Thoroughbred Sales Assessment; Update from the Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures, 2019
By Tom O’Keeffe
The Beaufort Cottage Educational Trust Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures took place this year at the National Horseracing Museum in Newmarket and a host of international and local veterinary specialists and industry leaders were present to discuss the veterinary aspects of the sales selection of the thoroughbred.
Gerald Leigh was a prominent breeder and racehorse owner until his death in 2002; and his friend and vet Nick Wingfield Digby opened the seminar and introduced the speakers. The Gerald Leigh Charitable Trust has established this annual lecture series to provide a platform for veterinary topics relating to the thoroughbred to be discussed amongst vets and prominent members of the industry.
Sir Mark Prescott described his take on the sales process and some of the changes he has noted since his early involvement in the industry. He recalled how the first Horses in Training sale he attended had only 186 horses. In those early days, his role was to sneak around the sales ground stables late at night on the lookout for crib biters. Back then, there was no option to return horses after sale, and as a result, trainers preferred to buy horses from studs they were familiar with—a policy Sir Mark still follows to this day.
Sir Mark went on to explain that he believes strongly that the manner in which an animal is reared has a strong bearing on their ability to perform at a later date. Sir Mark also mentioned that horses can cope with many conformational faults nowadays that would have been deemed unacceptable in his early years. He attributed this to improvements in ground conditions, such as watering and all-weather surfaces. Mike Shepherd, MRCVS, of Rossdales Equine Practice in Newmarket had been tasked with describing and discussing the sales examination from a veterinary viewpoint and in particular attempting to define what vets are trying to achieve in this process.
Shepherd’s key message was that the physical exam is the cornerstone of any veterinary evaluation. A vet examining a horse on the sales ground is not a guarantee that the horse will never have an issue—there is no crystal ball. Owners and trainers should be aware there are several limitations of the vetting process, and it is helpful to think in terms of a “pre-bid inspection” rather than a “pre-purchase examination”. The horse is away from its home environment, and this puts a lot of stress on the animal. In most cases, pre-purchase exercise is not possible, so conditions that are only apparent when the horse is exercising and in training may go undetected.
Time is a major challenge, with both vendors and prospective purchasers pushing for everything to be done as quickly as possible. A busy sales vet may have a long list of horses to examine, and information on each must be transferred to their client coherently and clearly—all before the horse is presented for sale. It can be challenging to acquire a detailed veterinary history. Previous surgeries, medication and vices displayed by the animal ought to be reported, but in many cases the person with the horse is not in a position to accurately answer questions on longer-term history.
Everyone involved—the vendor, the prospective purchaser, and the auction house—wants the process to go ahead. The horse to be bought/sold and the vet can be seen as a stumbling block. Prospective purchasers may want the horse to be examined clinically, its laryngeal function examined by endoscope, radiographs of the horse’s limbs either reviewed or taken, ultrasound examinations of their soft tissue structures and heart performed. The role of the vet is to help the purchaser evaluate all this information and make an evidence-based decision on whether to purchase the horse.
Examining vets can face conflicts of interest when examining horses that are under the ownership or care of one of their clients. Shepherd explained how Rossdales, and some other practices involved in sales work, have a protocol that an examining vet will not perform a vetting on a horse in the care of one of their own clients, and will disclose to the prospective purchaser if the vendor is a client of the practice. It is crucial to avoid working for both buyer and seller as a conflict of interest becomes unavoidable.
It is also essential that the vet understands exactly what the horse is expected to do following the sale. Thoroughbred horses in flat racing have short timescale targets and, as a result, certain parts of the examination carry more weight than others. For example, the knees and fetlock joints are commonly implicated in lameness in flat racehorses; thus particular attention must be paid to these joints when examining yearlings. Soft tissue injuries are impactful in all young thoroughbreds, but there is a particular emphasis on tendon integrity in the National Hunt racehorse because career-threatening tendon injuries are particularly prevalent in these horses. When evaluating potential broodmares, good feet are very relevant, and overall conformation is particularly important if the aim is to breed to sell. Vetting horses for clients aiming to pin hook their purchases places different requirements on the examining vet. These horses need to be able to cope with the preparation required for another sale, and they must also stand up to the scrutiny of vets at a later sale. The horse’s walk and conformation rank high in the foal/ yearling stage but may be judged to be less significant if the horse breezes in a fast time at a breeze up sale.
It is also critical that purchasers recognise that many of the common veterinary issues encountered in training are not detectable at the Sales stage. …
TO READ MORE —
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
Good Going – are ground descriptions accurate across Europe?
By Lissa Oliver
The state of the going is one of the touchiest topics in racing. One trainer will be doing a rain dance as another prays for sunshine, while all the time the Clerk of the Course has an eye on his weather app as he tries to balance the protection of his turf with the provision of safe ground for racing. Few would envy him, but many will criticise him. Just what are the issues both sides are facing?
Heinrich Sievert, head groundsman at Baden-Baden, speaks for all those in charge of the turf at racecourses when he explains the complexities of his role and the importance of the root system. It’s not what we see above the track that really matters, it’s what is keeping it alive below.
“Before the race meeting starts we must improve the root system. We make sure the grass is growing to the ideal depth, and most importantly we try to create a solid root system. Shallow roots are not good for horses to race on. We improve aeration and allow water to infiltrate to encourage the root system. We use a small amount of fertiliser, but really we want to feed the roots and we don’t want too much growth above ground. We try to keep growth as natural as possible.
“We must ensure we do good work throughout the whole year to maintain the ground. We work closely under instruction from the Direktorium, who have a checklist to ensure safe ground for horses and riders. If the ground is not safe, the Direktorium stops everything and we cannot race. If they are happy and approve the ground, it’s my job to keep it OK.
“We can’t change the ground conditions on the day; we can only water if the ground becomes too hard, but we can’t do a lot more other than keeping it in the best possible condition before racing. Watering is not ideal, it can make the ground slippery and unsafe.
“On the day of racing, I use a penetrometer and I test the ground all over the course. Unless we have a heavy thunderstorm and rain, the going will not change, and the jockeys will be in agreement with the stated going”.
The good news is that it’s clear that Sievert and all clerks of racecourses are singing from the same hymn sheet as the trainer. The discrepancies arise then from the highly personalised needs of individual horses and prioritising between this afternoon’s track condition or the long-term protection of the track. It is all very well to argue against watering a track and changing the going from firm to good, but it isn’t ideal to race on bare patches of ground, and some consideration must be given to the grass as well as the horse.
There is a common suspicion among trainers that Clerks of the Course intentionally water a track to prevent a description of firm going, but following any successive dry days in warm weather the turf will require watering, with no ulterior motive regarding the going description. Grass is a plant and needs water to remain healthy. Recently at Sandown Park, 5mm (millimetres) was added three days before the meeting, which was run on good to firm.
“For a high-quality card we are aiming for the fast side of good”, says Sandown Park Clerk of the Course Andrew Cooper. “We’ve had almost four full days of dry weather and you’re going to lose 2-3mm of moisture a day. If you did nothing you'd be good to firm, firm. It's a judgement call what you do and when you do it. It's easy to be critical of something on Monday morning when what it all boils down to is what it's like at 6pm on Thursday night".
We are all at the mercy of the weather and while water can be added, if needed, it cannot be removed. State-of-the-art drainage systems may help, but ultimately the ground is what we, and the clerks, are given.
Scientific advances in both groundskeeping and measuring of going may help, but even the GoingStick cannot remove the subjectivity of descriptions. In January 2009, the BHA introduced into the British Rules of Racing a requirement that a GoingStick reading be made available by racecourses for each race meeting at the declaration stage and again on race day itself. The readings are published alongside the Clerk of the Course's official going description. The GoingStick is also used in France, Sweden, Norway and one Irish racecourse (Gowran Park).
The GoingStick accurately measures the penetration and the shear (the energy needed to pull back to an angle of 45 degrees from the ground), combining the two measurements to represent a scientifically-based proxy for the firmness of the ground and level of traction experienced by a horse during a race.
