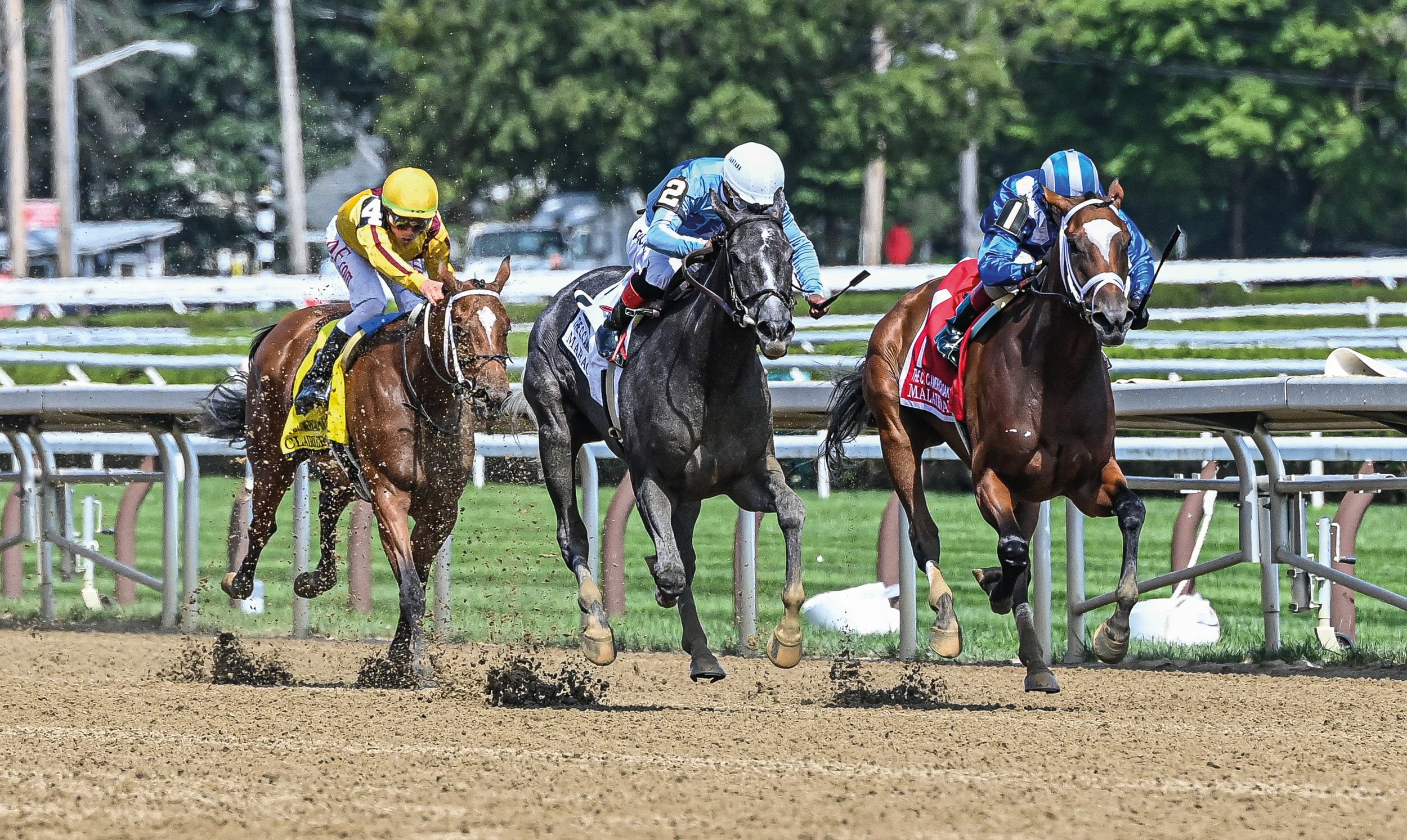
John Sadler - Trainer of superstar racehorse Flightline
Article by Annie Lambert
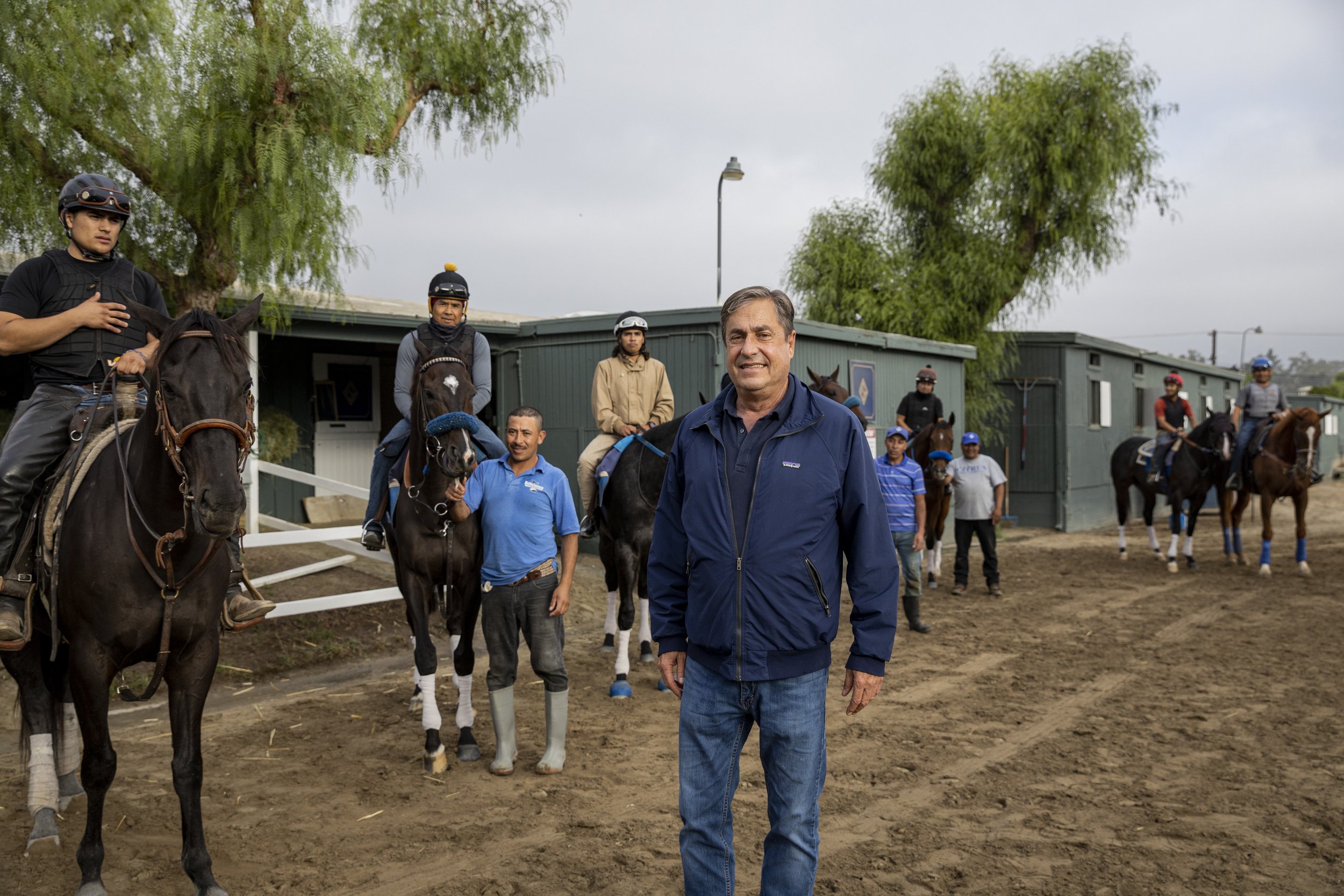
Trainer John Sadler has aimed at a career in the equine industry since he was a small child. His resolve landed him exactly where he needed to be.
Who knew that a little boy’s encounter with horses in a field adjacent to a family’s summer vacation home would set a course toward a lifelong career with horses? That young boy was California-based trainer John Sadler.
It was Sadler’s connection to horses that kept him on course to become a successful horseman. “I always wanted to work with horses,” he recalled.
The trainer’s equine experiences evolved from simple riding lessons to appease his mother, to showing hunters and jumpers and then, on to a natural progression within the Thoroughbred racing industry. Each chapter of Sadler’s equine journey has been fruitful.
He was an outstanding rider in the show ring and now sits among the best trainers in the racing industry. As of October 11, 2022, Sadler has amassed earnings of $141,058,895. Horses like Accelerate, Stellar Wind, Switch, Higher Power and current superstar Flightline have greatly enhanced his coffers.
While Sadler seems a humble guy, his accumulating milestones are worth boasting about. The kid attracted to horses at first glance is definitely making the most of his passion.
Lessons Learned
John Sadler - jumping - mr cove
Sadler was born in Long Beach, California, but was raised in nearby Pasadena. His family was summering at a house near the beach in Palos Verdes when his equine passion bloomed.
“We spent one summer at the beach, and some people had horses in their backyard,” Sadler recalled. ”I told my mother I’d like to ride the horses, but she told me I had to take lessons if I wanted to ride. So, when I was very young, I took riding lessons in Palos Verdes.”
When summer ended, the new equestrian wanted to keep up with his lessons and found himself riding at Flintridge Riding Club in La Canada, in the shadow of the Rose Bowl, all through high school. Riding with Jimmy A. Williams, a renowned horseman, helped Sadler excel at riding show horses.
Dianne Grod, a respected trainer and rider of Gran Prix jumpers now retired and living in Ocala, Florida, remembered Sadler’s ability. “He rode hunters well, he rode the jumpers well and he equitated well,” Grod said. “And back then, everybody did all three divisions on the same horse.”
During his high school years, Sadler competed for a position on the United States Equestrian Team during their West coast screening trials held at Foxfield Riding School at Lake Sherwood, outside of Los Angeles.
During Sadler’s show jumping era, his parents became involved in Thoroughbred racing on a small scale.
“My parents had a fractional interest in a couple of racehorses with a group from Pasadena and San Marino,” Sadler explained. “Impossible Stables, Inc., was a fun group of people who were social friends. I would go out to the track with my parents and watch the horses run, so I got involved with the track early.”
Sadler admits the years have somewhat run together, making exact dates hard to recall, but during a couple of high school summers he found himself walking hots at Del Mar.
His racetrack career had begun.
Racetrack Basics
With his family spending a couple summers near Oceanside, Sadler headed to the track and a job walking hots for now retired trainer Tom Pratt, (Chiapas, Mexico). Pratt was a stepping stone on Sadler’s career path.
“He was a good and talented employee,” Pratt offered. That was high praise for a teenaged hotwalker learning the ropes.
Once he graduated high school, Sadler headed to the University of Oregon in Eugene. The Liberal Arts/English major self-admittedly that he “was not really a focused student.” He did, however, confess to taking half of the fraternity house to Portland Meadows racetrack one day, which was “a good trip.”
It was not hard to believe that the young horseman made a beeline back to the track following college. His learning was more focused around the horses, and he began studying the industry from within.
Sadler went to work as an assistant to veterinarian Dr. Jack Robbins during the 1970s. Robbins, who passed away in 2014, remains an iconic figure in the history of racing.
“I was his assistant for a couple of years,” Sadler said. “I always credit him a lot; I learned a lot from him. He was a great guy…a successful owner, a very successful veterinarian and he was one of the founders of the Oak Tree Racing Association. Not only did he have the veterinary knowledge, he had a good overview of the whole game.”
Sadler did not give serious consideration to becoming a veterinarian, but he did learn a lot from Robbins and the doctor’s top tier clientele.
“It was just fun to go into all these barns, every single day,” Sadler reminisced. “You’re talking about names like Noble Threewitt, Lester Holt, Joe Manzi, Ron McAnally, Gary Jones, Warren Stute, John Sullivan, Buster Millerick…I mean, all the guys that were kind of the backbone of California. I always tried to take something from all of them—all of those great trainers.”
The Conditioner
After working for Robbins, Sadler went to work for David Hofmans as an assistant trainer for a year or more. “There is no nicer person than Dave,” Sadler recalled. The boss also appreciated his assistant.
“He was great—a real help to me,” Hofmans said of Sadler. “Working with Jack Robbins gave him an overall picture of what was going on [with veterinary issues]. Dr. Robbins worked for many people, so John got to learn and understand medications and stuff. John was a very smart guy, very astute, and he paid attention to detail. He was great, and I was sad to see him leave.”
In about 1978, Sadler had the opportunity to oversee the late Eddie Gregson’s Northern California string—his first job training on his own.
“Eddie had a lot of horses at that time and was looking to have a trainer up north,” Sadler explained. “He proposed the idea of me going up there on his behest; I trained up there for a year or a year and a half.”
Tom Pratt decided to retire about that time and kindly offered Sadler an option of taking over a few of his horses.
“Pratt said he had four or five horses that I could train,” Sadler said. “I came back to Southern California and of the 30 horses I had up north, about four or five were good enough to come down here, so that’s how I got started here. These guys were all so good to me.”
Pratt’s trust in Sadler was evident.
“When I quit training, I turned over most of my clients to him,” he recalled. “I also bought a few horses with partners and gave him those to train. I had confidence in him and was happy to give him a big leg up to what has become a very successful career.”
Keeping Course
His first year as a licensed trainer Sadler ran Gregson’s horses as well as a few starters of his own. His 1978 Equibase records showed four starters with one running third and earnings of $2,700. But, that was just the beginning. He currently has 2713 wins, and counting.
Sadler’s first winner was Top Taker (Top Conference). His record has grown exponentially over the past 44 years as a trainer. As he put it: “As the years progressed, I got better stock, obviously. It’s been kind of a natural progression.”
That progression included a slew of graded stakes winners. Accelerate (Lookin At Lucky)—the top earner to date with $6,692,480—was the Eclipse Award 2018 Champion Older Dirt Male. His accolades include winning five Gr. 1 races and the 2018 Breeders’ Cup Classic. The stallion now stands at Lane’s End Farm in Kentucky. Sadler has several of his first crop two-year-olds in training.
“I’ve got four or five nice ones,” he revealed. “One ran third the other day; they are good looking prospects.”
Stellar Wind (Curlin) was a star for Sadler—being his second highest earner to date with $2,903,200. Owner Hronis Racing sold her through the 2017 Keeneland November Mixed Sale for $6 million, going to M.V. Magnier/Coolmore. Trainer Chad Brown ran her in the Pegasus World Cup Invitational Stakes (G1) the following January. The mare finished out of the money after a bobbled start in her final race.
Switch (Quiet American) earned $1,479,562 for owner CRK Stable. She was twice second and once third in the Breeders’ Cup Filly & Mare Sprint between 2010 and 2012. She was sold at the 2012 Fasig-Tipton Kentucky Fall Mixed sale for $4.3 million to Moyglare Stud Farm.
“She almost beat Zenyatta one day at Hollywood Park,” Sadler recalled. “She lost narrowly, by a head or something. One of the times she ran second at the Breeders' Cup, she was beaten by Musical Romance, who was ridden by my assistant trainer, Juan Leyva.”
Higher Power (Medaglia D’Oro) added $1,594,648 to the Hronis Racing coffers. He won five of his 20 lifetime starts, including the 2019 Pacific Classic (G1) as well as running third in the 2019 Breeders’ Cup Classic. The bay now stands at Darby Dan Farm in Kentucky.
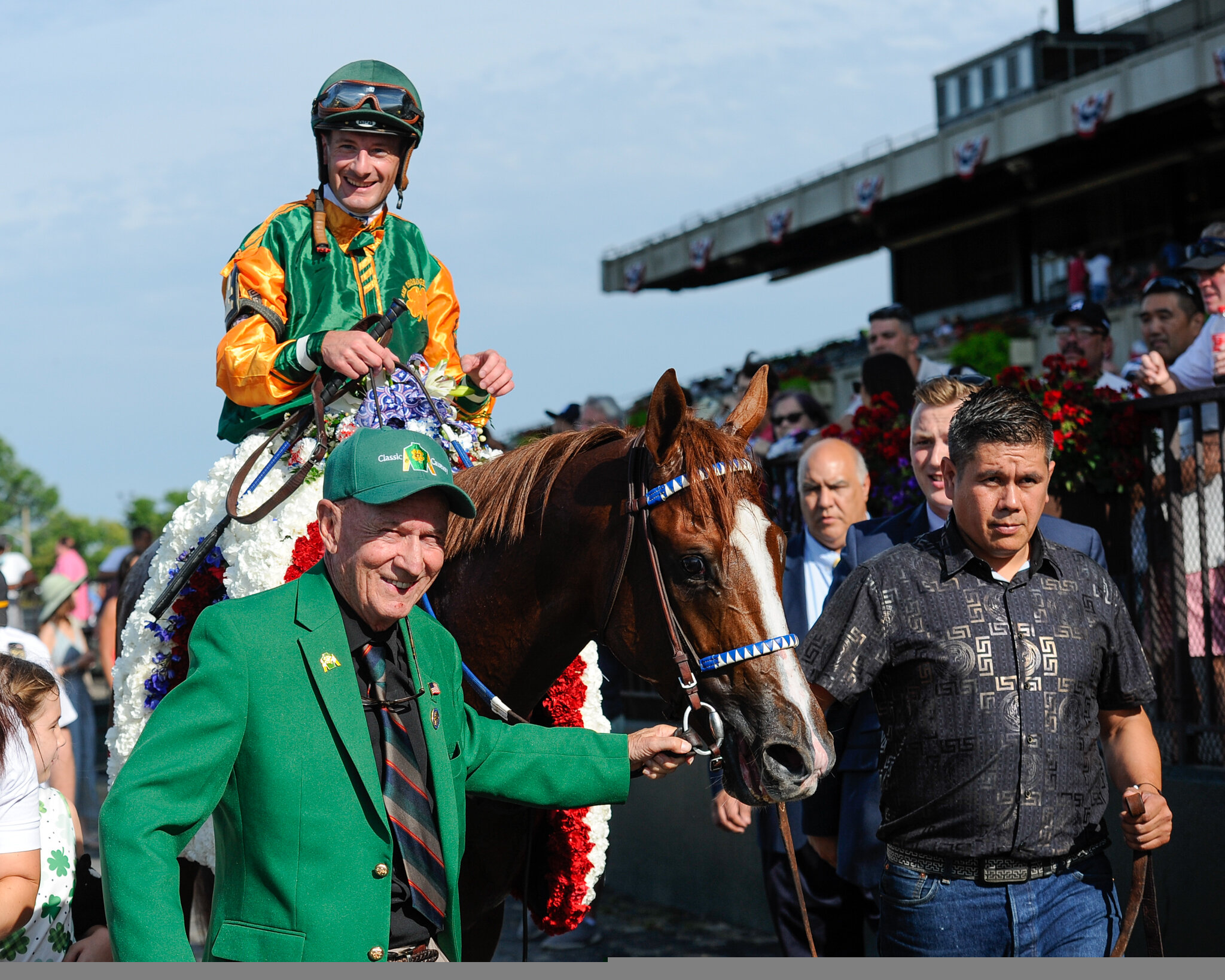
Sadler currently has Flightline (Tapit), arguably the best dirt horse in the world, and ranked globally a close second to champion British turf star Baaeed (Sea The Stars (IRE). Flightline is (at the time of writing) five-for-five and a likely starter in the Breeders’ Cup Classic. The colt, owned by Hronis Racing, Siena Farm, Summer Wind Equine, West Point Thoroughbreds and Woodford Racing was a $1 million yearling purchase. And, he was more than worth the price.
Flightline has proven his prowess with amazing ease so far; competitors are not able to touch him. With Flavien Prat, his only jockey to date, the four-year-old won his first three starts, last year, by a total of 37 lengths.
In June this year, he won his fourth start in the Metropolitan Mile at Belmont by six lengths. His most mind-boggling win came when he dominated his rivals with a nearly 20-length victory in the Pacific Classic (G1) at Del Mar, effectively extinguishing doubts that he could go the mile and a quarter. Prat looked over his shoulder when he couldn’t hear hoof beats behind him and eased his colt to the wire.
Admirers calculate he has won his five races by a total of more than 62 lengths. Let that sink in.
Flightline may have dominated the 2021 Triple Crown series had he not been injured while being started as a two-year-old. The colt was in Ocala when the latch on a stall door compromised his hind leg.
“I wasn’t there, but it was at least six to eight inches,” Sadler said of the wound. “It was pretty deep, pretty ugly. That was one of the reasons he didn’t get to me until later.”
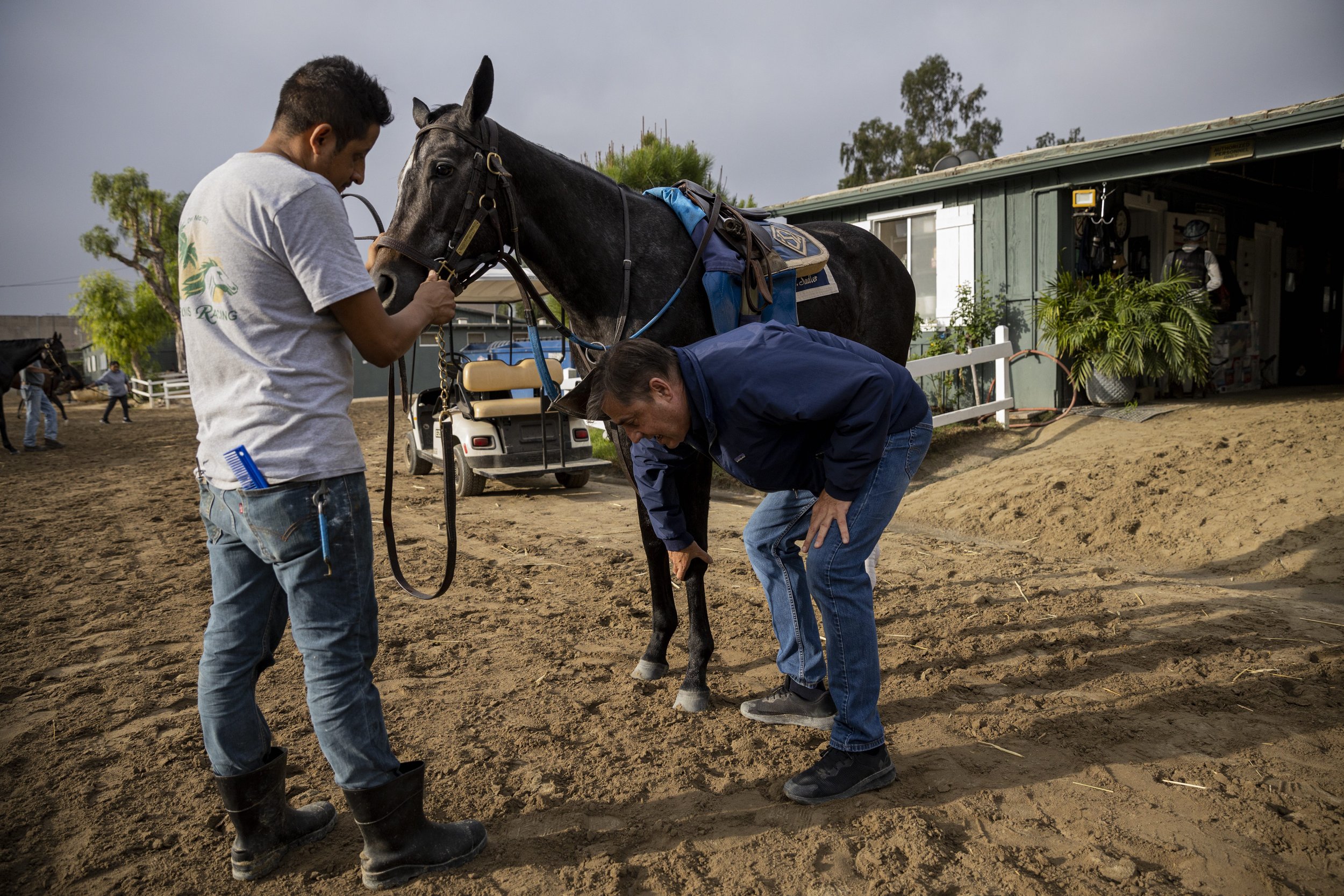
Flightline’s effective stride probably has a lot to do with his effortless proficiency over the racetrack. But with all his talent, the colt is not a piece of cake to train. His personality could be called cheeky, exuberant or brazen on any given day.
