Conformation - factors for racing ability - what might increase the chances to pick a future star on the racecourse
By Judy Wardrope
Everyone wants to be able to pick a future star on the track, ideally, one that can compete at the stakes level for several seasons. In order to increase the probability of finding such a gem, many buyers and agents look at the pedigree of a horse and the abilities displayed by its relatives, but that is not always an accurate predictor of future success. When looking at a potential racehorse, the mechanical aspects of its conformation usually override the lineage, unless of course, the conformation actually matches the pedigree.
For our purposes, we will examine three horses at the end of their three-year-old campaigns and one at the end of her fourth year. In order to provide the best educational value, these four horses were chosen because they offer a reasonable measure of success or failure on the track, have attractive pedigrees and were all offered for sale as racing prospects in a November mixed sale. The fillies were also offered as broodmare prospects.
Is it possible to tell which ones were the better racehorses and predict the best distances for those who were successful? Do their race records match their pedigrees? Let’s see.
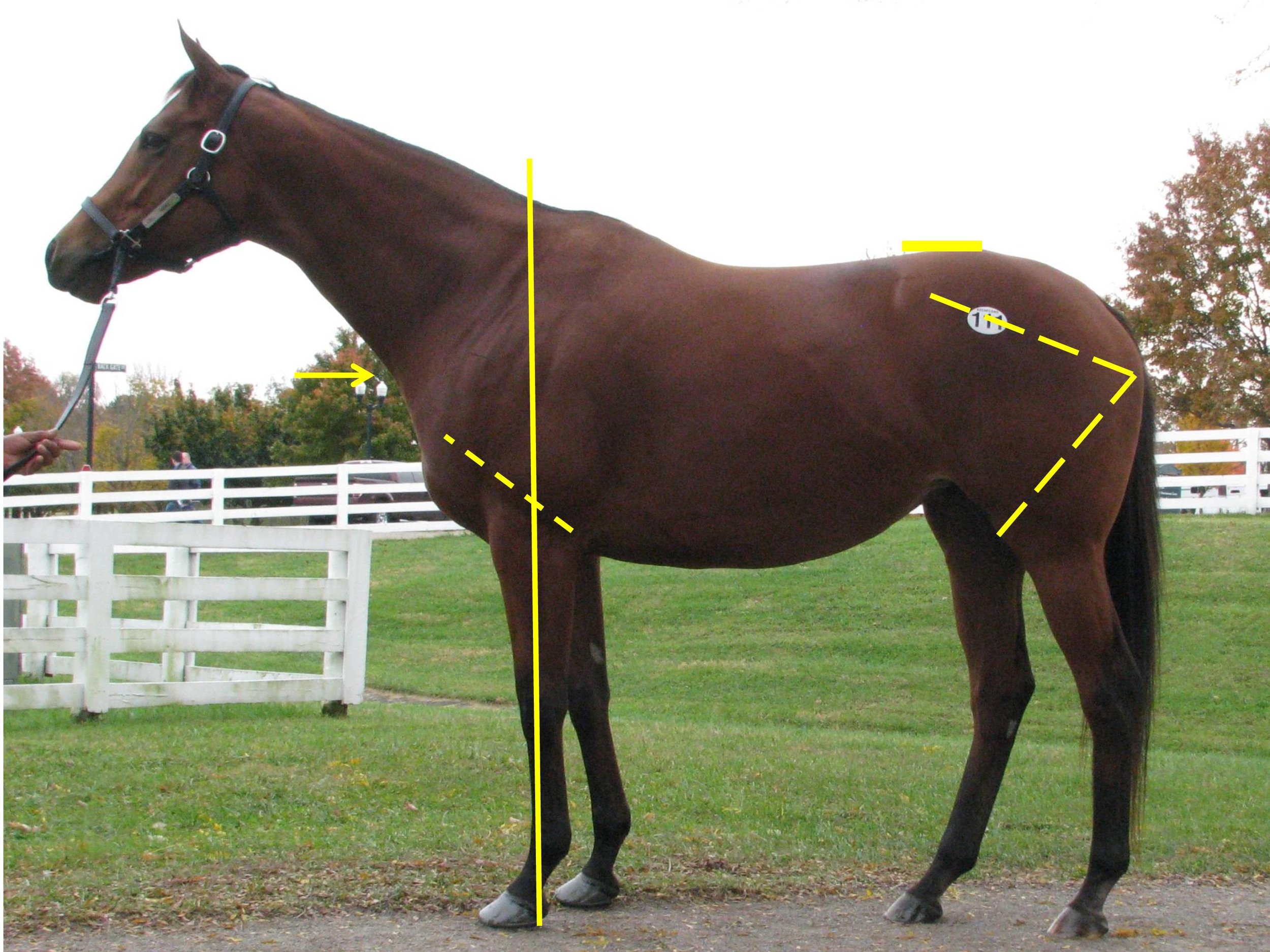
Horse #1
Horse #1
This gelding (photographed as a three-year-old) is by Horse of the Year Mineshaft and out of a daughter of Giants Causeway, a pedigree that would suggest ability at classic distances. He brought a final bid of $275k as a yearling and $45k as a maiden racing-prospect at the end of his three-year-old year after earning $19,150. His story did not end there, however. He went back to racing, changed trainers a few times, was claimed and then won a minor stakes at a mile while adding over $77k to his total earnings. All but one of his 18 races (3-3-3) were on the dirt, and he was still in training at the time of writing.
