in the race and the plan was abandoned.
Zahara – recently awarded the accolade as one of the ‘Magical Villages of Spain’ - was certainly a hit with the EBRA delegates. Apart from the tuna and the fish restaurants that abound, the village is famed for its live music, and the festival weekend has cleverly brought the jazz and racing worlds together. The Jazzahara Music Festival took place in an atmospheric al fresco setting, surrounded by the towering ancient walls of the Palacio de Pilas, former residence of the Dukes of Medina Sidonia which doubled up as a defence against pirates and a place in which to store the nets of the almadraba. And if your view of tuna is (as was mine) sullied by the canned variety, the Zaharan version is a culinary revelation! The number of different, sumptuous ways in which the fish was presented in the hospitality tents during racing was something to experience.
The additional equestrian attraction of a horse-ball tournament completed the entertainment. Horse-ball requires - of both the horses and their riders - extraordinary agility, and the Thoroughbred has proven wonderfully adept. Many of the horses on show were ex-racehorses, enjoying a second career.
The EBRA meeting received a presentation from Stefan Gast, creator of the vision of Pegasus Land - an ambitious new high-end, equine-focused development in Portugal. Part of that vision is to establish Beach Racing on the expansive and fashionable Comparta Beach, just south of Lisbon and the EBRA stands ready to give advice and share its members’ experiences and expertise.
It is to be hoped that Portugal will embrace the initiative. After all, in neighbouring Spain, Sanlucar and Zahara provide compelling evidence of beach racing’s enormous potential to enhance a coastal area’s touristic appeal and boost the local economy.
Look out for the dates of the 2024 European Beach Racing Fixture List, which will be displayed, when decided, at www.euromedracing.eu/beach-racing. Pop them in your diaries for a holiday or weekend away.
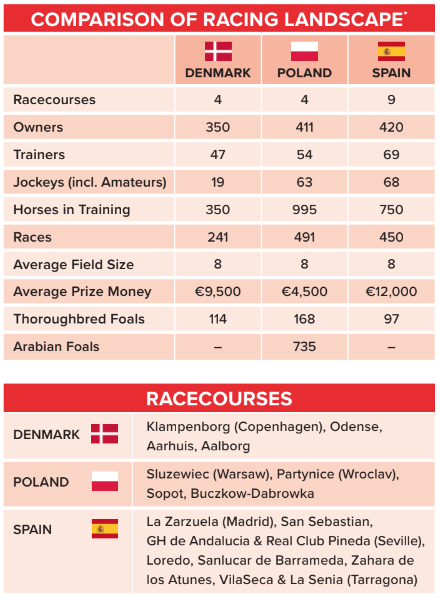
Smaller nations - the challenges facing trainers in Denmark, Poland and Spain
In the last issue, we featured a table of champion trainers and jockeys across Europe, compiled by Slovakia’s Dr Marian Surda. In this one, we have selected three of those champion trainers—those of Denmark, Poland and Spain—and tried to find out a little more about them and what it is like to be at the top of the training tree in their respective countries. While there is plenty of positivity and success to report, the challenges of sustaining viable businesses in the ‘smaller’ racing nations of our region, even for those at the top of their profession, are evident. It is a salutary finding that two of the three are looking to move on from the countries in which they have made their names.
Of our chosen trio, Guillermo Arizkorreta was the most highly ranked (by earnings), finishing 7th of 19 with earnings of €886,250 achieved through 61 winners at a strike rate of 19.3%. Niels Petersen not only finished 9th with his €311,537 in Denmark, but he also finished 8th as champion in Norway, with a further €443,856. And Cornelia ‘Conny’ Fraisl, one of only two females on the list, came in at No 14, earning €131,791 from her 50 wins in Poland.There are many similarities between the three. All happen to be of a similar ‘vintage’, being in their late 40’s or 50’s.
Denmark has the fewest horses in training but has ready access to those trained in neighbouring Sweden and Norway. The number of trainers among whom these horses are divided are roughly comparable, as are the numbers of their owners. There is some disparity in prize money, with Poland some way adrift of the other two countries. None has a thriving thoroughbred breeding industry, producing limited numbers of foals and therefore relying on foreign-bred imports and foreign-trained runners to achieve the near-identical average field sizes of eight runners per race.
Denmark has one thoroughbred-only track (Copenhagen’s Klampenborg) and three dual gallop and trotting courses. In Poland, Sluzewiec—the main track at the country’s capital—is joined by three others, including Wroclav (where most Polish jump races are run) and the seaside track at Sopot. Spain has four traditional tracks, headed by La Zarzuela in Madrid and, in addition, has three beach racecourses and two ‘pop-up’ tracks.
NIELS PETERSEN
Niels Petersen can claim a unique achievement among current European trainers, in that he is Champion Trainer not only in Denmark, but also in Norway. While Petersen was born and raised in Denmark, he has lived in Norway for the past 25 years, from which base he has stewarded a stellar training career. He has earned the title of multiple champion trainer in all three Scandinavian countries, with combined annual prize money often exceeding €1M and peaking at around €1.7M. Over the years, he has garnered 788 winners in Scandinavia, at a strike rate of around 16%.
Petersen is a prolific winner of Scandinavia’s richest race, the Group III Stockholm Cup International. Square de Luynes ran up a hat-trick of wins.from 2019 to 2021, and Bank of Burden was a four-time victor in a long career. “My most consistent horse was probably Bank of Burden, but my best horse has been Square du Luynes. The Racing Post called him ‘Frankel of the Fjords’”!
Asked for his view of the best trainers in Europe, he says, “People like to say it’s a numbers game, and of course it is, and I know they have the firepower; but the way Aiden O’Brien and John Gosden place their horses, and the level they maintain year after year is just amazing and fantastic to watch. And I greatly admire Karl Burke. To have bounced back and actually raised his game, as he has, after all he’s been through…”.
As for the riders: “Frankie Dettori is special, of course, and I think William Buick, whom I know very well, is a fantastic jockey”. And turning to racetracks: “Ascot and Longchamp are absolutely fantastic tracks, and here in Scandinavia, Bro Park is very level and fair”.
Petersen’s move to Norway was by way of circumstance, not planning. Having completed his education and military service, he worked in Baden-Baden, (alongside friends who included jockey William Buick’s father) for a couple of years, before returning to his homeland, where he suffered a serious riding accident. Forced to seek work opportunities which did not involve riding, his knowledge of the German language came in handy, and he was asked to accompany Scandinavian-trained horses when they raced in Germany. There he met a Norwegian trainer who invited Petersen to join him in Norway to help train his jump horses.
Last year and the year before, Petersen operated a satellite yard in Denmark, (just as once he did also in Sweden). Around 15 of his 55 horses were based at Klampenborg racecourse, and in both those years he claimed the Danish championship. However, despite that success, adverse exchange rate movements have led him to abandon the Danish base. “The Danish customers actually preferred to put the horse up with me in Norway. I haven’t lost any clients, and all their horses I have with me in Norway now.”
Petersen is quick to praise the integrated race planning across the Scandinavian nations, making it practicable for trainers to map out campaigns for their horses. So, for example “if you have an outstanding miler, you can target all the big mile races, more or less.”
Securing owners in any one country is challenging enough—how does Petersen approach the task of finding owners in three countries? He is clear that the trainer’s job is not simply to train the horses—the social component is also vitally important. For example, the path to Dubai for its Carnival is a well-trod one—its purpose for Petersen being as much to enrich social relations with and amongst his owners as the pursuit of prize money.
“I’ve got to make people enjoy the hobby I can provide them with. You do sacrifice a lot of time in doing that. But when you’ve sat on the beach and shared a bottle of wine in your swimming trunks, you become better friends!”
The travel and the socialising place a premium on having excellent staff back at base and has been fortunate to have had a long-standing assistant in the business in the shape of his elder sister. “I make sure that my staff are well paid, and I’m strict in observing proper working hours. It has become more difficult to find good staff, but word of mouth has ensured we have an excellent team, including a number from South America”.
Petersen has noticed a reduction in horses in training in all three countries. “I’m a bit pessimistic as to the future of racing here, especially in Norway, because our government is not supporting the industry at all. It classifies it as a hobby and, unlike in Sweden and Denmark and elsewhere, you cannot own horses as part of a business. It means owners have to pay 25% VAT on top of imports, which they can’t get back.”
Dubai’s allure is, of course, all the greater in the contrast it provides to the long, harsh Scandinavian winters. Petersen rues the fact that, from November to April, the Scandinavian climate renders virtually impossible the effective preparation of horses and, despite his huge success there, he has an eye out for opportunities abroad. “I would like to say I’m not looking for something outside, but I am. I live and breathe Scandinavian racing, but do I see myself here in five years’ time? I don’t think so. I don't see myself being here in five years’ time. I'm only 51 years old—not even at my peak—and I want the opportunity to challenge myself where I know I should be: on the bigger international scene”.
Until then, Scandinavia has given Petersen many special memories. What was his best day? “In Denmark, on Derby Day 2021, I had runners in seven races, and I won all seven of them!” If Square de Luynes was ‘Frankel of the Fjords’, then, after that ‘magnificent seven’, one could almost be forgiven for dubbing Niels Petersen ‘Frankie of the Fjords’.
CONNY FRAISL
Fraisl’s rise to the top in Poland has been meteoric. Her first year with a public trainer’s licence was as recent as 2020, when, with 44 winners, she finished second in the trainers’ table. Two years later, she was crowned Champion, with 50 winners. Fraisl is alone among our trio in concentrating almost exclusively on Arabian, rather than thoroughbred racing.
“I was born in beautiful Salzburg, Austria”, she explains. “My grandparents had a little farm and, when I was three, my dad bought me my first pony. It was a ‘typical’ stubborn Shetland Pony; and once I’d landed on the ground several times, I asked my dad to ‘sell this pony and buy me a guinea pig’!”
But the lure of riding returned a decade later. “Close to the place I lived, there was a training stable for trotters where I spent every free afternoon, all my holidays from the age of 13. Racing always was fascinating for me. Flat racing In particular but, due to the fact that there was no flat racing stable in my area, I stayed the next seven years with trotters. But I always had an eye on flat racing and, in 1996, when I moved from Salzburg to Vienna, I was finally close to a racetrack where regular flat races were held. So, I made contact with one of the trainers, started to ride regularly in daily training there, gained my amateur licence and bought my first own racehorse.”
“I had the possibility of riding work in Florida for several weeks, and I could learn a lot about starting young horses there. During my earlier days in the trotting stable, I learned a lot about intensity of training, interval training, feeding and the general needs of racehorses”.
As an amateur, Fraisl notched up around 25 winners in Austria and Hungary, where she rode for two seasons for different trainers. Turning professional in 2006, she has amassed 208 winners in the saddle to date, riding in countries as far afield as Malaysia.
For her training career, Fraisl moved to Poland, her then-partner’s homeland, where she set up a private breeding and training facility in Strzegom, not far from Wroclav. “At the beginning, we had in training only homebred horses, thoroughbreds. Step by step, one by one, came some Arabians from Austria, Germany, Sweden.... and when they started to win more and more races. Owners from different countries recognised the job we were doing and sent us more and more Arabian horses to be trained in Poland. Today, she has some 80 boxes and 40 places for youngstock. She is an advocate of turnout for horses’ well-being. “Twenty-five huge grass paddocks can be used all year round and all of our horses—including the racehorses—enjoy several hours outside every day. This is the most positive aspect for mental health. We also have an indoor arena and a horse walker as well as many possibilities to ride out into fields and forest to create the most individual training for our horses as possible”.
These days, Fraisl continues to ride out for nearly all the lots. “This is the best possibility for me to see how the horses in training work, how they behave—simply to ‘feel’ them”.
However, in Fraisl, we find another champion trainer wanting to move on from the country of their triumphs. “Actually we are dramatically reducing the number of our horses, and we are not accepting new horses and owners. The reason is that I am leaving Poland soon and will stop my job as a trainer here”.
Fraisl cites a multitude of reasons for this bombshell decision which, she says, she has taken after lengthy consideration. “The number of foreign Arabian horses—as we mainly have them in training—is also getting smaller and smaller. This means that we are forced to enter three, four or five horses from our stable together in one race, or that race will be cancelled. This makes no sense for us and our owners any more”.
Stagnant prize money and rising costs (of staff, transport, feed, bedding and veterinary and blacksmith services) are another factor. In addition, “there is a big lack of work riders. Most trainers work with a handful of enthusiastic amateurs, mainly young girls, who come to ride some lots before school or study or during holidays”. Fraisl also rues the talent drain of the best jockeys in Poland to other countries. She claims that drug and alcohol misuse is a real issue amongst riders and also that black-economy practices are common in the capital, with staff being employed without legal papers or insurance. “We have all our staff employed on a legal basis, and this is why we are the most expensive stable in Poland. We are already tired [of] explaining to the potential new owners why the prices of others are much lower—that's why we finally decided to close our training stable”.
These points were put to the Polish Jockey Club (PJC) racing secretary and the EMHF executive council member, Jakub Kasprzak. Kasprzak points to the fact that Poland is not alone in facing economic challenges, with high inflation being experienced generally across the continent. “It is true that prize money has not risen for some years, but it still compares favourably with that in, for example, Czechia or Slovakia. We are currently trying to support breeders and owners of Polish-bred horses. We have put in place a five-year programme to help this group of people. Ms Fraisl’s yard has 95% foreign-bred horses, so she is unable to participate in that programme. We have been paying transport only to horses to travel to Sopot (just four days’ racing per year) because there are no horses in training within 100km of that racecourse.”
“It is true that Polish riders, of all levels of ability, will often seek happiness abroad. But a shortage of racing staff is something that is being experienced throughout Europe. We are now seeing many staff coming from countries such as Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. However, I don’t recognise her point about insurance and illegal workers. Every rider MUST have official insurance to be licenced. We at the PJC are very exacting about it. And as to drug and alcohol problems, every rider has a medical control before the start of a race. If the medical officer sees anything incorrect, he will report it to the stewards. Two years ago, one rider was suspended for one year for being drunk on race day”.
Where will Fraisl relocate to? “Time will tell. I hope to find a nice place where I can continue my work with Arabian horses.”