“He’s a very tough horse to gallop,” Sadler said. “In the barn he’s not a pussycat—he’s all horse. He’s all man, that’s for sure.”
“He really does have a big stride,” Sadler added. “He’s just one of those exceptional horses that comes along very rarely in the Thoroughbred world. I’m just trying to enjoy him every single day, because he’s that special. It’s really exciting; I feel very blessed to have him.”
Flightline’s future will be determined following his run in the Breeders’ Cup Classic. According to Sadler, the ownership group is an agreeable lot. Upon retirement, he will stand at Lane’s End Farm.
“The decision will be made after the Breeders' Cup,” Sadler confirmed. “You want to see where the horse is after that race. And it’s not like anybody has a closed mind, one way or the other. We’ll wait and see what happens.”
It seems obvious that Sadler truly enjoys horses and particularly training racehorses. His barn is a well-oiled machine, with some employees that have been with him 20 and even 30 years. His barn is a team, a group effort.
“You want to like your employees because you spend so much time with them out here at the track,” he said. “I’m really pleased—I’ve got a really good crew; I’m blessed that way. Horses are hard; there are no cutting corners—no way to take two days off. It doesn’t work that way. I think a lot of guys like the routine. They know what’s expected of them; and if they like to work, it’s a great job.”
Sadler is not a man who toots his own horn. Hofmans remembers him as “a quiet guy” who always paid attention. John Sadler’s modesty seems refreshing in such a competitive industry.
A Fast Match
California-based trainer John Sadler has many accolades to his credit. One event that has gone fairly unnoticed through the years is a match race that took place in 1991.
The race was an idea that spun out of the racing office at the time. They wanted to match the three-time Quarter Horse 870-yard champion Griswold with a Thoroughbred sprinter.
“They proposed matching a really good half-mile horse from Los Alamitos, which really dominated over there,” Sadler said. “At that time, I had three or four really good sprinters. I thought I had the right horse for it—a horse called Valiant Pete.”
The race, boasting a $100,000 winner-take-all purse, was held April 20 at Santa Anita. The race was run at a distance of four furlongs (880 yards) and is remembered as “thrilling” to the few who remember it.
An obituary for Griswold (Merridoc), who died at the age of 25 in 2011, described the action:
“…the pair raced neck and neck throughout, with the Thoroughbred leading all the way to a world record-tying clocking of 44 1/5 seconds.”
Griswold later found revenge by beating Valiant Pete in the Marathon Handicap at Los Alamitos.
Probiotics – The key to a well-balanced equine gut
Article by Kerrie Kavanagh
It is no surprise that the health maintenance of the racehorse is a top priority for trainers. And probiotics can be used as a treatment modality to manipulate the gut microbiome to improve or maintain health. Equine studies to date have shown that probiotic strains can offer an advantageous approach to minimising disturbances in the gut microbial populations, repair these deficiencies—should they occur—and re-establish the protective role of the healthy gut microbiome. Other probiotic-associated health benefits include reducing diet-related diseases such as colic and laminitis, preventing diarrhoea, conferring host resistance to helminth infection, improving stress-related behavioural traits (e.g., locomotion) and even promote the development of an effective gut-brain communication pathway.
Probiotics have been used by humans for more than 5,000 years with their development closely linked to that of dairy products and fermented foods. Today, probiotics are seen as an excellent non-pharmaceutical way to improve the health of both humans and animals, and there are a plethora of products to choose from. But what exactly is a probiotic, and how do they work? Why would your horse need one? What types of probiotics are available for horses? These are all questions that horse trainers ask frequently, which we will attempt to answer here.
The Equine Gut Microbiome
Probiotics and the equine microbiome can benefit from a valuable symbiotic relationship; probiotics are seen as a restorative treatment modality for the gut, to re-establish the bacterial populations there and also to re-establish the protective role that the health gut microbiome confers to the host. But when we discuss the equine microbiome, what are we really talking about?
The gut microbiota/microbiome can be categorised by anatomical location such as the oral microbiota/microbiome in the mouth and the intestinal microbiota/microbiome in the intestines, etc. Therefore, the gut microbiome pertains to the microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract. This population of microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa) is referred to as the ‘microbiota’ of the gut, while the term ‘gut microbiome’ refers to the genetic material associated with these microorganisms. The microbiome can be defined as the sum of the microbes and their genomic elements in a particular environment. If we look at the definition of the microbiome having the propensity to an equation, then any equation must be balanced; to maintain that balance is key. If the microbial community exists in an environment in a balanced state, then any upset or disturbance to the microbial populations will cause the balance to shift (known as dysbiosis). To maintain the balance, we need to firstly understand the way the microorganisms exist within their community (i.e. their microorganism-to-microorganism interactions and also microorganism-to-environment interactions) and secondly, their functioning role. If we can understand their (microorganism) position and role, then we can maintain the balance or re-establish the balance if a shift occurs.
The human intestinal microbiome is now recognised as an organ and likewise, the equine intestinal microbiome is deemed an ‘organ’ of the body and is vital for the breakdown of complex food and subsequent release of energy, protection against the pathogenic bacterial colonisation and in regulating the immune system and metabolic functions. There has been much debate regarding the content of the healthy equine microbiome, and even to deduce what ‘healthy’ or ‘normal’ is requires a level of understanding of the microbiota associated with healthy horses. This question has been posed by many researchers and frankly has yet to be answered with certainty. There are many reasons why the ‘normal’ microbiota keeps eluding us; and this can be attributed to the many reasons as to why the gut microbiota (of a healthy horse) can be affected (see Figure 1). It is thought that the diversity of the human gut microbiota and the general assembly of microbial communities within the gut (with the dominant phyla being classed as belonging to Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes) is a shared hypothesis across most species (i.e., humans and animals share a similar gut microbiome structure). Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes have been shown to constitute the main dominant phyla in equine, bovine, canine and feline gut microbiome studies indicating the cruciality of the role they play in the maintenance of a healthy microbial ecology in the gastrointestinal tract. Several studies do agree that dominant phyla of the equine gut microbiota are obligate anaerobes: the gram-positive Firmicutes and the gram-negative Bacteroidetes; other phyla are identified as Proteobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Actinobacteria, Euryarchaeota, Fibrobacteres and Spirochaetes. Ninety-five percent of the Firmicutes phyla contains the Clostridia genus in addition to genera related to gut health such as Lachnospiraceae, Faecalibacterium and Ruminococcaceae. The other main dominant phyla, Bacteroidetes, on the other hand contains a large variety of the genus.
Role of the Equine Gut Microbiota
The role of the gut intestinal microbiota serves to protect and prevent disease. The gut microbiota has several purposes: prevention of pathogen colonisation by competing for nutrients, enrichment and maintenance of the intestinal barrier—their ability to renew gut epithelial cells and repair damage to the mucosal barrier, the breakdown of food and releasing energy and nutrients, such as synthesising vitamins D and K and also conserving and restoration of the immune system by the formation of antimicrobial metabolites and blocking access to the binding sites of the mucosal wall. The gut microbiota is also thought to play some role of influencing the neuro-active pathways that affect behaviour. It is not surprising to see that gut disorders and gastrointestinal diseases can arise when gut dysbiosis occurs. The role of the gut microbiota may have even more importance than is realised and may have a role to play with developing illness or disease later in life.
The microbial colonisation of the intestinal tract begins at birth. The foal begins its colonisation through contact with the microbiota of the mare’s vaginal and skin surfaces plus the surrounding environments to which the foal is exposed and reaches a relatively stable population by approximately 60 days in age. It is perhaps a fight for dominance to achieve establishment in the gut among the bacterial populations that sees the foal’s microbiota as being more diverse and quick to change when compared to that of the older horse. The subsequent colonisation of the intestinal tract will reflect the foal’s diet, changing environment, introduction to other animals, ageing and health.
Figure 1: Factors that can lead to gut dysbiosis
What exactly is a probiotic?
The word ‘probiotic’ is of Greek origin meaning ‘for life’ and the WHO/FAO have defined probiotics as ‘live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host’. People have long believed that exposure to non-pathogenic microorganisms can benefit the health of humans and animals. The thinking behind this is that daily consumption of sufficient numbers of ‘good’ microorganisms (either bacteria or fungi) can maintain a healthy population of microorganisms in the gut and benefit overall health.
Probiotics are used to manipulate the bacterial populations of the gut in order to re-establish the delicate microbial balance there which, in turn, confers health benefits on the host. As the benefits associated with some of the ‘good’ bacteria within the gut became known, these were referred to as probiotic bacteria.
How do probiotics work?
There are 4 main mechanisms by which probiotics are thought to exert their effects.
By inhibiting pathogen colonisation in the gut through the production of antimicrobial metabolites or by competitive exclusion; in other words, they prevent the ‘bad’ bacteria from growing in the gut.
By protecting or re-stabilising the commensal gut microbiota, probiotics can be a means to re-establish the balance of the gut microbial populations.
By protecting the intestinal epithelial barrier, they maintain the health of the intestinal wall.
By inducing an immune response, probiotics can boost the immune response and help prevent disease.
If we consider the definition of a probiotic as ‘live non-pathogenic microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host’, then this reference to ‘adequate amounts’ must be emphasised, and the dose administered is critical to ensure that the probiotic has the desired effect. For horses, we must consider the route through the digestive tract that the probiotic strains must travel to arrive at their destination is a distance over 15 metres long. It is a race for survival! The gastrointestinal system has many obstacles along the passage such as the acidic stomach environment and the dangers of exposure to bile and digestive enzymes, in which they must survive. The initial dose of ‘live’ probiotic strains is therefore crucial to ensure survival in the gut. Prebiotics are ingredients such as carbohydrates and fibre, which promote the growth of these probiotic bacterial/yeast strains in the gut. Prebiotics are essentially the food for the probiotic strains and can help form a symbiotic relationship with the probiotic to improve the overall health status of the horse.
Why would you need to give your horse a probiotic?
Gut dysbiosis is a fluctuation or disturbance in the population of microorganisms of the gut, which may be linked to a wide range of diseases in horses. Gut dysbiosis can be caused by many factors ranging from dietary changes, antibiotics, disease, intense exercise and training, age, worms, environment, travel, or even minor stress events—resulting in major consequences such as colic. Dysbiosis is generally associated with a reduction in microbial species diversity.
Diet is one of the major factors contributing to gut dysbiosis. Unlike the ruminant cattle and sheep that use foregut fermentation, horses are hindgut fermenters. The large intestine is the main area where fermentation occurs. The horse utilises the microbial enzymes of the hindgut microbial population in the colon and caecum to break down the plant fibres (cellulose fermentation) sourced mainly from grasses and hay. The horse itself does not possess the hydrolytic enzymes that are required to break the bonds of the complex structures of the plant carbohydrates (in the form of celluloses, hemicelluloses, pectins) and starch; so therefore, it strongly relies on the microbiota present to provide those critical enzymes required for digestion. The main phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes possess enzymes capable of breaking down the complex carbohydrates (such as starch and cellulose).
Research has shown that forage-based diets (grasses and hay) promote the most stable gut microbiomes, but ultimately the equine athlete requires far more energy than a forage-based diet can supply. Supplementing the diet with concentrates containing starch such as grain, corn, barley and oats can affect the number and type of bacteria in the gut. Optimising diet composition is so important as carbohydrate overload—as seen with high-starch diets (>1g/kg body weight per meal)—can change the populations of bacteria in the gut, alter pH, upset digestion and the gut environment, and ultimately result in diseases such as colitis, colic and laminitis. The correct diet is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of bacterial populations. Probiotics can be used to either replace the bacteria missing in the gut and/or can help maintain the delicate microbial balance even in the face of adversity such as abrupt dietary changes, antibiotic treatment and stress.
What types of probiotics are available for horses?
There are several probiotic products on the market, and most are in powder or liquid form. There are two main categories of probiotics: generic and autogenous. Generic probiotics are off-the-shelf products that contain specific strains of bacterial or yeast, singularly or in combination. The Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium families, Enterococci and yeasts such as Saccharomyces cerevisae and boulardii are the most common equine probiotic strains. Advantages of generic probiotics are that they are widely available, easy to administer, and they may be beneficial to horse health (if the strains are alive in sufficient numbers). Autogenous probiotics are specifically formulated using bacteria obtained from the horse’s own faecal sample and, as such, are uniquely adapted to that individual animal. These host-adapted bacteria are more likely to survive in the gut than non-adapted generic strains and can quickly replenish absent or low levels of bacteria unique to the individual horse, thus maintaining health.
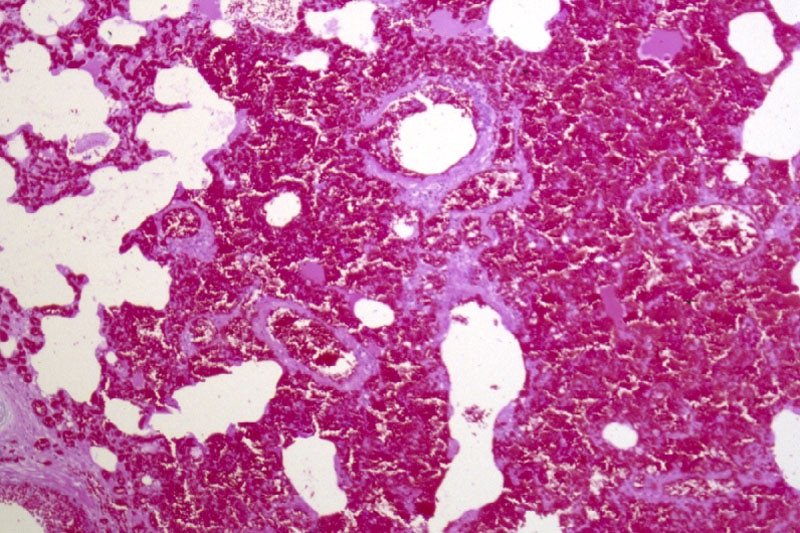
EIPH - could there be links to sudden death and pulmonary haemorrhage?
Dr Peter W. Physick-Sheard, BVSc, FRCVS, explores preliminary research and hypotheses, being conducted by the University of Guelph, to see if there is a possibility that these conditions are linked and what this could mean for future management and training of thoroughbreds.
"World's Your Oyster,” a three-year-old thoroughbred mare, presented at the veterinary hospital for clinical examination. She won her maiden start as a two-year-old and placed once in two subsequent starts. After training well as a three-year-old, she failed to finish her first start, easing at the top of the stretch, and was observed to fade abruptly during training. Some irregularity was suspected in heart rhythm after exercise. Thorough clinical examination, blood work, ultrasound of the heart and an ECG during rest and workout revealed nothing unusual.
Returning to training, Oyster placed in six of her subsequent eight starts, winning the last two. She subsequently died suddenly during early training as a four-year-old. At post-mortem, diagnoses of pulmonary haemorrhage and exercise-induced pulmonary haemorrhage were established—a very frustrating and unfortunate outcome.
Across the racing world, a case like this probably occurs daily. Anything that can limit a horse's ability to express its genetic potential is a major source of anxiety when training. The possibility of injury and lameness is the greatest concern, but a close second is respiratory disease, with bleeding from the lungs (most often referred to as exercise induced pulmonary [lung] haemorrhage or EIPH) being high on the list.
EIPH is thought to occur in as many as 85 percent of racehorses, and may initially be very mild without obvious clinical consequences. In some cases it can be associated with haemorrhage of sufficient severity for blood to appear at the nostrils, even at first occurrence. In many racing jurisdictions this is a potentially career-ending problem. In these horses, an impact on performance is unquestionable. Bleeding from the lungs is the reason for the existence of ‘Lasix programs,’ involving pre-race administration of a medication considered to reduce haemorrhage. Such programs are controversial—the justifications for their existence ranging from addressing welfare concerns for the horse to dealing with the performance impacts.
Much less frequently encountered is heavy exercise-associated bleeding from the nostrils (referred to as epistaxis), which can sometimes be accompanied by sudden death, during or shortly after exercise. Some horses bleed heavily internally and die without blood appearing at the nostrils. Haemorrhage may only become obvious when the horse is lying on its side, or not until post-mortem. Affected animals do not necessarily have any history of EIPH, either clinically or sub-clinically. There is an additional group of rare cases in which a horse simply dies suddenly, most often very soon after work and even after a winning performance, and in which little to nothing clearly explains the cause on post-mortem. This is despite the fact most racing jurisdictions study sudden death cases very closely.
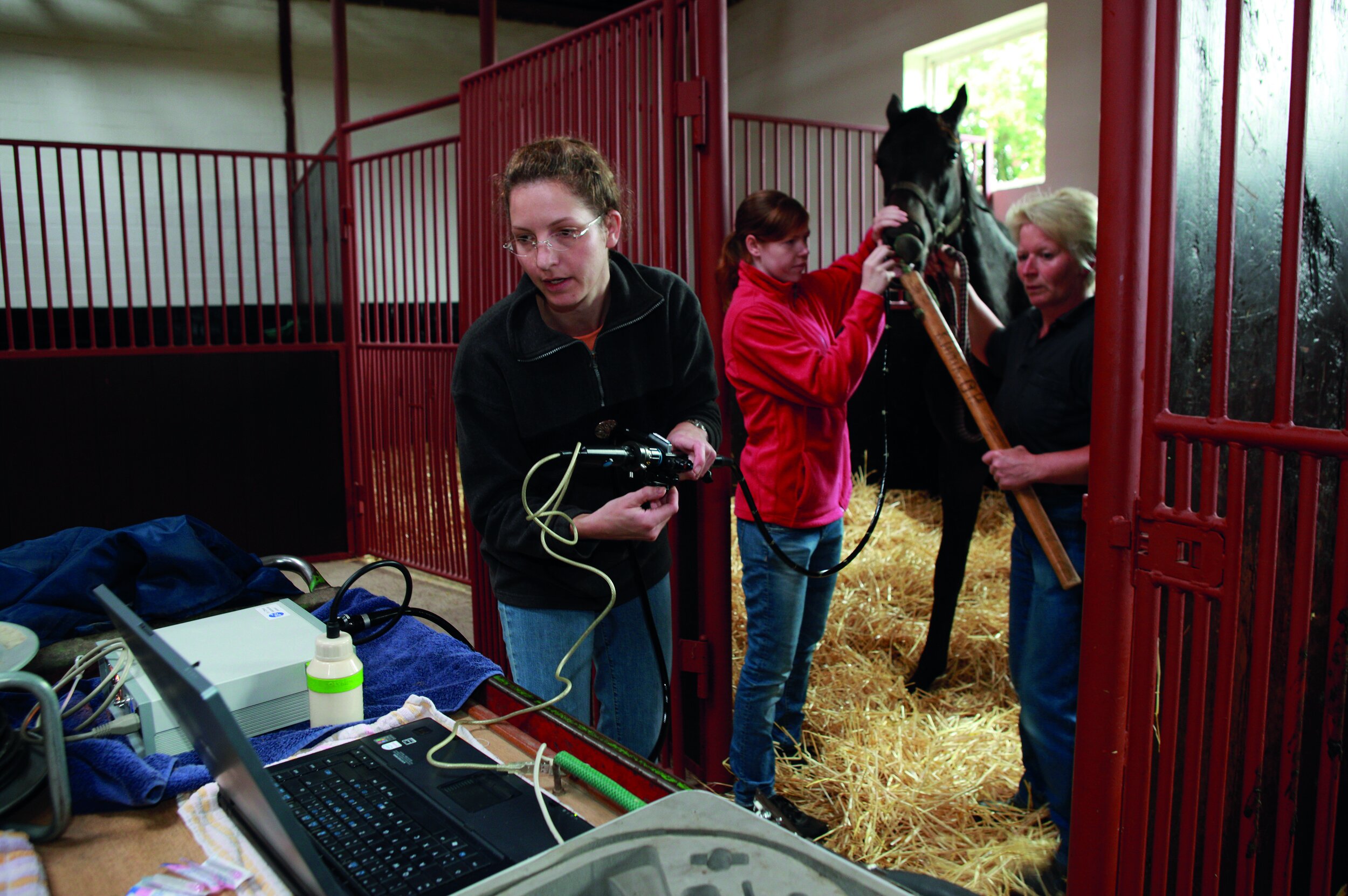
EIPH is diagnosed most often by bronchoscopy—passing an endoscope into the lung after work and taking a look. In suspected but mild cases, there may not be sufficient haemorrhage to be visible, and a procedure called a bronchoalveolar lavage is performed. The airways are rinsed and fluid is collected and examined microscopically to identify signs of bleeding. Scoping to confirm diagnosis is usually a minimum requirement before a horse can be placed on a Lasix program.
Are EIPH, severe pulmonary haemorrhage and sudden death related? Are they the same or different conditions?
At the University of Guelph, we are working on the hypothesis that most often they are not different—that it’s degrees of the same condition, or closely related conditions perhaps with a common underlying cause. We see varying clinical signs as being essentially a reflection of severity and speed of onset of underlying problems.
Causes in individual cases may reflect multiple factors, so coming at the issues from several different directions, as is the case with the range of ongoing studies, is a good way to go so long as study subjects and cases are comparable and thoroughly documented. However, starting from the hypothesis that these may all represent basically the same clinical condition, we are approaching the problem from a clinical perspective, which is that cardiac dysfunction is the common cause.
Numerous cardiac disorders and cellular mechanisms have the potential to contribute to transient or complete pump (heart) failure. However, identifying them as potential disease candidates does not specifically identify the role they may have played, if any, in a case of heart failure and in lung haemorrhage; it only means that they are potential primary underlying triggers. It isn't possible for us to be right there when a haemorrhage event occurs, so almost invariably we are left looking at the outcome—the event of interest has passed. These concerns influence the approach we are taking.
Background
The superlative performance ability of a horse depends on many physical factors:
Huge ventilatory (ability to move air) and gas exchange capacity
Body structure including limb length and design - allows it to cover ground rapidly with a long stride
Metabolic adaptations - supports a high rate of energy production by burning oxygen, tolerance of severe metabolic disruptions toward the end of race-intensity effort
High cardiovascular capacity - allows the average horse to pump roughly a brimming bathtub of blood every minute
At race intensity effort, these mechanisms, and more, have to work in coordination to support performance. There is likely not much reserve left—two furlongs (400m) from the winning post—even in the best of horses. There are many wild cards, from how the horse is feeling on race day to how the race plays out; and in all horses there will be a ceiling to performance. That ceiling—the factor limiting performance—may differ from horse to horse and even from day to day. There’s no guarantee that in any particular competition circumstances will allow the horse to perform within its own limitations. One of these factors involves the left side of the heart, from which blood is driven around the body to the muscles.
A weak link - filling the left ventricle
The cardiovascular system of the horse exhibits features that help sustain a high cardiac output at peak effort. The feature of concern here is the high exercise pressure in the circulation from the right ventricle, through the lungs to the left ventricle. At intense effort and high heart rates, there is very little time available to fill the left ventricle—sometimes as little as 1/10 of a second; and if the chamber cannot fill properly, it cannot empty properly and cardiac output will fall. The circumstances required to achieve adequate filling include the readiness of the chamber to relax to accept blood—its ‘stiffness.’ Chamber stiffness increases greatly at exercise, and this stiffened chamber must relax rapidly in order to fill. That relaxation seems not to be sufficient on its own in the horse at high heart rates. Increased filling pressure from the circulation draining the lungs is also required. But there is a weak point: the pulmonary capillaries.
These are tiny vessels conducting blood across the lungs from the pulmonary artery to the pulmonary veins. During this transit, all the gas exchange needed to support exercise takes place. The physiology of other species tells us that the trained lung circulation achieves maximum flow (equivalent to cardiac output) by reducing resistance in those small vessels. This process effectively increases lung blood flow reserve by, among other things, dilating small vessels. Effectively, resistance to the flow of blood through the lungs is minimised. We know this occurs in horses as it does in other species; yet in the horse, blood pressure in the lungs still increases dramatically at exercise.
If this increase is not the result of resistance in the small vessels, it must reflect something else, and that appears to be resistance to flow into the left chamber. This means the entire lung circulation is exposed to the same pressures, including the thin-walled capillaries. Capillaries normally work at quite low pressure, but in the exercising horse, they must tolerate very high pressures. They have thin walls and little between them, and the air exchange sacs in the lung. This makes them vulnerable. It's not surprising they sometimes rupture, resulting in lung haemorrhage.