Structurally, he has some good points, but he is not built to be a superior athlete nor a consistent racehorse. His LS gap (just in front of the high point of croup) is considerably rearward from a line drawn from the top point of one hip to the top of the other. In other words, he was not particularly strong in the transmission and would likely show inconsistency because his back would likely spasm from his best efforts.
His stifle placement, based on the visible protrusion, is just below sheath level, which is in keeping with a horse preferring distances around eight or nine furlongs. However, his femur side (from point of buttock to stifle protrusion) of the rear triangle is shorter than the ilium side (point of hip to point of buttock), which not only adds stress to the hind legs, but it changes the ellipse of the rear stride and shortens the distance preference indicated by stifle placement. Horses with a shorter femur travel with their hocks behind them do not reach as far under their torsos as horses that are even on the ilium and femur sides. While the difference is not pronounced on this horse, it is discernable and would have an effect.
He exhibits three factors for lightness of the forehand: a distinct rise to the humerus (from elbow to point of shoulder), a high base of neck and a pillar of support (as indicated by a line extended through the naturally occurring groove in the forearm) that emerges well in front of the withers. The bottom of his pillar also emerges just into the rear quarter of his hoof, which, along with his lightness of the forehand, would aid with soundness for his forequarters.
The muscling at the top of his forearm extends over the elbow, which is a good indication that he is tight in the elbow on that side. He developed that muscle in that particular fashion because he has been using it as a brake to prevent the elbow from contacting the ribcage. (Note that the tightness of the elbow can vary from side to side on any horse.)
He ran according to his build, not his pedigree, and may well continue to run in that manner. He is more likely to have hind leg and back issues than foreleg issues.