The BHA claimed that, “Moving beyond the traditional subjective approach, the GoingStick is a device that clerks of the Course use to give an objective numerical reading that will reflect the state of the going at any given racecourse.” However, the specific GoingStick figure is subject to any number of course-specific variables and different tracks can produce different going descriptions, despite having the same reading. The verbal description by a clerk is still used alongside the numerical reading. Cooper reflects the views of many clerks when he admits, “I certainly wouldn't ever want to be putting out a GoingStick reading on its own; I think we need the verbal assessment as well”.
The GoingStick, far from providing an objective description, is user-specific and still depends on the pressure used by an individual to push it into the ground. It differs only from the traditional penetrometer in the fact it produces a calculated figure rather than the personal judgement of the user and many Clerks of the Course state they prefer the traditional penetrometer. Whichever version of stick is used, the course must still be measured at a minimum of 30 points across the track, always at the same points for consistency.
A greater issue is in the interpretation of the going description. Not only is it subjective, but even if we can all agree it’s soft, is that softer than one particular horse would like or firmer than the preference of another? Only the trainer of the horse can know. This brings us to the question of welfare, of both horse and trainer. Is it right to run a horse on unsuitable ground? And is it right to penalise a trainer if he or she withdraws a horse because of the ground?
TO READ MORE —
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
Finding Owners
By Alysen Miller
Millennials: as the younger generation of trainers comes of age, could they teach the old guard a thing or two about attracting and retaining new owners to the sport? As the racing industry collectively seeks to recruit a younger, more diverse demographic, and trainers are having to get increasingly creative in order to entice new owners into the sport, it is the trainers of the social media generation who are taking the reins.
The best way to make a small fortune in racing, so goes the proverb, is to start with a large fortune. But how large? £22,595, to be exact. According to the Racehorse Owners Association, that was the average cost of owning a flat racehorse in the UK in 2017 (the last year for which figures are available); and that’s before entry fees, veterinary bills and insurance are factored into the equation. Based on a horse’s running an average of 7.4 times a year, that gives a ‘cost-per-run’ of £3,053—in other words, a snip at £20 per second. Translated into Millennial parlance, that’s a lot of pieces of avocado toast. In short, you don’t have to be royalty to participate in the sport of kings, but it helps. So where do trainers find a pool of people willing to submit their bank balance to this particular kind of reverse equine alchemy?
Robert Cowell
The answer—as for where you turn when you want to find out what type of sandwich you are based on, your star sign or who would play your best friend in the movie of your life—is social media. Increasingly, trainers are turning to Facebook, Instagram and Twitter to advertise their wares to the wider world. These days, seemingly every trainer—Millennial or not—and his dog have a social media account (just ask the latest star of the Twittersphere, Jamie Osborne’s infamous whippet, Bad Bobby). “I think Facebook, Twitter and Instagram certainly help reach a larger audience”, says the decidedly non-Millennial Robert Cowell who, at 50, would doubtless be the first to admit that he is more au fait with winning posts than Facebook posts. “A lot of people that we have engaged with are very interested in the day-to-day life of what goes on in a racing yard. Short videos and little pictures every now and again—just giving them an update of what we do—is certainly no skin off our nose, and if it helps people to understand our industry, then I think it’s a very good thing”.
But though the tools at today’s trainers’ disposal may be relatively new-fangled, it remains to be seen just how novel this approach is in reality. From social media to syndicates, trainers have always sought new avenues to bring racehorse ownership to a wider public and diversify their portfolio of owners. Now a common sight on racecourses throughout Europe and, indeed, the world, the first syndicates in the UK were set up by Kennet Valley Thoroughbreds and then Highclere Racing more than 20 years ago. Today, Highclere is one of the largest manager of syndicates in Europe, where syndicate ownership is increasingly popular even as sole ownership is declining. In the UK alone, 5,447 people participated in ownership via syndicates or other shared ownership schemes in 2018—an increase of 6.2% year-on-year. Compare that with a 1.4% drop in sole ownership over the same period. So what is it about the communal approach that appeals to owners? The most obvious answer is the price: for a fraction of the cost of owning a racehorse outright, a syndicate member can rub shoulders with the Queen and Sheikh Mohammed in owners’ enclosures from Ascot to York. Yet the calibre of some of the celebrity clientele (high-profile syndicate members have included Sir Alec Ferguson, Elizabeth Hurley and Carol Vorderman, who can surely be counted upon to have done the math) belies the theory that cost alone is behind syndicates’ popularity.
Indeed, research shows that the satisfaction rating for syndicate members is 8.2 out of 10, compared to 7.5 out of 10 for sole owners, according to a 2016 survey undertaken by sports marketing agency Two Circles on behalf of the ROA and the BHA. Instead, the suggestion is that syndicate ownership appeals to civilians and celebrities alike because it confers a sense of being a part of something larger than oneself; of belonging to a community with whom to share in the highs and lows—in other words, that sounds rather a lot like a social network (Mark Zuckerberg, eat your heart out). So why not go all out for syndicates and the relative security they provide, rather than putting all one’s eggs in the gilded baskets of capricious individual owners?
Edward Bethell
“I think syndicates are a great thing”, says Edward Bethell who, at 26, sits squarely in the ‘digital native’ demographic. “I think trainers should do more of it. But then syndicates are a full-time job in themselves because you need someone to manage them. People need to be updated regularly”. So where does Bethell think trainers, and particularly young trainers, should focus their efforts? “I’m a big believer in social media. I think it gets you out there.
For a smaller trainer or for a young guy, you’ve got to create a niche in the market for yourself. I think social media can only be a good thing as long as you’re using it in a positive way”. Bethell, who has worked in Australia for Gai Waterhouse and sojourned for a stint in France, has overhauled his father’s social media profile and is making a name for himself as something of a social media maven.
TO READ MORE —
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
VAT and tax-deductable expenditure across Europe
By Lissa Oliver
The EU has supposedly similar tax laws and reciprocal VAT agreements to avoid double taxation, but in practise racehorse trainers are among the many businesses who discover this is not always the case. Invoices incorrectly issued with VAT can lead to problems in reclaiming the tax, if at all, and tax deducted at source from prize money can take up to four years to reclaim. Such is the difficulty involved—many simply don’t bother to try.
The European prize money payment system may not be fully unified but most racing authorities and organisations such as Weatherbys, Horse Racing Ireland (HRI) and France Galop, work together on a reciprocal payment system to make the transfer of prize money as straightforward as possible. The problems arise when additional costs are imposed, not by the racing authority, but by that country’s government.
Withholding tax, which can catch owners and trainers unawares, is out of the hands of racing authorities and beyond the scope of unification. If, for example, a person is deemed to have earned money in Germany—including prize money—they are deemed liable for the income tax on that money. In most cases this can be very simply avoided by completing the necessary forms beforehand, as the EU rules that if you have paid tax in one European country you do not have to pay it in another.
However, some Member States do not consider an EU VAT number as sufficient for withholding tax exemption or VAT-free invoicing, and their racing authorities are obliged by law to charge VAT on their invoices. Which countries these are is not always clear, as treaties to avoid such complications are in place but not complied with. As an example, in December 2017 the European Court of Justice (ECJ) decided that German anti-treaty shopping rules, which denied full or partial relief from withholding tax, was not compatible with EU directives. An amendment to German taxation law is expected to be made as a result but has yet to be introduced.
Weatherbys, France Galop and HRI have a withholding tax exempt form, which can be filled in before a horse races abroad. This is advisable because it is much harder to claim back any tax stopped afterwards. It can be a month later when the prize money arrives into an account, at which point the tax stopped becomes apparent, and it is difficult to apply for a refund. Double taxation conventions and treaties exist between cooperating countries, but stamped certificates from the relevant tax offices are still required in advance. Your racing authority will be able to help you with this.
Withholding tax rates shown in the table are the current statutory domestic rates that apply to payments to non-residents, which may be reduced if an applicable tax treaty is in place. Qualifying payments to EU residents may also be exempt under EU directives for all listed countries, with the exceptions of Hungary, Norway and Turkey.