Recent studies identified changes in the structure of small veins through which the blood flows from the capillaries and on toward the left chamber. This was suspected to be a pathology and part of the long-term consequences of EIPH, or perhaps even part of the cause as the changes were first identified in EIPH cases. It could be, however, that remodelling is a normal response to the very high blood flow through the lungs—a way of increasing lung flow reserve, which is an important determinant of maximum rate of aerobic working.
The more lung flow reserve, the more cardiac output and the more aerobic work an animal can perform. The same vein changes have been observed in non-racing horses and horses without any history or signs of bleeding. They may even be an indication that everything is proceeding as required and a predictable consequence of intense aerobic training. On the other hand, they may be an indication in some horses that the rate of exercise blood flow through their lungs is a little more than they can tolerate, necessitating some restructuring. We have lots to learn on this point.
If the capacity to accommodate blood flow through the lungs is critical, and limiting, then anything that further compromises this process is likely to be of major importance. It starts to sound very much as though the horse has a design problem, but we shouldn't rush to judgement. Horses were probably not designed for the very intense and sustained effort we ask of them in a race. Real-world situations that would have driven their evolution would have required a sprint performance (to avoid ambush predators such as lions) or a prolonged slower-paced performance to evade predators such as wolves, with only the unlucky victim being pushed to the limit and not the entire herd.
Lung blood flow and pulmonary oedema
There is another important element to this story. High pressures in the capillaries in the lung will be associated with significant movement of fluid from the capillaries into lung tissue spaces. This movement in fact happens continuously at all levels of effort and throughout the body—it's a normal process. It's the reason the skin on your ankles ‘sticks’ to the underlying structures when you are standing for a long time. So long as you keep moving a little, the lymphatic system will draw away the fluid.
In a diseased lung, tissue fluid accumulation is referred to as pulmonary oedema, and its presence or absence has often been used to help characterise lung pathologies. The lung lymphatic system can be overwhelmed when tissue fluid is produced very rapidly. When a horse experiences sudden heart failure, such as when the supporting structures of a critical valve fail, one result is massive overproduction of lung tissue fluid and appearance of copious amounts of bloody fluid from the nostrils.
The increase in capillary pressure under these conditions is as great as at exercise, but the horse is at rest. So why is there no bloody fluid in the average, normal horse after a race? It’s because this system operates very efficiently at the high respiratory rates found during work: tissue fluid is pumped back into the circulation, and fluid does not accumulate. The fluid is pumped out as quickly as it is formed. An animal’s level of physical activity at the time problems develop can therefore make a profound difference to the clinical signs seen and to the pathology.
Usual events with unusual consequences
If filling the left ventricle and the ability of the lungs to accommodate high flow at exercise are limiting factors, surely this affects all horses. So why do we see such a wide range of clinical pictures, from normal to subclinical haemorrhage to sudden death?
Variation in contributing factors such as type of horse, type and intensity of work, sudden and unanticipated changes in work intensity, level of training in relation to work and the presence of disease states are all variables that could influence when and how clinical signs are seen, but there are other considerations.
Although we talk about heart rate as a fairly stable event, there is in fact quite a lot of variation from beat to beat. This is often referred to as heart rate variability. There has been a lot of work performed on the magnitude of this variability at rest and in response to various short-term disturbances and at light exercise in the horse, but not a lot at maximal exercise. Sustained heart rate can be very high in a strenuously working horse, with beats seeming to follow each other in a very consistent manner, but there is in fact still variation.
Some of this variation is normal and reflects the influence of factors such as respiration. However, other variations in rate can reflect changes in heart rhythm. Still other variations may not seem to change rhythm at all but may instead reflect the way electrical signals are being conducted through the heart.
These may be evident from the ECG but would not appear abnormal on a heart rate monitor or when listening. These variations, whether physiologic (normal) or a reflection of abnormal function, will have a presently, poorly understood influence on blood flow through the lungs and heart—and on cardiac filling. Influences may be minimal at low rates, but what happens at a heart rate over 200 and in an animal working at the limits of its capacity?
Normal electrical activation of the heart follows a pattern that results in an orderly sequence of heart muscle contraction, and that provides optimal emptying of the ventricles. Chamber relaxation complements this process.
An abnormal beat or abnormal interval can compromise filling and/or emptying of the left ventricle, leaving more blood to be discharged in the next cycle and back up through the lungs, raising pulmonary venous pressure. A sequence of abnormal beats can lead to a progressive backup of blood, and there may not be the capacity to hold it—even for one quarter of a second, a whole cardiac cycle at 240 beats per minute.
For a horse that has a history of bleeding and happens to be already functioning at a very marginal level, even minor disturbances in heart rhythm might therefore have an impact. Horses with airway disease or upper airway obstructions, such as roarers, might find themselves in a similar position. An animal that has not bled previously might bleed a little, one that has a history of bleeding may start again, or a chronic bleeder may worsen.
Relatively minor disturbances in cardiac function, therefore, might contribute to or even cause EIPH. If a horse is in relatively tough company or runs a hard race, this may also contribute to the onset or worsening of problems. Simply put, it's never a level playing field if you are running on the edge.
Severe bleeding
It has been suspected for many years that cases of horses dying suddenly at exercise represent sudden-onset cardiac dysfunction—most likely a rhythm disturbance. If the rhythm is disturbed, the closely linked and carefully orchestrated sequence of events that leads to filling of the left ventricle is also disturbed. A disturbance in cardiac electrical conduction would have a similar effect, such as one causing the two sides of the heart to fall out of step, even though the rhythm of the heart may seem normal.
The cases of horses that bleed profusely at exercise and even those that die suddenly without any post-mortem findings can be seen to follow naturally from this chain of events. If the changes in heart rhythm or conduction are sufficient, in some cases to cause massive pulmonary haemorrhage, they may be sufficient in other cases to cause collapse and death even before the horse has time to exhibit epistaxis or even clear evidence of bleeding into the lungs.
EIPH and dying suddenly
If these events are (sometimes) related, why is it that some horses that die of pulmonary haemorrhage with epistaxis do not show evidence of chronic EIPH? This is one of those $40,000 questions. It could be that young horses have had limited opportunity to develop chronic EIPH; it may be that we are wrong and the conditions are entirely unrelated. But it seems more likely that in these cases, the rhythm or conduction disturbance was sufficiently severe and/or rapid in onset to cause a precipitous fall in blood pressure with the animal passing out and dying rapidly.
In this interpretation of events, the missing link is the heart. There is no finite cutoff at which a case ceases to be EIPH and becomes pulmonary haemorrhage. Similarly, there is no distinct point at which any case ceases to be severe EIPH and becomes EAFPH (exercise-associated fatal pulmonary haemorrhage). In truth, there may simply be gradation obscured somewhat by variable definitions and examination protocols and interpretations.
The timing of death
It seems from the above that death should most likely take place during work, and it often does, but not always. It may occur at rest, after exercise. Death ought to occur more often in racing, but it doesn't.
The intensity of effort is only one factor in this hypothesis of acute cardiac or pump failure. We also have to consider factors such as when rhythm disturbances are most likely to occur (during recovery is a favourite time) and death during training is more often a problem than during a race.
A somewhat hidden ingredient in this equation is possibly the animal's level of emotional arousal, which is known to be a risk factor in humans for similar disturbances. There is evidence that emotions/psychological factors might be much more important in horses than previously considered. Going out for a workout might be more stimulating for a racehorse than a race because before a race, there is much more buildup and the horse has more time to adequately warm up psychologically. And then, of course, temperament also needs to be considered. These are yet further reasons that we have a great deal to learn.
Our strategy at the University of Guelph
These problems are something we cannot afford to tolerate, for numerous reasons—from perspectives of welfare and public perception to rider safety and economics. Our aim is to increase our understanding of cardiac contributions by identifying sensitive markers that will enable us to say with confidence whether cardiac dysfunction—basically transient or complete heart failure—has played a role in acute events.
We are also looking for evidence of compromised cardiac function in all horses, from those that appear normal and perform well, through those that experience haemorrhage, to those that die suddenly without apparent cause. Our hope is that we can not only identify horses at risk, but also focus further work on the role of the heart as well as the significance of specific mechanisms. And we hope to better understand possible cardiac contributions to EIPH in the process. This will involve digging deeply into some aspects of cellular function in the heart muscle, the myocardium of the horse, as well as studying ECG features that may provide insight and direction.
Fundraising is underway to generate seed money for matching fund proposals, and grant applications are in preparation for specific, targeted investigations. Our studies complement those being carried out in numerous, different centres around the world and hopefully will fill in further pieces of the puzzle. This is, indeed, a huge jigsaw, but we are proceeding on the basis that you can eat an elephant if you're prepared to process one bite at a time.
How can you help? Funding is an eternal issue. For all the money that is invested in horses there is a surprisingly limited contribution made to research and development—something that is a mainstay of virtually every other industry; and this is an industry.
Look carefully at the opportunities for you to make a contribution to research in your area. Consider supporting studies by making your experience, expertise and horses available for data collection and minimally invasive procedures such as blood sampling.
Connect with the researchers in your area and find out how you can help. Watch your horses closely and contemplate what they might be telling you—it's easy to start believing in ourselves and to stop asking questions. Keep meticulous records of events involving horses in your care— you never know when you may come across something highly significant. And work with researchers (which often includes track practitioners) to make your data available for study.
Remember that veterinarians and university faculty are bound by rules of confidentiality, which means what you tell them should never be ascribed to you or your horses and will only be used without any attribution, anonymously. And when researchers reach out to you to tell you what they have found and to get your reactions, consider actually attending the sessions and participating in the discussion; we can all benefit—especially the ultimate beneficiary which should be the horse. We all have lots to learn from each other, and finding answers to our many challenges is going to have to be a joint venture.
Finally, this article has been written for anybody involved in racing to understand, but covering material such as this for a broad audience is challenging. So, if there are still pieces that you find obscure, reach out for help in interpretation. The answers may be closer than you think!
Oyster
And what about Oyster? Her career was short. Perhaps, had we known precisely what was going on, we might have been able to treat her, or at least withdraw her from racing and avoid a death during work with all the associated dangers—especially to the rider and the associated welfare concerns.
Had we had the tools, we might have been able to confirm that whatever the underlying cause, she had cardiac problems and was perhaps predisposed to an early death during work. With all the other studies going on, and knowing the issue was cardiac, we might have been able to target her assessment to identify specific issues known to predispose.
In the future, greater insight and understanding might allow us to breed away from these issues and to better understand how we might accommodate individual variation among horses in our approaches to selection, preparation and competition. There might be a lot of Oysters out there!
For further information about the work being undertaken by the University of Guelph
Contact - Peter W. Physick-Sheard, BVSc, FRCVS.
Professor Emeritus, Ontario Veterinary College, University of Guelph - pphysick@uoguelph.ca
Research collaborators - Dr Glen Pyle, Professor, Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Guelph - gpyle@uoguelph.ca
Dr Amanda Avison, PhD Candidate, Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Guelph. ajowett@uoguelph.ca
References
Caswell, J.I. and Williams K.J. (2015), Respiratory System, In ed. Maxie, M. Grant, 3 vols., 6th edn., Jubb, Kennedy and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, 2; London: Elsevier Health Sciences, 490-91.
Hinchcliff, KW, et al. (2015), Exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage in horses: American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine consensus statement, J Vet Intern Med, 29 (3), 743-58.
Rocchigiani, G, et al. (2022), Pulmonary bleeding in racehorses: A gross, histologic, and ultrastructural comparison of exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage and exercise-associated fatal pulmonary hemorrhage, Vet Pathol, 16:3009858221117859. doi: 10.1177/03009858221117859. Online ahead of print.
Manohar, M. and T. E. Goetz (1999), Pulmonary vascular resistance of horses decreases with moderate exercise and remains unchanged as workload is increased to maximal exercise, Equine Vet. J., (Suppl.30), 117-21.
Vitalie, Faoro (2019), Pulmonary Vascular Reserve and Aerobic Exercise Capacity, in Interventional Pulmonology and Pulmonary Hypertension, Kevin, Forton (ed.), (Rijeka: IntechOpen), Ch. 5, 59-69.
Manohar, M. and T. E. Goetz (1999), Pulmonary vascular resistance of horses decreases with moderate exercise and remains unchanged as workload is increased to maximal exercise, Equine Vet. J., (Suppl.30), 117-21.
Celebrating breeders - Tom Egan - the owner breeder of NY bred superstar - Red Knight
Words by Bill Heller
Winning a stakes race, let alone a graded stakes, is a thrill for any Thoroughbred owner. But what if you also bred that horse? That’s special—literally choosing the mating, then deciding to keep him rather than sell him at auction, and waiting a year or two to race him.
Now imagine—with just 151 career starts as an owner of 14 Thoroughbreds—that horse was the last one you own after 50 years of loving, working with and racing horses.
Like every other owner, 75-year-old Tom Egan was told never to fall in love with his horses. He couldn’t help himself with Red Knight, a remarkable eight-year-old gelding who returned from an 11-month layoff to capture the $156,000 Colonial Cup at Colonial Downs and the $694,180 Gr. 2 Kentucky Turf Cup Stakes at Kentucky Downs by a nose.
“Red is my last horse,” Egan said. “I’m very close to him.”
He just wishes his wife Jaye, who died December 30, 2016, at the age of 53 after a brave, 17-year battle with breast cancer, was with him to enjoy Red Knight’s success. “Racing isn’t the same without her. Marriage isn’t the same. We accomplished so much more than we could have hoped. My wife was such a beautiful person. Shared joy is better than joy.”
They met in July 1990. “I took her, with much trepidation, to Saratoga,” he said. “I thought, `Is she going to like it? What if she thinks it’s silly?’”
She thought it was wonderful. “Man, she loved it, she wanted to get there before the first race and stay until after the ninth.”
Egan’s interest in Thoroughbreds traces back to his father, Lester, an attorney in Hartford, Connecticut, who loved gambling and horse racing. “My dad was primarily a tax attorney; to me, it was too boring.”
Egan, who now lives in Ocala, also became an attorney after attending the University of Hartford and Quinnipiac Law School. “I did personal injury, criminal law and eminent domain.”
Asked if he enjoyed it, Egan said, “There were only two things wrong with the practice of law: judges and clients.”
Mostly retired now, he said he’s a “recovering attorney.” A couple of long-time clients still use his services.
Egan’s first visit to a racetrack came in 1971 at Rockingham. He then attended Suffolk Downs before visiting Saratoga and Belmont Park. In 1976, he took a job working as a hot-walker and groom at a farm in Massachusetts, then with John Russell, who was training for the powerful Phipps Stable.
But he didn’t stick to racing, attending law school and beginning a career.
His first horse was a pleasure horse, Rebel, in 1970. “I rode him on weekends. He did what I wanted him to do: run fast and true.”
Egan’s first Thoroughbred was Shadow, a grandson of Forward Pass. Egan began riding jumpers with him. “I got up to 3-foot-3. Shadow could jump 4-9.”
More than 30 years later, with the love of his life in hand, he plunged into Thoroughbred ownership—modestly. He decided to race and breed under the name of Trinity Stable, even though there is no stable nor farm. The 250-year-old Trinity Church behind his house was his inspiration.
In 2003, the Egans purchased the dam Isabel Away, a daughter of Horse of the Year Skip Away, at the Keeneland Sale, for $60,000. “My wife saw the mare and said that we just had to have her. I think the first thing she liked was her color, but upon closer examination, she really liked her an awful lot. When I saw her in the back walking ring before she went out to the sales ring, she was just very classy and composed. At that point, I said, `Yeah, sounds good.’”
Though she won just one of 11 lifetime starts, she would produce two New York-bred geldings who have combined to win more than $1.8 million. And Red Knight isn’t done racing.
The following April, the Egans were at Keeneland for the spring meet. “We met a trainer, and he said, `Ninety-five percent of owners get involved because of status.’ My wife calmly looked at him and said, `We’ve been here three days. We had no seats; we don’t know anybody, and we’ve had a lovely time.’”
Ten years later, the older of the two brothers, Macagone (pronounced Ma-ka-gon), a speedy son of Artie Schiller, took the Egans on quite a run. After being claimed away from the Egans for $40,000 on June 27, 2018, Macagone continued racing until the age of nine, finishing with 11 victories, six seconds and eight thirds from 47 starts with earnings of $654,981.
Identifying Macagone was easier than pronouncing his name correctly. “Tom Durkin, the greatest race caller ever, even got it wrong. I had a couple of friends talk to him about the pronunciation. He couldn’t get it. I was in downtown Saratoga at an Italian designer’s shop one morning and I was admiring one sports jacket. The owner of the store said he had made it for Tom Durkin, and he was picking it up the next morning. I put a note in his jacket with the horse’s name. Tom pronounced it correctly every time after that.”
Egan called Macagone “...a cool horse; he reminded me of Sonny Liston in the paddock—a bay with no white markings. He had that look about him: `I’m here, I know what I’m doing, and I’m going to kick your ass.’ He beat some very good horses.”
For the Egans, Macagone captured the stakes named for his sire, the Artie Schiller at Aqueduct, by three-quarters of a length at 34-1. Announcer John Imbriale made the call, “A son of Artie Schiller wins the Artie Schiller at 34-1!” Macagone also won consecutive runnings of the Danger’s Hour Stakes at Aqueduct before finishing third in it. After he was claimed, Macagone set a then track record at Saratoga, winning a one-mile New York-bred allowance in 1:33.13 on the Inner Turf Course.
Red Knight, a son of Pure Prize trained originally by Hall of Famer Bill Mott, put together a successful career in his first four years of racing, taking the 2020 Gr. 3 Sycamore at Keeneland and finishing second by a half-length a month later in the Gr. 3 Red Smith Handicap at Aqueduct.
Egan, acting on a tip from a friend, found out Red Knight loved raw, sliced sweet potatoes. “They’re palatable to the stomach of a horse,” Tom said. “A friend of mine suggested it.”
At the age of seven last year, Red Knight finished second in the Gr. 3 Louisville at Churchill Downs but didn’t hit the board in five other starts.
Egan decided to give him a long break and switch trainers. “It took him 11 months to get healthy,” Tom said. “I called Mike Maker. I said, `You don’t know me, but you might know my horse, Red Knight.’ He said, `Oh, yes I do.”
Maker has obviously done a splendid job with Red Knight, who in two starts has made 2022 Tom’s highest single-season in earnings. Red Knight’s success gave Egan a problem, a good problem to have: should he supplement Red Knight to the Gr. 1 $4 million Breeders’ Cup Turf for $100,000?
“I’m never going to have that problem again,” Egan said.
Either way, Egan has already been working with his good friend, Laura Fonde, a hunter-jumper rider, to transition Red Knight to a successful and meaningful second career. “He’s never going to be happy just standing out there in a field.”
He knows his horse, who has 10 victories, eight seconds and one third from 29 starts with earnings of more than $1.2 million. Earlier this year, he knew his horse wasn’t done racing at its highest level. If not, he would have retired him. “I could tell that he still had it in him.”
Tom Egan knew. Maybe Jaye Egan did too.
The Often Overlooked Equine Sacroiliac Joint
Horses that present as sore in the hindquarters can be perplexing to diagnose. Sometimes the problem is found in the last place you look – the sacroiliac joint.
Article by Annie Lambert
Even though the sacroiliac joint (SI) was on veterinary radars long ago, due to its location buried under layers of muscle in the equine pelvic region, the joint and surrounding ligaments were tough to diagnose and treat.
The sacroiliac joint is often a source of lower back discomfort in race and performance horses. Trainers may notice several clinical signs of a problem. These hints include sensitivity to grooming, objections to riders getting legged up, stiffness of motion, pain to manual palpation of the rump or back, resistance to being shod behind and poor performance.
Of course, those symptoms could describe other hind limb soundness issues, making the origin of the problem arduous to ascertain. A thorough physical examination with complete therapeutic options can relieve sacroiliac pain. The treatments are complicated, however, by the anatomy of the SI area.
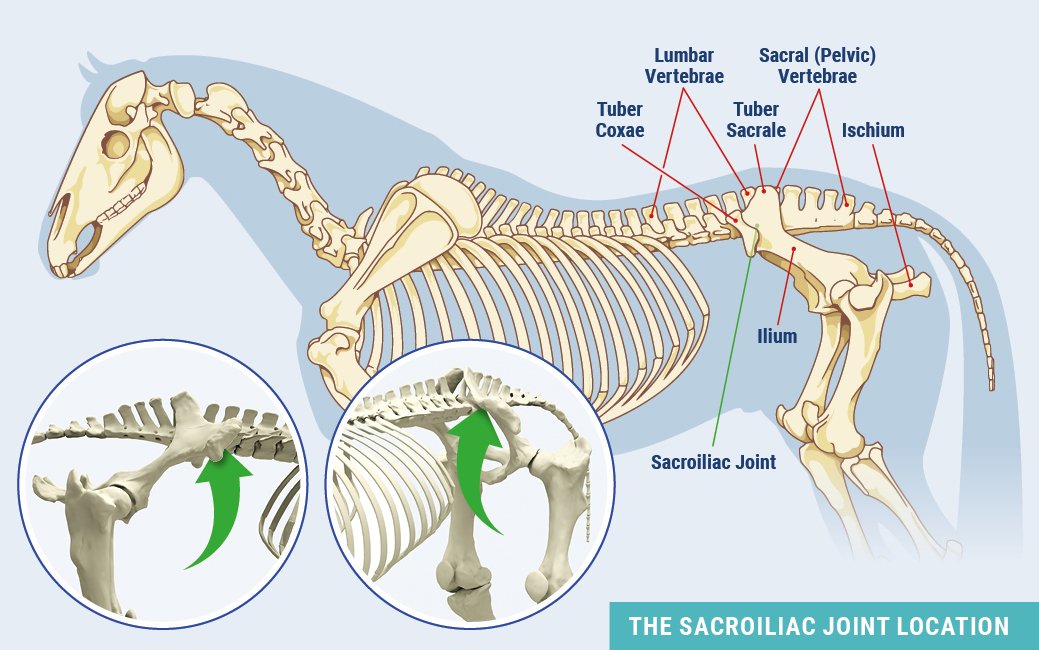
The equine pelvis is composed of three fused bones: ilium, ischium and pubis. The sacrum, the lower part of the equine back, is composed of five fused vertebrae. The sacroiliac joint is located where the sacrum passes under the top of the pelvis (tubera sacrale). The dorsal, ventral and interosseous sacroiliac ligaments help strengthen the SI joint.
The SI and surrounding ligaments provide support during weight bearing, helping to transfer propulsive forces of the hind limbs to the vertebral column—creating motion much like the thrust needed to break from the starting gate.
Sound complicated? It certainly can be.
Diagnosing Dilemmas
It wasn’t until modern medical technology advanced that the SI could be explored seriously as a cause of hind lameness.
“The sacroiliac is one of the areas that’s very hard to diagnose or image,” explained Dr. Michael Manno, a senior partner of San Dieguito Equine Group in San Marcos, California. “[Diagnostics] of the area probably correlated with bone scans or nuclear scintigraphy. You can’t really use radiographs because the horse is so massive and there is so much muscle, you can’t get a good image.
“About the only time you can focus on the pelvis and get a decent radiograph is if the horse is anesthetized—you have a big [x-ray] machine and could lay the horse down. But, it’s hard because with anything close to a pelvic injury, the last thing you want to do is lay them down and have them have to get back up.”
The nuclear scintigraphs give a good image of hip, pelvis and other anatomical structures buried deep in the equine body, according to Manno, a racetrack practitioner. “Those images can show areas of inflammation that could pretty much be linked right to the SI joint.”
The other modern technological workhorse in the veterinary toolbox is the digital ultrasound machine. Manno pointed out that veterinarians improved diagnostics as they improved their ultrasounding skills and used those skills to ultrasound areas of the body they never thought about before. Using different techniques, frequencies and various heads on the machine’s probe, the results can be fairly remarkable.
“The ultrasound showed you could really image deeper areas of the body, including an image of the sacroiliac joint,” Manno said. “It can also show some ligament issues.”
Where the SI is buried under the highest point of a horse’s rump, and under heavy gluteal muscles, there are two sets of ligaments that may sustain damage and cause pain. The dorsal sacroiliac ligaments do not affect the sacroiliac joint directly, but help secure the ilium to the sacral spine. The ventral sacroiliac ligaments lie deeper, in the sacroiliac joint area, which they help stabilize. These hold the pelvis tight against its spine. The joint itself, being well secured by these ligaments, has little independent movement and therefore contains only minimal joint fluid.