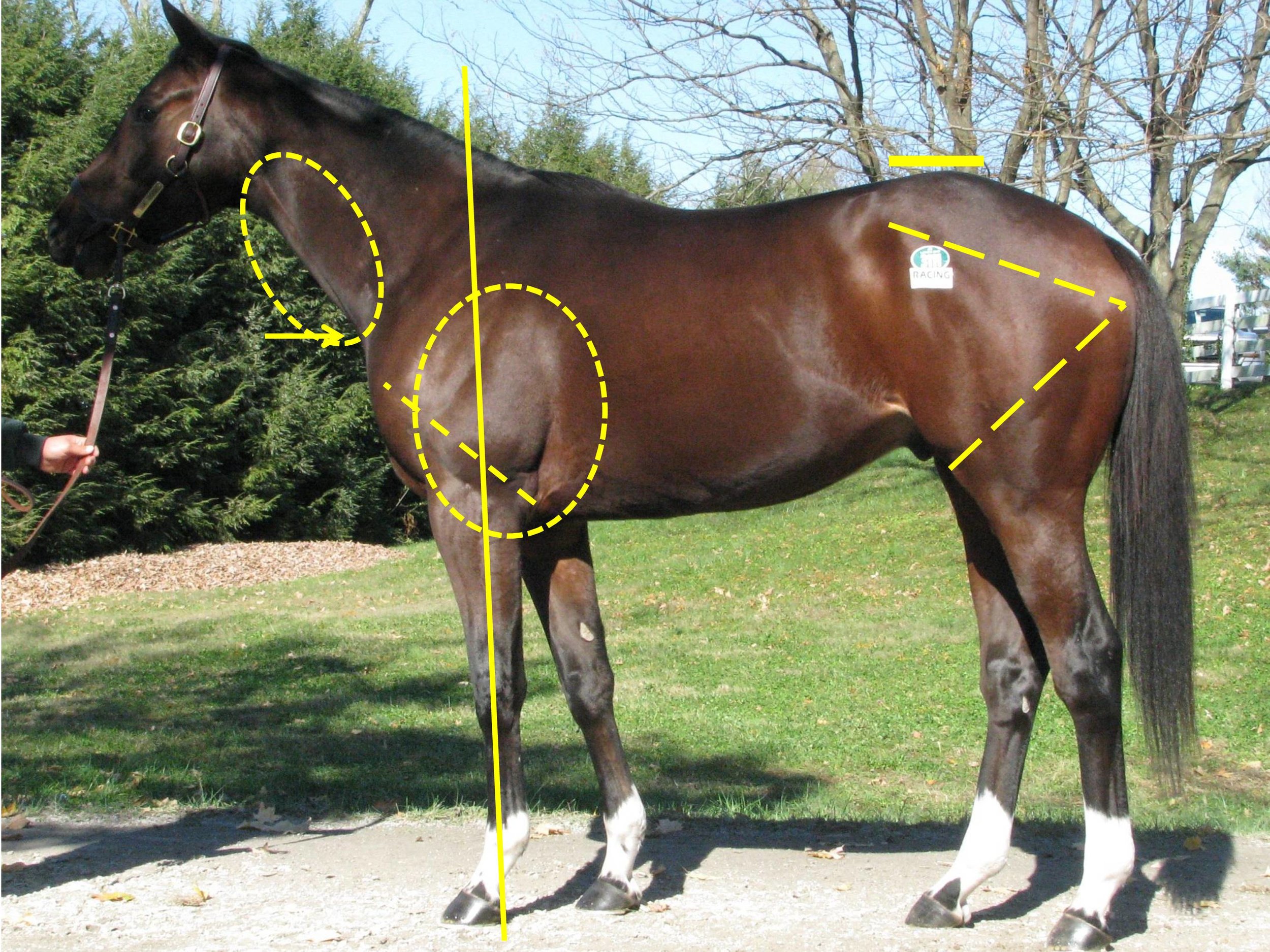
Horse #2
Horse #2
This filly (photographed as a three-year-old) is by champion sprinter Speightstown and out of a graded-stakes-placed daughter of Hard Spun that was best at about a mile. The filly raced at two and three years of age, earning $26,075 with a lifetime record of 6 starts, one win, one second and one third—all at sprinting distances on the dirt. She did not meet her reserve price at the sale when she was three.
Unlike Horse #1, her LS gap is much nearer the line from hip to hip and well within athletic limits. But, like Horse #1, she is shorter on the femur side of her rear triangle, which means that although her stifle protrusion is well below sheath level, the resultant rear stride would be restricted, and she would be at risk for injury to the hind legs, particularly from hock down.