Fraisl has not been averse to sending horses abroad to compete ‘whenever it makes sense’. Indeed it has been the forays abroad that have provided her with her most treasured racing memories. “As key moments, I would mention the experience [of taking] part and finishing fifth in the UAE President Cup - UK Derby in Doncaster this year with Bahwan and especially our first Group winner last year in Jägersro, Sweden. For me as a trainer, this was the first Group race abroad. For our young stable jockey it was the first big chance to ride a Group race and show his talent abroad so we said ‘let's go and try’. We had no idea how the colt would do on a dirt track and without the whip (in accordance with the rules in Sweden). In the event, it was the first Group win for me as trainer, for our jockey, and for the breeder....it was an unforgettable day for all of us”.
GUILLERMO ARIZKORRETA
One man has enjoyed a stranglehold on the Trainers’ Championship in Spain for over a decade. Guillermo Arizkorreta first topped the table in 2012 and has remained there ever since.
By contrast with the other featured trainers, Arizkorreta trains at shared facilities, with some 25 others, at the La Zarzuela racetrack, very close to Madrid. It helps contain costs and has in turn contributed to the fact that Arizkorreta’s owners have enjoyed an enviable return on their annual costs, of over 75%. “It is very easy for the trainer. The owner pays €200/month to the racecourse, and it includes stabling, water supply, electricity, use of gallops, etc. Overall, having a horse in the yard costs around €1500/month, all included. It means that it is not that difficult to cover the cost of having a racehorse. On average, my horses have earned €13.500/year since I started”.
His operation supports some 70 horses in training and a workforce of around 25. “We have very nice staff, from many countries: Germany, Chile, Czech Republic, Italy, Nicaragua, Bolivia. As everywhere, there is a shortage, and it is not easy to find good riders. We have around 17 full-timers who work approximately 40 hours a week, a couple of part-timers, and some jockeys who are self-employed. The staff that work full-time work one weekend in two and the same for the evening stables. The basic wage for a full-time rider is around €19.000/year”.
“I started in a pony club in Oiartzun (close to San Sebastian) which was owned by a racehorse owner. There I met (four-time French Champion jockey) Ioritz Mendizabal, who had a keen interest in racing; and we started to ride racehorses in our local track in San Sebastian. From then on, I started following Spanish racing, and afterwards I started to follow racing and breeding around the globe, which became my passion”.
Arizkorreta singles out three key events in his rise to the top. “First, being able to compete in the FEGENTRI series as an amateur rider opened my eyes, and I was lucky to ride in many countries. Secondly, after finishing my degree, I spent nearly six years working as [an] assistant in the UK to Mr Cumani and in France to Mr Laffon Parias; and I learned a lot with them.
“Lastly, Madrid racecourse was closed between 1996 and 2005, and I was lucky to be ready to start my career at the same time as the racecourse reopened. I was known as an amateur rider in Spain, and all the background from my experience abroad helped me a lot to get some clients in very exciting times”.
“We have won 878 races from 4,450 runners. In Spain, we have won all the major races and probably our biggest achievement abroad was to win a Gp3 and a Gp2 on the same weekend in Baden Baden in 2021”.
Loyal support from some of the country’s biggest owners has been a hallmark of Arizkorreta’s career. “I have a good bunch of owners. The majority of them have been with the yard for a long time. At the moment, we have around 20 different ownership entities—33% sole ownership and the rest partnerships. The majority of them used to come racing when they were children and have a good knowledge of the sport”.
Arizkorreta has not been shy of campaigning his horses abroad and has reaped healthy rewards, capped by that dual Group-winning day in Germany. “Since I started, I have always tried to race as much as possible abroad. We have had 112 winners abroad—mainly in France, but we have also won in Dubai, Germany, Morocco and Switzerland; and we have had runners in Saudi, Sweden, UK, and Italy”.
“I feel we have done pretty well abroad, and in the right races, our horses are usually competitive”.
The trainer has much that is positive to say about racing in his country. “Madrid Racecourse is our ‘shield’, classified, as it is, as a monument. It is a fabulous racecourse, with lovely stands, a good turf track and a good crowd of people every meeting. It is very close to the city centre and is a track definitely worth visiting. Prize money could be better for the big races but in general is good, especially for the low-grade races. Being close to France helps us find suitable races for some horses”.
As to what could be improved, Arizkorreta would welcome improved planning of the race programme and greater unity between trainers, jockeys, and owners to “push in the same direction and to improve the basics of our industry”. And financial structures also mean that there is not the opportunity to access horse walkers or equine swimming pools.
All in all for Arizkorreta, the future, if not stellar, looks stable. “I think in five years’ time we will be in a similar position. Things could be much better but, realistically, with politicians not giving us the tools to develop the betting and our industry; it is hard to imagine an improvement in the short term. We need them to make a long-term plan for racing and breeding and to consider it as an industry that can create wealth and employment in many areas. Since 2005, the ruling government has helped us with prize money, which covers nearly all the races run in the year; and I see no reason why it should change, especially in Madrid.
“We have some lovely racecourses, which are always attended by a good crowd. In our biggest racecourse in Madrid, the weather is usually lovely, and it is becoming very popular in the city. There is scope to improve in many areas, and I can see it being one of the nicest racecourses in Europe. San Sebastian needs more support from the local government, but it is a historic racecourse in an amazing city. And I hope Mijas racecourse will reopen at some point”!
It was heartening to find that at least one of our ‘smaller nations’ champion trainers shows no signs of wishing to leave the country.
Polish horse racing gets a major boost
Article by Dr. Paull Khan
Night Tornado (11) and jockey Stefano Mura on their way to winning the Wielka Warszawska 2022, a race they won for the second year running at Sluzewiec Racecourse
Warsaw’s impressive Sluzewiec Racecourse
On Sunday, October 1st, Poland’s first ever internationally recognised Listed Race will be staged. The €100,000 Wielka Warszawska, for three-year-olds and upwards, is run over 2600m/13f of the impressive, 50-metre wide, turf track at Warsaw’s Sluzewiec Racecourse.
At its meeting in Ireland in February, the European Pattern Committee (EPC) confirmed its decision to award Black Type to the race, deeming it to have met the conditions of the recently introduced ‘flagship race’ scheme. Poland is the second country (after Spain) to benefit from this scheme, introduced last year, which gives EMHF member nations (which have no internationally recognised Group or Listed races) the opportunity to apply for a single ‘flagship race.’ This race is treated slightly more leniently than other races when being assessed for Black Type. Normally, the average internationally agreed rating of the first four finishers in the most recent three runnings of the race should be 100 or over. Under this scheme, a score of 95 in any two of the three most recent renewals is the threshold.
How did the Polish race meet the standard? It was undoubtedly given a boost in 2020, when the globe-trotting Czech-trained Nagano Gold (GB) – who had recently run second in both the Gp.2 Hardwicke Stakes at Royal Ascot and the Gp.1 Grand Prix de Saint Cloud – graced Poland’s premier track with his presence. Nagano Gold, then a six-year-old, prevailed by just a ½ length from a locally trained three-year-old named Night Tornado.
No one could tell at the time that Night Tornado would go on to be quite the star of the show, winning both the 2021 and 2022 editions, more recently with French- and German-trained raiders in his wake, including Nania (GER), who was fresh off a victory in a Hannover Listed Race.
Attaining Black Type is not only an honour for Polish racing but has wider implications, according to Jakub Kasprzak, racing secretary at the Polish Jockey Club and recently voted onto the nine-strong executive council of the EMHF – another example of Polish racing’s growing profile.
Jakub Kasprzak
Kasprzak reflected on the prospect in the run-up to the EPC’s decision: “If the Wielka Warszawska receives the Black Type status, it will undoubtedly be a great distinction and appreciation of Polish racing. The race has a long tradition, and several horses have appeared in the international arena. In addition, for the entire central and eastern European region, it will be a great opportunity to popularise racing.”
But Kasprzak is keeping his feet firmly on the ground: “Of course, we know that receiving such an award is really the beginning of the hard work, to show that it was not a ‘fluke.’ Personally, I am very happy, but I approach it with caution, being aware of the new challenges it poses for us.”
The journey that Polish racing has taken to get to this point is tumultuous. It has featured the need to rebuild from scratch on no fewer than three occasions and can only be understood in the context of the history of Poland overall.
Sluzewiec opening, 1939
The first organised races were run in Warsaw in 1841, on the Mokotow Field, now a large park just south of the city centre, which houses the Polish National Library. At the time, there was no ‘Poland.’ This was in the middle of a 123-year period during which Poland did not exist—having been partitioned in the late eighteenth century between Austria, Prussia and Russia. Warsaw fell into the Russian area and, since 1815, within a semi-autonomous state entitled Congress Poland. The Russian regime curtailed economic and public activity in the region, and racing in Warsaw was, for example, completely suspended between 1861 and 1863.
Originally a dirt track, four stands were erected along its finishing straight. In 1888, it moved to turf, at a time of fresh prosperity: pool betting had recently been introduced and was providing funds for prize money.
Sluzewiec, 1973
At this time, the horses were predominantly domestically bred, oriental horses, initially favoured by Polish breeders as they had historically provided Poland with success on the battlefield. However, the supremacy of the thoroughbred over racing distances (2km–5km) began to be recognised over time; and a thoroughbred breeding industry developed, drawing stallions and broodmares predominantly from England, France, Germany and Austria.
The stud of Count Ludwik Krasinski was pre-eminent in the four decades leading up to the first World War. Based in Krasne, (100kms to the north of Warsaw), it ranked top across the whole Russian Empire on 14 occasions. It produced the winners of five all-Russian derbies, in Moscow, including the famed Ruler.
Lwow Racecourse, 1943
This was an outward-looking period of international competition and success, with Polish-breds winning Classic races in Austria, Germany and Hungary. Two-year-old racing was introduced in the 1880s. (Initially, races were for four-year-olds and up only.) Trainers and riders were often brought in from abroad, and a breakthrough in riding styles occurred in 1901 when American jockey Cassius Sloan showcased the shorter-stirruped style to great effect and was soon mimicked by the domestic riders.
World War I put a stop to all this. In 1915, the racing stables were evacuated to the East. However, the racing spirit was not snuffed out and the president of the Horse Racing Society at the time, Fryderyk Jurjewicz, gathered most of the Polish stables at the track in Odessa (Ukraine) and organised races there throughout the rest of the war. Following which, in the Spring of 1919, about 250 thoroughbreds began their return home, arriving at the Warsaw track on June 28, laying the foundations for thoroughbred racing and breeding in a newly reborn independent Poland. In 1919, over 22 racing days, 193 races were run and a Western European-style racing programme, capped by traditional Classic races, was adopted.
There followed a spell of great growth and optimism. In 1924, the first volume of the Polish Stud Book was published. The following year, the Horse Racing Act was passed, establishing the Horse Racing Committee, with representation from a remarkably broad range of government departments: the Ministries of Agriculture, Military Affairs, Interior Affairs and Treasury all had seats, alongside representatives of the racecourses and breeders.
Lwow Racecourse, 1943
Breeding stock was imported in significant numbers – over 1,000 broodmares from the disintegrated Austro-Hungarian Empire, as well as from England, France, Russia and Germany. By 1930, the number of mares bred – often a useful barometer for the health and scale of the sector as a whole – had climbed back up above pre-war levels.
Many racing societies and racetracks emerged in the 1920s at places like Lublin, Lodz and Katowice. From 1933, racing was staged over the winter at the southern town of Zakopane. These regional tracks not only played an important role in the development of the thoroughbred sector, they also enriched the society by providing focal points for social life. Sadly, for most, their time in the sun was short-lived, as Poland was hit especially hard by the Great Depression of the 1930s, leading to their closure.
Even during these straitened times, a grand project was undertaken to construct a modern track on land from the Sluzewiec farm, which had been purchased by the Society for the Encouragement of Horse Breeding. With the help of international experts and renowned landscape architects, the racecourse – which is present-day Poland’s most important track and host to the Wielka Warszawska – was opened on June 3, 1939.
The Second World War caused a complete dispersion of breeding stock. For the third time in a century, thoroughbred breeding had to be started from afresh, and this time, under the constraints of Communism. Private breeding was banned and state studs were established in the place of the liquidated private studs. Slowly, activity increased from the 45 thoroughbred mares registered in 1944. A draft of 230 thoroughbreds reclaimed from Germany provided a timely fillip. By 1950, the mares’ roster had risen to 150, and this figure grew by an average of 10 per year for the next four decades.
Then, in 1989, came the seismic political changes in which Poland played such a pivotal part and saw the overturning of communism. Several state studs were closed down, and private stud farms re-appeared in their place. Individuals could now own and lease racehorses, and racing stables began competing on the principles of the free market. Broodmare numbers shot up to 900 – returning at last to the pre-WWII levels.
The story of Polish racing is, indeed, one of immense resilience. It is a vivid example of how societies – in so many parts of the world, after conflict or disaster – hasten at the earliest opportunity to re-establish horse racing, emblematic as our sport can be of normalcy resumed.
Runners pass the stands at the Baltic Sea resort track of Sopot.
What, then, of Polish racing in the 21st century? The exploits of two horses might be highlighted: those of Galileo (POL) and Va Bank (IRE) – both of whom made waves in Western Europe: the first in the jump racing sphere, the second on the flat.
Let us consider the ‘Polish Galileo’ first. Poland’s Ministry of Agriculture continued to own stallions for some years after 1989 (an example of state involvement that was only eventually ended when, in 2004, Poland entered the EU) and one of the last such was Jape (USA), whose second crop included Galileo, who had won the Polish St Leger, had placed second in the Polish Derby and had been voted Horse of the Year. Galileo was put up for sale at the Sluzewiec Sale in Autumn 2001 and was purchased by British trainer Tom George to go hurdling. Winning on his British hurdling debut in February 2002, George went directly the following month to the Cheltenham Festival, where Galileo was famously victorious in the 27-runner Gr.1 Royal and SunAlliance (now Ballymore) Novices Hurdle.