Diagnosing the SI can be complex because horses often travel their normal gait with no change from normal motion—no signs of soreness. Other horses, however, are sore on one leg or another to varying degrees, sometimes with a perceptible limp.
“I don’t know that there is a specific motion,” Manno explained. “You just know that you have a hind end lameness, and I think a lot of performance horses have mildly affected SI joints.
“The horses that are really severe become acutely lame behind, very distinct. You go through the basic diagnostics, and I think most of these horses will show you similar signs as other issues behind. We palpate along the muscles on either side of their spine and they are sore, or you palpate over their croup and you can get them to drop down—that kind of thing. Other times you do an upper limb flexion on them and they might travel weird on the opposite leg. So, it can be a little confusing.”
In the years prior to the early 2000s, the anatomical location of the SI hindered a definite diagnosis; decisions on hind soreness were more of a shrug, “time and rest” treatment evaluation. As one old-time practitioner called it, a SWAG – “Scientific Wild Ass Guess.”
Even with modern tools, making a conclusive diagnosis can be opaque.
“The less affected horses, through exercise and with medications like Robaxin [muscle relaxer] or mild anti-inflammatories, seem to be able to continue to perform,” Manno said. “I don’t know how you can be perfectly sure of an inside joint unless you try to treat it and get results.”
“That’s why bone scans came into play and are really helpful,” Manno added. “You can image that [SI] area from different angles with the machine right over the path of the pelvis, looking down on it or an angle view into it, and then you see it from the side and the back very often. We can get an idea from the different views and angles of where the inflammation is and pinpoint the problem from that.”
Once Manno has a generalized idea of where the problem is, he fine-tunes his hypothesis using more diagnostics with a digital ultrasound machine.
“You can ultrasound from up above and see the joint that way,” he said. “As ultrasound has progressed, we’ve found that the rectal probes the breeding vets have used can also be tuned in to start looking for other things. If you turn them upwards, you can look at the bottom of the pelvis and the SI joint. You can see things through the rectum by just looking straight up. That is a whole new thing that we probably never thought about doing. I don’t profess to be very great at it; it’s not something I do a lot, but there are people that are just wonderful at it.”
Treating a Theorem
But, if the diagnosis is incorrect, the prescribed treatment may be anything but helpful.
“In many cases, if a horse is really sore, you need to be very careful,” cautioned Manno. “What you don’t want to do is go from a strain or some sort of soft tissue injury into a pelvic fracture by trying to keep them going. In many cases you are back in the old rest and time type of treatment.”
Manno pointed out one treatment that has advanced over many years is injecting the SI joint directly. There are a couple of techniques used when injecting the SI. With a blind injection the practitioner directs a long, straight needle into the joint by relying solely on equine anatomy. The other technique employs an ultrasound machine to guide the placement of the needle into the joint.
“Normally we are just injecting cortisone in those cases,” Manno noted. “We are trying to get the inflammatory response to settle down. Hopefully that gives the horse some relief so that they’re a bit more relaxed in their musculature. You know how it is when you get a sore back; it’s hard to keep yourself from cramping, which makes everything worse.”
A slight tweak of that technique is to use a curved needle. When you are positioning the curved needle, it follows the curve of the horse’s anatomy and helps the practitioner direct the injection into the joint.
“It curves right into position for you; it gives you a little help,” Manno confirmed of the curved needle. “Some people are really good with that technique; others still like to go to the straight needle. [The curved needle] helps you approach the site without interference from the bones in that area.”
SI joint injuries affect most performance horses, including Standardbred trotters and pacers, Western performance athletes as well as hunters, jumpers and dressage horses.
The older show horses are often diagnosed with chronic SI pain, sometimes complicated by arthritis. These chronic cases—and admittedly some racehorses—are treated with different therapies. These conservative, nonsurgical treatments have been proven effective.
In addition to stall rest and anti-inflammatories, physical training programs can be useful in tightening the equine patient’s core and developing the topline muscles toward warding off SI pain. Manno, a polo player who also treats polo ponies, believes the hard-working ponies avoid having many SI injuries due to their fitness levels.
“I think these polo horses are similar to a cross between a racehorse and a cutting horse,” Manno opined. “They are running distances and slide stopping and turning.”
Other treatments utilized include shockwave, chiropractic, acupuncture, therapeutic laser and pulsed electromagnetic therapy.
Superior Science
With the new diagnostic tools and advanced protocols in their use, veterinarians can pinpoint the SI joint and surrounding areas much closer. This gives them an improved indication that there definitely is an issue with the sacroiliac.
When there is a question about what is causing hind end lameness, most practitioners begin with blocking from the ground up.
“In many cases with hind end lameness that we can’t figure out, we block the lower leg; if it doesn’t block out down low, we conclude the problem is up high,” Manno said. “Once you get up to the hock you’re out of options of what you can figure out. You start shooting some x-rays, but by the time you get to the stifle, you’re limited. Bone scans and ultrasounds have certainly helped us with diagnosing.”
Manno doesn’t see a lot of SI joint injuries in his practice, but he noted there were cases every now and again. He also opined that there were probably other cases that come up in racehorses on a short-term basis. He also noted that, although it may not be a real prominent injury, that’s not to say it has not gone undiagnosed.
“I think we realize, in many of the horses we treat, that the SI joint is something that may have been overlooked in the past,” Manno concluded. “We just didn’t have the ability to get any firm diagnosis in that area.”
Patrick O’Keefe - Kentucky West Racing
Article by Bill Heller
Growing up in Ogden, Utah, Patrick O’Keefe never saw a racetrack. But it didn’t prevent him from falling in love with a horse.
Patrick did bond with his father through railroads. “I’m a two-generation railroad worker,” he said. “My dad worked for the Union Pacific Railroad. I worked there while I was going to college at the University of Utah. Just before I graduated, he had a heart attack and died. My railroad career ended at that point. So I hooked up with a good friend, Dennis Bullock. I loved golf. We went looking for a property to build a golf course. We looked all over the country. We didn’t have a lot of money, but we had a lot of energy.”
Their search took them to Bear Lake, Idaho, near the southeast border of Idaho and Utah, and Patrick liked what he saw. They found the property owner and made a deal. “I gave him $10 down,” Patrick said. “I had to come up with $2,000.”
He did. They built a golf and country club, and then sold some 1,000 lots on the property. “I was pretty good at sales,” Patrick said.
On a fateful day, one of Patrick’s buddies from home, Wayne Call, paid a visit. He’d moved to the east and was back visiting family. “He lived right next to me in Ogden,” Patrick said. “His dad worked for Union Pacific.” Wayne, who had worked in bloodstock and trained a few horses, told Patrick he thought Bear Lake would be a great place to raise Thoroughbreds. Patrick told Wayne he thought it was too cold to raise horses but Wayne told him the cold kills parasites and limits disease. In Ray Paulick’s February 2022, story in the Paulick Report, Patrick said, “We have good water and several hundred acres, so I said I’d give it a try. I was dumb as a post. I had no background in racing whatever.”
So he leaned on Wayne and they took off for a nearby off-track betting facility in Evanston, Wyoming. “Wayne told me to look for a mare that’s won a lot of races that had good breeding,” Patrick said. He settled on Rita Rucker, a granddaughter of Danzig who’d won 21 races, including four stakes and earned $249,767. Her last start was in a $16,500 claimer, and Patrick got her for $7,500.
Patrick chose Kentucky West Racing—a courtesy to Wayne who once owned a hotel named Frontier West—as a stable name and bred Rita Rucker to Thunder Gulch. Patrick decided to raise the foal on his farm in Bear Lake. “My ranch is 200 acres,” he said. “We fenced a paddock. We had a little manger—a lean-to. When they unloaded Rita Rucker, she was absolutely gorgeous. I couldn’t believe my eyes.”
Rita Rucker foaled a filly. Patrick named her Private World, fitting his farm’s secluded area. “I’d drive up to the ranch two or three times a day,” Patrick said. “She’d see me coming and start to run along the fence line. That was her. She just loved to run.”
One snowy evening, she ran away. “Lots of snow, and I came to watch her one night,” Patrick said. “The fence was broken, and she was gone. My ranch adjoins the National Forest. What happened was an elk got through the fence to go after my feed. I saddled another horse and got a lariat. She was at the top of the mountain. I worked my way up to the top of the mountain. It was snowing. It was amazing. It took me hours to get her.”
But he did. “She was just a yearling,” Patrick said. “I built a barn for her.”
When it was time to find a trainer, a friend recommended Bob Hess, Jr. Hess and Patrick quickly discovered they had a talented two-year-old filly. Private World won her first three starts, a maiden race at Del Mar, an ungraded stakes at Santa Anita and the $100,000 Moccasin Stakes at Hollywood Park.
“I’m offered a million and a half after the race,” Patrick said. He didn’t take long to say ‘no.’ “Let me tell you something, I was in love with that horse,” Patrick said. “I was in love with her from the day she was born. I just figured that this horse was going to be the start of something fantastic.”
Her next race was anything but. In the Gr. 1 Hollywood Starlet, Private World tired to finish last—11th by 20 ¼ lengths. She then finished second in a $96,000 stakes and fourth in an $83,000 stakes. She had posted three victories and one second in six starts and earned $166,058.
She never raced again. “She ran through an iron fence and broke her leg,” Patrick said. “I didn’t have any insurance. I lost her for racing, and I thought we would have to put her down.”
Patrick brought her back to Bear Lake, and she slowly recovered. “I spent months with her,” he said. “I hauled in bale after bale of straw. I slept in the barn with her. I bawled my eyes out for a month. I told her as long as she’s alive, I would stay in the business.”
He meant it, and now, at the age of 80, his business is thriving with a partner, Clarke Cooper. After Private World recovered, Patrick bred her to Giant’s Causeway and was rewarded with the three-year-old speedy colt Classic Causeway, who took Patrick and Clarke on a heck of a Triple Crown ride, capturing the Gr. 3 Sam F. Davis and the Gr. 2 Tampa Bay Derby for trainer Brian Lynch.
After Classic Causeway finished 11th in both the Gr.1 Florida Derby and the Gr. 1 Kentucky Derby, Patrick and Clarke switched trainers to Kenny McPeek. In his first start for his new trainer, the Gr. 3 Ohio Derby, Classic Causeway fought on the front end before weakening to third.
McPeek thought Classic Causeway would handle turf, and he gave his new horse quite the challenge: the mile-and-a-quarter Gr. 1 Belmont Derby at Belmont Park July 9. Sent off at 26-1 under Julien Leparoux, Classic Causeway went wire-to-wire, winning by three-quarters of a length. Subsequent good races, thirds in the Gr. 1 Saratoga Derby Invitational and the Gr. 3 Jockey Club Derby Invitational, leaves his connections plenty of options in a promising future.
Private World has since foaled a colt and a filly weanling by Justify, and she’s in foal to Maximum Security. “We’re loaded; we’re loaded with potential,” Patrick said. “I didn’t take the money when I needed it. I just wanted to go on this journey and see where it takes us.”
On August 31, the journey took him to a destination he’d never envisioned growing up in Ogden, Utah. He was named the Thoroughbred Owners and Breeders Association September Member of the Month. And he knows who to thank.
Asked what he thinks of when someone says “Private World,” he said, “I think of love.”
Donato Lanni - X-Men Racing
Article by Bill Heller
Thoroughbred bloodstock agent Donato Lanni cherished trips to the racetrack with his father, Giuseppe, who grew up in Italy and settled in Montreal, making a career as a construction contractor. He did well enough to pursue his passion. “My dad had a love and a desire for horses and horse racing,” Donato said. “He had some claiming horses.”
They were harness horses and Donato and his father shared evenings at Blue Bonnets Racetrack. “I grew up around it,” Donato said. ”As a kid, there’s something inside you that gets alerted. You catch the bug. I don’t think that’s a myth. I was eight or nine.
“Summertime, I got more involved. I spent all my time at Blue Bonnets going to the barn. I became a groom when I was 13 or 14. There I got to meet some really cool guys—some of the most legendary guys in harness racing: Andre LaChance, Sylvan Filion and Duncan MacTavish. Andre never talked and was not very pleasant to be around, but he was a hell of a horseman. He took a liking to me for some reason. I drove in qualifier (non-betting) races.” Donato was 16 when he bought his first horse.
Though Donato graduated from Concordia University in Montreal, he realized that he wanted to head south—far south. Taking advantage of a summer program at Concordia, Donato got a temporary visa to work in the United States, fixating on Kentucky.
“I didn’t see a future in Canada,” he said. “I asked, `How am I going to make a living with horses?’ I thought I had to go to Kentucky and see what it was like. I left Canada, knowing I was never going back.”
But he had no connections in America. “You take a chance and go to work,” Donato said.
And when you can’t find work? Running out of money, Donato bought a tent and camped out at the Kentucky Horse Park.
He got a huge break when he met John Cashman of Castleton Farm, one of the premier harness farms in North America. “I got a job with John,” Donato said. “He was very nice to me. I became the yearling manager in 1996. I was 25. I kept working. Grind, grind. Eventually doors open and you meet people.”
He counts himself lucky for meeting and then working for John “Big Johnny” Jones, the founder of Walmac International Farm in Lexington, where such super stallions as Nureyev and Alleged stood. Jones was also the founding partner of Four Star Sales. Initially, Donato landed a job with Walmac selling stallion services.
“If there was one person most responsible for any success that I had, it was Johnny Jones,” Donato told Murray Brown in his October 2021 story in Harness Racing Update. “Johnny was a noted bloodstock agent who ran Walmac International. It was from him that I learned my craft. He sold and bought horses. Eventually, so did I. While I was at Walmac, Johnny supported me on my first route towards becoming an American citizen.”
While with Walmac, Donato got to know Thoroughbred owner and movie theater magnate George Krikorian. He told Donato to let him know if one yearling caught his eye at any of the sales. One did—Starrer. She sold for $35,000 and won multiple Gr. 1 stakes on the way to becoming Donato’s first millionaire. In an article in Blood-Horse magazine, Krikorian said of Donato, “I don’t know anyone who had a better eye for horses than he does.”
Eventually, Donato worked for John Sikura’s Hill ‘n’ Dale Farm as director of Bloodstock Services, and became friends with Hall of Fame trainer Bob Baffert. “I met Bob 20 years ago at a sales,” Donato said. “He took me around and showed me what to look for. We’re still pretty close. I learned my craft through Bob Baffert. He’s a great horseman. He’s the best.”
Donato has paid Baffert back by selecting two Horses of the Year: Arrogate (2016) and Authentic (2020).
In 2006, Donato reconnected with Canadian horsemen, specifically trainer Kevin Attard. Attard trained Leonnatus Anteas, a yearling colt Donato picked out for Nob Hill Farm. The following year, Leonnatus Anteas won all three of his starts and was named Canadian Champion Two-Year-Old Colt. “That was the start of our relationship together,” Kevin said. “He sent me a couple horses over the years. For me to be associated with him has been a boost to my career. He respects me as a trainer.”
A few years back, Donato decided to start a new team. He convinced several Canadian horse owners and hockey fans to form X-Men Racing and then partnered with SF Racing and Madaket Stables. Lanni nicknamed the partnership “The Avengers. We put a fund together and bought a dozen horses,” Donato told Murray Brown in his story. “They’re all guys that are in the horse business—some of them with Standardbreds. But what they all have in common, besides being friends with me, is that they’re all lucky.”
One of the original dozen X-Men Racing horses was Moira. All the filly did in August was defeat colts while taking the $1 million Gr. 1 Queen’s Plate by seven lengths in track-record time. Less than a month later, their two-year-old filly Last Call won the Gr. 1 Natalma.
Through all the ups and downs, all the twists and turns of his colorful career, he never lost that feeling he first experienced when he went to the track with his father. “They’re majestic animals,” Donato said. “They’re beautiful to look at. You go work with them; it’s very challenging and it’s fun. We got started because we love the horse.”
Dr. Robert and Laura Vukovich
Article by Bill Heller
Going to the track with your father is a powerful experience for a little boy—a treasured memory. “I grew up on the Jersey shore, and my dad used to take me out to Monmouth Park,” Dr. Robert Vukovich of WellSpring Stables said. “I was probably nine or 10. He taught me how to read the Racing Form, and sometimes he would place a bet for me. I’ve always loved horses and horse people. I decided if I ever had the chance, I would try to get involved somehow.”
Seven decades later, he is involved up to his gills and wouldn’t want it any other way. The fact that he can share it with his wife Laura makes it even more special. “She’s been there every step of the way,” he said.
Why did he wait until the 1990s to get involved in Thoroughbred racing? “College and my pharmaceutical career got in the way,” he joked. “I started in pharmaceutical research.”
He eventually developed his own company, Robert’s Pharmaceutical, and sold it to a large United Kingdom company in the late 1990s. That allowed him to return to horses.
Asked if he ever misses his pharmaceutical career, Robert said, “No. I don’t miss all the pressures. I don’t miss all the deadlines and the regulatory commissions.”
That didn’t prevent him from being successful in his industry. “He came from nothing and has worked very hard,” Laura, a native of Brooklyn with no prior history with horses, said. “We both did. He’s just a warm, caring person even to his horses. He says, `You only go around once—no rehearsal.’”
He’s never been happier than he is now with horses. “I wake up in the morning, and I think of horses,” he said. “I talk to people all day about horses, and sometimes I even dream about them—horses like Leave No Trace. Could this be really happening? Did we win the Spinaway?” They did.
In 1999, the Vokoviches bought a horse farm in Colts Neck, New Jersey, where they now also live. “We started with 100 acres and added pieces,” Robert said. “We currently have 168 acres. Laura names most of our horses.”
She named their two-year-old filly star Leave No Trace after a movie she watched some time ago. “I didn’t see the whole movie,” she said. “It was about a father and a daughter and some tragedy.”
Their horse operation has been the complete opposite. They began breeding horses and then started buying them at auctions and racing them. “Over time, I got to appreciate that I could do better than breeding by carefully selecting horses at auctions,” Robert said. “We now buy most of our bloodstock.”
His initial success came with the help of late trainer Dominick Galluscio, who saddled Organizer and Dr. Vee’s Magic to consecutive victories in the rich Empire Classic for New York-breds in 2006 and 2007. “He was a great trainer and a friend,” Robert said.
Now he uses Phil Serpe and Jim Ryerson as his trainers. “After Dominick passed, I asked Jim Ryerson if he’d take a few horses,” Robert said. “He did. I asked him who would be useful to me as a trainer who races in New York and Florida, and he nominated Phil Serpe. Phil and I have been doing business for seven years. We train our horses in the winter down in Florida and bring them up in the springtime and decide whether to send them to Jim or Phil.”
Robert and Laura now have 15 horses in training, including eight yearlings and five weanlings. They have never done better than the last two years. In 2021, Safe Conduct won the Queen’s Plate. Unfortunately, Peter and Laura weren’t there at Woodbine. “We couldn’t get up there to watch in because of Covid,” Robert said. “We had a bunch of people here. When he crossed the finish line, I was stunned. I couldn’t believe it. It was remarkable.” More recently he finished second in the Gr. 3 Monmouth Stakes. “He’s still a special horse,” Robert said.
So is Leave No Trace, who followed a 2 ¼ length debut in a restricted maiden debut at Saratoga by capturing the Gr. 1 Spinaway there at 14-1. Serpe trains both Safe Conduct and Leave No Trace. Robert and Laura purchased Safe Conduct for $45,000 as a yearling at the Keeneland November Sale and Leave No Trace for $40,000 as a yearling at the Fasig-Tipton Mid-Atlantic Fall Sale. Combined, they have earned more than $900,000 with a lot of racing still ahead of them.
But, again, Robert and Laura weren’t at the track when Leave No Trace won the Spinaway. “We were in Switzerland when she won the Spinaway,” Laura said. “We watched it on the telephone. It was around midnight. My husband went bananas. We were very proud. Now Phil is asking us not to be there in her future races. He said he’d buy us cruise tickets.”
Regardless, Robert and Laura are embracing the ride. “To see a little baby grow up and become a rockstar in horse racing, it’s very fulfilling.” Robert said.
Actually, they enjoy every horse they have, regardless of their performances. “Horses are very honest,” Robert said. “They’re the best employees you can have. They just give you all they have, and they never question it. Mother Nature created these animals so beautiful, so powerful and, for most cases, very gentle around you. You sit and watch them in awe. They always give you their best. They give you everything they’ve got. You can’t ask for more. I’m going to be 80. The horses keep me young.”
Is sexual harassment an issue on the backstretch?
Words - Ken Snyder
“You’ve come a long way baby” was a slogan for a cigarette brand back in the late ‘60s. And while more and more women trainers are commonplace on racetracks, the problem is they and other females are still addressed as “baby” and far, far worse by male workers…in the early 2020s.
Sexual harassment at racetracks, like practically all workplaces across America, exists. And things far worse than a “honey,” “sweetie,” or yes, “baby” is directed at women by men unfamiliar with them, creating uncomfortableness or offense.
To wit, at one racetrack, female workers living on the backside above the barns generally can’t leave their rooms at night by themselves.
At another racetrack, a female assistant trainer living on the backside had to make sure to lock her tack room door as there were persons, presumably drunk and/or drugged men, pounding on it on many nights.
The locations of the instances above are not important because sexual harassment is everywhere on every racetrack. Extremes like the situations above are seemingly minor forms of harassment, not physically threatening but damaging on another level.
Sandra Washington, a 21-year-old assistant trainer to John Alexander Ortiz, is the tack room survivor. Much to Ortiz’s credit (and were all trainers this thoughtful and generous) he moved Washington into his home with his wife and family for two years. He expressed his reason succinctly: “There are some bad people back here.”
There are bad people everywhere, but the racetrack is an environment with living arrangements and working hours that make for far more dangerous scenarios.
A member of one racetrack chaplaincy, who is female and ministers specifically to female backside workers, said, “I am not allowed to work here when it is dark.” Not surprisingly, the racetrack she serves is where female barn workers also can’t go out when it is dark either.
“Most of them take showers right after they work. They don’t want to be out of their room” she said.
“If they do go out, they make sure to be part of a group,” she added, “but most completely avoid it.”
To say the racetrack is different from other workplace environments is comparing Mother Earth to the moon. Where to begin? The biggest difference is a huge majority of female workers on the racetrack do not leave their place of work for homes elsewhere. As many as 85% of workers live in racetrack dorms or above barns (and also above the horses). Life with male co-workers in some kind of proximity is 24/7.
Demographically, female racetrack workers are overwhelmingly Hispanic. In fact, racing in the U.S. might employ more Hispanics, per capita, than any other industry. If this is not a factor in the degree or number of instances of harassment, it certainly is a factor in how female victims respond to it. (More on this later.)
Add to that an outdoor environment. “Catcalls are a common commodity back here,” according to Washington—something that will bring you before Human Resources in a hurry in office settings, typically.
Lastly, there are cultural and economic issues unique to the racetrack.
Understanding the impact of coming to a foreign country and an environment that can be virtually inescapable is a factor in being preyed upon, according to Karen Jemima Davila. She is a student at Southern Baptist Seminary in Louisville and assistant to Churchill Downs racetrack chaplain, Joseph del Rosario. “It’s just work, work, work. They [Hispanic women] save a little bit for themselves and the rest they send back to their homes. It affects how they do things and how they understand themselves.”
Most do not know what is out-of-bounds as far as treatment from men because they are not integrated into American culture, lifestyle, and, most important, rights. And if they do know what is permissible and what is not, they fear reprisal or job loss if they report harassment.
“I’ll lose my job--that’s the biggest fear. ‘If I come forward, are they going to kick me out and take my license?’” said Eli Hernandez, racetrack chaplain at Santa Anita, Del Mar, and San Luis Rey.
“That’s the problem right there. ‘I keep my mouth shut; I’ll keep my job.”
Social pressures also exist to prevent either coming forward or pursuing a complaint to a conclusion and action by the racetrack against a perpetrator. “The word starts getting around that it’s their fault. ‘You brought this on yourself.‘ ‘You’re easy.’ People start whispering,” said Hernandez.
“That’s a lot of pressure. You’re talking about 25-, 26-, 27-year-olds. All they’re trying to do is make a living and support their families. It’s bad enough they’re away from their families,” said Hernandez.