While withholding tax only applies to prize money won abroad, a more regular taxation issue is VAT, applied to purchased goods and services. The EU has standard rules on VAT, but these rules may be applied differently in each EU country. For EU-based companies, VAT is chargeable on most sales and purchases within the EU. If you are registered for tax, theoretically VAT can be reclaimed, but where it is deducted by another EU country, this can lead to “double taxation” problems.
In an attempt to ensure tax is paid only once on EU services and purchases, double taxation conventions and treaties have been agreed between cooperating EU countries. However, there are growing concerns at cross-border tax problems facing individuals and businesses operating within the EU and, at time of writing, the EU Commission is currently considering closely the possible conflicts between the EC Treaty and the bilateral double taxation treaties that Member States have agreed with each other and with Third Countries.
A study completed by the Commission in 2001 on taxation highlighted a number of problems that have yet to be tackled, including the question of equal treatment of EU residents and the application of bilateral treaties in situations where more than two countries are involved. A possible solution is the creation of an EU version of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Model Convention that serves as a guideline for establishing tax agreements, on which Member States' bilateral tax treaties are based, or a multilateral EU tax treaty.
The double taxation agreements of Member States will continue to be subject to review by the EU Commission, particularly in trying to address the problems resulting from a current lack of coordination in this area—most pronounced where more than two EU countries share a treaty or where a Third Country is included.
Belgium has a network of treaties for the prevention of double taxation with 88 countries, including Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and the UK.
Germany has treaties with, among many others: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Russia, Sweden, Switzerland, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey and the UK. As identified by the ECJ, those treaties are not always honoured. France likewise has a long list of treaties that includes the EU Member States, and Ireland has signed comprehensive double taxation agreements with 74 countries.
Some racing jurisdictions have very clear guidelines set by government, and the German Federal Central Tax Office has a special procedure for exempting foreign taxpayers from certain taxes deducted at source, requiring a tax certificate and withholding tax exempt form well in advance. Foreign individuals are subject to limited tax liability in respect of the income they derive in Germany, and this tax is otherwise automatically withheld at source.
TO READ MORE —
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
Brexit Preparations?
By Lissa Oliver
At the time of writing, 29th March draws closer but we are no nearer clarity on the Brexit issue. Will there be a deal? Will there be no deal? Will there be an extension, leading to a second referendum and no Brexit at all?
We may not know what the future holds, but indications are that all governments are preparing for the possible border controls, which will have a serious impact on the movement of racehorses to and from the EU and the UK.
Ireland, the Netherlands and Germany are the countries with the closest trade links with the UK, and the Netherlands launched a major information campaign at the end of January. Trade Minister Sigrid Kaag commented, “After Ireland, the Dutch economy is most entwined with that of the UK," and warned that many small and medium companies had failed to make sufficient preparation for a no-deal Brexit.
The Netherlands has made provision for more than 1,000 future jobs created in customs and food safety agencies, but the government points out that a no-deal could also provide positive new opportunities for businesses. Whether or not there is a deal or the UK leaves on 29th March, the European Medicines Agency is relocating from London to Amsterdam.
France, closely linked with the UK and Ireland within the racing industry, published a draft bill in January for a no-deal contingency, which will reinstate checks on goods and passengers to and from the UK, as well as inspections of food, plants and live animals. An additional 250 customs staff have already been recruited in 2019, and this is expected to increase to 700 by the end of next year.
Edouard Philippe
Prime Minister Edouard Philippe announced a €50m investment in ports and airports to cope with a no-deal Brexit. “The plan consists of legislative measures that aim to ensure that the rights of French citizens and businesses are protected”, he said.
Germany has apparently lagged behind in providing public information and support for businesses regarding Brexit contingency plans but has also recruited additional staff to deal with new economic relations with the UK. No-deal preparations include dealing with the status of approximately 100,000 British citizens residing in Germany, as well as Germans living in the UK.
Spain has at the time of writing made no public information available on its no-deal plans but is expected to agree reciprocal arrangements for 310,000 British citizens living in the country. A protocol on Gibraltar, due to be attached to the Brexit Withdrawal Agreement, will not come into effect if there is a no-deal, but Gibraltar is already outside the Customs Union and has a border control in operation. Staffing in Spanish immigration offices has been stepped up.
In Ireland, the government has been proactive in providing public information and supporting businesses. In February it launched a free-to-use Brexit SME Scorecard, an interactive online risk assessment tool for Irish companies to self-assess their exposure to Brexit. The assessment is based on six key pillars: business strategy, operations, innovation, sales and marketing, finance and people management.
Irish companies are told they can and should be taking immediate action to mitigate the potential risks and take advantage of any arising opportunities. The Scorecard, at www.prepareforbrexit.ie, identifies risk points, allowing managers to assess where planning and preparation are most required.
Companies are advised to:
identify risk
identify opportunity
review supplier base for vulnerability
consider the resources needed for extra administration
consider potential impact of Brexit on your customers
consider the impact of compliance with possible new standards and regulations in the UK
amend sales and marketing plans
assess impact of currency volatility
consider potential for price changes with your customers and key suppliers
consider how potential restrictions on the movement of people may impact recruitment
The Irish government also drew up the Consequential Provisions Bill 2019—Brexit Omnibus Bill—at the end of February, covering primary legislation to address the immediate issues likely to arise in the event of a no-deal Brexit, ensuring key measures and protections are in place. Financially, supports include a €300m Future Growth Loan Scheme and a separate €300m Brexit Loan Scheme for Business.
Helen McEntee
Helen McEntee, Minister of State for European Affairs, stated, “Revenue will have 400 additional customs staff trained and in place by the end of March, and they can recruit an additional 200 by the end of this year. The Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine is implementing the necessary steps to facilitate more Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) controls. Veterinary personnel and 70 other support staff are now being recruited to implement animal and health (SPS) checks, as are 61 extra Environmental Health Staff”.
While an alternative for the Tripartite Agreement has not yet come closer to being agreed, the Irish Thoroughbred Breeders Association (ITBA) remains positive and in early February hosted a 2019 Action Plan, at which Michael Treacy, the ITBA EU consultant, warned a Brexit no-deal is the worst possible outcome from all points of view.
Treacy emphasised the ITBA had been very significant at key EU meetings and assured the audience the EU Commission has stated it will engage with affected Member States and endeavour to assist, saying of the thoroughbred industry in particular, “Everyone in Brussels is really aware of the problems we have”.
Treacy later accompanied the European Federation of Thoroughbred Breeders’ Associations (EFTBA) Chairman Joe Hernon with a delegation to Brussels, highlighting the concerns of the European thoroughbred industry, which contributes in excess of €100bn to the EU economy, with around €800m of thoroughbreds sold annually. Approximately 220,000 people are employed in the equine industry throughout Europe.
The delegation also included Hubert Honore and Paul Marie Gadot of France, Andreas Tiedtke of Germany, Giovanna Romano of Italy and Des Leadon, EFTBA veterinary consultant. The EFTBA delegates met with senior EU officials, including EU Commissioner for Agriculture Phil Hogan, and Dr Alf-Eckbert Fussel, EU Commission’s Directorate General on Animal Health.
One of the concerns raised was the free movement and transportation of thoroughbreds post-Brexit. Hernon confirmed, “The EU Commission and the respective Departments of Agriculture appear to be well-versed in our needs and desires for international trade to continue”.
Ireland’s Tánaiste (deputy prime minister), Simon Coveney, was among those addressing the ITBA Action Plan seminar and concluded, “Ireland has extraordinary solidarity across Europe. This is a sector that is extremely exposed to the wrong outcome. We need racing and equine health managed on an all-Ireland basis but don’t have an agreement from the UK on that yet. The derogation for movement of livestock is applicable to Member States only and not Third Countries. If the UK leaves with no-deal, there will be 100% animal inspection at the border”.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
Why are leg boots not commonly used in racing?