She only has two of three factors for lightness of the forehand: the top of the pillar emerges well in front of the withers, and she has a high point of neck. Unlike the rest of the horses, she does not have much rise from elbow to point of shoulder, which equates with more horse in front of the pillar as well as a slower, lower stride on the forehand. In addition, the muscling at the top of her forearm is placed directly over her elbow… even more so than on Horse #1. She would not want to use her full range of motion of the foreleg and would apply the brake/muscle she developed in order to lift the foreleg off the ground before the body had fully rotated over it to avoid the elbow/rib collision. This often results in a choppy stride. However, it should be noted that the bottom of her pillar emerges into the rear quarter of her hoof, which is a factor for soundness of the forelegs.
Her lower point of shoulder combined with her tight elbow would not make for an efficient stride of the forehand, and her shorter femur would not make for an efficient stride of the hindquarters.
Her construction explains why she performed better as a two-year-old than she did as a three-year-old. It is likely that the more she trained and ran, the more uncomfortable she became, and that she would favor either the hindquarters or the forequarters, or alternate between them.
She did not race nearly as well as her lineage would suggest.
Horse #3
Horse #3
This filly (photographed as a three-year-old) is by champion two-year-old, Midshipman, and out of a multiple stakes-producing daughter of Unbridled’s Song. She raced at two and three years of age and became a stakes-winner (Gr3) as a three-year-old, tallying over $425k in lifetime earnings from 12 starts. Although she did win one of her two starts on turf, she was best at 8 to 8.5 furlongs on the main track. She brought a bid of $775k at the sale and was headed to life as a broodmare.
Her LS gap is just slightly rearward of a line drawn from hip to hip and is therefore well within the athletic range. Her rear triangle is of equal distance on the ilium and femur sides, plus her stifle protrusion would be just below sheath level if she were male. She has the engine of an 8- to 9-furlong horse and the transmission to utilize that engine.
Aside from all three factors for lightness of the forehand (pillar emerging well in front of the withers, good rise of the humerus from elbow to point of shoulder and a high base of neck), the bottom of her pillar emerges into the rear quarter of her hoof to aid in soundness.
Although she shows muscle development at the top of her forearm, the muscling does not extend over her elbow the way it does on the previous two horses. Her near side does not exhibit the tell-tale muscle of a horse with a tight elbow, and thus, she would be comfortable using a full range of motion of the forehand.
Proportionately, she has the shortest neck of the sample horses, which may be one of the reasons she has developed the muscle at the top of her forearm. Since horses use their necks to aid in lifting the forehand and extending the stride, she may compensate by using the muscle over her humerus to assist in those purposes.
Of the sample horses, she is the closest to matching heritage and ability. …
CLICK HERE to return to issue contents.
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
4 x print issue and online subscription to European Trainer & online North American Trainer. Access to all digital back issues of both editions.
Your subscription will start with the October - December 2025 issue - published at the end of September.
If you wish to receive a copy of the most recent issue, please select this as an additional order.
Conformation and Breeding Choices
By Judy Wardrope
A lot of factors go into the making of a good racehorse, but everything starts with the right genetic combinations; and when it comes to genetics, little is black and white. The best we can do is to increase our odds of producing or selecting a potential racehorse. Examining the functional aspects of the mare and then selecting a stallion that suits her is another tool in the breeding arsenal.
For this article we will use photos of four broodmares and analyze the mares’ conformational points with regard to performance as well as matings likely to result in good racehorses from each one. We will look at qualities we might want to cement and qualities we might hope to improve for their offspring. In addition, we will look at their produce records to see what has or has not worked in the past.
In order to provide a balance between consistency and randomness, only mares that were grey (the least common color at the sale) with three or more offspring that were likely to have had a chance to race (at least three years old) were selected. In other words, the mares were not hand-picked to prove any particular point.
All race and produce information was taken from the sales catalogue at the time the photos were taken (November 2018) and have not been updated.