Another factor is a fear of deportation if they come forward—a fear not grounded in fact. According to Hernandez and others questioned, a Hispanic woman who is an illegal immigrant is regarded as a possible victim of an offense and that only. Nothing more, nothing less. With representatives at every jurisdiction interviewed for this story, the message was the same: immigration status is not and will not be an issue with a woman lodging a complaint.
Are Hispanic women unaware of immunity from deportation proceedings if they file a complaint for sexual harassment? Lynn McNally of the Nebraska Horsemen's Benevolent and Protective Association (HBPA) responded, “That’s a good question.”
“Probably more could be done to communicate that there wouldn’t be repercussions in their immigration status because they reported something.”
Racetracks—it is safe to say and to their credit—are not ignoring the issue or standing still on measures to prevent it. Churchill Downs and the racetrack chaplaincy, along with non-profit organizations historically supporting efforts there and the Kentucky HBPA are re-instituting meetings from pre-Covid days to make female workers aware of what is and what isn’t sexual harassment, and what to do if they are harassed.
Before Covid, Churchill Downs conducted three meetings a year in the on-track chapel there.
“There are always new people, so this has to be ongoing—something that we continually address,” said del Rosario.
“The purpose is to encourage women to not accept that kind of behavior…to speak out, that Churchill Downs Security is not going to tolerate it, and to pass the word to others.“
One initiative that was also pre-Covid was hiring a women’s ministry director—a position now filled by Davila. “That has helped build trust. A woman talking to another woman will make it easier,” said del Rosario.
Nebraska tracks are similar to Churchill Downs in that harassment prevention seems to be a collective effort from various racetrack constituencies.
Both the Nebraska HBPA board members and management at racetracks in the state are at the core of a shift in attitudes of mutual respect, according to McNally. “I think that that gives us a tremendous advantage in moving things forward and having women feel comfortable in the workplace.
“There’s a difference between being internally supportive and actually taking action to prevent behaviors from occurring with employees. Our president, Gerald Wilson, has been extremely vocal about treating all employees respectfully. He’s been very, very proactive and vocal about it.”
Women-to-women relationships, counsel, and guidance are probably the most important keys to prevention on Nebraska racetracks as well, according to Lynne McNally. “We are an all-female staff at the HBPA.”
Hernandez, as well, is mindful of gender in building trust issues in his work in Southern California.
“I always have my wife there,” he said of encounters with female barn workers reporting harassment. “Sometimes they just want to talk to my wife.
“‘Who can I trust? Who can I come to where I’m not going to be judged? ‘You’re not going to put me down.’ ‘You’re not going to blame me, but you’re going to listen to me,’” Hernandez said, echoing what he has heard and what he has seen in serving as a chaplain in Southern California.
“I told my wife when we started four years ago, ‘Let’s show people our hearts before we ask them to show us their hearts.’”
Hernandez believes he and his wife have built a foundation where women are less hesitant about coming forward.
Coming forward, however, is only the beginning of a process that often is short-circuited by the victim.
He recalled driving a female racetrack worker to make a report who, on the way, told him she didn’t want to proceed with a report after all. “‘I don’t want to get a bad reputation. I don't want people to start talking bad about me,’” he recalled her saying in response to why she wouldn’t file a report.
“It will happen. Everybody is going to know. Everybody is going to say she’s a slut, or she’s the one who gave in.”
The number of individuals coming to Hernandez—two female workers last year and three in 2020—would seem to indicate the issue is not a big one, at least at Southern California racetracks. The fact is, the number of harassment offenses unreported is inestimable.
The need expressed by everyone responsible for harassment in the racetrack environment is better communication to female barn workers about their rights and making certain of good resources for protection.
Hernandez is an example, perhaps, of resources and equally important, a thoughtful, careful approach to aiding and supporting a victim. “Our main goal is to build trust by having a safe zone here where people just come here.
“We put out clothes, water, toiletries, shoes, and Pampers every day. We also make breakfast for people who don’t have money.
Perhaps more impactful and important for harassment victims is how he and his wife approach the individual. “Let’s do one ‘stitch’ at a time,” said Hernandez, using a wound analogy to describe both what he sees in harassment victims and the care that he and his wife try to bring to women coming to them. “We won't try to close up the wound in one day. Let’s talk a little bit today and then tomorrow we’ll visit it again.”
Let’s hope racing will have fewer “wounds” for the Sandra Washingtons of racing and the many, many Hispanic female workers simply trying to make a living for themselves and their families in their home countries.
A living is not always a life.
What's happened to Jerry Dixon Jr. since the Kentucky Derby?
Article by Ken Snyder
There is always someone absent from the post-Kentucky Derby press conference presenting the winning owner, trainer, and jockey to the media. If you consider the missing person is the individual closest to the winning horse who spends the most time with them, it doesn’t make sense. It also carves away from reportage a beautiful dimension to horse racing. Absent this year, as is always the case, was the groom. Jerry Dixon, Jr. had work to do: lead Rich Strike to the test barn and then to the horse’s barn for a bath and feed.
Today, four short months later, Dixon is absent from Derby-winning trainer Eric Reed’s barn. He mucks stalls now for trainer David Wilson, Jr. at Belterra Park in Cincinnati, 107 miles northeast of Louisville and Churchill Downs and eons away in terms of racing prestige. The last horse Dixon took to a paddock at the time of writing was for another Belterra trainer in a $5,000 claiming race. The reasons for Dixon’s departure from Reed are undisclosed, private, and depending on whom you ask, likely to be disputed.
It’s the racetrack.
The sport of racing demands resilience to disappointment and occasional heartbreak. Ask Steve Asmussen, maybe the hardest working trainer on the racetrack, who is the all-time leader in wins but winless with 24 Derby starters. The very best trainers like Asmussen see roughly only one out of five of their horses winning. Horses purchased for hundreds of thousands of dollars, and occasionally seven figures, flop as racehorses or worse—suffer an injury. Many never make it to the racetrack at all. As for horse owners, there’s an old joke that you can become a millionaire owning racehorses…if you start out as a billionaire. It’s a tough sport. But it has a soul.
That soul is manifested in people like Jerry Dixon, someone who, in less than half a year, has gone from the highest of highs to, well, Belterra Park.
Whatever may have happened with Jerry, there’s no denying in the opinion of many that he gave Rich Strike all of himself. Lindsy Reed, Eric’s daughter, perhaps overstated it only minimally when she said in the wake of the Derby that “Jerry didn’t let that horse out of his sight” during the two weeks the horse was stabled at Churchill Downs before the big race. Horse and groom adopted the same rest schedule, and Jerry slept on bags of wood shavings with his head in Rich Strike’s stall. He would also lie down in the stall. Waking up was left to Rich Strike who, Dixon said, would drop hay or drip water on him to wake him up.
In all sports, there are relationships between teammates, player and coach, and competitors—the best example being jockeys who are de facto guardians of each other’s lives. But horse racing, all by itself, offers animal and human relationships with discoveries that, if they don’t touch you someplace in your heart, they should. There is a unique bond not duplicated between humans. Grooms and horses develop their own language—a kind of telepathy that no other person shares. A good, if not great, groom like Dixon (and he falls more to the latter of those two adjectives) is the protector, caretaker and “interpreter” for the horse, reading the body, the behavior and most importantly the changes that tell a groom first, and subsequently a trainer and others, how the horse is doing and what might be expected. Dixon did all these things in the crucial two weeks leading up to the astounding triumph of an 80-to-one longshot.
Breaking the bond has not been easy for Dixon.
“I think about Rich Strike every day. I go through my phone and look at pictures. I even look at the Derby still.”
Dixon’s pairing with Rich Strike and the relationship that followed was not happenstance but one that was carefully considered and thought through by Eric Reed and others, given the already apparent talent of the horse well before the Derby.
Lindsy Reed introduced Dixon to Rich Strike at her family’s training center after her dad claimed him out of a race at Ellis Park. “’I’m going to leave you and Richie alone,’” Lindsy told Dixon and, without another word, walked off, leaving Dixon befuddled and a tad fearful. He knew of the horse’s potential and his importance to the stable. Whether it was a test for Dixon isn’t known but likely.
“So, he didn’t eat you alive,” Lindsy said when she returned to Dixon and Rich Strike. The horse had stood quietly, allowing Dixon to pet him, prompting her to say, “He likes you.” She said nothing more. That may have been when he won the job of the groom for Rich Strike. Before this introduction, trainer Eric Reed had seen what he called a “soft touch” with horses in Dixon that he felt might suit Rich Strike.
The choice of the relatively young Dixon, 31, who has worked on the racetrack for several trainers (including Shug McGaughey), proved to be a good one. Horse and groom established a bond that was relaxing to the energetic, if not high-strung, three-year-old.
Dixon laying down in the stall became Rich Strike’s cue to lay down as well.
Some waking hours were not so easy, however.
A few days before the Derby, Dixon needed to jog Rich Strike in front of the state veterinarian as required. “I was trying to jog Rich Strike, and he kind of just wanted to walk. Once I smooched to him a little bit to jog, he wanted to put his two front hooves in my pockets.” Rearing up in protest provided a clear message: “I’d rather not jog—maybe another time.
“I was watching the way he was training every morning. He got better and better every day; that was the biggest indicator [of coming performance]. He would bow his neck every morning while he was going. It didn’t matter if it was the day after we breezed him.” Fast recovery from a prior-day breeze or timed workout seemed to have no effect. It was what impressed Dixon most about Rich Strike before the Derby.
Watching a horse and knowing what you are seeing are two very different things. Dixon knew what he was seeing, and it pointed to everything coming up roses, as in the garland draped over Derby winners. He was confident the horse could at least hit the board in the Derby, and the win was not a total shock. “He loved the racetrack.”
A win belongs first to the horse and jockey and, of course a team—starting with the owner who writes the checks, the trainer, the groom, down to the hotwalker.
As for the post-Derby press conference, Dixon had a job to do, which he had done hundreds of times: get his horse back to the barn after a race. It’s hard to imagine this quiet, extremely polite young man, who liberally sprinkles “sirs” or “ma’ams” in his conversation, seeking or enjoying the spotlight. He was where he wanted to be: with the horse.
There were tears and a lot of them for Dixon in the wake of Rich Strike’s Derby victory.
There were tears, too, when the relationship between Dixon and Rich Strike came to an end. Psychologists might say Dixon is going through the stages of grief. Whatever the reason Dixon said, “it’s probably going to take a while to jump back in the stall and feel like I’m doing right for a horse.
“I know I still have the eye for it and the talent for it. It’s all about wanting to do it.”
In the meantime, he bides his time raking out soiled straw from stalls, pushing it in a wheelbarrow to a collection area, and spreading fresh straw. It is menial and mindless, but it keeps Dixon home in Cincinnati with his wife and daughter.
The Triple Crown trail, with its excitement and attention from the media and racing world, was “living the dream,” usually expressed sarcastically but true for Dixon. But it had a downside.
“It’s hard to have a family. You have to be all the way in or not at all,” said Dixon. All is demanded of every racetracker who wants to succeed in racing, from trainer to hotwalker. “My wife and daughter missed the family time they wanted to have with me while I was chasing my dream.
“Stepping away from grooming has given me downtime with my family.”
The racetrack itself is also family for Dixon. A lady in the racing office at Belterra has talked to him daily, telling him over and over, “’Don’t forget. You’re a part of that horse winning the Kentucky Derby.’
“She’s making sure I’m all right. I know where it’s coming from. It's not people just being kind.”
History is unerasable no matter what is going on in the present or what may come in the future. Dixon obviously heeds the encouragement of the lady in the Belterra racing office. “He won the biggest race in America. That solidifies his greatness. I’m part of the history with the horse.”
Jerry is a fourth-generation horseman, but he and he alone accomplished something no one in his family ever did or likely ever will do. Forevermore, he will be pointed out to generations of Dixons that follow: that Jerry Junior was a groom for a Derby winner.
On a recent muggy summer morning at Belterra as Jerry mucked stalls and spread new straw, an aged hotwalker passing by stopped to ask if I had ever interviewed a Derby-winning trainer (yes) or jockey (yes). “Have you ever interviewed a Derby-winning groom?” he asked with a smile and a twinkle in his eye, knowing the answer as he pointed to Jerry Dixon, Jr.
Racing, again, has its ups and downs, but the triumphs are permanent.
A Kentucky Derby is what people around the world see. What’s not seen is the day-to-day that gets a Derby starter and all other horses down to the cheapest claimer to the starting gate.
For grooms, days can begin as early as 4:00 a.m. in pitch-black darkness, of course, with bathing horses, tacking them up, and readying them for workouts. In Jerry Dixon Jr.’s case, past roles in various barns included coating legs with medication, then applying bandages or wraps, and sending a horse out under an exercise rider. The process is repeated on a second horse while the first is out on the track. When horses return, they must be bathed, their legs medicated, or simply wrapped again and fed. The merry-go-round of horses going out and coming back in from workouts, and the work needed for each horse, is virtually non-stop through 10:30 or 11 a.m.
The day, however, isn’t over. There’s an afternoon feeding, and on race days, there’s taking a horse to the paddock before a race, getting them back to the barn, bathing and feeding. During racing at Turfway Park just across the Ohio River from Cincinnati, which has night racing, the day begins at 5 a.m. for Dixon and can end as late as 10:45 or 11 p.m., if one of the horses in his care runs in the last race. “I don’t get home till midnight,” he said.
His hours during racing at Belterra are only marginally better. He has to be at the track at 4 a.m. and be there at least through feed time at 5:30 in the afternoon. A horse in the last race of the day means an extra hour at the track.
The job is a tough one and getting tougher all the time as not just most, but all racetracks have a shortage of barn help. The shortages, according to Dixon, are going to mean “somebody is getting cheated.” Something as obvious as a missing horseshoe can be overlooked in the rapid-fire process of getting horses out for workouts in the morning. “There are so many horses and so few people with a limited amount of time to get things done.”
There are other issues related to an individual trainer’s style and the regard with which they hold grooms. “Sometimes it feels like people look at the grooms as if they’re just workers and not in the aspect of being a part of the organization to have some knowledge to be able to give back to the trainer, the assistant, or whoever. Like I’ve said, we spend more time with the horse than anybody else does. We’ll see something before the trainer will. I’ve been in barns where you don’t see the trainer. It’s more of a phone type of deal.”
It’s not uncommon for grooms to sometimes double as assistant trainers, managing the barn for stables—something Jerry did at Turfway. “If we had horses in, I’d make sure I was in contact with the vet. I’d get the Lasix, or, if we had any problems, make sure we got any medication needed for the horse, take them to the races, cool them out, load them on the trailer, unload them—everything,” he said.
Races were, of course, after a full morning. “I would get there and do the stalls, do the groundwork, get the horses out with the exercise riders—find out how far we would train the horses each day.
Days off are two Sundays a month…maybe.
Dixon credits Eric Reed and his daughter Lindsy; other trainers; Reed’s groom Benito Luna, who now cares for Rich Strike; and members of his own family—his father and uncles he describes as “great horsemen”—for mentoring and helping him in his career.
It is a career that is not over. He plans to take the test for a trainer’s license and hang his own shingle perhaps as early as later this year.
Rob Atras - the 'up and coming' NY based trainer in profile
Words - Bill Heller
Trainer Rob Atras wasn’t born into racing; he was into racing before he was born. His mother didn’t let her pregnancy at the time prevent her from visiting the winner’s circle after her horse won a race at Assiniboia Downs in Winnipeg.
“She has the win picture,” Rob laughed. “She said, `You were in my stomach when the picture was taken.’ When I was old enough, I went around the track with her. I was probably five or six. ”
Three decades later, Rob is a rising star in New York—a young conditioner steeped in old school horsemanship with an uncanny knack of claiming horses. He was good enough to finish tied for seventh with Brad Cox in the 2021 Saratoga Meet, when he won his first Gr. 1 stakes, the Coaching Club American Oaks, with Maracuja. At the current Belmont Park Summer Meet, he is tied for sixth with David Donk. Rob’s earnings grew from $1.8 million in 2019 to $2 million in 2020 and $3.9 million in 2021. He’s already topped $2 million in the first six months of this year. Rob, who is 37 years old, ranked 37th nationally in earnings last year and is 37th this year through the end of June.
He is strengthened by his wife/assistant trainer/best friend Brittney, who is proud of Rob’s horsemanship. Asked why he is successful, she said, “I think because he treats each horse individually. It’s so true—how they train, how their legs are wrapped. Rob is very hands-on. He’s always feeling their legs. He’s really good at reading a condition book. Rob is very realistic about the horses we have and where they need to race to be successful.”
Rob’s equine education began with his mother, Tanis, who owned a couple of horses while working at a bank. When she retired, she had all the time she wanted with horses. “She grew up always riding,” Rob said. “She owned a couple of horses with trainer Jack Robertson. We were very close to his farm. She would help him out. I was too young at first. I’d be in the track kitchen reading the Form. I had a pretty good background from my mom.”
She couldn’t be prouder of her only child, and she saw his love of horses as a child. “That was his passion,” she said. “To be that successful at the New York tracks, we’re very proud of him. He puts his heart and soul into it. He’s done that his whole life. He loves it. He’s got a great wife, and they’re a great team.”
Rob’s father, Jim, was an undercover investigator for the Royal Canadian Mountain Police for 30 years in the province of Manitoba. “Sometimes he was gone for a week,” Rob said. “He wasn’t really involved in horses, but he’s been really supportive of me.”
Still. “We never miss a race,” his mother said. “It’s so exciting for us. We love watching him.”
Rob’s journey from Portage la Prairie in Manitoba to New York had plenty of interesting stops.
He worked summers for Jack Robertson when he was 16 and 17. Asked what he learned from him, Rob replied, “All the fundamentals—taking care of the horses, the legs, keeping track of the horses.”
After he graduated from high school, he took a job in a steel factory. “I left the job, and with everything I made, I bought a horse,” Rob said. “With no plan. I went to the University of Manitoba for a year and a half.”
Then he bolted back to the track for life.
Rob began working for trainer Bert Blake. “He’s a legend up in Canada, and he had a small stable,” Rob said. “He asked me if I could work for him. I had two horses. He said I could keep them. I trained a little on my own. Bert let me do that. I worked up to assistant trainer. It was really cool.”
His next job was even cooler. He got an offer to come to Kentucky and work for trainer Rebecca Maker, whose top horse at the time was It’s No Joke, a multiple stakes winner who earned $685,612. He was eighth in the Gr. 1 Clark at Churchill Downs, but Rob still has a good memory of the race. “I was standing next to Todd Pletcher; I emailed my mom and told her, `You’ll never believe who I was standing next to.’ After Churchill Downs, Rob worked for Maker at the Fair Grounds.
“It really opened my eyes—how big the racing world is,” Rob said. “I was so green. I was a sponge and took in everything. I wanted to be there and learn as much as I could. I was 22.”
He returned to Canada and cobbled together a stable of 15 to 20 horses. His first winner was a $5,000 claimer, Forgotten Battle, September 3, 2010, at Assiniboia Downs. Like many other trainers at Assiniboia, he wintered in Turf Paradise in Phoenix. That’s where he had the good fortune of meeting trainer Robertino Diodoro in 2014. “He sent me a couple horses to run in Canada,” Rob said. “I think I was finishing my fourth or fifth year training on my own.”
Diodoro offered him a job. “I didn’t have a ton of horses in my barn; as much as I loved Turf Paradise, it was a struggle financially. I felt like I was spinning my tires a little bit. I wasn’t really moving up. He asked me to go to Oaklawn Park. That meant giving up my horses and clients. I was going from trainer to assistant trainer, but it didn’t take long for me to decide. I’m going to take this opportunity and see where it goes.”
He has never regretted that decision. “I got along very well with Robertino; you feel like you’re working with him, not for him. We developed a friendship.”
Rob would eventually handle Robertino’s horses in New York before striking out on his own in the toughest circuit in the country. “He talked to a few people, and I wound up with six horses.” Rob said. Now he has 50.
He began on his own in the 2018–2019 winter, a calculated gamble, racing at Aqueduct while many of New York’s top outfits shipped to Florida for the winter. He knocked his opportunity out of the park, winning five races in his first nine starts.
In New York, he found a baseball team to root for, the love of his life and a goat.
“When I came to New York, I started watching the Yankees,” he said. “They had Aaron Judge. I went to a couple games.” Judge is currently leading the majors in home runs, and Rob wears a Yankees cap almost all the time.
Brittney, like her husband, was introduced to horses at a young age. “Both of my parents are horse people,” Brittney said. “My father (Larry Dixon) was a trainer and had a training center in Virginia; my mom is a vet. I grew up with horses.”
She got the opportunity of a lifetime in Godolphin’s Flying Start program, traveling all over the world. “It was amazing,” she said. “I met a lot of contacts and got to see the greatest horses in the world.”
Unsure of what she wanted to pursue in horse racing, she took a job working for Fasig-Tipton after she graduated from the University of Georgia, then worked for Bridlewood Farm.
Her mom was a vet at Belmont Park, administering Lasix shots. Brittney decided to tag along with her and then do the same with veterinarian Dr. Michael Galvin. On her first morning with him, she met Rob.
Galvin and Brittney stopped by Rob’s barn. “I was still working for Robertino at the time,” Rob said. “Dr. Galvin asked him how one of my horses did in his race. I said, 'No good!’ Then Galvin introduced Brittney. “I said, `Hi,’ and that was it,” Rob said. “I was still pissed off about the race.”
Brittney took that experience favorably. “He had no interest in talking to me; that made me more interested.”
Fate, karma or coincidence happened the next day when Rob and a friend went to Trotters, a bar and restaurant in Franklin Square. Brittney was living with her mother, and they decided to go there as well. They sat next to Rob and his pal. “We talked for two hours,” Brittney said.
While she was leaving, though, she slipped and fell down. “I slipped; I wasn’t drunk,” she said. “I was super embarrassed.”
She felt she had to tell Rob that, so she stopped by his barn the next morning. Then she invited Rob to join her and her mother for dinner. “We have been together ever since,” she said. “He’s literally the most kind, thoughtful person I know.” They married in September 2018.
Gilbert the goat
Then there’s the goat, Gilbert, possibly the greatest goat of all time. Or maybe the greatest Gilbert of all time. “I had never had a goat,” Rob said. “We had a wild horse, a Tapit colt, Tappin Vegas, who was very tough to manage. Someone said, `Why don’t you get a goat? They’re supposed to calm down horses.’ I asked around.”
Rob bought three-month-old Gilbert. He was not an instant success. “The goat was wild—running all over the place, jumping up and down,” Rob said. “We tied him down between two horses’ stables.”
Gilbert wanted nothing to do with the problem horse he was supposed to calm down, Tappin Vegas. The horse in the other stall was Becker’s Galaxy, an older gelding. “He fell in love with Becker’s Galaxy,” Rob said. “Whenever Becker’s Galaxy would leave his stall, Gilbert would cry out. But Gilbert’s calmed down. Now he listens to his name like a cat or a dog.”
Does he come when he’s called? “Sometimes,” Rob said.
Rob is much better at training horses than goats.
One of Rob’s happiest clients is Sandy Goldfarb, a long-time successful owner who had temporarily left the game. “I was with Diodoro,” Sandy said. “Then I was out of the game for five years.”
He credits Rob and Brittney for getting him back into the game. “They’re really amazing—the most down-to-earth people, and the care they give their horses is unbelievable,” Sandy said. “I just really believe in Rob, his talent, his ability. He’s done an incredible job. I have eight to 15 horses with him now. They get claimed left and right.”
Two horses they claimed gave Rob instant credibility in New York. “We claimed American Power in Saratoga for $40,000 (on July 29, 2020),” Rob said. All American Power did was win four straight, including the $145,500 Gr. 3 Toboggan Handicap, January 30, 2021, at Aqueduct. It was Rob’s first graded stakes victory.
Sandy and partners had similar success with Mr Phil—a $32,000 claim on February 27—this year who won three straight allowance races before taking on sprint superstar Jackie’s Warrior and finishing fifth in the Gr. 2 True North Handicap, June 10.
In between those two successful claims, Rob’s Maracuja gave him his first Gr. 1 stakes, taking the Coaching Club American Oaks by running down Malathaat to win by a head last July 24. “We came in as an underdog,” Rob said. “We were hoping for second, but we would have settled for third. It was quite a thrilling race, an oddly-run race.”
Indeed.
Maracuja (2) Coaching Club American Oaks 2021 - Atras’ first Gr.1 winner
“I would never have expected my first Gr. 1 to be at Saratoga,” Rob said.