By Dr. David Marlin
Lower leg injuries are extremely common in all types of race and sport horses. Risk factors for traumatic injury from shoes on other legs due to over-reaching or brushing or even from other horses in racing or polo include high speed, jumping and rapid turning. Injuries can also occur from sharp stones being thrown up from the ground. Whilst in sports such as eventing and showjumping, it’s unusual to see horses competing without leg protection at least over the forelimb tendon area; in racing the use of protective boots is much less common. This is also true for polo—a sport which would present a high risk of injury to the lower leg due to balls, sticks, high speed, turning and close proximity to other horses. So is the risk much lower than we might expect, or is their some other reason why boots are not commonly used in racing?
Epidemiological studies of injuries to racehorses in training and racing certainly don’t point to a large risk for interference-type injuries from shoes within or from other horses. In the younger flat racehorse population, fractures remain the greatest concern both in training and racing. Injuries due to forelimb Superficial Digital Flexor Tendons (SDFT) tendonitis and Suspensory Ligament (SL) desmitis are not uncommon, with a prevalence of around 10-20%. However, information on the rate of injuries due to interference in racehorses is generally lacking.
Whilst an injury to the lower forelimb where the skin has been cut and there is clear penetration is easily identified, this is not the only way that tendons may be injured. Blunt force which does not result in obvious superficial injury may still lead to internal bruising and inflammation. Repeated traumatic insults due to interference may therefore still contribute to tendon inflammation. As we now recognise that most tendon injuries are due to chronic inflammation and damage as opposed to isolated accidents, anything that contributes to tendon inflammation is a cause for concern.
The risk to tendons from the heat generated during exercise may be one of the reasons why racing has tended to shy away from the widespread use of boots, except perhaps in the case of individuals suffering repeated or severe injuries. Wilson and Goodship at Bristol Vet School showed in the 1990’s that equine tendons reached temperature of around 45°C during galloping. Tendons are essentially large elastic bands which store and release energy on each stride—one of the adaptations that makes the horse such a supreme athlete. In the same way that if we stretch an ordinary rubber band, it will heat up. Tendons have a poor blood supply, and so the heat accumulates and the tendon increases in temperature during the gallop; the longer and faster the gallop, the higher the temperature. Why is tendon temperature a concern?
Heat: Tendon cells appear to be sensitive to increases in temperature. When isolated tendon cells in culture were heated for 10 minutes at 45°C (113.0°F), around 10% died; but when they were heated to 48°C (118.4°F) for 10 minutes, then around 80% died. Similar results were found in a later study by a group from Japan. Even though the number of live tendon cells in a tendon is low, compared with the elastic matrix that makes up the majority of the tendon, injured or dead cells release inflammatory mediators which in turn can lead to tendon damage. And of course, anything that insulates the leg reduces heat loss and can lead to even higher tendon temperatures. This is likely one of the primary considerations for not using a protective boot, although there are others.
Abrasion/rubbing: Boots (or bandages) that do not fit correctly or that are applied incorrectly may lead to skin abrasion and an increased risk of skin infections. In addition, boots that allow the ingress of surface material between the boot and the skin will likely lead to rubbing.
Restriction of blood flow to and from the foot: Morlock, et al. (1994) observed pressure under bandages applied to the lower limb during galloping which they concluded were high enough to restrict blood flow. In bandages or boots applied over the fetlock and cannon, high pressures due to the method of application, the tightness of the application and the type of material used the lateral and medial digital arteries and veins could be compromised.
Restriction of range of motion: Restricting the range of motion of a joint will change the loading dynamics of the joint. This may be beneficial in the case of a joint that is injured, but this will reduce the extent to which that joint dissipates forces during the loading phase. This may in turn lead to overloading of other limb structures. If the restriction is only on one limb, then this may lead to asymmetry and an increased risk of injury in the un-restricted limb. The effect of various equine boots on range of motion both in vitro and in vivo has been reported (Balch, et al. 1998; Kicker, et al. 2004).
Contact dermatitis: Boots and bandages have the potential to cause contact dermatitis. Neoprene is commonly used in boots, but it has been estimated that around 6% of horses are allergic to neoprene. Rosin (also known as colophony), which is commonly found in the resin of pine and conifer trees, can cause skin contact sensitisation. It is used in neoprene adhesives and may also pose a risk of contact dermatitis in horses. The risk of skin infection is also increased by boots and bandages that do not allow sweat to evaporate and therefore result in hyper-hydration of the skin under the boot or bandage. This results in both an increased susceptibility to mechanical trauma to the skin from friction and an increased risk of infection, particularly by fungi.
Increase in weight….
TO READ MORE —
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
Should horses be paid to race?
By Chris Cook
Horseracing has never been the kind of sport to rely on a maxim like: 'If you build it, they will come.' If you want people to run horses at your racecourse, you have to give them a good reason, like prize money or the promise of a good time or the chance of landing a prestigious and historic contest.
And some go further than that, offering an additional payment as incentive to owners to show up. Racing has, over the years and in several countries, dabbled with various schemes that might broadly be grouped under the heading of appearance money, without really talking through the implications.
This might be a good time to have that conversation because the incentive for tracks to attract the big-name horses is only going to increase. For evidence of that, one only has to ask Nick Smith, director of racing and communications at Ascot, about the benefits that flow now and will eventually flow to the Queen's track from having a good number of international raiders at the Royal meeting every summer.
"We started chasing international horses just because we wanted to make the meeting more interesting and develop an identity," Smith said. "The Gold Cup is a wonderful race, but it's a long time since people woke up in the winter talking about the Gold Cup at Ascot. It doesn't happen.
"So the Royal meeting needed an identity over and above fashion, globally. And that's why we worked from the start on bringing the internationals in, to make it Europe's international hub. Now the benefits are really starting to flow in because the media rights money is all linked in, the betting will become linked in -- that's a bit further down the line but it's coming -- and there's the intangible sponsorship benefits. Plus, it's what people talk about in the pub, they talk about the Australian winner, the American winner. It's one of the key selling points."
Thanks to a steady stream of US-trained winners at Royal Ascot in recent years, notably the star mare Tepin, NBC covered at least four races in that country on all five days this summer, broadcasting from two fixed positions at the course. Smith adds: "If you can put a presentation together for new sponsors that [shows coverage by] NBC, Channel 7, NHK, Fuji TV, and ITV, then you can go to sponsors and say, ‘This is what we deliver.’ Everything comes together for the general good."
As you might expect, Ascot has sought to be responsible in its means of attracting those valuable raiders to Britain. Smith pays a fixed sum to each runner from outside Europe, depending on which part of the world they're coming from, the aim being to cover about half of their travel costs. But he will only pay for "Group One horses in Group One races," with the result that Wesley Ward's many two-year-old raiders have never qualified and must pay their own way.
"What you don't want is too many horses coming just because it's a good gig. Whilst we're really happy to have a 115-rated horse run in our Group One races and we are very happy to pay a travel allowance towards that, if we did full payments for those kind of horses, we would be overwhelmed and most of them would be out of their depth."
Smith stresses that what he is paying is "a travel allowance," to avoid any suggestion that it might be appearance money as understood in some other sports, ie an amount that might actually be greater than the prize money on offer. No one can hope to secure a net profit just by having a runner at Ascot; for that to happen, the horse must perform well.
Nevertheless, Smith is considering whether to introduce a "double allowance" for horses rated 130 or over, on the basis that there will only be one or two in the world at any time. "What I wouldn't do is change the rules for a particular horse. Black Caviar got the same allowance as everybody else and they wanted to run, so they invested in it as well, like every other horse owner.
TO READ MORE --
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD -
Why not subscribe?
Don't miss out and subscribe to receive the next four issues!
Brexit - How high are the stakes?
By Lissa Oliver
When Britain submitted its notice to withdraw from the EU in March 2017, one of the biggest issues became border control and movement of horses, particularly between the EU Republic of Ireland and its bordering British Northern Ireland. A hard border between the adjoining counties of Ireland presents its own physical and political difficulties, but any restriction on the movement of horses between Ireland, Britain, and mainland Europe gives rise to problems that affect us all.
The uncertainty of border control also impacts on the safety of the national herd and disease control. The main principle of the Tripartite Agreement was to prevent the spread of disease and that, as Irish Horseracing Regulatory Board’s chief veterinary officer Dr Lynn Hillyer reminds us, is crucial and arguably the biggest issue when it comes to Brexit negotiations.