Polish superstar Va Bank
Va Bank’s remarkable career began with a 12-race unbeaten sequence, which included the Wielka Warszawska, Polish Derby and a German Gp.3. Later, while in training in Germany, he added a further German Gp.3 and Italy’s Premio Roma (Gp.2) to his tally. He now stands as a leading sire in Poland.
Today, Poland has three active racecourses, all turf, of which Sluzewiec is the youngest. Partynice in Wroclav, not far from the Czech and German borders, was founded in 1907 and is dual-purpose, hosting all the country’s 36 jump races. The Baltic Sea track of Sopot is the daddy of the trio, dating back to 1898.
Sixty trainers are licenced in Poland, with a quarter of these confined to training their own horses – just over half train from their own premises; the rest occupy stables at either Warsaw or Wroclav. Training fees average around €6,500pa, excluding veterinary and transport costs. The champion thoroughbred trainer last year, Adam Wyrzyk, notched up 36 wins.
Average prize money on the flat is around €4,600; over jumps, it approaches €7,000. Field sizes are knocking on the door of the ‘magic 8,’ with the flat averaging 7.9 and the jumps 7.1.
All of Poland’s jump races are open to foreign competition, including the Crystal Cup (€37,000) and Wielka Wroclawska (€43,000). On the flat, of the 278 races, the top 35, including all five Classics, and a few lower-class races, are open. Last year, 82 foreign-trained runners were attracted to race in Poland, from Slovakia, Czech Republic, France, Sweden and Germany.
Recent years have seen a growing reliance upon foreign-bred horses, which now represent the slight majority of horses-in-training. Of the 386 imports, 164 were from Ireland, 128 from France and 43 from Britain. Six years earlier, the picture was very different, when over 70% of horses-in-training were home-bred – a cause of some concern in Poland.
Tight finish in front of packed stands at Wroclaw
Despite a new television racing channel and internet betting platform, on-track betting is still the predominant channel for horse racing bets. Turnover is buoyant, but the returns to racing from betting turnover are modest.
The Polish Jockey Club, established in 2001, sits beneath the Ministry of Agriculture. Polish racing is heavily dependent upon government support, with 90%–95% of prize money emanating from that source. It is a relationship that is not without its frustrations:
“If we need to change something, like a rule of racing,” explains Kasprzak, “we are unable to do so without specific governmental approval; and we, as just one among many organisations, often find we are waiting and waiting for this approval to come through.”
What does Kasprzak consider to be Polish racing’s prime challenges and opportunities?
“The first challenge is the support of Polish-bred horses, to rebuild our breed. At this moment, we have a few stallions with good pedigrees and race records. Their first offspring will race this year.
2022 Polish champion thoroughbred trainer Adam Wyrzyk and daughter Joanna, who became the first woman to win the Polish Derby when winning in 2021 on Guitar Man
“Second, we need new racing rules. Third, we have problems in sourcing stewards. People don’t want to be stewards; it is a very hard and responsible job.”
“As regards opportunities, these days, there are many possibilities when it comes to spending free time, but in Poland, our three racecourses offer something special. You can meet friends, eat and drink as well as watch horses compete in the flesh. We have the chance to sell to a new audience this unique way of having a good time.”
This year, Poland is taking centre stage within European racing in another respect. It will, for the first time, host the EMHF’s General Assembly over two days in May. Immediately following this, the inaugural EuroMed Stewards’ Conference will take place at the same Warsaw venue.
And then, thoughts will turn to the Wielka Warszawska, whose shiny new Black Type status has been rewarded with a hefty boost in prize money – the winner taking home €58,000 (up from €38,000 last year). So, trainers seeking a realistic shot at Black Type (remember, statistically, the race has been easier to win than any other European Listed Race) and a nice prize money pot with a 2400m+ horse rated around the 95 mark, consider a trip to Warsaw this October.
What is racing's "Social Licence" and what does this mean?
Paull Khan expands upon a presentation he gave at the
European Parliament to the MEP’s Horse Group on November 30th
As World Horse Welfare recently pointed out in its excellent review of the subject—while social licence or the ongoing acceptance or approval of society may be ‘intangible, implicit and somewhat fluid’—an industry or activity loses this precious conferment at its peril. Examples, all too close to home, can be seen in greyhound racing in Australia and America or jumps racing in Australia.
What is clear is that our industry is acutely aware of the issue – as are our sister disciplines. The forthcoming Asian Racing Conference in Melbourne in February will feature a session examining what is being done to ‘ensure that (our) a sport is meeting society’s rapidly evolving expectations around welfare and integrity’. And back in November, the Federation Equestre Internationale (FEI) held a General Assembly whose ‘overriding theme’ was ‘that of social licence, and the importance for all stakeholders to understand the pressing needs for our sport to adapt and monitor the opinions of those around us’.
Considered at that meeting were results of a survey, which indicated that two-thirds of the public do not believe horses enjoy being used in sport and have concerns about their use. Those concerns mainly revolve around the welfare and safety of the horses. Intriguingly, a parallel survey of those with an active involvement in equestrian sport revealed that as many as half of this group even did not believe horses enjoyed their sport; and an even higher proportion than the general public—three-quarters—had concerns about their use.
While it is likely true, to an extent at least, that the public tends not to distinguish between equestrian sports, the specific concerns about horse racing are certainly different from those about Olympic equestrian disciplines, which centre on such matters as bits, bridles, spurs and nosebands.
Upon what, then, does our social licence in European horse racing critically depend? What are the major issues about which the public has opinions or worries, and on which the continuance of our social licence may hang? It should be said at the outset that what follows is not based upon scientific evidence (and the research should certainly be undertaken) but merely reflects the belief of the author. But it is suggested with some confidence that the following (in no particular order) are the three issues uppermost in public consciousness. They are:
Use of the whip
Racecourse injuries/fatalities
Aftercare – the fate of retired racehorses
There are, of course, other matters – the misuse of drugs and medications, gambling harms, etc., but the three topics above seem to account for a large proportion of the public’s anxieties about racing. There are likely to be subtle differences in the views of the public between one European country and another. Certainly, it is true that the volume of public disquiet varies very considerably between nations. In Scandinavia and Great Britain, for example, horse welfare and animal welfare more generally are very much front of mind and near the centre of public discourse. It is far less evident in several other countries.
But it is illuminating to look at what racing has been doing in recent years in the three areas listed above, and what the future looks like. A survey was conducted among member countries of the European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation (EMHF); and it is clear that, while there is much still to be done, there has been significant and sustained progress and good reason to believe that this is likely to continue – and in fact accelerate – over the next few years.
Use of the whip
Let us consider whip use first. At the most recent World Horse Welfare Annual Conference in London in November, straplined ‘When Does Use Become Abuse’, one speaker was called upon to give strategic advice as to how to counter negative perceptions of equestrianism.
What he decided to major on was striking. With the whole breadth of the equine sector from which to draw, he chose to hone in on horseracing and—more specifically yet—on the issue of whip use. It was a salutary further example of how, while the whip may be a tiresome distraction to many, it is front and centre in the minds of many of the public.
Is there any more emotive or divisive issue within racing than the whip? Admittedly, most racing professionals hold that it really is very difficult to hurt a horse with the mandated padded crops, even if one wanted to. And, with veterinary supervision at all tracks, it is impossible to get away with, even if one did. In brief, they don’t consider this a welfare issue, but rather one of public perception.
But it is then that the divisions set in. Some conclude that all that is necessary to do has been done, and that any further restriction on the whip’s use would constitute pandering to an ignorant public. Others argue that, even if it is just a matter of public perception and the horses are not being hurt or abused, the sight of an animal being struck by a human is now anathema to increasingly broad swathes of society—in a similar way to the sight of a child being struck by an adult: a commonplace 50 years ago, but rare today. Therefore, the sport must act to be ahead of the curve of public sentiment in order to preserve its social licence.
How is this argument playing out? Let us look at a key element of the Rules of Racing in 18 European racing nations—the maximum number of strikes allowed in a race is a blunt measure, indeed, and one that takes no account of other variables such as the penalty regime for transgressions, but one that, nonetheless, paints a telling picture.
The first map shows how things stood 20 years ago. The majority of the countries are shown in black, denoting that there was no specified limit to the number of strikes. Just one appears in white – Norway banned the use of the whip as long ago as 1986.
The second paints the picture as it was 10 years ago. Eleven of the 18 countries had, in the intervening decade, changed their rules and applied a lower maximum number of strikes, and are shown in a lighter colour as a result.
Today’s situation is shown in the third map. All but one of the countries (excluding Norway) have tightened up their whip use rules still further over the past decade. None now allows unlimited use, and countries now banning the use of the whip for encouragement, number four.
It can be concluded that all countries across Europe are moving towards more restricted use of the whip. At different speeds and from different starting points, the direction of travel is common.
What will the situation be in another 10 years? Many administrators within EMHF countries, when asked to speculate on this, gave the view that there would be no whip tolerance within ten years and that the Scandinavian approach will have been adopted.
On the other hand, Britain has recently concluded that the biggest public consultation on the subject and the new rules that are being introduced do not include a reduction in the number of strikes, but rather a series of other measures, including the possible disqualification of the horse and importantly, the requirement only to use the whip in the less visually offensive backhand position.
Whether or not we will see a total ban within the next decade, it must be long odds-on that restrictions on whip use, across the continent, will be stricter again than they are today.
Aftercare
Twenty years ago, little thought was given to the subject of aftercare. There were some honourable exceptions: in Greece, the Jockey Club required its owners to declare if they could no longer provide for their horse, in which case it was placed in the care of an Animal Welfare organisation. Portugal had a similar reference in its Code. Most tellingly, in Britain a trail-blazing charity, Retraining of Racehorses (RoR), had been launched, following a review by the former British Horseracing Board.
Ten years ago, RoR had nearly 10,000 horses registered, had developed a national programme of competitions and events in other equestrian disciplines, and was holding parades at race-meeting to showcase the abilities of former racehorses to enter new careers.
Di Arbuthnot, RoR’s chief executive, explains, “In the UK, a programme of activities for thoroughbreds had started to encourage more owner/riders to take on former racehorses. This was supported by regional volunteers arranging educational help with workshops, clinics and camps to help the retraining process. Other countries were looking at this to see if similar ideas would work in Europe and beyond.
“Racing’s regulators had begun to think that this was an area they should be looking to help; retraining operators and charities that specialised in thoroughbreds were becoming recognised and supported; and classes at equestrian events began in some countries. Owner/riders were looking to take on a thoroughbred in place of other breeds to compete or as a pleasure horse; the popularity of the thoroughbred was growing, not just by professional riders to use in equestrian disciplines, but also by amateurs to take on, care for and enjoy the many attributes of former racehorses.
“The aftercare of the thoroughbred was on the move.”
But not a great deal else was different in the European aftercare landscape.
Since then, however, there has been little short of an explosion of aftercare initiatives. In 2016, the International Forum for the Aftercare of Racehorses (IFAR) was born, “to advocate for the lifetime care of retired racehorses, to increase awareness within the international racing community of this important responsibility.” In this endeavour, IFAR is not in any way facing resistance from Racing Authorities – far from it. It is pushing against an open door.
The International Federation of Horseracing Authorities has, as one of its twelve objectives, the promotion of aftercare standards. And the chair of its Welfare Committee, Jamie Stier, said some years ago that there is ‘now a better understanding and greater recognition that our shared responsibility for the welfare of racehorses extends beyond their career on the racetrack’.
This direction from the top has been picked up and is increasingly being put into active practice. Also in 2016, France launched its own official charity Au Dela des Pistes, (‘beyond the racetrack’), in 2020 Ireland followed suit with Treo Eile (‘another direction’). By 2019, in Britain, remarkably, many more thoroughbreds were taking part in dressage than running in steeplechases!
So now the three main thoroughbred racing nations in Europe all have active and established aftercare programmes; and many other smaller racing nations are moving in that direction. It is not just a matter of repurposing in other equestrian pursuits – many of those horses retiring from racing that are not suited to competitive second careers are simply re-homed in retirement and others find profitable work in areas such as Equine Assisted Therapy.
Arbuthnot (also chair of IFAR) adds: “For racing to continue as we know it, we must assure the general public, those that enjoy racing, that thoroughbreds are not discarded when their racing days are over and that they are looked after and have the chance of a second career. It is up to all of us around the world to show that we care what happens to these horses wherever their racing days end and show respect to the thoroughbred that has given us enjoyment during their racing career, whether successful or not on the racecourse. If we do this, we help ensure that horse racing continues in our lifetime and beyond.”
It is important to publicise and promote the aftercare agenda, and the EMHF gives IFAR a standing platform at its General Assembly meetings. EMHF members have translated the IFAR ‘Tool Kit’—for Racing Authorities keen to adopt best practice—into several different European languages.
Time Down Under and Justine Armstrong-Small: Time Down Under failed to beat a single horse in three starts but following his retirement from racing, he has reinvented himself, including winning the prestigious showing title of Tattersalls Elite Champion at Hickstead in June 2022. Images courtesy of Hannah Cole Photography.
British racing recently established an independently chaired Horse Welfare Board. In 2020, the Board published its strategy ‘A Life Well Lived’, whose recommendations included collective lifetime responsibility for the horse, incorporating traceability across the lifetimes of horses bred for racing.
Traceability will be key to future progress, and initiatives such as the electronic equine passport, which has been deployed among all thoroughbreds in Ireland and Britain, will play a vital part. Thoroughbred Stud Book birth records are impeccable, and we know the exact number of foals registered throughout this continent and beyond. The aim must be to establish the systems that enable us to ascertain, and then quantify the fate of each, at the least until their first port of call after retirement from racing.
Racecourse injuries
There can be nothing more distressing – for racing professionals and casual observers alike – than to see a horse break down. The importance of minimising racecourse injuries—and, worse still, fatalities—is something everyone agrees upon. What is changing, though, it would appear, is the potential for scientific advances to have a significant beneficial effect.
Of course, accidents can and do befall horses anywhere and they can never be eliminated entirely from sport. But doing what we can to mitigate risk is our ethical duty, and effectively publicising what we have done and continue to do may be a requirement for our continued social licence.