Brittney still gets emotional talking about it nearly a year later: “Literally, I think I’m going to cry. I get serious goosebumps. It was so amazing and so beautiful. I am still not sure she won it.”
She did. And the common denominator for those two successful claims and the Gr. 1 stakes winner was the care they received from Rob and Brittney.
“You learn to train a $3,000 claimer as a stakes horse,” Rob said. “In feeding him, taking care of him. We just believe in that. The people I learned from were very good trainers. Everything matters: the type of feed, the hay in the stall, every little item. They’re going to be happy if they’re healthy.”
In terms of making claims, Rob said, “Obviously, the horse’s form is the first thing you look at. I like to look at a horse’s conditions. What level is next for this horse? I like to look at the back class. When I worked with Jack Robertson, that’s one thing he would do. A lot of times, he’d bring horses up from the states, who were off form. A lot would go on to be stakes horses up here (at Assiniboia).”
At Assiniboia, Rob was the leading percentage trainer in 2014. Now he’s in the Top Ten at Saratoga and Belmont. “It’s something I never really expected.” Rob said. “It’s a pretty cool feeling. When I was a youngster, I was watching New York racing and seeing all these great trainers. Then you get here as a trainer. It’s a different world. It really keeps you focused all the time. I don’t like to get ahead of myself. I think about this week. Never get complacent because you’re running against the best. It’s very tough, but very rewarding.”
Alan Balch - Inspiring Ascot
Although I’ve never been to Royal Ascot, I first went to the course in October 2012, for the second British Champions Day, where Frankel “miraculously” recorded his 14th straight and final win after having been left at the start of the rich Champion Stakes.
On a cold, damp day, with the going “soft, heavy in places,” a capacity crowd of 32,000 was in attendance, and somewhat uncharacteristically for the British (I was told), yelled itself crazy for Frankel’s super effort. Not to mention trainer Henry Cecil.
Actually, however, Ascot has a true capacity far in excess of that day’s attendance. In the most recent Royal meeting, in June this year, crowds of over 60,000 were there. The television coverage of the masses of humanity in the stands, the infield and the various enclosures all along the mile straight, the paddocks, and on both ends of the strikingly beautiful permanent stands, gave any racing fan a thrill.
At the Cheltenham Festival for jump racing in March this year, attendance over four days ranged from 64,000 to 74,000 . . . “almost capacity,” according to management. And that left the media speculating about possibly adding a fifth day to its schedule, “like Royal Ascot.”
I was in London myself this year, late in March, amazed (and pleased) to see abundant advertising for Royal Ascot almost everywhere I went. Even though Opening Day was over two months away! Track managements in Britain clearly don’t take such attendance figures for granted . . . they believe in strong promotion and marketing, at least for their major racing, and undoubtedly their commercial sponsors (of which there are many high-profile brands) do as well.
What I see here in American racing attendance is virtually the opposite. And it’s a grave concern. Have we given up trying to persuade fans to go to the races?
The exceptions here seem to be the Triple Crown races, Breeders’ Cup, some Oaklawn days, the short summer meetings at Del Mar and Saratoga, and the two short Keeneland sessions. As one of racing’s dinosaurs, I admit to living in the past. But when I joined Santa Anita in 1971, I was told by one of racing’s most authoritative figures that I’d never see a crowd of 50,000 at our track again: “Those days are long gone.” Within five years, however, the Santa Anita Handicap, Derby and Opening Day were regularly drawing well over 50,000. More importantly, our daily average attendance 15 years later, over 17 weeks of 5 days each, peaked at just under 33,000 in 1986. And that was when announced attendance in California was scrupulously honest and audited.
I mention this because now I hear the old pessimism again, all the time, walking through the nearly vacant quarter-mile long stand at Santa Anita . . . that the days of regular big crowds at race tracks, actually any real crowds at all, are long gone. The reasons cited are obvious: Internet, satellite and telephone betting, pervasive competition from other sports and gaming, and the proliferation of all sorts of simulcasting—all disincentives for going to the races.
What worries me most is hearing track executives and horsemen saying, “It really doesn’t make any difference, not having fans at the track, as long as the total handle’s there, generating purses.”
Actually, I believe it does. Not just because bets at the track contribute way more to purses than any others, and non-wagering revenues are critical to a track’s finances. It’s also an enormous difference for the future prospects of the sport. Where are those future off-track bettors going to come from if they’ve never been to the races? And how about future owners, too—how much fun is it to win a race with a few loud yells echoing through an empty stadium, whether you’re an owner or a horseplayer?
Consider, in geographical terms, that California by itself is 1.7 times larger than the United Kingdom, and a few years ago this state surpassed that entire nation in annual gross domestic product. Competitive gaming and sporting opportunities in the British Isles equal or probably exceed those available in California, at least in terms of access. Yet—I am told—the reason there’s apparently so much more interest in racing there than here is “cultural.” Her Majesty the Queen and all that?
It's true that in many respects Great Britain is the birthplace of all equestrian sport. Queen Anne founded Ascot itself in 1711, official colors were invented and approved in 1783, and then the British Empire ruled the world for so long . . . until it didn’t.
However, the Belmont Stakes and Saratoga commenced in the 1860s, the Kentucky Derby in 1875, and organized California racing in fits and starts beginning in the early 1900s. For a very long time, racing was far and away America’s most popular sport. That it hasn’t maintained a true competitive popularity here, despite the advent of so much competition, are sheer failures of management, marketing and promotion. American racing’s commitment to sophisticated, creative marketing as an investment, rather than a troublesome expense to be cut, then cut even more, has seriously waned or even disappeared over the last quarter-century.
It's never too late to rediscover and share the magical spectacle of racing. Whatever troubles our sport faces, its intrinsic allure of intersecting superlative beauty, elegance, human and equine athleticism beyond compare, coupled with its enormous array of gaming opportunities, is a marketer’s dream.
As anyone who attended Royal Ascot or watched it on television can attest.
Electrolyte Balance – vital to the proper functioning of a racehorse's system
Words - Dr. Cath Dunnett
Electrolytes are essential components of the racehorse’s diet as they are vital to the proper functioning of the body’s basic physiological processes, such as nerve conduction, muscle contraction, fluid balance and skeletal integrity. The major electrolytes, sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium and magnesium are widely distributed within the body, but can be more concentrated in particular organs and tissues.
For example, the level of potassium is very high in red blood cells but quite low in plasma, and the level of calcium in blood is low, but comparatively very high in bone and in muscle cells. The body has in-built mechanisms that work to maintain the correct electrolyte balance within the tissues, fluids and cells. These modify the absorption of electrolytes in the gut, or their excretion by the kidneys. These mechanisms are not foolproof however, and electrolyte loss through sweat can be a major issue for Thoroughbreds. The sweat of the equine athlete, unlike its human counterpart, is hypertonic; meaning that horse sweat contains higher levels of electrolytes than the circulating blood plasma. Consequently, the horse loses comparatively large quantities of electrolytes through sweating.
Although the electrolyte composition of equine sweat varies between individuals, on average a litre would contain about 3.5g of sodium, 6g of chloride, 1.2g of potassium and 0.1g of calcium. From this we can see that the majority of the electrolyte lost is in the form of sodium and chloride or ‘salt’. The amount of sweat produced on a daily basis and therefore the quantity of electrolytes lost differs from horse to horse and depends on a number of factors. As sweating is primarily a cooling mechanism, how hard a horse is working, i.e. the duration and intensity of exercise and both the temperature and humidity of the environment are all significant. Horses can easily produce 10 litres of sweat per hour when working hard in hot humid conditions. Stressful situations can also cause greatly increased sweating.
For example, during transport horses can lose a significant amount of electrolyte through sweating and the opportunity for replenishing this loss through the diet may be less as feeding frequency is reduced. Use of electrolyte supplements either in the form of powders or pastes is advocated before, during and after travel, especially over long distances. A number of air freight transport companies advise trainers to use a powdered electrolyte supplement added to the feed on a regular basis given for the 3 days prior to travel. As this helps offset much of the loss normally incurred during transport and subsequently the horses arrive at their destination in better shape. Electrolyte supplementation is a valuable attribute in the ongoing battle to reduce in-flight dehydration.
Electrolytes lost from the body in sweat must be replenished through the diet. All feeds, including forages, have a natural electrolyte content and in concentrate feeds this is usually enhanced by the addition of ‘salt’, which is sodium chloride. Forages such as grass, hay, haylage or alfalfa (lucerne) naturally contain a large amount of potassium, as can be seen from the table 1 below. In fact, 5kg of hay for example, would provide in the region of 75g of potassium, which largely meets the potassium needs of a horse in training. It is therefore questionable whether an electrolyte supplement needs to routinely contain very much potassium unless forage intake is low. Calcium is another important electrolyte, but it is lost in sweat in only very small amounts and its availability in the diet tends to be very good.
Calcium is particularly abundant in alfalfa with each kilogram of the forage providing nearly 1.5g of calcium. A kilo of alfalfa alone would therefore go a long way towards replacing the likely calcium loss through sweating. In addition, the calcium found in alfalfa is very ‘available’ to the horse in comparison to other sources, such as limestone. Calcium gluconate is another very available source of calcium, however, it has a relatively low calcium content compared to limestone (9% vs. 38%) and so much more needs to be fed to achieve an equivalent calcium intake. Interestingly, there is great variation between individual horses in their ability to absorb calcium, however, scientific studies carried out at Edinburgh Vet School showed that this variability was considerably less when a natural calcium source in the form of alfalfa was fed.
By far the most important electrolytes to add to the feed are sodium and chloride or ‘salt’. The levels of sodium and chloride found in forage are quite low and due to manufacturing constraints only limited amounts of salt can be added to traditional racing feeds. A typical Racehorse Cube fed at a daily intake of 5kg (11lbs) would provide only about 20g of sodium and 30g of chloride. As can be seen from table 2 this is a fair way short of meeting the daily requirements for these particular electrolytes by a racehorse in hard work.
It is therefore very important that supplemental sodium and chloride is fed. Ordinary table salt is by far the simplest and most economical electrolyte supplement, but the downside is the issue of palatability as the addition of larger quantities of salt to the daily feed can cause problems with horses ‘eating up’. As an alternative salt could be added to the water, but only when a choice of water with and without salt is offered. Salt should not be added to the water if it puts a horse off from drinking, as dehydration will become a problem.
Inadequate water intake can also contribute to impaction colic. Saltlicks are another alternative, although intake can be very variable and we rely on the horse’s innate ability to realise its own salt requirements, which is questionable. So addition to the feed is by far the best route for adding salt or electrolyte supplements to the diet. Splitting the daily intake between two or three feeds can reduce problems with palatability.
Mixing salt and Lo Salt can make another simple DIY electrolyte supplement in the proportion of for example 500g to 250g respectively. Salt is sodium chloride (NaCl), whilst Lo Salt contains a mixture of sodium chloride and potassium chloride (KCl). This formulation provides 3g of sodium, 6g of chloride and 1g of potassium per 10g measure. This DIY mixture will replace these electrolytes in the approximate proportions that they are lost in sweat. What are the implications of a racehorse’s diet containing too little or too much of an electrolyte and how can we assess this? An inadequate level of certain electrolytes in the diet in some horses may simply result in reduced performance. In other individuals, it can make them more susceptible to conditions such as rhabdomyolysis (tying up), or synchronous diaphragmatic flutter (thumps), both of which are regularly seen in horses in training. Conversely, an excess electrolyte intake is efficiently dealt with by the kidneys and is ultimately removed from the body via the urine.
Therefore, the most obvious effect of an excessive electrolyte intake is increased drinking and urination. For this reason, the use of water buckets rather than automatic drinkers is preferred, as whilst the latter are far more labour efficient, the ability to assess water intake daily is lost. Excessive electrolyte intake can also be a causative factor in diarrhoea and some forms of colic. There is also some recent evidence in the scientific press that suggests that repeated electrolyte supplementation might aggravate gastric ulcers. However, these early studies used an electrolyte administration protocol typical of that seen during endurance racing, rather than simply a daily or twice daily administration, which is more commonly used in racing.
Supplements that contain forms of electrolyte that dissolve more slowly in the stomach, however, may be less aggressive to the sensitive mucosa. Unfortunately blood levels of sodium, potassium, chloride or calcium are poor indicators of whether dietary intake is sufficient or excessive unless it is very severe. This is because the body has effective systems for regulating the levels of these electrolytes in blood within very tight physiological limits. A creatinine clearance test, which measures the electrolyte content of a paired blood and urine sample is a much more useful indicator of dietary electrolyte adequacy.
There are a large number of commercial electrolyte products available, with a wide range in the breadth of ingredients that they contain. Consequently, they vary enormously in the amount of electrolyte that they deliver per recommended daily dose, as can be seen in table 3. In addition, whilst some glucose or other carbohydrate can help improve palatability, its presence should not compromise the amount of electrolyte that is contained within the supplement. In humans, it is recognised that the uptake of sodium from the gut is improved in the presence of glucose, while this effect in horses has not been firmly established. Electrolyte paste products are also often used either before and or after racing or travel.
These products are useful as they allow rapid electrolyte intake even when feed eaten may be reduced following racing. These electrolyte pastes often provide a more concentrated form of supplement and it is extremely important to ensure that the horse has access to water immediately following their use. Failure to do this may mean that the concentration of electrolytes in the gut actually draws water from the circulating blood, which can exacerbate dehydration. Another disadvantage with paste supplements is that if they are not formulated well, with an appropriate consistency, they can be difficult to dispense from a syringe and the horse may also be able to spit most of the product out after administration.
Some simple rules of thumb for choosing a good electrolyte are that salt should be one of the first ingredients listed on pack, as all ingredients are listed in descending order of inclusion. Additionally, be wary of supplements that taste sweet, as they may contain a lot of carbohydrate filler and little electrolyte. Some electrolyte supplements also contain many superfluous ingredients such as vitamins and trace minerals. The inclusion of these latter ingredients is largely unwarranted and their presence could cause issues with oversupply if the electrolyte is multi-dosed daily. Some electrolyte products specifically marketed towards racing may also contain bicarbonate.
The theory behind its inclusion is sound as ‘milk shaking’, whilst outside the rules of racing, has some scientific validity. However, the limited amount of bicarbonate contained in such electrolyte supplements is unlikely to have the positive effect on performance attributed to the former practice. Other extra ingredients such as pre-biotics may be more useful as they may improve the absorption of some electrolytes. In Summary, electrolyte supplementation in one form or another is essential within a racing diet. Ensuring that you are using a good electrolyte supplement is important and the quantities fed must be flexible and respond to changes in the level of work, degree of sweating and climate.
Racetrack Fracture Support Equipment - coming to North America this summer
Words - Ian Wright
Over the last six months, British racecourses have taken a major step forward in racehorse welfare by being provided with fracture support systems (Figure 1). These consist of two sizes of compression boots and flexion splints, both for use in the forelimbs; and a set of modular adjustable splints. Together, these provide appropriate rigid external support for the vast majority of limb fractures that occur during racing. The general principles are that management of all fractures is optimized by applying rapid and appropriate support to provide stability, reduce pain and relieve anxiety.
Figure 1
The fracture support systems are about to make their debut in North America with trials due to take place this summer and fall with the support of the National HBPA.
The fracture support system is provided in two mobile impact resistant carrying boxes that protect the equipment and allow it to be checked before racing. All boots and splints are permanently labeled with individual racecourse identification to ensure return of equipment if it leaves the racetrack.
In the last 25 years there have been major improvements in fracture treatment due to significant advances in surgical techniques (particularly with internal fixation), minimally invasive approaches (arthroscopy) and the use of computed tomography (CT). Arthroscopy and CT allow accurate mapping and alignment of fractures, which is important for all and critical for athletic soundness. All have contributed to improvements in survival rates; and it is now safe to say that with correct care, the vast majority of horses that sustain fractures in racing can be saved. Equally importantly, many can also return to full athletic function including racing.
Fracture incidences and locations vary geographically and are influenced by race types, track surfaces and conditions. There is good evidence that the majority of non-fall related fractures, i.e. those occurring in flat racing and between obstacles in jump racing, are caused by bone fatigue. This is determined by the absolute loads applied to a bone, their speed/frequency and the direction of force application. As seen with stress or fatigue failure in other high-performance working materials in which applied forces are relatively consistent, fractures in racehorse bones occur at common sites, in particular configurations, and follow similar courses. Once the fracture location has been identified, means of counteracting forces which distract (separate) the bone parts can therefore be reliably predicted and countered.
Worldwide, the single most common racing fracture is that of the metacarpal/metatarsal condyles (condylar fracture). In Europe, the second most common fracture is a sagittal/parasagittal fracture of the proximal phalanx (split pastern). Both are most frequent in the forelimbs.
In the United States, particularly when racing on dirt, mid-body fractures of both proximal sesamoid bones, which destabilize the fetlock (almost always in the forelimbs), are the most common reason for on-course euthanasia. They occur less frequently when racing on turf.
There is no specific data documenting outcomes of horses that have sustained fractures on racecourses. However, there is solid data for the two most common racing injuries. The figures below are a meta-analysis of published data worldwide.
CONDYLAR FRACTURES
Repaired incomplete fractures: 80% returned to racing
Complete non-displaced fractures: 66% of repaired fractures returned to racing
Displaced fractures: 51% raced following repair
Propagating fractures: 40% raced following repair
SPLIT PASTERN
Short incomplete fractures: 65% returned to racing
Long incomplete fractures: 61% returned to racing
Complete fractures: 51% returned to racing
Comminuted fractures in most circumstances end racing careers but with appropriate support and surgical repair, many horses can be saved. There is only one comprehensive series of 64 cases in the literature of which 45 (70%) of treated cases survived.
MID BODY SESAMOID FRACTURES
Uni-axial (single) fractures: 53% raced following screw repair
Bi-axial (both) fractures are career ending but can be salvaged with appropriate emergency support and arthrodesis (fusion) of the fetlock joint. Results of a single series of 52 cases are available in which 65% of horses were able to have unrestricted activity post-operatively primarily as breeding animals
The science behind the development of the fracture support systems comes from two directions. The first is data collected from racecourse injuries and the second, improved understanding of fracture courses and behavior. Data collected from UK flat racecourses between 2000 and 2013 demonstrated that 66% of fractures occurred in the lower limb (from knee and hock down) and of that over 50% of fractures involved the fetlock joints. Condylar fractures are most common, representing 27% of all reported fractures; and of these, approximately two thirds occurred in the forelimbs. Split pasterns were the second most common, accounting for 19% of all fractures with three quarters of these occurring in the forelimbs. These fractures have predictable planes and courses, which means that once recognized, they can effectively be immobilized in a standard manner that is optimal for each fracture type. For condylar fractures and split pasterns, this principally involves extension of the fetlock joint. By contrast, in order to preserve soft tissues and blood supply to the lower limb, fractures of the sesamoid bones require fetlock flexion.
Figure 2
Figure 3
The compression boot is readily applied “trackside” and can be used to stabilize most distal forelimb fractures sufficiently for horses to be humanly moved off the course. It is the temporary immobilization of choice for forelimb condylar fractures and split pasterns (Figure 3). Radiographs can be taken with the boot in place (Figure 4), and this can be maintained for transport. The boot is a rigid construct of fiberglass made from a single mold. The divided front portion is contiguous with a foot plate on which the back of the boot is hinged. Two sizes are available with internal foot widths of 135 and 160mm (5–6 inches). Removable foot inserts are also provided to make minor adjustments for hoof size. The boot is lined with foam rubber and has a rubber sole plate that protects the shell and provides a cushion grip for the foot. When the boot is opened, the injured limb is placed into the front of the boot while the back is closed and secured by sequential adjustment of ski boot clips. When the boot edges are apposed (it cannot be over tightened), immobilization is secure. It is made with a fixed fetlock angle of 150o which counteracts distracting forces and allows horses to weight-bear and load the limb to walk.
Figure 4
Flexion splints (Figure 5) are critical for the survival of horses with breakdown injuries such as sesamoid fractures. They are also suitable for other lower limb injuries, which are supported by fetlock and pastern flexion such as tendon and suspensory ligament injuries and lacerations. The splints are made of aluminum alloy with a secure work-hardened foot plate and conjoined compressed foam-lined front splint, which is angled 30o at the level of the coffin joint and extends to the top of the cannon. Here, there is a shallow foam-covered concavity in which the upper cannon sits, allowing the horse to lean into the splint and load the leg while flexed. The splint is secured to the leg with nylon and Velcro straps. Splints are provided with internal foot widths of 135 and 160mm (5–6 inches) to accommodate variations in horse/hoof sizes.
The modular adjustable splints (Figure 6) are made from heat-treated aluminum alloy. They are lightweight and can be configured to fit the individual horse and regional needs. The splints are 38x19mm (1.5x0.75in) rectangular tubes with an enclosed locking screw I beam. They are light but rigid and secure and are tolerated well. In the hindlimb, the reciprocal apparatus which combines stifle, hock and fetlock joint positions precludes use of a compression boot. However, modular splints provide rigid support for condylar fractures and split pasterns in hindlimbs and are secured—over a bandage to create a parallel sided tube—on the inside and outside of the limb. The splints can also be adjusted and assembled to splint fractures that occur above the fetlock (Figure 7).
Figure 7
Appropriate immobilization effectively stops fracture progression (i.e., getting worse) which not only improves the horse's prospects for recovery but also provides effective relief from pain and anxiety. As flight animals, loss of limb control or function is a major contributor to stress. The relief provided by effective immobilization is substantially greater than provided by any pain killer or sedative. It is also recognized that when fractures occur in the high-adrenaline environment of racing, horses exhibit latent pain syndrome. Application of appropriate rigid support at this time (i.e., on the track) limits pain generation and allows humane movement for considered evaluation, X-ray, etc., away from the racetrack.
In the UK, techniques for application of the boots and splints are taught to racetrack veterinary surgeons at annual seminars run by the Association of Racecourse Veterinary Surgeons (ARVS). The Racecourse Association (RCA) has provided forms to record use and to collect data centrally which, in the fullness of time, will determine impact and help to guide future welfare strategies.
Providing modern, scientifically rational equipment to racecourses has done two things in the UK. First, injured horses are optimally cared for immediately and secondly, it sends out a strong positive public relations message that people involved in racing care. The initiative has been widely welcomed by the British racing industry. “This new equipment will provide the best possible chance for an injury to be properly assessed while discomfort to the horse is significantly reduced and give the best chance of future rehabilitation” Caroline Davies, RCA (Racecourse Association) - Racecourse Services Director.
“The fracture support [system] kit is a major advance in the treatment of horses on the racetrack. It allows immediate effective support to be applied to an injured horse, resulting in pain control and stability, facilitating safe transport from the racecourse to a center of excellence without risk of exacerbating the injury. This will optimize the chance of horses to return to athletic function. This innovation must be seen as a major step forward in horse welfare for the participants in racing and all other equine disciplines.” Simon Knapp, Horse Welfare Board.
Go Canada - innovations to support breeders and buyers in Ontario
Words - Ken Snyder
With apologies to patriotic Canadians everywhere, the “O” that begins the nation’s stirring and beautiful national anthem might be adopted and altered by the Ontario horse industry to “Go Canada.” A reason? Divide 173 race days (133 at Woodbine, 40 at Fort Erie) by approximately $65 million CAD in purse money. Go Canada indeed.
“If you have a good horse, there is an opportunity to make significant money here in Ontario,” said Peter Berringer, president of the Canadian Thoroughbred Horse Society and also someone with “skin in the game,” as they say.
He is a trainer with both a small string stabled at Woodbine and broodmares and stallions at his farm, Aurora Meadows in Rockwood Ontario, west of Toronto. He, like other Canadian trainers, is in the hunt for purse money that might surprise those in the horse industry. Statistics for 2021 from The Jockey Club (TJC) show that 1,853 Ontario starters earned $43,612,419 USD ($56,790,117.87 CAD) or $23,536 ($30,646.39 CAD) in earnings per runner last year. The figure beats the same statistics for California, Florida, Louisiana and Texas.
Earnings, however, are only a part of the story. Financial incentives to breeders in Ontario through a Mare Purchase Program (MPP) and Mare Recruitment Program (MRP)* make investments in Ontario racing worthwhile both for the present and in the future in breeding and racing. The MPP provides Ontario buyers of in-foal mares at select U.S. horse sales 50% of the purchase price up to $25,000 CAD. Sales include Wannamaker’s Online Sale; Fasig-Tipton November Breeding Stock, MidAtlantic Winter Mixed, and Kentucky Winter Mixed sales; the OBS Winter Mixed Sale; and Keeneland November Breeding Stock Sale and January Horses of All Ages Sale. Additionally, there is a $2,500 CAD incentive for every mare bred back to a registered Ontario sire.