Dr Lynn Hillyer
Currently, 10,000 horses move freely between the UK and Ireland every year. Seven thousand horses move overland between the Republic of Ireland (EU) and Northern Ireland (GB); 5,100 horses move between Ireland and France, the majority using Britain as a land bridge; and 5,000 horses move between Britain and France, according to Horse Racing Ireland (HRI) figures. Such freedom of movement is dependent upon the Tripartite Agreement, which will no longer be valid after 30th March 2019.
The Tripartite Agreement simplified the travel of horses between France, Britain, and Ireland and reduced the cost of moving horses between the three countries, allowing racehorses to be shipped without pre-movement veterinary checks and certification, and without the requirement for isolation and quarantine periods at their destinations.
“It’s not just about movement, it’s the protection of the herd against disease, and it’s absolutely critical that’s protected,” warns Dr Hillyer, who has been working with her French counterparts in ensuring that safeguards are in place in advance of the end of the Tripartite Agreement. “There has been added pressure on us because of the enormity of movement involved.”
Adding to the difficulty in resolving issues has been the British government’s reluctance to commit to decisions and state definite demands. MEP Mairead McGuinness has been advocating on behalf of Ireland and warned in January at the Irish Thoroughbred Breeders Association (ITBA) National Symposium, “We hope when we sit down to negotiate, common sense will prevail, but the EU is not prepared to tweak its principles to accommodate the UK. If we cannot overcome our problems, there will be real difficulties for your industry.”
Fortunately, there has been a concerted team effort between all sectors of the thoroughbred industry in France and Ireland as they united to draw up a proposal to replace the Tripartite Agreement. Rather than sit back and wait, they decided to put together a draft for an improved alternative to the Agreement, the High Health Status (HHS) document for horses. “What is lovely is how the racing bodies and breeding associations have all pulled together, and that’s something that has come through the talks really strongly,” Dr Hillyer says.
Working with the Turf Club were HRI, the ITBA, Horse Sport Ireland – the representative body for the sport horse sector of show jumpers, dressage, and eventers – and France Galop. Paul Marie Gadot, head of the horses and control department at France Galop, explains, “The EU Commission draft doesn’t fulfil all our wishes as the breeding stock isn’t included in their proposal. A lot of work is still to be done. To be clear, we are working on an expedited movement system for high health horses.
“Currently, we are going to suggest a solution to the European Commission, which is working on the new legislation regarding movements of horses in the European Community and with the third countries. Actually, we are trying to address the modification of the European Law regarding horse movement, which isn’t linked to the Brexit negotiations. This way is more technical and also safer. I will be happy when a new system allowing easy horse movements will be in place.”
Both Dr Hillyer and Gadot have been happy with the level of awareness and support from their respective governments. “Our contacts in the Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) have been fantastic and their response to our queries have come back by return,” says Dr Hillyer.
“The public information seminars here are probably less frequent than in Ireland,” agrees Gadot. “The preparatory work is done with the representatives of the equine industry, especially at racing and breeding levels, and we are in permanent contact with the hard core in charge of preparing the future of racing and breeding in Ireland and UK.
TO READ MORE --
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD -
Why not subscribe?
Don't miss out and subscribe to receive the next four issues!
Stable Staff: How do European governments classify and enforce racing's workforce?
By Lissa Oliver
Just over a year ago, in February 2017, the Workplace Relations Commission (WRC) served four Compliance Notices on Ballydoyle, the training establishment owned by Coolmore. Irish trainers held their breath as the result of an appeal by Ballydoyle was anxiously awaited. That appeal was rejected in January of this year and will result in major repercussions for the industry.
The WRC was established in October 2015 under the Workplace Relations Act 2015 and replaced the National Employment Rights Authority, the Labour Relations Commission, and the Director of the Equality Tribunal. During an inspection of Ballydoyle in May 2016, WRC inspectors identified breaches of the Organisation of Working Time Act, involving failure to provide sufficient breaks and rest periods for five grooms and exercise riders.
This situation arose from what many would argue to be the unnecessary February 2015 Irish Amendment of the 1976 Industrial Relations Act, which was amended to exclude the rearing and training of racehorses from being recognised as agricultural labour. Interestingly, stud farms and their staff are not affected by this ruling, as horse breeding is still considered to be an agricultural activity.
The amendment made was not required by European law, but individual nation states are free to make such exemptions within their own legal system as they deem necessary. Therefore, since February 2015, Irish racehorse training yards do not qualify for the same working hours exemptions that have been agreed in agricultural workplaces, as defined by industrial relations law.
The 2015 Amendment was not widely publicised and escaped the attention of most trainers, but the WRC targets two industries each year for inspections, and the equine industry was among those specifically targeted for 2017, with around 60 inspections carried out.
Why Ireland’s racing staff are not agricultural workers...
TO READ MORE --
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD -
Why not subscribe?
Don't miss out and subscribe to receive the next four issues!
Amateur Riders - More than just a tradition
By Chris Dixon
Courage, honour, elegance, and fair play. That is the list of values that underpin the ethos of the Fegentri – the International Federation of Gentlemen and Lady Riders. They are values that Elie Hennau refers to regularly as he speaks with enthusiasm and pride about the organisation of which he is now president, and his own career as an amateur rider.
“I won the Amateur Riders’ Derby at Epsom in 1999 on a 25/1 shot and beat Ryan Moore who was second on one for his father. My whip did not comply with the British standards and I had to borrow one. It was Frankie Dettori who gave me his whip for the race so I beat Ryan using Frankie’s whip – this is probably the thing I’m most proud of in my whole life!”
Now 44, Hennau held down a full-time job whilst enjoying a 15-year spell in the saddle, during which time he rode in around 1000 races and partnered almost 100 winners. As a rider in the Fegentri series he met new friends, experienced different countries, and got a great thrill from the sport. Racing helped him grow, and now it’s time to give something back. “If I’m completely transparent then this wasn’t the best time in my life to take on this presidency as I already have too many things to do and this is an unpaid job. But I do it for the love of the sport. Maybe I was expecting to do this when I was a little older, but the opportunity was there and I wanted to give back to racing all of the great things racing gave to me.”
Created by a group of enthusiastic amateurs at St. Moritz in 1955, Fegentri has expanded and developed into an organisation whose membership currently consists of ‘clubs’ in 23 different countries across four continents and has a high-profile sponsor in Longines. The mission of the organisation is to promote international races for amateur riders and to organise the Fegentri World Championship. As Hennau explains, “We don’t organise the races as such, but we provide the riders for them and organise the championships. There are two world championships, one for gentleman riders and one for lady riders. This year there were 60 races across 40 different tracks in 15 different countries, and we had seven gentleman riders and 10 lady riders.”
Not every member sends a representative every year, and the idea is for the series to be contested by the best amateurs around the world, with each member currently able to send just one rider, either a male or female, to represent them. “There is a minimum of five wins required to ride in the series and every country can decide who they send, but normally they should be the champion. Ideally they should be the best and if not, they must be one of the best.”
Hennau regularly speaks about the emphasis on quality riders competing in the series. “I am not worried about quantity; I care about the quality. By that I mean the quality of riding ability, which is the first element, but also the quality of values.” He then explains the other key component of selection to race as part of Fegentri: “It is also important that the riders represent our values, and the message to our members is, ‘Please send a rider that corresponds to our values of courage, honour, elegance, and fair play.’ It is only when a member has a rider of the right quality who holds the right values that they should be put forward.”
Fegentri President briefing the Gentleman Riders in Madrid.
It’s by ensuring quality amateurs are in place to ride and through sticking to these values that Hennau can have confidence in the capabilities of riders taking part in Fegentri, and he is keen to press the point home to help ensure the series continues to thrive. “It’s a combination of having racing authorities that understand the need to keep this alive, of having local clubs that explain the series to their trainers, and going to those trainers to tell them that we need their help.” He is aware and understands that some trainers, especially in the major racing jurisdictions where the quality of horse is that much higher, may have some reservations about trusting an unknown rider to give their charge a safe ride that they are happy with. However, he believes that these reservations are misguided. “My message is that we have top quality riders. I want to let trainers know that the boys and girls riding in these races will be top quality riders, comparable to the best amateur riders you could have in your own country.”