There is much that can be said. It is possible to point to a large number of measures that have been taken over recent years, with these amongst them:
Better watering and abandonment of jump racing if ground is hard
Cessation of jump racing on all-weather tracks
Cessation of jump racing on the snow
Safer design, construction and siting of obstacles
By-passing of obstacles in low sunlight
Colouring of obstacles in line with equine sight (orange to white)
Heightened scrutiny of inappropriate use of analgesics
Increased prevalence of pre-race veterinary examinations, with withdrawal of horses if necessary
The outlawing of pin-firing, chemical castration, blistering and blood-letting
Abandonment of racing in extreme hot weather
Many of the above relate to jump racing, and Britain has witnessed a reduction of 20% in jump fatality rates over the past 20 years. But there is more that must be done, and a lot of work is indeed being done in this space around the world.
One of the most exciting recent developments is the design and deployment of ground-breaking fracture support kits which were distributed early in 2022 to every racecourse in Britain.
Compression boots suitable for all forelimb fractures
By common consent, they represent a big step forward – they are foam-lined and made of a rigid glass reinforced plastic shell; they’re easily and securely applied, adjustable for varying sizes of hoof, etc. They reduce pain and anxiety, restrict movement which could do further damage, and allow the horse to be transported by horse ambulance to veterinary facilities.
X-rays can then be taken through these boots, allowing diagnosis and appropriate treatment. These kits have proved their worth already: they were used on 14 occasions between April and December last year, and it would appear that no fewer than four of these horses have not only recovered but are in fine shape to continue their careers. It is easy to envisage these or similar aids being ubiquitous across European racetracks in the near future.
Modular splints suitable for slab fractures of carpal bones
Perhaps of greatest interest and promise are those developments which are predictive in nature, and which seek to identify the propensity for future problems in horses.
Around the world, there are advances in diagnostic testing available to racecourse vets. PET scanners, bone scanners, MRI scanners and CT scanners are available at several tracks In America, genetic testing for sudden death is taking place, as is work to detect horses likely to develop arrhythmias of the heart.
Then there are systems that are minutely examining the stride patterns of horses while galloping to detect abnormalities or deviations from the norm. In America, a great deal of money and time is being spent developing a camera-based system and, in parallel, an Australian-US partnership is using the biometric signal analysis that is widely used in other sports.
The company – StrideSAFE – is a partnership between Australian company StrideMASTER and US company Equine Analysis. They make the point that, while pre-race examinations that involve a vet trotting a horse up and down and looking for signs of lameness, can play a useful role, many issues only become apparent at the gallop.
There are, in any case, limitations to what is discernible to the naked eye, which works at only 60 hertz. StrideMASTER’s three-ounce movement sensors, which fit into the saddlecloth, work at 2,400 hertz, measuring movements in three dimensions – forward and backward, up and down and side to side, and building up a picture of each horse’s ‘stride fingerprint’.
In a blind trial, involving thousands of horses, 27 of which had suffered an injury, this system had generated a warning ‘red-flag’ for no fewer than 25 of them. The green lines in the centre of this diagram are this horse’s normal stride fingerprint; the red line was the deviant pattern that would have flagged up the potential problem, and the grey line was where the horse then sadly injured itself.
The ‘stride fingerprint’ of a racehorse
While the false-positive rate is impressive for such screening tools, another enemy of all predictive technologies is the false positive, and ways need to be found to take action on the findings without imposing potentially unnecessary restrictions on horses’ participation. At present, the StrideMASTER system is typically throwing up three or four red flags for runners at an Australian meeting—more in America.
A study in the spring by the Kentucky Equine Drug Research Council, centering on Churchill Downs, will seek to hone in on true red flags and to develop a protocol for subsequent action. David Hawke, StrideMaster managing director, expands, “Protocols will likely vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, depending on the imaging modalities available. At Churchill Downs, they will have a PET scan, and we will be going straight from red-flag to PET scan.”
There will be other approaches available to regulators involving, for example, discussion with the trainer, a requirement for a clean vet’s certificate, or perhaps for a normal ‘fingerprint’, before racing next.
CONCLUSIONS
There is a need for continued investment and resource allocation by Racing Authorities. But the will would seem to be there. In Britain, €7M from betting will, over the next three years, fund an extensive array of no fewer than 26 horse welfare projects, covering such matters as education and support for re-homers, analysis of medication data and clinical records, fatalities occurring off the track, ground/going research and obstacle improvement and development. That is a serious statement of intent and an illustration of just how high in importance the welfare of racehorses has now become.
Of course, not all racing nations have the resources to conduct such research. It will be vital, therefore, that the lessons learnt are shared throughout the racing world. In Europe, this is where the EMHF will play a vital role. The federation has always had, as primary aims, education and the adoption of best practice across its membership.
The hope must be that, through all these measures and many others in combination, we can assuage the concerns of the public sufficiently to retain our social licence. But let our ambitions not rest there. We must also strive to shift the debate, to move onto the front foot and invite a focus on the many positive aspects of racing, as an example of the partnership between man and horse that brings rich benefit to both parties.
Elsewhere in this issue, there is a feature on racing in Turkey, and it was the founding father of that country, Kemal Ataturk, who famously said:
“Horseracing is a social need for modern societies.”
We should reinforce at every opportunity the fact that racing provides colour, excitement, entertainment, tax revenues, rural employment, a sense of historical and cultural identity and much more to the human participants. It is also the very purpose of a thoroughbred’s life and rewards it with ‘a life well lived.’
We have a lot more to do, but let’s hope we can turn the tide of public opinion such that people increasingly look at life as did Ataturk.
Racing and breeding in Turkey
Article by Paull Khan
The true scale of the thoroughbred industry in Turkey is surely widely underestimated. Turkey is indeed a big hitter in the racing and breeding world, but much of its activity flies under the international radar. This is perhaps not unsurprising, as Turkish racing is almost completely closed. Of the 3,159 thoroughbred races run in the country annually, all but six are closed to foreign-trained runners. All its races may be broadcast across two television channels, but pictures of Turkish racing are rarely seen abroad; and unless one has a Turkish identity number, one cannot place a bet on those races on the Turkish Jockey Club’s platforms. There are only 10 foreign-based owners in the country, and hardly any of its racehorses were bred anywhere other than in Turkey.
But shine a light on this sunniest and most welcoming of countries, and the vibrancy of the industry is remarkable.
Let’s take breeding first. The latest figures available to the International Stud Book Committee (the 2020 foal crop) show that Turkey is one of the few major thoroughbred breeding nations whose foal numbers have actually grown over the past decade. In 2010, Turkey ranked 15th in the world, in terms of number of foals bred, with 1,500. She now ranks as high as 9th in the world, with 2,103 foals – a 40% increase, no less, at a time when global production is in marked decline. Turkey is, in fact, the fastest-growing major breeding nation in the world. Amongst the top ten, only Ireland’s and Japan’s foal crops have increased over this decade, and both have seen much more modest growth than Turkey’s (15% and 11% respectively). And this Turkish expansion continues: some 2,280 foals were registered in 2022 – a further 8% rise.
Look down a racecard in Turkey, and you would be lucky to see a foreign-bred suffix beside any of the runners’ names. With only 24 out of 3,500+ horses having been foaled outside the country, such a racecard would be something of a collector’s piece. The explanation can be found in a regulation that only allows Thoroughbreds to be imported in the year of their birth. A striking example of the closed nature of Turkish racing, this rule is in place to support local breeders. Another disincentive to buying foreign-breds is that imported horses only receive 75% of the normal prize money.
So, it is domestic production that, almost exclusively, fuels Turkey’s racing product. But that does not mean Turkey is closed to the purchase of foreign bloodstock. Far from it. It has embraced a long-term policy of importing stallions and broodmares strategically to build up the quality of its herd over time. Ten of these stallions are currently owned by the Turkish Jockey Club (TJC) and stand at one or another of their various Stud Farms, which also hosts 47 privately owned stallions. In this way, they are able to offer world-class stallions to their mare owners at knock-down prices.
The most expensive stallion, at least of those whose fees are in the public domain, Luxor, stands at under €8,000.
Current Champion Sire, 1998 Belmont Stakes winner Victory Gallop (CAN), heads the roster of TJC-owned stallions. By the time TJC bought him from America in 2008, he was the sire of multiple-stakes winners. His nomination fee: around €3,000.
2007 Derby hero Authorized (IRE) now stands in Turkey.
A more familiar name to many European Trainer readers among the TJC’s team is 2007 Derby hero Authorized (IRE). Having stood at Dalham Hall, Newmarket and Haras de Logis in France, this sire of six individual Gp1 winners, as well as of Grand National winner Tiger Roll, was acquired by the TJC in 2019, where he stands at some €2,500.
Daredevil (USA), dual Gr1 winner for Todd Pletcher, was purchased by the TJC in 2019.
Daredevil (USA), dual Gr1 winner for Todd Pletcher, was purchased by the TJC in 2019 and stood the 2020 season in Turkey, before returning to his native USA to stand at Lane’s End Farm. However, the TJC have retained ownership of the horse.
Ahmet Ozbelge, General Secretary of TJC, explains the rationale behind this arrangement and the Turkish philosophy on stallion purchases. “After we bought Daredevil, his offspring Shedaresthedevil and Swiss Skydiver performed incredibly well; and we subsequently received many offers from various US stud farms to buy or to stand him. We evaluated all offers and decided not to sell him because of his young age but to stand him at Lane’s End. This is a first for the Turkish breeding sector, and we are glad to be in such a collaboration, to the benefit of the global breeding industry.
“In Turkey, we have very strict criteria for breeding stock purchases from abroad, based on performances of the stallion or the mare in question but also of his/her progeny’s performances. On top of that, we work hard to select the best-suited ones for our country’s specific conditions, including racetrack types, race dıstances, conformation and bloodlines. We also try to build up a good variety in our stallion pool in order to meet the various expectations of our breeders.”
Rising foal numbers are but one example of how Turkey is, in many ways, swimming against the tide. While many countries are seeing a slow decline in their racecourse numbers, Turkey is adding to its roll. Antalya is the latest addition, and it would take a brave punter to bet against further tracks opening their doors in the coming years.
Some €70M will be distributed across Turkey’s national race programme, creating a more than respectable average prize money of €8,200 per race, with owner’s and breeder’s Premiums boosting this to €11,300 per race.
The TJC has no fewer than 2,300 people on its payroll and an outlook that places social engagement higher up the list of priorities than do many racing authorities – perhaps in part to win over the hearts and minds of a populace which tends to be disapproving and to conflate racing and betting. For example, the racecourses offer not only pony and horse rides for the general public but also free equine assisted therapy for the handicapped.
Pony Rides for children and the disabled are routinely offered at Turkish racecourses.
How is an industry of this size sustained? In a word – and unsurprisingly – through betting. Horserace betting has long provided a rich seam of income for the TJC via a formula of which most racing governing bodies can only dream and which is likely to have yielded some €190M in 2022.
By international standards, the Turkish punter gets a raw deal, indeed, with only a 50% return on his stakes. The TJC retains an eye-watering 22% of monies staked, with the remaining 28% slice going to the government. Other income streams for the TJC pale into insignificance: any money from sponsorship, for example, is heavily taxed at a rate of 74%.
Enviable though the TJC’s position may be to many Racing Authorities, it rues the fact that sports betting enjoys yet more favourable treatment. “This is a key point, actually,” explains Ozbelge. “There is a seven-point tax gap between the two sectors in favour of sports betting, which allows them to offer higher payouts. As football is so popular and the most beloved sport in Turkey, we have so many common punters to both racing and football. As a result, they can easily be driven away from the lower payout environment to high payouts.” The paucity of the horseracing return is most evident in single bets, and least apparent in exotics such as the Pick 6 - the Turks’ favourite bet.
To support Ozbelge’s point, sports betting dwarfs horserace betting, accounting for no less than 90% – to racing’s 10% – of legal betting activity. To what extent this is due to the payout differential is difficult to tell. There is also the underlying relative popularity of football which he alludes to; and a further factor may be that, while racing offers pool betting, sports betting is fixed odds. (Exchange betting is outlawed in the country due to integrity concerns).
What is clear is that, with payouts so low, the temptation to bet via the illegal websites is high. “We import race meetings from different countries to prevent Turkish citizens from betting on illegal sites on these races,” continues Ahmet Ozbelge. Even so, it is estimated that the scale of illegal betting at least matches that of legitimate betting.
If European punters and bloodstock agents are likely to find the Turkish landscape somewhat alien, so too might trainers and owners, as the structure is, again, very different.
General Secretary Mr. Ahmet Ozbelge .
There are 795 trainers in the country whose licences allow them to train thoroughbreds or purebred Arabians. There are almost as many Arab races as thoroughbred races, and the prize money is similar. Between the codes, there are over 8,000 horses in training.There is no jump racing nor trotting. A quarter of the race programme is on turf: the majority of races are run on sand with around 10% on a synthetic surface.
To retain their licences, trainers must attend compulsory training sessions, which have heretofore been annual, but are about to be moved onto an ‘as required’ basis. The great majority of trainers train US-style on the racetracks, and each track has plentiful boxes for the local horses-in-training.
But here’s the thing: for the most part, trainers do not charge a fee to their owners, in the manner of those in Western Europe. Their sole remuneration is, rather, a percentage of their horses’ earnings – 5% or 10%. (Some do strike separate agreements with their owners for a fixed salary, but this is not the norm).
The owner, for his or her part, is then responsible for all their horses’ expenses. However, what one might imagine would be a hefty part of those costs – that of the horse’s stable at the racetrack – is again heavily subsidised by the TJC, who charge just €15 to €20 (depending on the racecourse) per annum per box. The owner’s total expenses – including the salary and insurance of the stable staff, feed, bedding, veterinary expenses, etc. – are not far in excess of €1,000 per month. But, lest this information should start a goldrush amongst European owners, salivating at the potential returns on investment, it should be explained that not everyone can become an owner in Turkey. One must have a Turkish residence permit and be able to demonstrate financial sufficiency. This explains why there are only 10 foreign-national owners on the TJC’s books.