With Ontario horse sales under the recruitment program, mare owners bringing an in-foal mare into the province can receive $5,000 CAD through a Thoroughbred Improvement Program (TIP). The incentive applies to up to five in-foal mares per owner or entity. The $2,500 CAD incentive for breeding back to a registered Ontario sire applies also as with mare purchasing.
Berringer said a few new stallions annually come into the province but that “the issue is we don’t have a large number of resident mares.
“Mare Recruitment is trying to help us build Ontario-bred numbers,” said Berringer. “People will foal here and hopefully, with the incentives, people will breed back here. Then, when they have their horses, they’re probably going to benefit the most financially by racing in Ontario because you’re running for 40-percent bonuses if you’re running an Ontario-sired, Ontario-bred horse.” He added that the goal is twofold: to drive the Ontario horse population and increase the quality of the stock running in the province.
PETER BERRINGER
Funding for both the MPP and the MRP is through the TIP and comes from a pari mutuel tax returned by the government to the horse industry. Breeding programs total over $7 million CAD from the TIP, according to Berringer.
Ontario-breds are more than just important to racing in the province, according to Berringer. “It’s pivotal to racing. A strong breeding development program relates directly to our local horse sales and the racing product. We need a strong breeding program to have sustainable racing.”
Government statistics estimate that 45,000 people in Ontario depend on or benefit from horse breeding and racing, but Berringer thinks the figure might be low. “You have to be able to sustain all those farms and spinoff jobs on the farm and farm-related, which are imperative to the economic sustainability of rural communities.”
Berringer, as a farm owner, is sensitive to the impact of breeding and racing on operations and individuals not directly related to horse racing. His introduction to Thoroughbreds was working as a teenager at an uncle’s farm. “It was a multifaceted Thoroughbred farm with usually 60 to 120 horses at capacity in the winter. There were stallions and broodmares, yearlings and racehorses. I was lucky to have exposure to handling stallions, breeding and reproductive exposure, foaling, yearling sales prep, yearling sales, and breaking and training,” he said.
Transitioning to training came in his late 20’s when he was, at that time, the farm’s general manager/trainer. “I started to focus on training and racing because of the action and reducing my farm business to outside clients and a successful horse quarantine operation that I was operating for international horses.” On the farm, he met and worked with successful trainers and owners, and had exposure to top-tier Canadian champions.
Increased responsibilities on the farm along with obtaining a university degree while still working on the farm in the 1980s fed a burgeoning passion not just for the horses but the business.
This passion puts him on the tip of the spear for challenges not just facing his own racing and farm operations, but all Canadian horsemen and horsewomen. Canada’s tax structure for the horse industry is, according to Berringer, “the biggest detriment to our racing program.” It calls for a write-off of $17,600 [CAD] per entity per owner, a pittance compared to the U.S. tax structure that this year allows a 100% deduction of the purchase price of a horse. Lobbying efforts to improve the tax structure in Canada have been ongoing for some time but without much, if any, progress.
In addition to incentives, there are also efforts on the racetrack to benefit Ontario horsemen and horsewomen. The Heritage Series of eight races for three-year-old Ontario-sired horses—four for fillies and four for colts—is in its second year divided between six races at Woodbine and two at Fort Erie between July and September. The Series provides an obvious boon to Ontario-sired horses to run in restricted stakes races. Last year, the first for the Series, purses for the eight races totaled $750,000. This year purses will increase from $80,000 to $100,000 per race. Horses accumulate points over multiple races with the points leader among fillies and colts earning a $20,000 bonus. Second- and third-place finishers in points earn bonuses of $10,000 and $5,000.
Lastly, if not most importantly, Ontario’s annual Premier yearling sale, this year at the Woodbine Sales Pavilion on August 31, generates interest and sales for Ontario-breds and not just within the province. Berringer said many American owners with Canadian trainers as well as American trainers who race in Canada shop the Premier sales. “If you’re racing up here, it’s good to have an Ontario-bred horse because it gives you eligibility to a substantial and lucrative incentive program and bonuses as well as a possible place in the Queen’s Plate with a million-dollar purse as well as other stakes races.”
Probably surprising to U.S. buyers are Canadian exports to U.S. sales. “There are 100 to 150 yearlings that sell every year down in Kentucky that are Ontario-bred,” said Berringer.
If Ontario racing is highly aggressive among racing jurisdictions in its breeding programs and incentives, it is, quite frankly, because it has to be. The COVID pandemic provides a prime example. “COVID really knocked the industry down when there were no spectators. At least in the U.S., spectators were allowed and business went on. We didn’t have any of that.” Adding to empty grandstands, Ontario racing, which usually begins in April, was pushed back to a June start in both 2020 and 2021. American racing, for the most part, continued the same meet schedules in the COVID restrictions.
Of course, Ontario racing right now experiences the same issues facing other racing jurisdictions in the U.S. All have horse shortages. Ontario may be complimented, though, for creating a means to minimize the effect on field sizes and typically producing fields larger than that in the U.S. Berringer points to racing secretaries at Woodbine both adding conditions and combining them to draw more entries into races. A recent Saturday at Woodbine and Santa Anita showed 84 starters for 10 races at Woodbine (8.4 per race) and only 68 starters for the same number of races at Santa Anita (6.8).
Another issue shared by Ontario with the U.S. is a chronic labor shortage. The situation may be more acute in Canada than in the U.S. with a smaller immigrant base from which to draw. “A lot of the people that come to Canada are from Barbados and Jamaica to work on the backstretch, and it’s getting more and more difficult to obtain work permits. It’s increased over COVID,” said Berringer. The U.S., by contrast, has Central and South American countries with larger populations that have traditionally supplied their horse industry. The impact can be seen, said Berringer, by some U.S. stables who formerly came to Ontario to race, no longer coming north.
Home-grown efforts are underway to address labor shortages. Berringer points to a new program that the Ontario government started this year, which trains people for the horse industry and then provides financial assistance for the continuation of training. He takes a wait-and-see attitude toward the impact it may have. “It’s hard to find people to do this work early in the morning.” That goes for both Ontario and the U.S.
The one major difference between Canadian racing and American, and where Canadian racing is most lacking in comparison is with new owners. There is just not the population base or large enough body of families historically involved in racing in Canada as in the U.S. “Racing struggles with this everywhere and probably the creation of a large fractional owner syndicate, and introducing people to the sport and excitement of it all, hopefully, will encourage new participants and they’ll purchase more and invest more in the industry once they get a taste for it; but it’s a struggle to find new breeders and owners,” said Berringer.
He noted that leading Canadian trainer Josie Carroll, along with other top trainers in the U.S., receives horses bought by MyRacehorse, a syndicate offering “micro shares” that has been successful both in terms of business and on the racetrack. MyRacehorse, still in relative infancy, was part owner of the 2020 Kentucky Derby winner, Authentic.
Canada’s horse industry, not surprisingly, is dependent on its larger neighbor to the south, with a much larger selection of stallions. “It used to be a couple of years ago; it was 70 percent local horses produced [in Ontario],” said Berringer. “Now, it’s a fifty-fifty split.” He added that it is a trend more attributable to a decrease in Ontario of local breeding participants than an increase in U.S. stallions.
Quantity, however, does not necessarily dictate quality. Bigger purses divided by a smaller pool of horses, as cited in the opening of this story, improve the odds for earnings with Ontario horsemen and horsewomen. “You’ve got to put it in perspective. In Ontario, we’re probably producing just over 750 foals a year. Statistically, there’s a lot more money for our foals than a lot of other jurisdictions.”
A point of pride with Berringer and other Canadians in the horse industry is the success of Ontario-breds. Say the Word, Channel Maker, and Count Again, who recently won a Gr. 1 race in California are only three of many Ontario-breds succeeding on the racetrack. Recently retired Pink Lloyd, sired by Old Forester, is, perhaps, the biggest star of Ontario-breds. Career earnings totaled $2,455,430 and included five Sovereign Awards for Champion Male Springer and the 2017 Sovereign Award for Horse of the Year. Incredibly, his wins were in 26 stakes races. Let it not be forgotten as well that the dam of this year’s Kentucky Derby winner Rich Strike is Gold Strike, Canada’s Sovereign Award Champion 3YO Filly in 2005.
The issue for Ontario racing isn’t good horses, apparently; it is just the need for more of them. With breeding programs, added racing for Ontario-breds, and the Premier sales, it won’t be for lack of trying. That especially holds true for Berringer, who is quick with a quip: “I still love horses and horse racing and still enjoy going home to the farm every day--ok most days--to work.
Go Canada.
*Applications for the MPP and MRP by Ontario horsemen and horsewomen are available at the Canadian Thoroughbred Horse Society’s website, cthsont.com, under “Breed” and then “Incentives.”
HISA: Devilish details defined
Words - Annie Lambert
Not everyone required to opt into the Horseracing Integrity & Safety Act is pleased to oblige. The confusing regulations have left many with less than a clear understanding of what the new rules actually mean. Those details have constantly fluctuated and will probably continue to shift past their application.
Not everyone hates the idea, however. The intent was to make United States Thoroughbred racing safe, fair and ethical for everyone involved through national uniform standards. The legislation, H.R. 1754 passed in 2020 as part of a COVID-19 relief bill. Once signed by President Donald J. Trump, HISA officially became law.
The legislation includes racetrack safety program protocols that began July 1, as well as anti-doping and medication control regulations, under the direction of Drug Free Sports International, to be finalized by January 1, 2023. The governing body of HISA, referred to as the “Authority” in the legislation, did not leave an abundance of time for the busy and independent members of the racing community to thoroughly digest the new rules and oversights before being asked/required to become obligated by registering themselves and their horses. The Authority refers to those within their jurisdiction as “covered,” such as covered horses and covered persons.
According to the Authority, as of June 29th, 20,537 people and 23,070 horses were registered. In addition, 20 of 24 states under HISA Authority were in agreement or expected to comply.
Not signing up means a person or horse may not participate in racing. Once signed up, however, being misinformed or not following the rules can land people and equines severe punishments, large monetary fines and/or disqualification from industry participation.
To date, stakeholders who feel the regulations are overly invasive and confusing appear to outnumber those who believe HISA is necessary to save the horseracing industry.
Digesting the Law
Signing your name to a contract that is technically not complete and subject to changes that may influence your livelihood understandably terrifies any human nature. The extensive rules, regulations, protocols and punishments for non-compliance seem daunting.
An undertone from the backsides of many racetracks suggests that horsemen would feel more comfortable if they had additional time to digest the legislation prior to registering. Instead of the July 1, 2022 deadline, how about pushing the implementation to 2023?
HISA’s CEO, Lisa Lazarus, implied publicly the law was the law, in spite of aggressive timelines; the Authority has been responding to some of the many questions posed by the public. They will continue to educate racing industry participants.
According to HISA’s Liz Beadle, they are unsure what to expect when it comes to the number of probable stakeholder registrations.
“We aren’t going to venture a guess,” Beadle offered via an email. “Since such a registration process has never existed at the national level before, it’s unclear how many people and horses are or will be participating in racing. It should be noted that the universe of people expected to register is limited to the 24 states conducting covered horse races under HISA’s authority.”
Basically, everyone now licensed by any state racing commission must be registered by HISA to continue to work and/or run horses or work with horses (such as vendors) within restricted areas of the tracks. Any horse in training or racing at an approved racing facility must also be registered. There are no fees required to register, and you need only register one time. Those registered may unregister at any time.
People responsible for registering horses, usually the trainer, are required to keep daily records for each animal. Records required include any administered medications, therapeutic procedures, treatments and surgical procedures. Those records must be given to regulatory veterinarians, stewards and HISA when requested, making it important that they be updated daily.
Owners and jockeys must also register for HISA “to participate in Thoroughbred racing.” If an owner’s horse is not in the care of a trainer, it is the owner’s responsibility to register his horse.
Trainers are required to complete continuing education classes for licensing, in addition to registering all horses in their care. As noted previously, they must agree to keep health, vaccination, training and daily treatment records for each horse in their care. Fortunately there is Equine MediRecord, a relatively new enterprise, specializing in securing those daily records. (See Sidebar #1)
Trainers entering a horse into a claiming race have given their consent to transfer that horse’s veterinary and treatment records from the prior 60 days to the new owner, should it be claimed. Claims will be voided if the horse dies or is euthanized on the track, has a positive test, bleeds or is unsound within one hour post-race.
Claimed horses are required to go to the test barn. Whether those horses will be tested is unclear. If tested, who will pay for that protocol? The claimed horse will be immediately transferred to new connections, but what happens if a test comes back positive weeks later? A voided claim could end up in more litigation.
Covered riders—jockeys and exercise riders—are required to participate in continuing education, to take a physical exam and complete a baseline concussion protocol test. They will be required to use HISA-approved safety vests and helmets. A medical history card is to be carried inside the vest when on a horse. Riders are also obliged to study and follow new riding crop rules.
Only approved riding crops will be allowed under HISA rules and may be inspected by the safety officer, stewards and the clerk of the scales. The specifications include being a maximum weight of eight ounces, no more than 30 inches in length with a set amount of shock-absorbing material.
Enforcement of the crop specifications may be postponed to August 1, 2022, due to a shortage of manufacturing resources.
Use of the riding crop, for jockey or exercise rider, is only to maintain the horse’s attention for safety and encouragement. A rider may only use the crop on the hindquarters a maximum of six times during a race. The crop is only to be used two or fewer times before allowing at least two strides for the horse to respond before using the crop again.
A rider may tap the horse on the shoulder with the crop when both hands are on the reins and touching the neck. It is legal to show/wave at the horse with the crop without physical contact. It is not legal to raise the crop with the rider’s wrist above the helmet.
New horseshoe regulations will not be enforced until August 1, 2022, to ensure adequate inventory of HISA compliant shoes.
Basically, on both fore and hind feet, toe grabs, bends, jar calks, stickers and traction nails will be prohibited on all dirt, synthetic and turf surfaces during training and racing. The only exception is for full rim that is two millimeters or less in height from ground surface of the shoe and that extends the entire circumference of the shoe, used only on dirt and synthetic surfaces.
Purportedly, bar shoes, pads, glue on shoes, quarter crack patches may only be applied by a covered veterinarian. Those official regulations, however, will come in another phase of the bill.
Edicts & Concerns
An open letter was sent to Lazarus on behalf of the Thoroughbred Horsemen’s Associations, Inc, Kentucky Thoroughbred Association, Thoroughbred Owners of California and Thoroughbred Owners and Breeders. The communication pointed to several areas of concern for stakeholders within the legislation.
Many horsemen outside the organizations cited by this letter have similar concerns and more. Here are a few:
HISA has been vague in defining some of the rules and protocols. For example, there is not clear guidance as to what is permitted at training facilities and out of competition horses (layups) as compared to racetracks. Perhaps a list of approved training facilities and farms, including which HISA rules will be enforced at these facilities.
Medication lists, classification types and protocols seem to be lacking clarification. To date there is no list of controlled medications with guidance for legal usage. Most medication violations stem from controlled therapeutic medications used to enhance equine quality of life. A therapeutic use exemption could be useful.
There should be a distinction between prohibited medication and controlled medication violations. As now written in HISA, every violation of every type requires unnecessary and costly legal defense costs. Prohibited substances that show up during testing due to accidental contamination causes reputational harm to stakeholders when officials overreact and go public before investigating thoroughly.
There should be distinct definitions between punishments prescribed to prohibited substances, specified substances and controlled medications. After all, very few positive tests can be attributed to actual doping incidents each year.
The confusion and conflicts created by the aggressive enactment of the HISA legislation causes concern that egregious problems could arise when the Anti-Doping and Medication Control Program (ADMC) is executed January 1, 2023.
So many factors within HISA deserved more oversight by horsemen before being written into the law. Little things like allowing suspended horses to train while not able to race. Allowing ownership groups to decide which principle should be the managing partner. Collecting a post-race urine sample at the horse’s stall (with regulatory oversight) when he cannot relax and provide urine at the test barn.
Better definitions for “race day” and “official timed works.” The overreach of the HISA Authority having a say in when a horse should be retired is wrong in any horseman’s realm. Owners, not a non-horseman entity, should make the decision of retirement.
Litigation & Money Woes
Multiple lawsuits have been filed on behalf of state racing commissions and other racing entities. The courts have overruled most suits, while others are pending appeal. The Texas Racing Commission (TRC) has declined to abide by HISA’s federally mandated program.
Texas law cites that only the TRC can make rules and regulations for Texas racing. HISA demands that state racing commissions enforce the rules and regulations per HISA.
Amy Cook, executive director of the TRC, has announced that Texas will allow wagering on out-of-state racing signals at simulcast locations in the state. The TRC will not, however, allow pari-mutuel wagering at a Texas meet that is HISA-compliant or the export of simulcast signals to other states.
According to Cook, all pending requests for approval of the import and export of pari-mutuel simulcast signals will be considered and approved on a case-by-case basis. Texas horse racing will therefore be confined to Texas. It has been predicted that the state will take a financial hit from the decision; it remains to be seen if the ominous financial predictions come to fruition.
Litigation was recently filed on behalf of Louisiana and West Virginia, their respective state racing commissions, the Louisiana Horsemen’s Benevolent and Protective Association, Louisiana Thoroughbred Breeders Association, the Jockeys’ Guild and several Louisiana individuals considered “covered persons” under the Authority.
The complaint basically cited that HISA was unconstitutional by overstepping state racing commissions, has multiple violations of the Administrative Procedure Act and violated the Fourth and Seventh Amendments of the U.S. Constitution, which guarantee a right to a jury trial and protection against unreasonable search and seizures.
A federal judge in Louisiana denied the litigants’ request but gave the defendants in the suit—HISA, its CEO Lisa Lazarus and the Authority’s board members, the FTC and individuals associated with the FTC—until July 14 to respond to the motion.
One of the great unknowns regarding HISA has always been, “Who pays what and how?” That question has only been partially and vaguely answered. Racetrack operators, industry stakeholders and the betting public obviously have monetary concerns. HISA’s first year operating budget is roughly $14.3 million.
Fees are calculated whereby those states or tracks with the highest handle, purses and number of starts will pay the largest assessments. Each state racing commission decides whether to opt in or out of collecting and remitting fees for the program. If a commission opts out, the responsibility falls to the tracks and horsemen.
Five states have chosen to fund their portion of HISA: California, Colorado, Kentucky, Minnesota and Virginia. Each state has a little different formula for collecting their fees.
For example, California will owe $1.4 million to the Authority for 2022. The state purportedly will split the payment between Thoroughbred horsemen, through purse revenues, and Thoroughbred racetracks, via commissions, from their share of Advance Deposit Wagering (ADW). The California Horse Racing Board has stated this will not affect bettors.
The other states are funding their HISA invoice in a variety of ways, and some have yet to make a decision.
Out in the Cold
A Facebook page titled Horsemen Arguing HISA has arguably exposed sincere concern and even fear from stakeholders who are looking at their livelihoods vanishing directly in front of them.
Their main concerns circle around fairness to backstretch workers, the fact that not enough input in the HISA legislation came from horsemen and that the true welfare of the horses has been overlooked in some areas. Were stakeholders left out in the cold as rules and regulations were written?
With no or little input from horsemen, those industry workers have suspicions that animal activists like People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) and the Humane Society of the United States (HSUS) may have influencers among those within HISA. Many questions and concerns submitted to the HISA website and at various meetings across the country went unanswered.
Prohibited protocols and penalties are also worries for the horsemen. Why is it taboo to ice a horse pre-race? Human athletes use ice in competition regularly. How can it be prohibited to fire shins on horses (beginning with the 2022 foal crop), but legal to fire splints and curbs?
Investigative powers seem over-the-top to many on the backside. The Authority would have access to all properties and places of business with the right of seizure for covered persons in question?
The concerns go on and on, as does a growing distrust. Covered persons have had trouble being heard by those in charge of HISA—a lack of communication and transparency. Those under the HISA legislation would like to see it simplified using a more common sense approach.
On the Record
Equine MediRecord principles worked this year’s Preakness, including (l to r) Finlay Dargan, COO, Maryland Governor Larry Hogan, Pierce Dargan, CEO, and his fiancé, Alexandra May.
Most horsemen have a vivid aversion to bookkeeping. Understandably so… They’d much rather concentrate on training horses and keeping owners happy and informed.
The new Horseracing Integrity & Safety Act (HISA) requires trainers and veterinarians to maintain detailed, daily health and treatment records for equines in their care. Those records must be made available to regulatory veterinarians, stewards and HISA upon request. The record keeping also applies to layups that are being given rest time at off-track facilities.
Imagine the daily hours to keep up with a barn full of trainees. There is a solution—a software program—to ease the struggle.
Equine MediRecord became operational in 2018, the brainstorm of Pierce Dargan in County Kildare, Ireland. Dargan, a fifth-generation horseman, is the company’s CEO. Dargan’s system was created for his family’s training operation in Ireland to help keep current with racing regulations they faced at the time.
Trainers sign up with Dargan’s company platform, which allows them to keep the precise and tedious records required by HISA. Those with multiple stables and facilities can add assistant trainers and veterinarians to assist with inputting information.
“What our system then does is notify the trainer when a record has been put in by someone else for them to sign off, ensuring they know at all times what is being given to their horses,” Dargan explained. “Any horse with an open treatment on our system will [be marked], to remind the trainer to check this horse before entering into any races as there is still a treatment in the horse’s profile; this ensures the withdrawal period is completed before they race.”
Presently, the cost is $1.50 per horse, per month for the initial year, increasing to $3.00 per horse-month the second year. “We wanted to make sure this was a tool that all trainers, big and small, could afford,” Dargan said. “One of the benefits of having clients globally is we can spread the costs, making it cheaper for all.”
“We have done the Breeders’ Cup World Championships for the last two years, as well as the Pegasus World Cup, Saudi Cup and Preakness in 2022,” Dargan pointed out. “This has meant that top trainers such as Todd Pletcher, Chad Brown, Steve Asmussen and many others had to use the system to keep records for those races.”
“Seeing as [HISA] is the first time in the U.S. that trainers will be having to keep these records nationwide, we are now in discussions with multiple trainers to keep the system outside of these large racing events,” he added.
Sorting Through HISA
The Horseracing Integrity and Safety Act of 2020 (HISA) contains many, many of pages of government speak. It can be confusing and difficult to discover the answers you are seeking. Perhaps knowing how the general categories are listed may help. HISA will hopefully include a search engine in the future.
Additional Perspectives on the Horseracing and integrity Act
Words - Peter J. Sacopulos
As the effective date of July 1, 2022, approached, the issues and inquiries regarding the Horseracing Integrity and Safety Act (HISA) became immediate. These questions include inquiries from racetrack veterinarians as to their obligations for registering and reporting medication and treatment of Thoroughbred horses and from jockeys seeking guidance on whether the new rule regulating the use of the crop is effective between HISA’s start date of July 1, 2022, and the delayed enforcement of the use of the new crop on August 1, 2022. So too have been questions regarding the pending constitutional challenges and legal efforts to enjoin HISA. These issues have received significant attention by way of journal articles, HISA-sponsored “Town Hall Meetings” and national seminars. Conversely, HISA’s impact on those in the Thoroughbred industry outside of the United States have received limited analysis and discussion.
As a practitioner representing licensees before regulators, I have received multiple inquiries from trainers outside the United States as to their obligations and their owners’ obligations relative to HISA. Additionally, I have received questions as to what, if any, impact HISA has regarding simulcast signals from tracks outside of the United States such as Woodbine in Canada.
To comply with HISA, the foreign national trainer must register as a covered person. In fact, compliance with regard to registration and licensing is a three-step process for the foreign national Thoroughbred trainer. First, to comply with HISA, the international trainer is required to register as a covered person pursuant to 15 U.S.C.S. §3054(d). Second, he or she is required to apply for and secure a Thoroughbred trainer’s license from the jurisdiction (state) in which they will enter and race. For example, if the foreign national trainer has a Thoroughbred that will compete in this year’s Breeders’ Cup event, then he or she must have a current valid Thoroughbred trainer’s license issued by the State of Kentucky for the 2022 season. Third, the foreign national trainer must properly register the Thoroughbred horse(s) that he or she will enter and start with both the state and the HISA Authority.