Mare 1
Her lumbosacral gap (LS) (just in front of the high point of croup, and the equivalent of the horse’s transmission) is not ideal, but within athletic limits; however, it is an area one would hope to improve through stallion selection. One would want a stallion with proven athleticism and a history of siring good runners.
The rear triangle and stifle placement (just below sheath level if she were male) are those of a miler. A stallion with proven performance at between seven furlongs and a mile and an eighth would be preferable as it would be breeding like to like from a mechanical perspective rather than breeding a basketball star to a gymnast.
Her pillar of support emerges well in front of the withers for some lightness of the forehand but just behind the heel. One would look for a stallion with the bottom of the pillar emerging into the rear quarter of the hoof for improved soundness and longevity on the track. Her base of neck is well above her point of shoulder, adding additional lightness to the forehand, and she has ample room behind her elbow to maximise the range of motion of the forequarters. Although her humerus (elbow to point of shoulder) shows the length one would expect in order to match her rear stride, one would likely select a stallion with more rise from elbow to point of shoulder in order to add more lightness to the forehand.
Her sire was a champion sprinter as well as a successful sire, and her female family was that of stakes producers. She was a stakes-placed winner at six furlongs—a full-sister to a stakes winner at a mile as well as a half-sister to another stakes-winning miler. Her race career lasted from three to five.
She had four foals that met the criteria for selection; all by distance sires of the commercial variety. Two of her foals were unplaced and two were modest winners at the track. I strongly suspect that this mare’s produce record would have proven significantly better had she been bred to stallions that were sound milers or even sprinters.
Mare 2
Her LS placement, while not terrible, could use improvement; so one would seek a stallion that was stronger in this area and tended to pass on that trait.
The hindquarters are those of a sprinter, with the stifle protrusion being parallel to where the bottom of the sheath would be. It is the highest of all the mares used in this comparison, and therefore would suggest a sprinter stallion for mating.
Her forehand shows traits for lightness and soundness: pillar emerging well in front of the withers and into the rear quarter of the hoof, a high point of shoulder plus a high base of neck. She also exhibits freedom of the elbow. These traits one would want to duplicate when making a choice of stallions.
However, her length of humerus would dictate a longer stride of the forehand than that of the hindquarters. This means that the mare would compensate by dwelling in the air on the short (rear) side, which is why she hollows her back and has developed considerable muscle on the underside of her neck. One would hope to find a stallion that was well matched fore and aft in hopes he would even out the stride of the foal.
Her sire was a graded-stakes-placed winner and sire of stakes winners, but not a leading sire. Her dam produced eight winners and three stakes winners of restricted races, including this mare and her full sister.
She raced from three to five and had produced three foals that met the criteria for this article. One (by a classic-distance racehorse and leading sire) was a winner in Japan, one (by a stallion of distance lineage) was unplaced, and one (by a sprinter sire with only two starts) was a non-graded stakes-winner. In essence, her best foal was the one that was the product of a type-to-type mating for distance, despite the mare having been bred to commercial sires in the other two instances.
Mare 3 ….
BUY THIS ISSUE IN PRINT OR DOWNLOAD
WHY NOT SUBSCRIBE?
DON'T MISS OUT AND SUBSCRIBE TO RECEIVE THE NEXT FOUR ISSUES!
An Introduction to the Functional Aspects of Conformation
By Judy Wardrope
Why is one horse a sprinter and another a stayer? Why is one sibling a star and another a disappointment? Why does one horse stay sound and another does not? Over the course of the next few issues, we will delve into the mechanics of the racehorse to discern the answer to these questions and others. We will be learning by example, and we will be using objective terminology as well as repeatable measures. This knowledge can be applied to the selection of racing prospects, to the consideration of distance or surface preferences and, of course, to mating choices.
Introducing a different way of looking at things requires some forethought. Questions need to be addressed in order to provide educational value for the audience. How does one organise the information, and how does one back up the information? In the case of equine functionality in racing, which horses will provide the best corroborative visuals?