Turkey is one of a select few European countries with internationally recognised Group races (the others being France, Germany, Great Britain, Ireland, the three Scandinavian countries and Italy). The Gp2 Bosphorus Cup (3yo+, 2,400m/12f) and Gp3 Topkapi Trophy (3yo+, 1,600m/8f) are the richest, worth north of €150,000. The Istanbul Trophy (Gr3), for fillies and mares, makes up its Group-race trio. All are run over the turf course at Istanbul’s impressive Veliefendi racetrack – the main centre and flagship of Turkish racing. They are joined by the International Thrace Trophy (turf) and International France Galop FRBC Anatolia Trophy (dirt), both of which are international Listed Races. The only other open race takes place at the nation’s capital, Ankara, being the Queen Elizabeth II Cup for two-year-old thoroughbreds; but this has never attracted any European runners.
The start of the Gazi Derby.
Richer than all of these is the Gazi Derby, a €330,000 race run over the classic mile and a half in late June.
Veliefendi is not, however, Turkey’s oldest racecourse. That honour goes to Izmir, at which members of the EMHF’s Executive Council spent a most enjoyable day’s racing in September, following this year’s annual meeting.
The window into Turkish racing has for some years been its International Festival, at which all Veliefendi’s international races are run. Its wide – up to 36 metres – turf track and attractive prize money once proved highly popular with foreign trainers, who frequently made the journey to Istanbul in September. The Topkapi Trophy , for example, saw a 10-year unbroken spell of foreign-trained winners, with Michael Jarvis, Mike De Kock, William Haggas, Richard Hannon Snr., Kevin Ryan, Andrew Balding and Sascha Smrczek all making the scoresheet. However, COVID has brought about a sea-change in behaviour, and there has not been a foreign-trained winner of any Turkish Group race for the past five years.
EMHF ExCo members at Izmir Racecourse.
Inevitably, the quality of the race fields has suffered. In 2022, the Topkapi Trophy had to be downgraded from Gp2 as a result, and the pressure on all the Turkish Group races is unlikely to ease unless and until the raiders can be enticed back.
Turkey’s governance structure is also a little unusual. The Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry plays a very hands-on role when it comes to regulation – appointing the Stewards and taking responsibility for race day operations and doping control. The Jockey Club itself operates under the provisions of a triad agreement with the Ministry of Agriculture and the Turkish Wealth Fund, which is the holder of the licence for racing and betting in Turkey.
The TJC prides itself on its not-for-profit status and ethos. Ozbelge explains: “Having a centralised governing system of the racing, breeding and betting activities by a nonprofit organisation with a non commercial approach, but rather a ‘horsemen’ one, with a main goal being to develop [the] racing industry by improving the racehorse breed in the country, has many advantages. This system supports the horse owners and breeders by offering them world-class stallions for very reasonable covering fees, offering boarding and veterinary services of high quality for minimum possible costs to them. Also, supplying the industry with well-educated jockeys in its own Apprentice School and delivering live broadcasting of all races through two TV channels and so on.
“But when one thinks about the cost of all of these investments as well as all the facilities that the Club has to operate with its staff of 2,300 experienced people, with betting revenue being its sole income, it’s easy to see that this has many challenges that come with it. But the main challenge is the unfortunate general perception of ‘gambling’ of our beloved sport, which is considered the king of sports and the sport of kings throughout the world. With a little bit of support or at least a ‘fair approach’ in comparison to betting on other sporting activities, Turkey has great potential to be a major player in the world league of horse racing.”
So, what are the prospects of the veil over Turkish racing being lifted?
There is hope of a new media rights deal which promises to bring pictures of Turkish races to an international audience. But those hoping to see Turkey adopt the policy of most of its European neighbours – namely that of having open races – are likely to be disappointed. Ozbelge again: “As Turkey is not in close proximity to major racing countries in Europe, horses cannot travel frequently by road as between central European countries, but only by air in order to participate in international races. As one can imagine, this is quite costly, and in order to attract some horses from abroad, the prize money is the key factor here. So, it all comes down to the economics of the industry and of the country for sure. We do plan and hope to have more international races, but we can realise it only if and when we have the right infrastructure and dynamics for it.”
First European Pony Racing Association meeting in Budapest
Article by Paull Khan
Those in charge of pony racing travelled to Budapest from all over Europe to attend the inaugural annual meeting of the European Pony Racing Association (EPRA) on September 11th. Representatives from Belgium, Czech Republic, France, Great Britain, Hungary, Norway, Slovakia and Sweden had, the previous day, witnessed three pony races that kick-started the quality thoroughbred card at Hungary’s sole track, Kincsem Park. They were universally impressed at the professionalism of the pony racing, the hospitality and the great strides which Kincsem Park has made in recent years. It is a very different racecourse from the one that hosted an early EMHF meeting in 2013 and as striking an example of diversity as one can find. Today, every square metre of the track’s footprint is put to productive use. In addition to the flagship thoroughbred racing, there is greyhound racing, trotting, a training centre, show jumping, four-in-hand driving and more. There is even a rugby pitch inside the greyhound track!
Increased internationalisation of pony racing, with the best young riders having the opportunity to experience race-riding in other countries, is an aim of the EPRA, and it was pleasing to witness history being made. Czech youngster Sophy Bodlakova became the first foreign-based winner of a Hungarian pony race when she scored on her pony Saman!
While for some EPRA member countries, such as France, Sweden and Britain, pony racing is a well-established pursuit; for some, it is a very new endeavour, and for others yet, it is something to be established in the near future. The imparting of knowledge and identification of best practice will therefore be central to the fledgling association.
Slovakia’s experience bears witness to the fact that countries need not wait for long, after setting up a pony racing structure, to see the benefits begin to flow, in the shape of new jockeys. It was only last year that the first pony races took place at Bratislava racetrack, but from the alumni of that first cohort, there are this year no fewer than four amateur riders licence-holders. For those many countries experiencing difficulties in sourcing competent race riders, a pony racing structure is a must-have.
At the EPRA meeting, a minute’s silence was observed in honour of Jack de Bromhead, who tragically lost his life in a pony racing incident in Ireland.
For many delegates, it was the first experience of pony racing outside their own countries. Next year, the EPRA has accepted a kind invitation from France to host.
Botond Kovacs, head of pony racing in this year’s host country, commented: “We have been thrilled to host the first European Pony Racing Association meeting. The rise in profile of pony racing is very refreshing to see. The European Pony Racing community is taking shape and it feels like we’ve been put on the map—a map that the world of racing has a keen eye on.”
Racing in Switzerland - it's not just about racing on snow!
Article by Paull Khan
Think of racing in Switzerland, and the fabulous White Turf meeting on Lake St. Moritz probably comes to mind. This is no surprise, of course. The EMHF was fortunate to hold its General Assembly there in 2015, and for many of our delegates, including your columnist, it remains among the most memorable racing adventures of all. But there is so much more to racing in that country.
Sadly, St Moritz’s little sister track, which provided racing on the frozen lake at Arosa, is no longer with us. Weather conditions in recent years meant that there had become a worse than even-money chance of abandonment—a situation that was just not financially sustainable.
But the full roster of Swiss thoroughbred tracks still extends to seven. (Although one of the tracks, at Fehraltorf, which had upheld a 75-year tradition of racing over the Easter holiday, remains in a state of hiatus following an altercation last year with a neighbour farmer, who took the dramatic and disruptive decision to plough up the racing surface.)
Jump racing is the primary focus at Aarau and Maienfeld, while the flat dominates at Zurich-Dielsdorf, Frauenfeld (home of the Swiss Derby) and at the track that is the financial powerhouse of Swiss racing, Avenches.
This August saw celebrations for the 150th year of the Zurich race club, which coincided with 50 years of its current racecourse, at the small nearby town of Dielsdorf. A two-day festival was crafted, during which the 1500-metre, pancake-flat turf track staged 14 races: nine thoroughbred flat, two trotting and three pony. This left-hand track also boasts a jump course, but this is used infrequently these days.
Interwoven with the races, there was an appearance of the 250-year-old Bernese Dragoons, a mesmeric display from world-renowned Jean-Francois Pignon’s ‘free dressage’ horses, after-racing musical acts and, notably, a parade of former equine stars of Swiss racing showing off their expertise in new-found careers. Aftercare has long been a feature of Swiss racing. Horses tend to stay in training for longer than the norm on the flat, allowing the public to build up the kind of rapport with them normally associated with jump racing. In addition, they tend to race more frequently than in most countries, averaging nearly eight starts annually and this helps to buoy field sizes and makes for attractive, competitive racing generally.
The substantial crowds were engaged and relaxed, and it all made for a wonderfully rewarding racing experience.
When it comes to funding, Swiss racing is swimming against the tide, in many ways akin to the experience in Belgium, described in the last issue of Trainer. This is because, with one principal exception, there is no opportunity for people within or outside the country to place bets on Swiss races unless they are on-track. The twin State-installed institutions (one French-language, the other German), which between them enjoy a betting monopoly, decline to include domestic racing within their product mix. The exception is Avenches, where the bulk of the races has been taken on by the French betting giant PMU, are shown on the Equidia channel, and are available to Swiss and French citizens to bet on, in cafes, bars and kiosks and online. (In 2022, a few PMU races were also held in Frauenfeld and Dielsdorf). The commission from this betting activity is vital to Avenches and also helps support Swiss racing generally, but the other Swiss tracks rely critically on donations and sponsor contributions.
Unsurprisingly, the scale of the industry has suffered a worrying contraction. What had been a slow but steady reduction in the numbers of owners, horses, races and prize money between 2015 and 2019 accelerated dramatically in the COVID year of 2020. Over the past seven years, prize money has halved, and the numbers of horses and owners have reduced by 51 percent and 48 percent, respectively.
The Swiss race programme is heavily weighted towards staying races. While Handicaps are out of bounds to foreign-trained runners, they only constitute a modest proportion of the race programme and all conditions races are open. Average prize money per race remains very respectable, at nearly €10,000. The Grand Prix von St Moritz is, at €100K, clearly the nation’s richest race. Other significant prizes include the Grand Prix d’Avenches (€20k for 3yo+, weight-for-ages, 2400m/12f), Zurich’s Grand Prix Jockey Club (€50k for 3yo+, weight-for-age, 2475m/12f+), and the Swiss Derby (€50K). The country’s main jump race is the €35K Grand Prix of Switzerland, run over (4200m/21f) in beautiful surroundings at Aarau in September with a limited weight range of just 3kgs.
For five years, between 2014 and 2018, both the Grand Prix d’Avenches and the Grand Prix Jockey Club boasted Black Type. Regrettably, neither managed to maintain the strict ratings threshold required of such races in Europe. Fresh hope has been generated by the new scheme, agreed this year, whereby EMHF member countries without a Black Type race can apply for such recognition for a single, flagship event which is allowed a rating 5lbs lower than normal. There is a real desire that one or another of these races can clear this lowered bar but, as is normally the case, this is likely to hinge on their attracting foreign-trained runners rated 95+ on the international scale. And, considering the decent prizes, foreign-trained runners are relatively thin on the ground, accounting for under five percent of starters. British and German raiders are attracted to the snow, Czech runners to some of the jumps races, but foreign runners on the flat have been in single figures over the past two years.
There was, in fact, a third milestone included within the Zurich celebrations: the tenth anniversary of Horse Park Dielsdorf. The Horse Park brings together the racing and equestrian worlds in a way which could surely be gainfully replicated in many more parts of Europe. Alongside the racetrack and training barns housing 150 horses, there are FEI-standard facilities for show jumping and dressage. A recent addition, completed within the past year, is a large stylish building which, in its restaurant configuration, comfortably seats 250 with a fine view of the racing. Various facilities around the complex are available year-round to the general public for hire. In investing some €8M into this project, Race Club President Anton Kraeuliger has demonstrated both a recognition of the importance of sweating the asset that is the racecourse and an enduring belief in Swiss racing. Let us hope that this confidence is well-placed and that racing in this most beautiful of European countries, can look forward to a thriving future.
Racing in Belgium
Words - Dr. Paull Khan
Belgium's Desert Orchid and French-trained Taupin Rochelais sail over the 'world's biggest water jump.' Credit: Photography Piet Eggermont Belgium.
The jumps track at the pristine little Flemish town of Waregem might just boast the shortest finishing straight in the world—the winning post being a matter of yards from the final bend. It is, however, the home of far and away the most valuable race in Belgium. The Grand Steeple-Chase of Flanders boasts a purse of €80,000 (€100,000 pre-COVID) and, August 30th will see the 154th renewal of this venerable 4,600-metre event.
“The race is part of the Crystal Cup,” explains course commentator Nicky de Frene, “thanks to the Gaverbeek—the largest water jump in the world at 6.5 metres—and the famous Irish Bank, which give this Steeple-Chase a little touch of a cross-country race. It’s recently attracted the attention of David Pipe and Jamie Snowden, but I fear that Brexit wasn’t a good thing for Waregem because of the extra travel costs.”
Nowadays, the race is virtually the preserve of French connections (Although Germany can boast a couple of second places in recent years; and Kildagin did win it for Britain back in 1975).
Nicky de Frene is in no doubt about its most remarkable winner. “In the last decade, we have seen the domination of the French trainer Patrice Quinton, who won the race 10 times in a row! That happened with five different horses, one of which was Taupin Rochelais, the near-white grey who won it four times running. At the time of his last victory, in 2018, he had to carry 76kg, (12 stone) and he beat a top-class horse from champion trainer Guillaume Macaire. That day, Waregem witnessed the highest-rated performance in its history.”
“We’re not a racing nation…” continues de Frene, warming to his theme, “but he’s our version of Desert Orchid! I don’t know of a top handicap in the world with a winner of four successive renewals. Even Makybe Diva has just three Melbourne Cups; Red Rum, three Grand Nationals. So Taupin Rochelais deserves, in my opinion, eternal fame.”
However, the Grand Steeple Chase of Flanders is one of just four Belgian jumps races, all run on a single day at Waregem. Flat racing, by contrast, is held year-round.
Belgian racing is, in fact, amongst the most open in the world. All of its races, including handicaps, are open to horses trained in all recognised nations. As long as an entry has a handicap mark in its home country, it will be assigned a mark in Belgium, which uses the same scale as in France.