TO READ MORE --
Order this issue in print or download
Why not subscribe?
Don't miss out and subscribe to receive the next four issues!
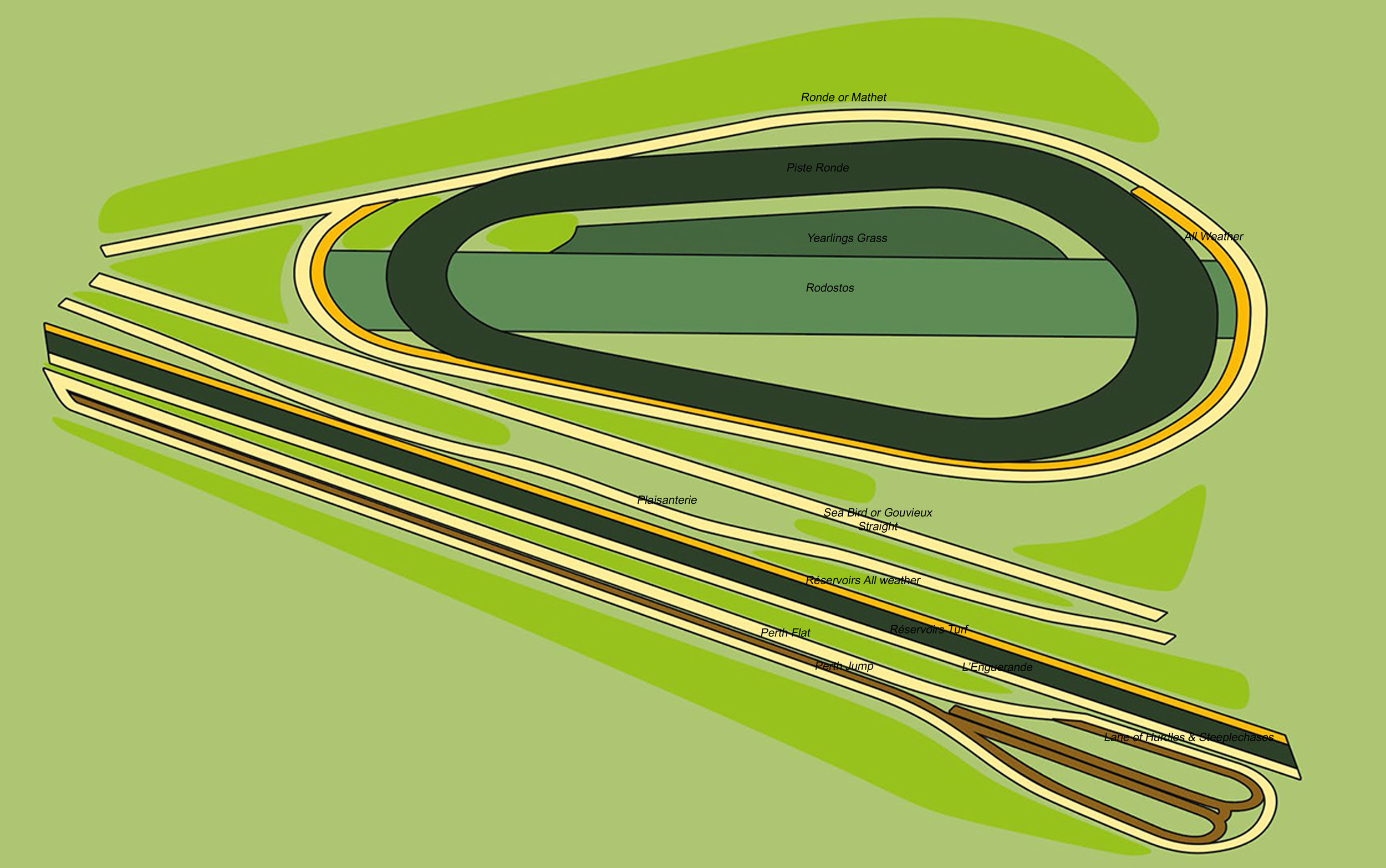
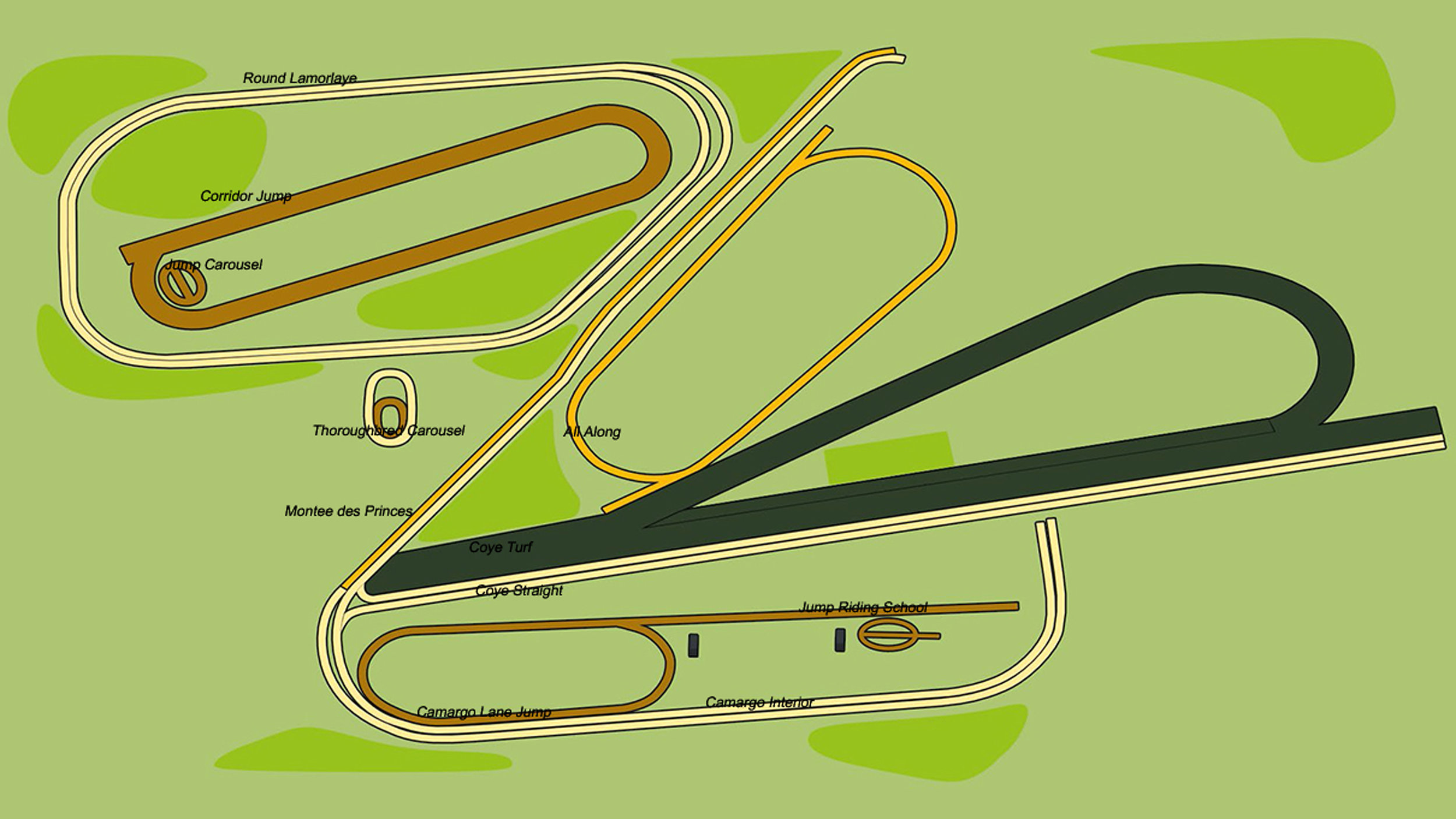
Chantilly - Looking ahead to the next generation
By Giles Anderson
Racehorses have been trained in Chantilly since anyone can remember. It would be fair to say that the horses are part of the fabric of the town, perhaps just as much so as the bobbin lace, which Chantilly was famous for in the 17th century.