The rules requiring HISA registration are codified at 15 U.S.C.S. §3054(d). Online registration is available at https://www.hisaus.org/registration. Additionally, only days before the effective date, the Authority issued the “HISA Trainer Handbook,” which can be found at https://www.hisaus.org/home#resources.
In registering, the foreign national trainer is responsible for and obligated to fully and completely understand and comply with all HISA requirements. Once properly registered and deemed a “covered person,” the foreign national trainer has certain ongoing obligations. For example, Thoroughbred trainers are required to complete four (4) hours of training annually pursuant to Section 2182(b)(5) of the rules governing the Racetrack Safety Program. Additionally, there are requirements for filing records relative to the medical care and treatment of horses. Also, the licensing and ongoing requirements for covered persons apply to owners of Thoroughbred horses. Therefore, it is recommended that the Thoroughbred trainer who is going through the registration process informs his or her owner of those requirements and sees that the owner(s) are properly registered as covered persons.
The issue of HISA and control of a track’s signal is one that has received discussion and attention. In fact, one racing jurisdiction, the State of Texas, has refused to honor HISA. In response, the HISA Authority is prohibiting Texas tracks from exporting their simulcast signal across state lines. What is clear and defined relative to the HISA Authority’s right to control a simulcast signal is that a state that refuses to recognize and comply with HISA may be placed in a position of having its tracks prohibited from exporting the simulcast signal. Conversely, what has received little or no discussion, is how, if at all, HISA’s rule regarding simulcast signals will affect Canadian or European simulcasting.
For example, it seems clear that HISA has no control or jurisdiction over Woodbine’s simulcast signal since it is outside the jurisdiction of the Authority and the FTC as it is located in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Less clear, is what, if any, control HISA/the Authority has or may have over Sam Houston Race Park and Lone Star Park (Texas tracks) exporting its signal to Woodlawn. Should the Texas track(s) do so, it could be argued that the signal is being transmitted across state lines and, therefore, subject to HISA regulation. Conversely, it may also be argued that the signal is not “crossing state lines” but rather being transmitted to a foreign jurisdiction and not subject to HISA control or restrictions. The answer is unclear. Equally unclear is whether additional states will adopt the “Texas position” on HISA when HISA announces the “rest of the story”—that being each jurisdiction’s proportional share of the costs for the Anti-Doping and Controlled Medication part of the program. This expense is expected to be a multiple, perhaps many multiples, of each state’s assessed cost for implementing the Racetrack Safety Program.
The passing of the effective date of HISA and the ongoing and repeated modifications and changes, has resulted in additional questions. For example, the new crop rule, covered under Rule 2280 of the Racetrack Safety Program rules, became effective July 1, 2022. However, the riding crop specification rule will not be enforced until August 1, 2022. And, there is ongoing concern including the mandated registration for participation despite the anti-doping and medication rules not being submitted for public comment and approval by the FTC.
Also, there are and continue to be multiple challenges to the legality of HISA. The HBPA, together with twelve (12) of its affiliates, have a pending appeal before the United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit in New Orleans, Louisiana. That lawsuit challenges the constitutionality of HISA on the basis that Article I, Section I of the United States Constitution, prohibits delegation of legislative authority to a private entity as well as for the reason that HISA violates the Due Process Clause of the United States Constitution. The State of Oklahoma, the Oklahoma Racing Commission, Tulsa County Public Facilities, Global Gaming RP, LLC d/b/a Remington Park, the State of Louisiana, the State of West Virginia, the West Virginia Racing Commission, the Oklahoma Quarter Horse Racing Association, Hanover Shoe Farms and the United States Trotting Association also have an appeal pending before the United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit in Cincinnati, Ohio. In July, the State of Louisiana, the Louisiana State Racing Commission, the Louisiana HBPA, the Louisiana Thoroughbred Breeders Association, the Jockey’s Guild, Inc., the State of West Virginia, the West Virginia Racing Commission, and several individuals filed an additional (third) challenge to HISA that is pending before the United States District Court. That action seeks not only to find HISA unconstitutional but also seeks injunctive relief in the form of a temporary restraining order. That matter is set for hearing later in the month of July.
The Horseracing Integrity and Safety Act is national federal legislation governing Thoroughbred racing in the United States. The authority and jurisdiction of HISA and its governing agency, the United States Federal Trade Commission, is limited to racetrack safety issues (presently) and anti-doping and medication issues next year in the U.S. However, the effects of HISA will be felt by those in Canada, Europe, and elsewhere outside the U.S. as the 2022 season continues and into the future.
The Long Game - what can be done to bolster the “staying” division?
Words - Annie Lambert
North American distance races appear to have an ever-shrinking number of entries. The pool of horses willing and able to run a route of ground has slowly contracted. Finding a reason as to why, however, does not have a singular answer.
The Jockey Club statistics expose a downward trend in foals produced in the United States. The mid-1980s saw the high point with the 1985 foal crop exceeding 50,000 registered foals. But since that peak, the numbers have slipped. The economic downturn in 2008 caused many breeders to sell off or curtail breeding operations, which led to the number of foals falling from around 32,000 in 2008 to just over 17,000 in 2021.
That stunning 45% decline of potential runners could explain smaller fields, but not necessarily a loss of distance runners. Or could it?
Fewer horses to enter races with certain conditions revolves into a vicious circle; when racing secretaries cannot fill longer races, for example, they will inevitably offer fewer of them.
It does not come across as though lagging purses are the biggest culprits, but it may be that breeders are looking toward pedigrees that produce runners with more speed than endurance. Do sprinters provide a faster return? Economics usually proves a strong motivator, especially in such a competitive industry as Thoroughbred horse racing.
Fewer breeders breeding fewer Thoroughbreds in general, plus more commercial breeders seeking speed that sells, could be a major factor.
One thing for certain is that no one can offer a definitive answer as to why it is difficult to fill races at classic distances. Solutions to the problem are also elusive. Those within the Thoroughbred racing industry will only offer personal hypotheses.
Nature, Nurture & Breeding
The modern Thoroughbred’s ancestry traces back to foundation sires imported to Europe around the turn of the 17th century. The Darley Arabian, the Godolphin Arabian and the Byerly Turk, from the Mediterranean Middle East, were crossed on native English equines. The result was a horse that could carry weight while sustaining speed over extended distances.
The foundation Thoroughbred originated in Great Britain with its genetic origin being Arabian, which might suggest endurance. Generations of selective breeding have sped up the North American Thoroughbred. Study condition books from any racecourse, and you’ll find only a small percentage of distance races— those being one mile and one eighth or further.
When it comes to breeding, experts often disagree on the heritability factor of genes—heritability being a measurement of how completely a trait is passed down through the genes.
E. Gus Cothran, PhD, was formerly a research professor with the University of Kentucky’s Department of Veterinary Science. The emeritus professor is currently an advisor and consultant to the Department of Veterinary Integrative Biosciences (VIBS) at Texas A&M University in College Station, Texas. The retired professor believes racing performance has a heritability of 30–35%. The remaining 65–70% he attributes to non-inherited factors, the likes of training, nutrition and health care.
“Very few people understand heritability,” Cothran said. “It’s the trait itself that has the heritability of roughly a third. That means that about 30% of what causes the trait is genetic, and the rest of it is environmental. It has to do with training and upbringing; about a third is nature and two-thirds nurture.”
Having a low genetic contribution to the trait means it will be more difficult to select for thorough breeding, according to Cothran. A complicated trait is probably made up of multiple genes having to interact. For example, there are multiple genes that would contribute to speed.
“Typical animal improvement breeding practices, which means you pick the animals that have the traits you desire to the highest degree you can find, breed them together and hope they will produce individuals that are equal or better than the parents,” Cothran explained. “And you’d have to do that probably several generations to make a large improvement, if it is even possible.”
“There may be one gene that has a maximum contribution to speed, one form of it, [for example] a particular gene with muscle characteristics,” the professor added. “But by itself, it is only going to make up a little bit of the total package of the speed.”
Andy Havens, founder of Havens Bloodstock Agency, Inc. in California, sees the trend toward speed; but he believes his ideas as to why things have changed are merely guesses as there are no statistics to back up the ideas.
“I think the phenomenon is real,” Havens said of vanishing distance horses. “For a number of years and for a number of reasons the trend has turned more toward speed-oriented racing on the dirt, going away from the European type distance horses. Most of the races, other than Del Mar, that were longer races have been shortened.”
A Turn of Foot
California-based, multiple-graded stakes-winning trainer Leonard Powell believes a lot of breeders are looking toward marketing their equine product. Since speed sells, there may be fewer classic-distance horses being produced. Powell hails from a racing family in France, riding races and training there prior to relocating to the United States. He has had plenty of experience with route horses.
“We run all day in Europe and have one pace, and it isn’t that way here,” Powell pointed out. “We bring middle-distance horses here; you want a horse that has a turn of foot. He can go a mile, mile and one eighth. With tactical speed, you can be in a good spot.”
Powell noted that the racing office has trouble filling races going one mile and one eighth or further. Those races might draw five or six horses on a good draw, but if they drop the race back to one mile and one sixteenth, it will have a full field.
Jeff Mullins is based at Santa Anita and recently set up an annex stable at Gulfstream Park. He was hoping the condition book in Florida would provide more opportunities, and larger purses, for his distance runners; that turned out not to be the case.
“A lot of those [classic distance] horses have gone elsewhere, where there is more money,” Mullins opined. “If you go to Churchill or Keeneland or Oaklawn, those purses are higher than California.”
Mullins, with career earnings approaching $55 million, has won graded stakes with imported horses, the likes of Itsinthepost (FR), Battle of Hastings (GB) and River Boyne (IRE). He and his customers choose European horses for their surface preferences as much as their running distances.
“We purchase some sprinters and some distance horses—it just depends on the horse,” he said. “The main thing that we look for over there are horses that like firm ground.”
According to Mullins, there are not enough distance horses in California to fill those races, but “there are not enough horses in California period.”
It’s Not Just Canada
Scott Lane, racing secretary at Woodbine in Ontario, Canada, was quick to point out that a lack of entries in stayer races was not solely a Canadian problem.
“It’s a North American issue,” he lamented, “not just a Woodbine issue.”
Lane did not have an “expert reason” why the problem exists, but thought there were many more stallions with shorter-distance pedigrees.
“You see a lot of middle-distance, milers now that are the vast percentage of the sires available in North America,” he pointed out. “You just don’t see many of those classic-distance horses that are going to stud, horses that race at a mile and a half and a mile and three quarters. You don’t see many of those turned into studs. That could be a reason why.”
Havens, a leader in bloodstock sales in California for over 30 years, would agree with Lane’s opinion on North American stallions. Very few stallions that are primarily distance horses seem popular with breeders.
“All I can really say is, it’s a function of selecting the stallions that we like,” Havens offered. “I think the choices of stallions that we go to stud with are speed oriented horses that like to run early. We like those really hot, brilliant horses that are precocious enough as two-year-olds to get enough experience to run in the classics [at three].”
Lane, who has written Woodbine’s condition book since 2019, leaned away from blaming North American purse structures. He cited Gulfstream’s $3 Million Pegasus World Cup (Gr. 1), as a case in point. In the field of nine, only first placed Life Is Good (Into Mischief) and runner up Knicks Go (Paynter) had won Gr. 1 stakes. The balance of the field, although most were graded stakes placed, had not.
“We have two Gr. 1’s [at Woodbine] going a mile and a half on the turf that we’ve seen very difficult to fill over the last couple of years, unless we get some European interest,” Lane cited. “With the [pandemic] travel restrictions we had to modify those races a little bit.
“For the Valedictory Stakes (Gr. 3) we cut back from a mile and three quarters to a mile and a half. The Singspiel Stakes (Gr. 3) used to be at a mile and a half and is now a mile and three eighths. We’ve modified our distances to try and suit some of the handicap horses that [normally] go a route of ground at a mile and a sixteenth to a mile and a quarter to try and help fill longer races.”
Those changes, and other distance race changes around North America, may prove a lack of quantity and quality of horses for the stayer divisions everywhere. Many more horses are bred to sprint or run middle distances, according to Lane.
“We never have problems filling Woodbine races from five furlongs up to seven furlongs,” he noted. “You start getting to a mile and a sixteenth, we still have a lot of interest for those races. A mile and a quarter and over, we don’t have as many of those horses with the classic pedigree, so to say, anymore. We definitely see the farther you go, the less and less pool of horses you have to pick from. It’s just the way it is now.”
Texas Hold ‘Em
Texas Thoroughbred racing has had its ups and downs for decades but is ascending in recent years with popular racetracks, high-value incentive programs and prospering horse auctions. Ken Carson is the general manager of Valor Farm in Pilot Point, Texas, which was founded by Dorothy and Clarence Scharbauer who campaigned 1987 Kentucky Derby and Preakness winner Alysheba (Alydar). Their son, Doug Scharbauer, now owns the farm.
Carson, who has been on the Texas Thoroughbred Association board for nearly 30 years, agrees breeding trends are at least partially responsible for decreasing distance horse numbers. He does, however, have a lot of clients that breed to race.
Although Carson is a Texas native, he spent a decade or more in Kentucky working many facets of the racing industry, including five years as pedigree consultant at Three Chimneys Farm in Versailles. Carson believes commercial breeders have contributed in part to the vanishing distance horse pool.
“The market drives the bus,” Carson voiced. “The speedier horses sell better; they look better at the sales, and you don’t wait as long on them. I’m not saying it’s right, but I think that’s driving a lot of it. The two-year-old in training sales—they work an eighth real fast, and they bring the big dough.”
Conformation traits of speedier pedigrees tend to portray a more precocious individual. They appear balanced as though they are mature and grown into their frame, even as a two-year-old. Distance horses are often rangier, long-bodied with leaner muscle leaving their overall look as not being finished, which they are not. It will usually take that immature looking distance-bred horse longer to mature physically as well. Thus, the economics of a quick return are diminished.
Carson has no doubt there are still North American mare owners breeding to increase those classic distance horses—even in Texas. After many years of deflated numbers, The Jockey Club report of the number of mares bred shows Texas annual foal numbers are rising.
Most acknowledge the trend toward fewer stayers is real. It seems to have crept into the industry slowly, but does anyone truly care? It would not seem so.
“I don’t think it is a planned influence,” Havens opined of the shorter-faster phenomenon. “I don’t know if anybody really thinks it’s a problem.”
Hybrid Stayers
With a shortage of distance horses in North America—those running one mile and one eighth or further—steeplechase horses occasionally take to the flat track to help alleviate the problem.
Scott Lane, racing secretary at Woodbine in Ontario, Canada, said the hybrids are “few and far between now,” but they can help to fill a race now and again.
“[Trainer] Jonathan Sheppard comes to mind as one that would have some of those hybrid horses,” Lane pointed out. “They’d see a flat race at Delaware, then go to Saratoga and run over the hurdles. You do see some horses that race here through the years that transition to the hurdles afterwards. Some of the United States interest will buy these horses that are no longer competing at Woodbine and transition them into the U.S. hurdle races during the summer months.
“They have extensive hunt meet racing from July through October with races in Virginia and Maryland; and I think probably South Carolina and Pennsylvania. The top ones run in Saratoga in the summer.”
Stacy and Robert Mitchell
Words - Bill Heller
With a dollar and a dream, Stacy, a critical-care nurse, and Robert Mitchell, a surgeon, became horse owners. With a willingness to learn, they became Thoroughbred breeders after purchasing 92-acre Briland Farm in Lexington. And with patience and a commitment to race only home-breds, they created a niche—one made so much sweeter when their three-year-old filly Secret Oath took them to the winner’s circle at Churchill Downs by taking their first Gr. 1 stakes, the Kentucky Oaks, rather easily by two lengths under Luis Saez.
“They do it all themselves—pretty much a ‘mom-and-pop’ operation with just a few horses,” their Hall of Fame trainer D. Wayne Lukas said. “To have that kind of success is phenomenal. They’re very protective of their horses. Stacy foals out most of them herself. We’ve had a great relationship.”
Along the way, Stacy and Robert learned the ups and downs of racing. “The Thoroughbred industry can be as high as possible and the lowest of lows with foals dying,” Stacy said. “You just never know. Every time you get a good one, you say, `This is the one.’”
She was right with Secret Oath. “This was the one!” Stacy said. “It’s been exciting. Very satisfying.”
She’s certainly satisfied with her legendary trainer. “He’s great,” Stacy said. “He’s just classy. We can call him anytime. My husband talks to Wayne on the way to work every day. They both start their day at 3 a.m. He sees all his patients before they operate.”
Stacy and Robert met in the intensive care unit.
Born in western Kentucky, Stacy said, “I never had a horse. I always wanted a horse.”
Turns out, Robert did, too.
After they were gifted an older Quarter Horse, their realtor told them that horses usually like companions. The Mitchells found someone with a young mare with a decent pedigree. The man offered to give them the mare. “My husband didn’t want it for free,” Stacy said. “He did it for $1. That made it a two-way transaction.”
The Mitchells bred that mare, Chao Praya, to Level Sands and got Level Playingfield, who won nine of 49 starts and earned $664,822.
Upping the ante, they bred Chao Praya to Empire Maker. They were rewarded with another star—Gr. 3 stakes winner Imposing Grace, who won five of 26 starts and made $326,743.
The Mitchells then purchased Rockford Peach, who was in foal to Running Stag, for $36,000. She produced Absinthe Minded, a multiple-stakes winner who earned more than $600,000. She is the dam of Secret Oath. She was also the last Thoroughbred the Mitchells bought.
“The bottom line is we’ve never bought a race horse,” Robert told Meredith Daugherty in her February 23, 2022, story in the Paulick Report. “Every horse we’ve ever raced was born on our farm. We haven’t bought any Thoroughbred for over 20 years.”
How have they succeeded with only home-breds? “Luck—a lot of luck,” Stacy said. And a lot of work. “We went to so many clinics,” Stacy said. We became sponges for information. We read breeding books.”
Having a great trainer certainly helped, especially when their best horse, Secret Oath, showed a ton of potential. After breaking her maiden in her second start, she finished fifth in the Gr. 2 Golden Rod Stakes before winning three straight, an allowance by 9 ¼ lengths, the Martha Washington Stakes by 7 ½ and the Gr. 3 Honeybee by 7 ½.
That prompted a shot against colts in the Arkansas Derby, and she made a powerful rally in early stretch before tiring to third as the 7-5 favorite under Luis Contreras. “I thought she was going to be second, but she got tired because she made that big move,” Stacy said.
Lukas made a jockey switch to Saez for the Oaks, and he contributed a fine ride. “You’re nervous all day,” Stacy said. “You see them going to the gate. When she made the move, I just hoped it was a timed ride and she wouldn’t get tired. I was yelling, `Hang on, hang on.’ The rest of it was a blur. She didn’t want the lilies. I got the flowers.”
Secret Oath then finished fourth against colts in the Gr. 1 Preakness and is being prepped for a summer campaign, possibly starting in the Gr. 1 Coaching Club and/or Alabama. Stacy missed the Preakness. “My husband was there,” she said. “I was here foaling mares. I think she made a good run. I’m just happy that she finished in the top half and came out of it healthy.”
Health is very important to Stacy: “I don’t think I could do horses if I wasn’t a nurse. Keep the broodmares healthy. I’m able to do a lot of it myself.”
Stacy and Robert’s 22-year-old daughter Jessica is a registered nurse, hoping to go to grad school. Jessica’s younger sister Hannah is hoping to go to nursing school.
Asked if she’s proud of her daughters, Stacy said, “Oh, yeah. Being a mom is the best job I ever had. I couldn’t be prouder of my daughters.”
And Secret Oath, the ultimate home-bred who will eventually become a broodmare, one with quite a resumé.
“We’ve been breeding since 2000,” Stacy said. “You always hope you have a Derby or Oaks winner.”
Now they do.
Fitri and Jim Hay
Words - Bill Heller
To racing’s “Golden Couple,” frequent fliers Fitri and Jim Hay, the United States is just one of many locales where their horses have had great success. They’ve won in England, France, America and Dubai—the base of Jim’s company JMH Group and where the couple now resides. “They’re racing enthusiasts,” Alex Cole, the Hays racing manager for the last 17 years, said. “It’s something they enjoy a great amount.”
Visiting the winner’s circle after graded and group stakes can do that to you. Their tremendous turf horse Cape Blanco (they owned 50 percent of the horse in partnership with Mrs. John Magnier, Derrick Smith and Michael Tabor) captured the Dante Stakes, the Irish Derby and the Irish Champion Stakes and was named the 2010 Irish Three-Year-Old Colt of the Year. The Hays had 27 winners in 2010, their highest total ever.
In 2011, trainer Aidan O’Brien sent Cape Blanco to the United States, and he quickly added to the Hays’ resume. After sweeping the Gr. 1 Man o’ War Stakes, Arlington Million and Joe Hirsch Turf Classic, Cape Blanco was named the 2011 Eclipse Champion Male Turf Horse.
That same year, the Hays purchased a 50-percent share of four-time Gp. 1 winner Fame and Glory. His victory in the 2011 Ascot Gold Cup culminated an unforgettable day for the Hays. “Some days can be beyond fable,” Fitri told Catherine McQueen in her December 26, 2019, story in Ccercle, a luxury magazine. “We were guests of the Queen [Elizabeth} for lunch at Windsor Castle. Much to our surprise, this was followed by being included in the royal procession down the track in one of the queen’s carriages—an unbelievable experience!”
The success of Cape Blanco and Fame and Glory helped the Hays purchase Birch Grove, the former mansion of Prime Minister Harold MacMillian. The property includes a private golf course.
Jim was born in Glasgow, Scotland, and Fitri in Jambi, Sumatra. They met in Jakarta, Indonesia, and married on August 25, 1996. They have two daughters, Jasmine and Catriona, who both enjoyed considerable academic success.
Horse racing has always added up for Jim, whose grandmother taught him addition by watching televised races and making pretend bets. “He was hooked after that,” Alex said.
Jim studied at Strathclyde University in Glasgow, earning a Bachelor of Science and a Doctor of Philosophy in applied chemistry. In 1975, he joined British Petroleum (BP) as an engineer and worked his way up to a senior executive.
After his 27-year run at BP, Jim founded the JMH Group, a private business with two divisions—one dealing with construction, the second with lifestyle and fashion. He also acquired Fosroc, a construction solutions firm.
He’d been increasingly attracted to Thoroughbred racing, and after he and Fitri moved to the United Kingdom in 1998, he began spending so much time at racetracks and sales that Fitri felt like a racing widow. So she took the plunge and fell in love with racing, too.
Together, they began buying horses to build a stable in 2001. They didn’t have their first winner, Baratjea Dream, until 2004, then progressed rapidly. In 2010, they had a breakthrough with Cape Blanco.
In the U.S., their horse—in partnership with Smith, Magnier and Tabor—Deauville, won the 2016 Belmont Derby at Belmont Park.
More recently, Highland Chief, owned completely by Fitri, captured the 2022 Gr. 1 Man o’ War in his second start for trainer Graham Motion at Belmont Park.
Paul Cole (Alex’s father) and Oliver (Alex’s brother) had been training Highland Chief in Great Britain. Four weeks after the Man o’ War, Highland Chief raced in the Gr. 1 Manhattan Stakes at Belmont, finishing a solid fourth.
More and more, the Hays have been shipping their top horses to the United States. “The way things are in Great Britain, they send them to the U.S. for prize money,” their racing manager Alex said.
The Hays spend their racing year at Newbury, Newmarket, York, Dante, Royal Ascot, Sandown, Newmarket again, Goodwood, Longchamp, Deauville and Dubai. Away from the track, they enjoy hunting, shooting, fishing, golf, rugby and soccer.
They have shared their success. The JMH Group was a major donor in the establishment of the Institute of Pharmacy and Biomedical Science at Jim’s alma mater, Strathclyde. The Group also supports various charities in the Middle East and in India including disaster relief. Fitri has supported various projects to help and educate street children in Indonesia.
Asked why she enjoys racing, she told McQueen in her article, “There are several aspects that cannot be defined in monetary terms. There is firstly the enormous thrill of owning a horse that wins a race. That applies to all races. The thrill is magnified when it happens in a big race. The thrill is further magnified when the horse has been bred by us.”
All made possible by not becoming a racing widow.