Some 18% of last year’s runners were foreign-trained—the great majority from Germany, some from Holland and a smattering from France. Gone are the days when British trainers like Michael Jarvis made regular raids over to the seaside resort track at Ostend. This compares starkly with the number of foreign sorties made by Belgian-trained horses, which are almost as likely to run outside Belgium as within it.
Marcel De Bruyne, Belgium’s representative on the EMHF and director of the Belgian Galop Federation, explains the simple truth: “French racetracks are nearby, and the prize money at those favoured by Belgian trainers is more than double ours.”
Average prize money last year was some €4,700 per race, peaking at €12,800 for Ostend’s Grand Prix de Prince Rose, the country’s most prestigious flat race. It is named after the most celebrated Belgian-trained thoroughbred who ran third in the ‘Arc,’ went on to win the Gp. 1 Prix du President at Saint Cloud and become an important stallion—leading sire in France in 1946 and great grand-sire of Secretariat.
Neither can the pool of home-trained horses be said to be extensive, having fallen from 348 pre-COVID to just 318 last year. However, the fixture list which these horses are asked to sustain runs to just 30 meetings and 150 races; and this controlled offering certainly pays dividends as regards competitiveness. Field sizes would be the envy of many top-tier racing nations: 10.8 at Ostende, 10.6 at Waregem and 9.4 at Mons.
Let’s take a look at the country’s three racecourses:
Mons: Two thirds of Belgium’s races are run at Mons, on the same type of All Weather track as can be found at Chantilly and Deauville, some 50km southwest of Brussels near the French border. A left-handed track of 1,200 metres’ circumference which favours front runners, particularly in the sprints, Mons’ Hippodrome de Wallonie races fortnightly from mid-September to the end of April, with a limited menu of five distances: 950m, 1,500m, 2,100m, 2,300m and 2,850m.
Wellington Racecourse at Ostend: Belgium’s high-summer track, racing on turf every Monday, July through August. With a slight incline to the finish, races cover a full range of distances from 1,000m to 4,000m, either on the track’s 1,400m right-handed oval or its 1,000m straight.
Waregem: Not far from Ghent, Waregem now offers four turf flat meetings in May and June, including the St Leger over 2,700m, to add to its flagship jumps day.
Nearly half the horses in training in Belgium are owner-trained. There are 18 professional trainers in the country. Jockeys are also in short supply: just 14 professional riders (with a further seven gentleman riders and seven lady riders.
The long-term sustainability of thoroughbred breeding in the country is, however, a concern for De Bruyne. The country produced just 24 foals last year. “Belgian-bred thoroughbreds are becoming an endangered species because owners prefer to buy race-ready horses; and Belgian breeders often breed in France to be eligible for French breeders’ and owners’ premiums.”
The backdrop against which Belgian racing is attempting to thrive is one of serious under-funding. It's only betting-based income stems from the very modest sums that are wagered by racegoers at its three courses and from bets placed into the French betting operator; PMU’s pools on 100 or so qualifying flat races—the so-called ‘Premium’ races. It is therefore heavily dependent upon this latter income stream. The sport derives no benefit whatsoever from the great bulk of relevant wagering—neither from bets placed by Belgian punters off-course (either in the 3,500 retail outlets or online)—whether on Belgian races or otherwise, nor by punters in other countries betting online on Belgian races (outside the PMU system).
Baron Philippe Casier—former president of the Belgian Jockey Club and a long-time advocate of statutory funding for the sport from betting thereon—describes two recent body-blows to this ambition. “Last year, a law introduced two years earlier, which required betting operators licensed in the country to enter into a funding agreement with racecourses, and which covered betting on both foreign and domestic races, was repealed before a single Euro had been handed over. And in 2018, a tripartite agreement that the Belgian tracks had struck with the PMU and international betting operators, through which common pool betting on the French system had, for a few years, resulted in healthy income for them, also ended.”
So, despite the numerous European Commission precedents, which have established the validity of statutory funding, there seems to be no current appetite for this within the Belgian national government, of which betting is a competency. Racing therefore must look to the largesse of regional governments. The Walloon region has been persuaded of the benefits of supporting this rural industry, and grants Mons a yearly operational subsidy. Hopes in Flanders, where there is currently no such support and into which Ostend and Waregem fall, rest with a proposal to establish a similar subsidy that is funded by raising the tax rate on online bets from 11% to the 15% that already applies to other betting. Despite these impediments, optimism remains, and perhaps we should leave the last reflections to Guy Heymans, Belgium’s chair of the European Trainers Federation: “Because of the repression we had in Belgian racing, a lot of owners stopped owning racehorses. And lots of those who kept on started training their horses themselves. That’s why we have a lot of owner/trainers in Belgium and why there are only a few professional trainers left”.
Racing in Belgium is no longer on a regular basis, as it used to be—there is now a race meeting only approximately every fortnight. But Ostend and Waregem are becoming very popular with the general public, with thousands of spectators at those meetings. For an owner it’s a real pleasure to win a race at one of these meetings with such crowds and all that cheering!
“Belgium is a very interesting place to have horses in training. First of all there is the geographical location: we have easy access to a lot of French and German racetracks (e.g., Paris within only three hours’ drive). Secondly, the trainers have excellent facilities—some of them private, others based on the racetrack in Mons.
Furthermore, the cost of putting a horse in training is cheaper than in our neighbouring countries. That makes it an interesting proposition for foreign owners to put horses into pre-training with a Belgian trainer.
“Belgian racing has been evolving positively over recent years. We hope that this trend will continue in such a way that new and old owners will find their way to the sport.”
Looking after our jockeys - Q&A with Denis Egan
Author - Dr. Paull Khan
In this issue, we conclude our series of Question and Answer sessions with the chairs of the various committees that operate in the EMHF region.
Following our features on the Pattern and doping control, we turn our attention to the well-being of our human athletes, the jockeys.
Denis Egan, who until recently was CEO of the Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board, has also been the driving force within the International Federation of Horseracing Authorities (IFHA) when it comes to the welfare of riders. Not only does he chair the European Racing Medical Officers Group, but he has also been at the helm of the global International Conference for the Health, Safety and Welfare of Jockeys (ICHSWJ) since its inception some 15 years ago.
This time, our questions have been posed by various jockeys’ associations.
Q: What is the ICHSWJ?
DE: The ICHSWJ is a biennial conference for racing administrators, racecourse doctors, researchers and jockeys’ associations. The first conference was held in Tokyo (Japan) in 2006, and the ICHSWJ was officially recognised as one of the sub-committees of the IFHA in 2009. There have been eight conferences to date, which were held in Tokyo, Japan (2006), Antalya, Turkey (2008), Monmouth Park, USA (2012 & 2013), Hong Kong (2015) and Dubai, UAE (2010, 2017 and 2019).
The conference features presentations from the world’s leading racing administrators, racecourse doctors and researchers who work closely with jockeys both on the racecourse and through research studies. We are hoping to hold the next conference in Dubai in 2022, subject to COVID-19 restrictions being lifted.
Q: What is the charter of the ICHSWJ?
DE: The mission of the ICHSWJ is to provide a forum to discuss and implement strategies to raise the standards of safety and the standards of care provided to jockeys and to create a safer and healthier everyday life for jockeys when they participate in the sport.
The ICHSWJ has seven strategic objectives, namely to:
• RAISE awareness of jockeys’ health, safety and welfare issues
• HARMONISE standards and procedures throughout the world
• HARMONISE the collection of injury data
• PROVIDE a forum for the sharing of information
• SHARE research findings and foster collaboration
• PROPOSE strategies to deal with issues on a global basis
• SET UP a more effective communication mechanism between countries
Q: What do you see as the main focus by the attendees and presenters re jockeys’ health, safety and welfare?Is it bone health, making weight in a healthy manner (e.g., saunas, nutrition and fluid intake), concussion, injuries and falls, psychological/mental health issues, PPE (e.g., helmets and vests), or all of the above?
DE: It is all of the above with an increasing focus on mental health, concussion and making weight safely.If you look back at the agendas for the eight conferences that have taken place, the focus of the initial conferences was on what could be described as ‘traditional’ jockey issues such as weights, injuries and safety equipment, with little or no research having been carried out in any of the areas. Now everything has changed, and the focus is on the increasing amount of research that has been carried out in jockey health and safety-related issues. In Ireland we have been funding research since 2003, and many other countries have now developed their own research programmes. There is now much greater research collaboration between countries than there would have been in the past, and this has contributed to better results.
The one thing that has surprised me most is the huge focus that is now on mental health. The first time it appeared on a conference agenda was in 2017, and it has now become such a major issue everywhere. There have been numerous studies carried out that have found there are significant levels of depression amongst jockeys; and the industry is now addressing this with most countries putting better support in place for jockeys.
Studies have found that the life of a jockey has major highs and lows, and while success is a high, there are far more lows such as wasting, injuries, failing, travelling and social media abuse, which can be very hard to take. Studies have also found that there is a complex interplay between physical and psychological challenges: weight, dehydration, making weight and mood.
Q: What do you think is the number one issue facing jockeys at the moment?
DE: There is no doubt that the number one issue facing jockeys at the moment is mental health; and the fallout from this is being addressed by both the governing bodies in collaboration with the jockeys, which is the way to go. Many countries make sports psychologists available for jockeys if they want to use their services. We have been doing this in Ireland for many years, and while some jockeys may have been reluctant to use these services in the past, more and more have come to realise the benefit of the service.
Q: There has been a lot of research into mental health and wellbeing issues in jockeys, especially in Ireland and the UK. What can governing bodies do to either proactively improve jockeys’ mental wellbeing or support those with issues?
DE: Practically every governing body is now aware of the importance of jockeys’ mental health and wellbeing. The best way of helping jockeys is to be aware of the issues they are facing and to work with the jockeys’ associations to address these issues. The recent collaboration between the Professional Jockeys Association in Great Britain and the BHA is testament to what can be achieved by working together where an outcome was delivered that benefited everyone.
The other way governing bodies can assist is through education and the provision of support services to jockeys, which are easily accessible. Jockeys sometimes need to be educated in the sense of making them aware of what is available and how the services can be accessed. It is sometimes difficult to encourage jockeys to use mental health support services as some see it as a sign of weakness that they need to access these services; and they don’t want their weighing room colleagues to know that they perceive themselves as having issues. In reality, it is a sign of mental strength that they (are) able to make the decision that they need the service.
Q: The issue of burnout is one that is increasing across all sports. How do you feel governing bodies deal with or recognise this as an issue?
DE: It is now being dealt with far better than it was in the past. Great Britain recently announced that jockeys will be restricted to riding at one meeting per day in 2022. This is the second year that this has occurred, and this was agreed in cooperation with the jockeys’ association there. In Ireland there was a holiday for the professional jump riders for a three-week period in early June this year. This worked very well as it gave the jockeys an opportunity for some down time to recharge and take a holiday.
Burnout may not be as big an issue for riders in countries where there are a small number of racecourses or where there is a restricted racing season, but nevertheless, all governing bodies need to be aware of it.
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Doping control in European racing the role played by the EHSLC
By Dr Paull Khan
AN Q&A INTERVIEW WITH HENRI POURET,
CHAIR OF THE EUROPEAN HORSERACING SCIENTIFIC LIAISON COMMITTEE
In this issue, we continue our series of Question and Answer sessions with the chairs of international committees in the European and Mediterranean regions. We began (Issue 72) with the subject of classifying the major, Black Type races across Europe, with our interview with the chair of the European Pattern Committee, Brian Kavanagh. Here, we move on to the subject of doping control, which is the remit of the European Horserace Scientific Liaison Committee. Its chair, Henri Pouret, answers your questions.
The EHSLC lists these amongst its Terms of Reference:
With the aim of achieving uniformity of approach, to provide advice to the Racing Authorities of the member countries on policy, scientific and procedural matters concerning the Rules of Racing as they relate to prohibited substances.
To recommend alterations to the Rules of Racing as they relate to prohibited substances.
To recommend common policies and procedures where appropriate in the areas of sample collection, sample testing (including confirmatory analysis) and prohibited substances, and to monitor compliance by the member countries with these policies and procedures.
To agree whether specified drugs fall within the List of Prohibited Substances.
To recommend the need, where appropriate, for new or varied threshold levels, for inclusion in the Rules of Racing.
To promote liaison and discussion between the official racing laboratories and the official racing veterinary surgeons of the member countries.
To promote inter-laboratory drug testing programmes, and to monitor the results vis-à-vis the official racing laboratories of the member countries.
To agree with research priorities and to promote joint approaches, where appropriate, for their achievement.
To publish detection periods, agreed jointly between the official racing laboratories and other interested parties in the member countries for therapeutic drugs commonly used in the horse.
To exchange drug intelligence and other relevant information between the member countries.
Pouret, who has a background in law, is the Deputy CEO of France Galop, in charge of racing and also represents France on the International Federation of Horseracing Authority’s (IFHA’s) Harmonisation of Racing Rules Committee.
Q: Let’s get some definitions out of the way first. One of the EHSLC’s Terms of Reference is ‘to recommend the need, where appropriate, for new or varied threshold levels, for inclusion in the Rules of Racing’. What is the difference between a ‘threshold level’ and a ‘screening limit’?
‘Threshold level’ and ‘screening limits’ are two critical indicators for doping control determined in urine and/or plasma.
A ‘threshold level’ is a numerical figure adopted by racing authorities for endogenous substances produced by horses and for some plants traditionally grazed and harvested to horses as feed. International thresholds are recommended by the IFHA’s Advisory Council on Equine Prohibited Substances and Practices and approved by the IFHA Executive Council.
A ‘screening limit’ (SL) is also a numerical figure determined by experts for legitimate therapeutic substances. Some are harmonised internationally and some are harmonised regionally (e.g,. within EHSLC for Europe).
Both ‘threshold level’ and ‘screening limit’ are applied by racing laboratories as a reference for the reporting of positive findings.