Matthieu Vincent, Trainer Centre and Racecourse Director and Marin Le Cour Grandmaison, Assistant to the Director, have the responsibility of managing the racecourse and training grounds.
Surrounded by forest and located some 30 kilometres from Paris, Chantilly is the iconic home of French racing and training. Managing the hectares of training grounds and the racecourse is no easy task, but the responsibility lies in the hands of Marin Le Cour Grandmaison and his boss Matthieu Vincent, who splits his time between Chantilly, Deauville, and Maisons-Laffitte. They see themselves as ambassadors for racing in Chantilly, evangelical about what the town has to offer and keen to expand the centre’s reach to up-and-coming young trainers.
Spending time in their company, it becomes clear that their primary focus is to give the trainers the tools they need to train horses better.
Site plan of Chantilly Training Grounds
Take Montjeu, who according to Vincent was not only his favourite horse but quite a quirky customer to train. “The horse was difficult and John (Hammond) did a great job with him. We would have him working at the racecourse at 5am. One day Cash Asmussen came to the racecourse to ride but John didn’t want him to gallop, just trot. He wanted him trotting for 500 hundred metres. But after 20 metres Montjeu wanted to go. So John stopped him and we ended up opening the racecourse to repeat the exercise five or six times and eventually he relaxed. We would do that for any trainer and it wouldn’t make any difference to us if they wanted to do something special at 5pm in the evening, we are here to help our clients.”
Chantilly is home to 110 trainers and approximately 2500 horses, of which 250 are jumpers (National Hunt). “In 2010 we had 2400 flat horses and 600 jumpers here and the average trainer was maybe 60 years of age,” says Vincent.
“If we compare Chantilly and Newmarket, Newmarket is more of a dream for some owners because they have a lot of classic younger trainers -- that’s good, the young. We need to have younger trainers, we want to help the young trainers here. It used to be every trainer’s dream to train here. Now we have the provinces, look at Jean Claude Roget: in 2005 he started to have classic horses but he’s not from Chantilly. So some said, ‘Maybe you can be a good trainer anywhere in France.’”
Chantilly Racecourse used to open for 12 days a year, but with the advent of all-weather racing in 2012 that number has jumped to 45. “But we have less and less horses in training in Chantilly since 2012. The track has helped us retain horses. It helps the trainers. Twenty years ago it was so quiet here and horses were just walking and trotting, but now with the all-weather tracks we’re training every day.”
The all-weather track has proven to be a good investment for the local economy, partly funded by the town, which put in €1,500,000 of the €5,000,000 cost. The annual tax income runs into a healthy seven figure sum. On top of that, the town is home to 2000 workers whose income comes from the racing industry, with a staggering 50% of the workforce being stable staff or riders. Who knows what the shrinkage would have been like if the all-weather hadn’t happened.
TO READ MORE --
Buy this issue in print or download
Why not subscribe?
Don't miss out and subscribe to receive the next four issues!
Lissa Oliver's Spring Sales Analysis
By Lissa Oliver
A question that has divided commercial breeders and racehorse trainers since Tattersalls first decided to auction thoroughbreds is the definition of The Big Day.
For trainers, it is a major race at a major festival. Although every commercial breeder dreams of a high-profile winner, their big day is a major price at a major sale. Why else do we differentiate between commercial breeders and those who breed to race, lamenting the loss of the traditional owner-breeder at every dispersal sale?
If the outcome of the matings and sales preparation resulted in The Big Day for both parties, there would be no complaints, but as some have learned to their cost, the sales topper doesn’t always reach such dizzy heights again. The excitement and anticipation generated by the final knock-down figure builds to hype if and when the sales topper makes its racecourse debut, but can sometimes be followed by immediate disappointment and obscurity.
But is this always the case, and for all of the elite sales horses? And how does a big day in the sales ring affect the elite two-year-olds, prepared for the breeze-up sales that are often referred to as ready-to-run sales? Are the juveniles ready to run or, as some trainers suspect, over-boiled?
To see if any emerging pattern can shed light on these questions, I looked at the racecourse performances of the best-selling breeze-up juveniles and three-year-old National Hunt store horses from certain sales. I chose the period of 2005 to 2014 to obtain 10 years of data and to allow for the most recent of the graduates to reach their potential on the track, and I followed the careers of the 10 highest-priced lots sold (not unsold or bought in) at each selected sale. Because the Goresbridge Breeze-Up sale only began in 2006, a total of 490 horses were included from the five selected sales.
As most trainers earn a living by trading horses, career earnings often have little relevance on whether or not a purchase turned a profit. Many of the graduates here have gone on to long careers in Japan, Hong Kong, Dubai, Australia, or the USA, so their second-hand value is likely to have exceeded their original purchase price. In the case of the fillies, a residual paddock value also renders their career earnings redundant. However, the earnings on track do provide a measure of the ability of the individual and the longevity of career. A non-blacktype winner amassing more than €30,000 has undoubtedly been a top-class handicapper or a tough and consistent performer throughout a lengthy career.
What is quite shocking to see is that some British-trained horses who have both won and placed second during their career have amassed only €4,000 or less in earnings. This covers just eight weeks of training fees and is surely scant reward for a winning horse, particularly when in Ireland, for example, minimum prize money has risen from €6,000 to €10,000 and a single win could pay the bills for five months.
Regardless of whether a Flat breezer or National Hunt store horse can recover its purchase price, we can be sure that the store horse will at least recover its physical and mental well-being by the time its career begins. Many trainers of two-year-olds argue differently when it comes to the breeze-up graduates and so we must also examine the results to see if the preparation for these sales has any negative effect. Though times are not officially taken at European breeze-up sales, it can be assumed that the 10 highest-priced two-year-olds put in the most impressive gallop, so it will be of interest to see how this impacts, if at all, their immediate career.
TO READ MORE --
Order this issue in print or download
Why not subscribe?
Don't miss out and subscribe to receive the next four issues!
Horseracing in South Korea: A GLOBAL VISION
Published in European Trainer, January - March 2018, issue 60.
On the evening of 19th January 2017, something special happened in Dubai. To the casual spectator it might have seemed like any other horse race, but to viewers in Korea, the 1200m District One Handicap at Meydan was a watershed moment in their nation’s sporting history. Because the winner of this race was Main Stay, a four-year-old colt trained by Kim Young Kwan and the first Korean-trained horse to win at a significant international meeting since thoroughbred horse racing was established in South Korea almost 100 years ago. What is more, the winner carried the (KOR) suffix in the racecard, underlining the fact that the country is now capable of producing internationally competitive thoroughbreds.
Yet as Main Stay crossed the line on that fateful night, even switched-on racing enthusiasts and professionals with a broad international perspective may have asked, “So they race in Korea?”
Indeed, this otherwise significant nation’s racing industry remains relatively unknown across the globe. Recent developments have brought Korean racing into the spotlight however, and notable domestic and international expansion projects put in place by the Korea Racing Authority (KRA) could soon see it established as an influential player on the global racing scene....
To read more - subscribe now!
Buy this issue online here
Gallery coming...
Staff Focus – You are Only as Good as Your Team
Published in European Trainer, January - March 2018, issue 60.
A major challenge facing trainers throughout Europe is the attraction and retention of skilled riders and grooms. Trainers are competing with many other industries, and fewer people favour the type of work offered in a racing yard, which means that trainers need to be more innovative and proactive when it comes to staff management, retention, and recruitment.
Entries for the Lycetts Team Champion Award in Britain closed on 1st December, but for those who didn’t enter, and for trainers in the rest of Europe, it is not too late to examine the aim behind the inaugural award and use the judging criteria to establish a team of excellence in your own yard.
The idea behind the Lycetts Team Champion Award is to reward the stables with good employment practices in place creating the best team ethos, and it is an initiative that will hopefully combat the long-term stable staff crisis affecting many yards. The award is judged on the methods trainers use to attract and retain staff, plus the safe working practices employed. The winning team receives an item of infrastructure or equipment that will improve working life within the yard.