Q: On the IFHA website, there are lists published of ‘international screening limits’ and ‘residue limits’. How do these differ?…
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
European Pattern Committee - regulating 'black type' races
By Dr. Paull Khan
THE EUROPEAN PATTERN COMMITTEE: CHAIR BRIAN KAVANAGH ANSWERS YOUR QUESTIONS
In this issue, we begin a series of articles in which we look at some of the EMHF region’s committees. We start with the European Pattern Committee, which controls the classification of black type races in Europe, monitoring the quality of the fields and agreeing when races should be upgraded or downgraded. In future issues, we will look at two further committees, which deal, respectively, with dope testing and the health and welfare of jockeys. In each, we will pose questions, from trainers, to the relevant committee chair.
The European Pattern Committee (EPC) members are France, Germany, Great Britain and Ireland. The ‘Part 1 countries’ within the International Cataloguing Standards book, often known as the ‘Blue Book’, which lists the world’s black type races. The contents of the Blue Book can be viewed online at https://www.tjcis.com/otherServicesDisplay.asp?section=5.
Any other European country that stages a Group race published in Part I of the Blue Book may become an Associate Member of the EPC. Currently, these are Italy, Scandinavia (covering Denmark, Norway and Sweden) and Turkey.
The EPC’s chair is Brian Kavanagh, who is also chair of EMHF. Brian is CEO of Horse Racing Ireland. We asked board members of the European Trainers’ Federation for questions to put to Brian and here are the results.
Q: Why do we not have both black type and the horse’s best achieved rating in catalogues? This would clearly indicate the quality of the horse and the information would be a huge plus.
BK: This question comes up from time to time and is essentially one for the Sales Companies. The European Pattern Committee would have no difficulty with ratings being shown in a sales catalogue, however, it is not a straightforward issue. By their nature, ratings are a subjective, albeit expert, opinion and can change significantly, upwards or downwards, over a horse’s racing career and the distance over which they race. A horse’s peak rating cannot tell the full picture and, in some cases, could be confusing.
Q: The EPC should put pressure on the countries that pay prize money very late and take away their status. (One of my colleagues has not received funds from a race three years ago from Italy; this should not happen.)
BK: We have done this, and the EPC has put considerable pressure on Italy to get its house in order with the result that payment turnaround times have improved, although they need to be improved further. In general, owners and trainers will ‘vote with their feet’ and be reluctant to participate in races where there is a doubt over payment being received. As the better horses stay away from races, the rating of those races inevitably suffers.
Q: Should there be a 'minimum' value for inclusion in the pattern, just as there is in the US? Germany seems to run a ton of cheap Listed races!
BK: This is an interesting question and not one that the Committee has formally discussed. We assess the quality of races based on their three-year average ratings rather than their prize money levels and, up to now, have taken the view that it is up to each member country to determine its prize money levels.
Q: Closing dates for races are a big bugbear amongst trainers—the fact that some races close so early and some don't.
BK: Again, this is not something within the control of the EPC but is rather a decision for each individual country. We know that this is frustrating in relation to the Irish Classics, for example, and as a result, we in Ireland have been progressively moving the entry dates for our Classics to later in the year.
Q: I know that I, and many of my colleagues, often say that the Pattern lacks a ‘narrative’. It's meant to be a European Pattern but everything is very country-orientated. Is there a way to make the race series flow better?
BK: I think good progress has been made on this issue with the creation of Longines Irish Champions Weekend, the expanded Arc weekend programme and British Champions Day, which provide a clear end-of-season narrative with three major championship events in the three leading European countries. Gp1 races are very well coordinated at the European level and attract international fields. I have sensed a more ‘European’ approach to various issues amongst the Committee in recent years.
Q: Why aren’t Listed, Gp3 and Gp2 races prefixed with a country code, e.g., ‘GB L’ or ‘FR L’? This would make Gp1 races stand out more as being European 'championship' races.
BK: This is a new suggestion to me and I would not favour it, as it would imply a lesser domestic status in certain countries, whereas races are measured to the same criteria across Europe. As I said above, Gp1 races already stand out at the major championship events.
Q: Why can there not be a common set of rules for all of the European Pattern? That way, everyone would know where they stand when they run.
BK: This issue strays beyond the remit of the EPC. However, it is a sensible suggestion and I believe things are moving in the right direction. Ultimately, every country controls its own Rules of Racing, but there has been a lot of harmonisation in recent times in relation to major rules such as interference and prohibited substances while we are moving towards a greater consistency among the major European countries in relation to use of the whip. As regards to the areas in the EPC’s purview, we operate to a common weight-for-age scale and fillies’ allowance system.
Q: What about the introduction of a points-based system for Gp1 races? This would open up multiple opportunities for additional revenue for sponsorship and betting.
BK: This has been looked at previously but did not find favour as the factors which influence running behaviours are generally prize money levels, prestige and history of the race. Various Championship and Horse of the Year awards are made at the end of each year and attract positive media coverage and sponsorship. In the UK there is a British Champions Series, which is a points-based system. However, I believe that the prestige and increased value of winning a major Gp1 race will always be the primary ambition and motivation.
Q: How does the EPC deal with pressure from racecourses to have races upgraded?
BK: Naturally, racecourses will seek to have their races upgraded, and this is a good thing. However, the duty of the Pattern Committee is to ensure that any changes are for the greater good rather than just to the benefit of a racecourse or a sponsor. There are strict limitations on the number of races which can be promoted each year, which has meant that EPC member countries have to focus on those changes that will have the most beneficial impact.
Q: The staying division seems to have more downgrades than upgrades. Why is this?
BK: That may have been so up to recent years, but in recent years the EPC has specifically focussed on the staying race programme, including those for three-year-olds and fillies only. A number of races were upgraded—including the Goodwood Cup and the Prix du Royallieu, both of which moved to Gp1—while there has been a five-year moratorium on downgrades in the same division as it is a long-term project aimed to alter breeders’ and owners’ behaviours and will therefore take time.
Q: I would be interested to know more about how the jumps pattern works—from talking to different Clerks of the Course, it seems that it's up to the individual country’s authority to have a race graded. Surely, there should be similar principles in place as per their flat counterparts?
BK: The jumps pattern is a matter for individual countries, although Britain and Ireland operate with virtually identical ground rules and rating parameters.
Q: My question concerns the European Pattern Book. Could there be more of an online format for all trainers across Europe to access?
BK: Moving online is certainly worthy of consideration, though many trainers I speak to would prefer the hard copy as well.
Behcet Homurlu, outgoing vice-chair.
EMHF WELCOMES NEW VICE-CHAIR
Like so many the world over in this annus horribilis, the EMHF has been forced to abandon all face-to-face meetings. Plans to stage our General Assembly in Warsaw, originally in May, were kept alive for a while, with hopes that an October alternative date might prove possible. …
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
News from the EMHF - It is time to celebrate - The European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation is 10 years old
By Dr. Paull Khan
The European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation is 10 years old. A mere stripling when compared to its counterpart regional federations in other parts of the globe, the Asian Racing Federation (ARF, formed in 1960) and Latin America’s yet more venerable OSAF (Organizacion Sudamericana de Fomento del Sangre Pura De Carrera – established 1958). So what has been the story of our first decade?
Who better to turn to first than the ‘Father of the EMHF’, Bjorn Eklund, ex-CEO of the Swedish Jockey Club? “I think I got my thoughts about the need of European racing integration and cooperation when I visited my first International Federation of Horseracing Authorities (IFHA) conferences in the late eighties. I say 'visited' and that is what it really was, from my point of view. They were grand meetings and offered a lot of hospitality but not much by way of discussion or democratic interaction. Everything seemed to have been discussed and decided in advance by the big racing nations. I asked some representatives from the minor racing countries if it was always like this. The answer was 'yes', and they were not too happy about it.
“So, together with my friend Harald Dörum from Norway, I invited some of the minor European racing nations to a meeting in Stockholm in 2000. The result of the meeting was an informal organisation called the European Racing Development Conference (ERDC). It was mostly a network organisation which met once a year. After a few years, we were able to arrange the meeting during the ‘Arc weekend’ in Paris, which increased the interest and more and more organisations took part. As chairman of ERDC I was invited twice to speak at the IFHA meeting by invitation of its chairman, Louis Romanet. And he was the first to suggest an integration into IFHA by setting up a European (and Mediterranean) organisation for both the big racing countries and the minor ones.”
Paull Khan, Behcet Homurlu, Bjorn Eklund, Dominique de Wenden, Brian Kavanagh and Zsolt Hegedus.
And so it was that representatives of 18 countries—Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark, France, Germany, Great Britain, Hungary, Ireland, Lithuania, Morocco, Norway, Poland, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and Turkey—gathered in Stockholm on June 1st 2010, and resolved to found the European and Mediterranean Horseracing Federation. Italy, a notable absentee, hosted the second meeting, three months later, and was included amongst the 19 founder members listed in the federation’s by-laws. Brian Kavanagh, CEO of Horse Racing Ireland and a vice-chair of the IFHA, was chosen as chairman, a position he still holds today.
Areas of focus suggested by those attending that inaugural meeting, as revealed by its minutes, included several which have become key themes for the federation: information exchange; tutorship, including in practical aspects of racing administration; and advocacy within the European Union amongst them. Zsolt Hegedus, representing Hungary, argued that it was extremely important for the major European racing nations to visit the developing ones to assess and assist them.
Within the first couple of years, during which time the Czech Republic and Lebanon came on board, the need for a more formalised secretariat became apparent and, in 2012, I was delighted to be approached and commissioned to give one day per week of my time to become its secretary-general—an arrangement that applies to this day.
Over the past eight years, we have sought to maximise the value derived by the members and to raise the profile of the federation, both within the racing and wider equine sector and in European political circles.
‘EMHF Chair, Brian Kavanagh and Secretary-General, Paull Khan dwarfed by the feared Pardubice fence at the 2018 Executive Council trip.’
Two formal meetings are held annually—an Executive Council meeting involving nine member countries, in addition to the General Assembly—and we have been determined to fulfil Hegedus’s wishes by holding these meetings over as wide a spread of countries as possible. In this way, our members have been able to experience the wondrous breadth of horseracing in our region. From the quirky Grand Steeplechase de Flanders at Belgium’s Waregem, to the swashbuckling ‘White Turf’ meeting on St Moritz’s frozen lake; from the urban oasis that is the racecourse in Casablanca, to the beauteous setting of Jersey’s elevated Les Landes racetrack. Small wonder that the EMHF membership is as one in recognising that the racing product and experience offered by each of its countries is unique and to be treasured and protected.
All EMHF members pay the same membership fee (currently €1,750pa). But those with the largest racing industries contribute in kind by hosting and delivering seminars on aspects of racing administration. This educational element of the federation’s work is among its most important. Topics have included farriery, handicapping, licencing, doping control, racetrack management, marketing and many more. Memorably, in 2016, Mark Johnston delivered a Trainer Masterclass to a rapt audience who had travelled from far and wide to Bratislava to hear him discuss the intricacies of purchasing and selling bloodstock, sourcing owners, recruiting and retaining staff, media relations, planning horses’ campaigns and many other aspects of the trainer’s job and art.
How do the ‘smaller’ racing nations view these efforts? Omar Skalli is CEO of Morocco’s racing authority; SOREC and has been a vice-chair of EMHF since its inception. “Since the very beginning,” he explains, “the aim of the founders (I was one of them) was to put EMHF, unlike equivalent structures, on these three strategic axes:
- Sharing practical experiences on structural themes for racing authorities
- Active participation of all members in defining topics of common interest
- A desire to develop the entire racing ecosystem
“Morocco has fully benefited and learned from this sharing to develop its own racing ecosystem, and I am proud to see that the EMHF is faithful today to these objectives and in line with what I had hoped and expected back in 2010.”
Several developing racing nations have elected to join the EMHF in recent years, including Azerbaijan, Channel Islands, Greece, Libya, the Netherlands and Portugal. …
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
News from the EMHF - the pandemic’s effects on Europe’s smaller racing nations and their trainers
By Dr. Paull Khan
There is no racing nation that has escaped the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. The impact on the major racing powers, in Europe and beyond, has been well chronicled. Racing industries in France, Great Britain and Ireland have all taken a significant financial hit with the period of forced inactivity. But what has been the experience of the smaller countries, with lesser financial resources with which to buffer themselves? Here we look at the situation in six countries—Belgium, Greece, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland and Slovakia—to try to get a sense of what the coronavirus crisis has meant for their racing generally and their trainers in particular. And what we see is a highly variable picture; while for some the impact—at least to date—has been mild, and there is confidence around the long-term prospects for the sport. For others, it has threatened the very existence of horseracing in the country.
The six countries between them boast just 228 trainers: 135 professionals and 93 amateurs. In several cases, the number of horses in the entire country falls short of those in a single large yard in Britain, France or Ireland. They average fewer than 10 horses in training each.
The importance of international competition is noteworthy. Of our six countries, only Greece operates pretty much as ‘an island’, with Greek-trained horses making few forays abroad, and no foreign-trained raiders entering its races. The rest are not self-sufficient. They rely on (i) races in neighbouring countries in which their horses can take part and/or (ii) horses from neighbouring countries bolstering the numbers in their own races to provide competitive sport. This is why COVID-related restrictions on international travel have been a key concern.
BELGIUM
Belgium’s three racetracks—at Mons, Ostend and Waregem—normally stage some 170 races per year. The cessation of racing started on March 5th and, at time of writing, a resumption behind closed doors was hoped for at the end of June. It will not be possible to reschedule all the races, and a reduction in opportunities of some 40% is expected.
Belgian trainers already rely, to a large extent, on supplementing race opportunities at home with those abroad—predominantly making raids across their southern border to France—to which over 80% of foreign raiders are directed. France’s closure to foreign runners therefore represented a significant blow.
Some owners transferred their horses to France when French racing resumed ahead of that in Belgium, but the damage was limited to seven horses.
Marcel De Bruyne, racing director at the Belgian Galop Federation, looks forward with optimism for a recovery next year: “I think and surely hope that 2021 will look like 2019, but our industry depends, to the tune of some 85% of revenues, on French premiums, (via the PMU). When they return to operating as in 2019, we will probably too”.