It is hoped that the stories emerging from the award will publicly celebrate the benefits of teamwork and demonstrate that racehorse trainers provide rewarding and well-supported jobs, and this is an ethos that can be easily extended beyond the award itself...
To read more - subscribe now!
A report from the Merial - Performance Horse CPD and Raceday at Gowran Park
Becky James BSc, MSc - Haygain
Published in European Trainer - October - December 2017, issue 59
Click here to order this back issue!
Vets from all over Ireland congregated at Gowran Park racecourse in July for a continuing professional development event on the Performance Horse. The event, organised by European Trainer Magazine and Merial Animal Health, was the second in a series of veterinary CPD events for 2017 and featured a panel of expert speakers. The event was co-sponsored by Haygain and Connolly’s RED MILLS.
Managing Inflammatory Airway Disease – Dr Emmanuelle Van Erck-Westergren
The first speaker Dr Van Erck-Westergren was due to fly in from Brussels on the morning of the event, so when her flight was cancelled at the last minute there was a moment of concern for the organisers but they arranged to bring her into the room via a video link so all was not lost!
Using her experience in practice at the Equine Sports Medicine Practice in Belgium, Dr Van Erck explained the importance of vets helping clients to manage the environment of the horses to prevent and manage Inflammatory Airway Disease (IAD). She described managing the horse’s environment to reduce exposure to noxious inhalable particles and improve hygiene and ventilation in the stable as the cornerstone to the success of treating IAD.
Important considerations for the environment include building design, bedding, stable activities and most critically, the forage, as this is in the horse’s breathing zone. Dr Van Erck explained that hay remains an important source of forage for horses but it is also a major source of dust and contaminants. Soaking hay is a cheap way of reducing airborne dust but it promotes bacterial proliferation and leaches out the nutritional value so well-made haylage or preferably steamed hay should only be fed to horses with IAD.
To read more of this report - subscribe here!
Lycetts Team Champion Award
Published in European Trainer - October - December 2017, issue 59
Click here to order this back issue!
The important role played by stable staff has always been recognised by the horsemen and women employing them, though perhaps not always shown. It has certainly been overlooked beyond the stableyard, with the apparent view outside of the racing industry that stable work is unskilled and without long-term prospects. This misguided view has been detrimental, discouraging young people outside of the industry to explore job prospects and consider a role with thoroughbreds.
Recognising the individual skillset of the various roles within a working yard is important and while it may take time to get used to new job titles, where for centuries Lad or Lass sufficed, the titles are helping to identify particular roles and logical career progression. Above all, we are learning to openly value our team members and reward their skill and dedication, which means a tremendous amount in terms of job satisfaction and morale.
A wariness of comparing our workplace to any standard business is understandable, but it is important to recognise it as a business and every trainer wants to operate successfully. Peter Burnet, of the Peplow Group, has delivered learning and development programmes for individuals, teams and organisations since 1992. It's interesting to note that many of Peplow's programmes relate to the horseracing industry, “but can be adapted to any sector or organisation.” In this instance, our industry is setting the target for other industries to aspire to. Teamwork is naturally at its strongest in a working yard and can be seen as our industry's greatest, and to date overlooked, asset.
The team at Peplow explain that, “effective teamwork lies at the heart of every well managed organisation. The need to have a common purpose, clear objectives and a will to work cooperatively with colleagues is essential to maximise performance.”
To read more of this article - subscribe now!
Iconic Gallops of Europe
Published in European Trainer - October - December 2017, issue 59.
Click here to order this back issue!
Why are Europe's public training areas so well known? Part of their uniqueness and fame rests with the very concept of public training grounds. There are very few public facilities throughout the world and the most common training practice is the use of racecourse tracks. In the majority of countries trainers are based at racetracks and simply use the racecourse facilities.
While many of Europe's renowned training centres are situated close to a racecourse, or are run in conjunction with that track, they are, nevertheless, separate facilities offering a wide choice of gallops and surface, often over a vast acreage. The benefit to the horse is variety and change of scenery without impacting on its daily routine or necessitating travel. For the trainer, a choice of gallops and surfaces can be tailored to a horse's individual needs and prevailing weather.
Hoppegarten
Typical of this, though less widely known, is Hoppegarten in Germany, where 13-20 public trainers are based. A common factor shared by many of Europe's renowned gallops is Hoppegarten's sand-based subsoil, allowing the racecourse track and various gallops to drain freely. As a result, coupled with modern artificial watering systems employed by groundsmen in drying weather, extreme ground conditions are avoided and consistent work surfaces are provided all year round.
Hoppegarten is home to the biggest training grounds in Germany, encompassing over 500 acres of woodland, with 10km of walking and trotting paths, and since 2013 it has been granted the status of a Landmark of National Importance.
To read more about iconic gallops across Europe - subscribe now!
Generation X
First published in European Trainer issue 58 - July - September 2017
Click here to order this back issue!
It's been a great spring for Irish horseracing, the record 19 wins at the Cheltenham Festival having been followed within a matter of weeks by Aidan O'Brien's double in the Newmarket Guineas.
But, believe it or not, there is a branch of the sport in which Britain is in the ascendancy while Ireland seems in dangerous decline, and this is pony racing, an unheralded but vital part of racing's grassroots and an excellent source of hard-working, talented riders.
Listening to people talk about the storied history of pony racing in Ireland, one would imagine it would be secure forever. "Practically every top jockey in the country has gone through pony racing at one stage or another," I was told by Denis Egan, The Turf Club's chief executive. But neither The Turf Club nor any other authority has responsibility for nurturing the health of pony racing, which is falling on hard times with a consequent loss of fixtures and equine talent.
Meantime, the sport, having long been popular in other European countries, is finally taking hold in Britain, where it was all but unknown 15 years ago. "I can't speak highly enough about it and the people who organize it," says Paul Nicholls, the 10-times champion jumps trainer, who regrets that no such introduction to jockeyship was available when he was a lad.
His daughter, Megan, and his nephew, Harry Derham, are among a swelling list of British jockeys who cut their teeth in pony racing. Others include Sam Twiston-Davies, Sean Bowen, Lizzie Kelly, Tom Marquand, and Hollie Doyle. The Pony Racing Authority (PRA) reckons that more than 100 of its graduates now hold a jockey’s license of some kind.
The Saviour of Greek Racing
First published in European Trainer issue 58 - July - September 2017
Click here to order this back issue!
Making progress and facilitating change in racing can be tough and time consuming. Doing it in a challenging economic environment makes it tougher still. With that in mind, the strides being made in Greece, where the racing industry had fallen to its knees, is both admirable and encouraging.
Making progress and facilitating change in racing can be tough and time consuming. Doing it in a challenging economic environment makes it tougher still. With that in mind, the strides being made in Greece, where the racing industry had fallen to its knees, is both admirable and encouraging.
The article “Greek racing hoping for revival of fortunes” published in Issue 45 of European Trainer offers a more detailed explanation of the decline of the sport in Greece. The scene at the new venue of Markopoulo, 35 kilometres from the capital, was far removed from the halcyon days of high betting turnover and large crowds at a vibrant track close to Athens.
However, in January, 2016, OPAP (a Greek-based betting company) was granted the licence to organise and conduct racing in Greece. Improved relations with the Greek Jockey Club, who are still responsible for the governance of the sport, have followed, as Costas Alexopoulos, chief of operations, explains. Alexopoulos says, “We have a very close relationship with the Jockey Club now. There have been differences but we cooperate very well.”
With the need for racing in Greece to become a commercial success, OPAP are keen to make the right calls, turning to Fin Powrie, a man with extensive international experience in the industry, to organise and implement a plan for change. The Australian previously worked in Dubai, Bahrain, India, New Zealand, and his homeland. Powrie speaks with enthusiasm about the work being done in Greece and seems encouraged by the progress made since his arrival.
Racecourse Security - Does it pass the test?
CLICK ON THE IMAGE ABOVE TO BUY THIS BACK ISSUE NOW!
First published in European Trainer issue 57 - April '17 - June '17