GREECE
Konstantinos Loukopoulos
Racing at Greece’s only racecourse, Markopoulo near Athens, was halted on March 14th and at time of writing it was hoped the cessation would be limited to three months. This crisis has come at a time when the Greek racing industry was pulling itself out of a slump which threatened its closure. A dozen years ago, the number of horses in training servicing racing was buoyant, at 1500. But by 2015 the tally had slumped to a scarcely-viable 250. This figure is critical to Greek racing since it has yet to attract foreign runners and relies entirely on local horses to populate its race fields. By 2019, through concerted efforts, numbers had recovered to 420, and prospects looked good. Konstantinos Loukopoulos is racing manager at Horse Races S.A., the company which holds 20-year pari-mutuel betting rights and the right to organise races in the country. He explains: “Unfortunately, the COVID-19 crisis hit us at the moment of our growth, as more than 170 new horses had come to Greece after our relaunch in 2019; and our newly introduced ratings-based handicapping system had started to work out well”.
“Our original schedule for 2020 was for 360 races (53% more than 2019). However, due to the period of closure, we will lose many races. In order to partly recover the loss, we will provide the option for up to 10 races per fixture, at least for the first month. Our goal is to give as many opportunities as possible to horses to get a run”.
Greece has mirrored the approach of many larger racing nations when determining where the axe of prize money cuts should fall. Those at the bottom end of the scale will escape, while the top races will see cuts of 13%-20%.
“Our races are open to all runners from abroad and we welcome any owner/trainer who wants to come and run in Greece. For our 2000 Guineas, Derby and Oaks there is a provision that the horses must be in Markopoulo 40 days prior to the race. For trainers that want to come for a specific period of time, we have in place incentives; and we can make, also, ad hoc facilitations, covering for example stabling costs.”
How does Loukopoulos view prospects for racing in his country? “We all are in uncharted waters and guessing is risky”, he answers. “I would say that one of the biggest issues that faces all racing industries—and especially the small ones—is the uncertainty that comes with COVID-19. Having said that, our major concern is the impact on the economy and the forecast for a recession of ~10%. Therefore, we may face a pause to the positive trend we created last year. On the other hand, I have to mention that Greek racing is now in better shape than in previous years”.
This is a view shared by Harry Charalambous, chair of the Greek Professional Trainers Association for Racehorses: “It’s been very hard for Greek racing. In 2019 we were shut for five months” (while disputes over administrative power were playing out), “and now we’re three and a half months closed with COVID. But things were going really well early this year, with 10 races and 80-100 runners per meeting, and I think we will get over it pretty quick”.
NETHERLANDS
The Dutch gallop racing sector is, on most measures, the smallest of our six countries. In common with several other European countries, it has but the one remaining racecourse, but what sets it apart is the fact that only 35 gallop races are staged at Duindigt in a normal year. The importance to trainers and owners of race opportunities abroad is as keenly felt in Holland as anywhere.
The situation for its eight professional and 20 amateur trainers could have been described as somewhat precarious even before the ravages of COVID-19. Sad, therefore, that the degree of disruption caused by the virus has been greater here than in most countries. Racing was stopped on March 15th and, as of early June, there is still no clear indication of a resumption date, with local and national governments taking different views as to the risks involved.
Racing at Holland’s sole gallop track at Duindigt.
Camiel Mellegers, racing secretary of the Dutch racing authority Stichting Nederlandse Draf- en Rensport (SNDR), predicts half of this year’s planned races will be run in the remainder of the season (for, as a consequence, half of the prize money). “This is as far as we can tell at the moment. Rescheduling will be a discussion to be had after we have re-started racing and as a result that might change in a positive way”. …
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
EMHF UPDATE - What’s been going on at The European Mediterranean Horseracing Federation - Dr Paull Khan reports on a busy end of year schedule
By Dr Paull Khan
WINDSOR AND CHELTENHAM: EMHF EXECUTIVE COUNCIL MEETING
Britain had never before hosted a meeting of the EMHF’s Executive Council. We try to move this annual event around, between as many member countries as possible, so as to further our education of the sport in our region and give the host country a chance to showcase its racing. We have had some memorable racing experiences to accompany our reunions in recent years, including the fearsome fences of Pardubice; the quirky charms of the Grand Steeplechase des Flandres; and the glorious ocean views of Jersey’s Les Landes racecourse. So the pressure was certainly on the British Horseracing Authority to provide an occasion befitting one of Europe’s major racing nations. They did not disappoint, although the British weather all but conspired to ruin the party. The Saturday of Cheltenham’s November Meeting always serves up some of the best jump racing outside the festival itself, and for several of our number, it was the first visit to jump racing’s beating heart. The management of Cheltenham were extraordinarily generous, receiving us all in its Royal Box.
The following day, it was time to do some business, and the spookily imposing Oakley Court Hotel in Windsor, on the banks of the River Thames, provided our base. For fans of the Rocky Horror Picture Show, this was Dr Frank N. Furter’s castle and was also a star of over 200 films including The Brides of Dracula and The Plague of the Zombies. A fitting venue, then, for our nine-strong Executive Council.
Our constitution dictates that representatives of France, Ireland and Great Britain, (as the three EuroMed countries with the largest-scale racing industries), have permanent seats on the ‘Executive Council’ (ExCo). In addition, at least one will always represent the Mediterranean countries, and another the non-European Union countries. This year, we re-elected our chairperson, Brian Kavanagh, also CEO of Horse Racing Ireland, who has held the role since the EMHF’s inception, in 2010. Omar Skalli, CEO of the racing authority of Morocco, was also re-elected as one of our three vice-chairs.
One of the seats on the ExCo of our parent body, the International Federation of Horseracing Authorities (IFHA), is reserved for the EMHF, to represent our ‘smaller’ racing nations. We agreed to repeat the nomination of Rudiger Schmanns, experienced racing director at Germany’s Direktorium.
Very sadly, we said farewell to both Austria and Libya. The continued political upheaval in Libya is well known to us all, and Austria’s thoroughbred racing activity has regrettably shrunk to such an extent that its Direktorium felt unable to continue as members. We hope very much that they will feel able to return one day.
On the positive side, there has been a flurry of interest in joining the EMHF, with Bulgaria, Romania and Russia all expressing an interest. A process of inspection precedes the accession of any new racing authority, and this will take place in these three countries over forthcoming months.
A key role of EMHF is to keep our members abreast of changes to the International Agreement on Breeding, Racing and Wagering (International Agreement). There have been more changes than ever this year, and the key ones were explained. We also discussed the prospects of more EuroMed countries being able, in future, to stage Black Type races.
We wanted to take advantage of being in Britain by arranging for presentations to be made covering some areas in which British racing has chosen to place more resources than have other racing authorities. One such are the efforts being made to increase the degree of diversity to be found within the sport. Rose Grissell, recently appointed as Head of Diversity and Inclusion in British Racing, described the work that she and the BHA’s Diversity in Racing Steering Group are engaged in. Tallulah Lewis then explained the role and aims of Women in Racing—the organisation of which she is the new chair. The second British ‘specialty’ we chose was the work done at the BHA on analysing betting patterns. Chris Watts, Head of Integrity at the BHA, presented on his team’s work identifying suspicious activity, thereby upholding the integrity of the racing and fending off race-fixing attempts.
ROME: INSPECTION VISIT, ITALIAN MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE
Not many racing authorities have their headquarters in a palace. The governing body for horse racing in Italy is the country’s Ministry of Agriculture (MIPAAFT), whose offices are situated in the magnificent Palazzo dell'Agricoltura, a building replete with paintings, frescos adorning ceilings and walls, wrought-iron decorations and stained-glass windows. It also houses a world-renowned library of all things agricultural.
In January 2019, the European Pattern Committee (EPC) announced that, in view of various ongoing concerns relating to the administration of racing in Italy, not least MIPAAFT’s record of prize money payment, the country would no longer be a full member of the Committee, but would become an associate member and be subject to monitoring. That process has now begun, and this was the first of three planned visits which I shall make by way of an inspection programme, likely to conclude in the summer. The inspection is not restricted in its scope to race planning matters and is therefore being undertaken under the EMHF’s auspices. Additionally, it is evidence of the EPC working ‘with Italy to try to progress matters as quickly as possible such that Italy will hopefully become a full member of the EPC again in the near future’.
SOFIA: INSPECTION VISIT, BULGARIAN NATIONAL HORSE RACING ASSOCIATION….
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
Diversity and inclusion in European racing
By Dr Paull Khan
When France decided in 2016 to introduce a weight allowance for female riders, it set the racing world murmuring and shone a light on the issue of gender diversity among jockeys.
Jean-Pierre Columbu, vice-president of France Galop, explains: “My president, Edouard de Rothschild, who had introduced Lady Riders’ races about a decade earlier, still felt they were something of a ‘ghetto’, and wanted to do more to see females compete on equal terms”. The 2-kg (4.4lbs) allowance applied to both flat and jump races, but excluded Pattern races. Last year, the allowance was reduced on the flat to 1.5kg.
It was a bold step and one that has quickly produced some dramatic results. Within three years, female professional flat jockeys are getting three times the number of rides they used to, and their winners tally has risen by a staggering 340%. Despite the exclusion of the most lucrative races, the prize money won by horses ridden by females has also nearly trebled, from €4.1M to €12M. To Columbu, this increase in earnings among lady riders is crucial to the recruitment and retention of women. “In our Jockey School”, he notes, “65% are now female. And there are, of course, many, many females in our stables who must have the opportunity to earn money”.
Indeed, it could be said that that the allowance has achieved its objective. Female riders’ percentage of rides, which are winners, has improved from 7.14% to 9.08%—rapidly closing in on the male riders’ equivalent figure of 9.73%. So has the experiment run its course, and will the allowance soon be phased out? Columbu does not think so.
“The allowance is going to stay”, he concludes. “I used to be a surgeon. In males, 35% of body weight is made up of muscle. In women, that figure is 27%. That is why the allowance is needed”.
Of course, France is far from being alone in experiencing under-representation of women riders.
Other countries have been studying the French experiment with interest from afar. In Britain, flag-bearer Hayley Turner’s exploits are well-known. However, not all in the garden is rosy. Rose Grissell, recently appointed Head of Diversity and Inclusion for British Racing, notes: “Recent successes should be celebrated and promoted, but there is further to go. Fourteen percent of professional jockeys are female, but women receive just 8.2% of the rides and, in 2018, no woman rode in a flat Gp1 race. So, while the trends are in many ways encouraging, they do not apply across the board”.
These concerns are echoed by the organisation Women in Racing. Established in 2009, Women in Racing was formed to encourage senior appointments at Board level across the industry and to attract more women into the sport. That ambition remains, but today, according to its chair, Tallulah Lewis, there is more focus on strengthening career development for women at all levels. For Lewis, a prime concern is the attrition rate; in other words, the fact that the 14% figure for female riders that we have noted above occurs despite the ratio of new recruits entering into racing through the two racing schools in Britain, being as high as 70:30 in favour of females. Understanding their lack of progression is a key aim.
Grissell, indeed, intends to examine issues of recruitment, training and retention, looking to help either remove the barriers to lady riders’ success or to lend support. One tactic might be to challenge the perception of the innate inferiority of the female jockey. Grissell again: “A study by PhD student Vanessa Cashmore identified that punters undervalue women riders: a woman riding a horse at odds of 9/1 had the same chance of victory as a man riding one at 8/1”.
Such findings call into question the need for a gender-based riders’ allowance and, indeed, British lady riders themselves have voiced opposition to the concept.
The French experiment—and its undoubted success—presents a dilemma to those who seek better outcomes for women riders but who are convinced that they are equally effective as their male counterparts, given the opportunities.
“We applaud what the French have done in this experiment, as it gives us all more information than we had before”, says Lewis. “Our concern is that it is based on the premise that women are not men’s equal when it comes to race riding—something the evidence disproves”.
Belgium, which boasts the highest percentage of the countries polled, has crunched the numbers and decided against following the French example. Marcel de Bruyne, director of the Belgian Gallop Federation, explains:
“We have the same percentage of females—43% among our professional and amateur riders and, as they achieve approximately the same percentage of winning rides as the men, we do not envisage giving a weight allowance for females”.
(All of which suggests Belgium would make an interesting case study.)
Spain, by contrast, is due to have introduced a 1.5-kg allowance for females by the time this magazine is published. It would be surprising if other countries did not decide to follow suit, either by replicating the weight allowance or conjuring some other incentive for the female jockey. A prize money premium for connections who engage female riders would be one such option, which would have the benefit of leaving the actual terms of competition undistorted.
Of course, gender diversity is but one aspect of diversity in general. It is often the first to be tackled because of the (at least traditional) binary classification applying to the sexes, and the relative ease of data collection. But diversity and inclusion in ethnic or racial terms, in sexual orientation and identification, in physical ability, etc. are all key components when assessing the extent to which a sub-group reflects the wider society in which it sits.
The argument is now widely accepted that homogeneity stifles innovation and that, in addition to any altruistic motivation for advancing the cause of the under-represented, there is also an economic, self-interested imperative for organisations to do so. And there is every reason to suppose that this applies equally to racing. The benefits, in terms of staff recruitment and retention, for example, that would likely flow from well-managed diversity should be just as applicable to, say, a trainer’s yard as to any other commercial operation.
Talking of trainers, the table below shows the percentage of female professional licensed trainers by country, and as with the professional jockeys, again reveals a very wide variation.
What, if anything, is being done to address this disparity? Or indeed, manifestations of a lack of diversity among other groups within racing: administrators and racecourse executives, for example, or, looking more broadly, among those who attend races, or place bets on horseracing?
The short answer would appear to be: not a lot. The country which has done by far the most work in this space would appear to be Great Britain where, two years ago, the British Horseracing Authority established a Diversity in Racing Steering Group.
The story starts in 2017, when Women in Racing jointly commissioned and published a study by Oxford Brookes University, entitled ‘Women’s representation and diversity in the horseracing industry’. The report found evidence of ‘a lack of career development opportunities (at all levels including jockeys), progression and support, some examples of discriminative, prejudice and bullying behaviour, barriers and lack of representation at senior and board level, and negative experiences of work-life balance and pastoral care’.