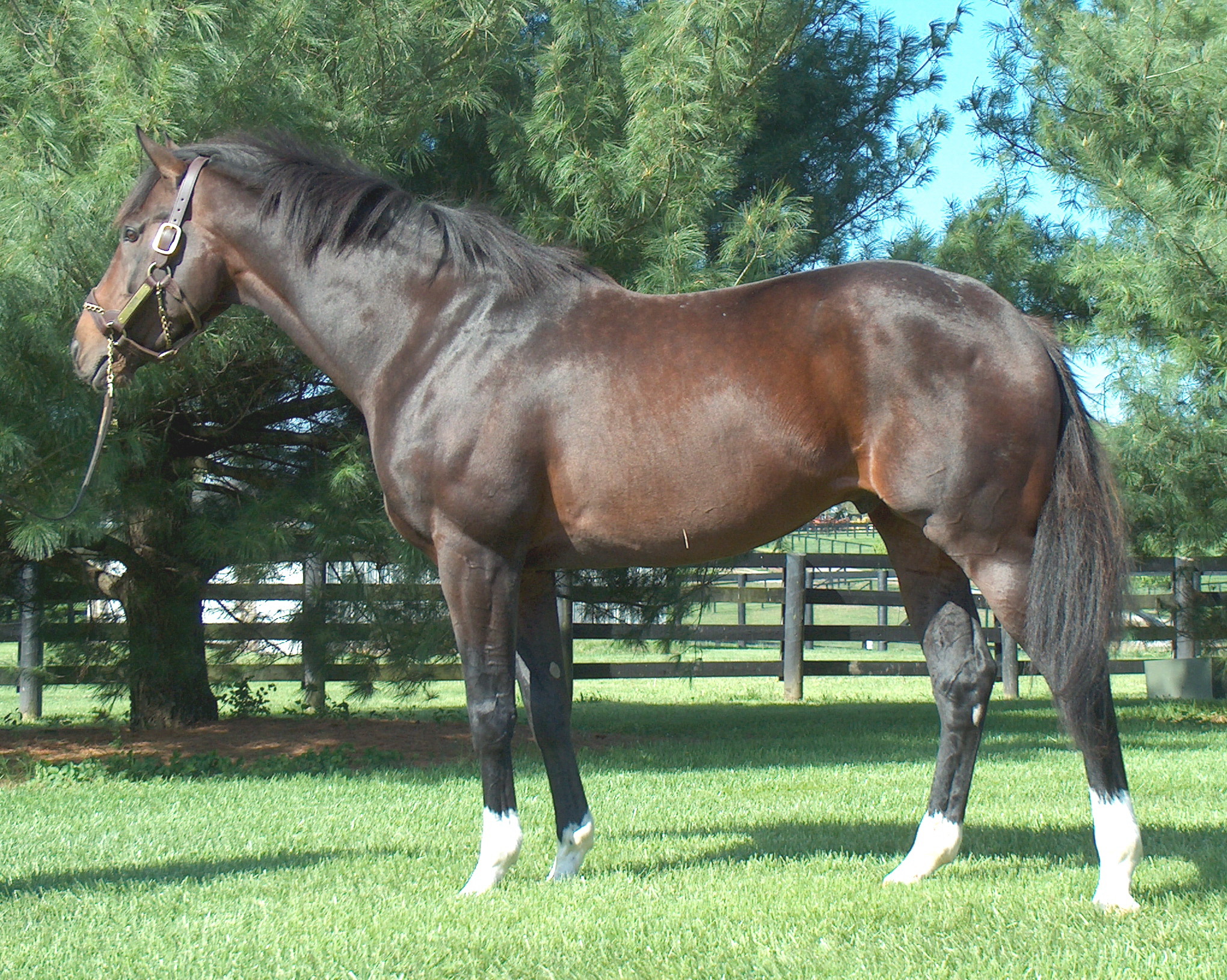
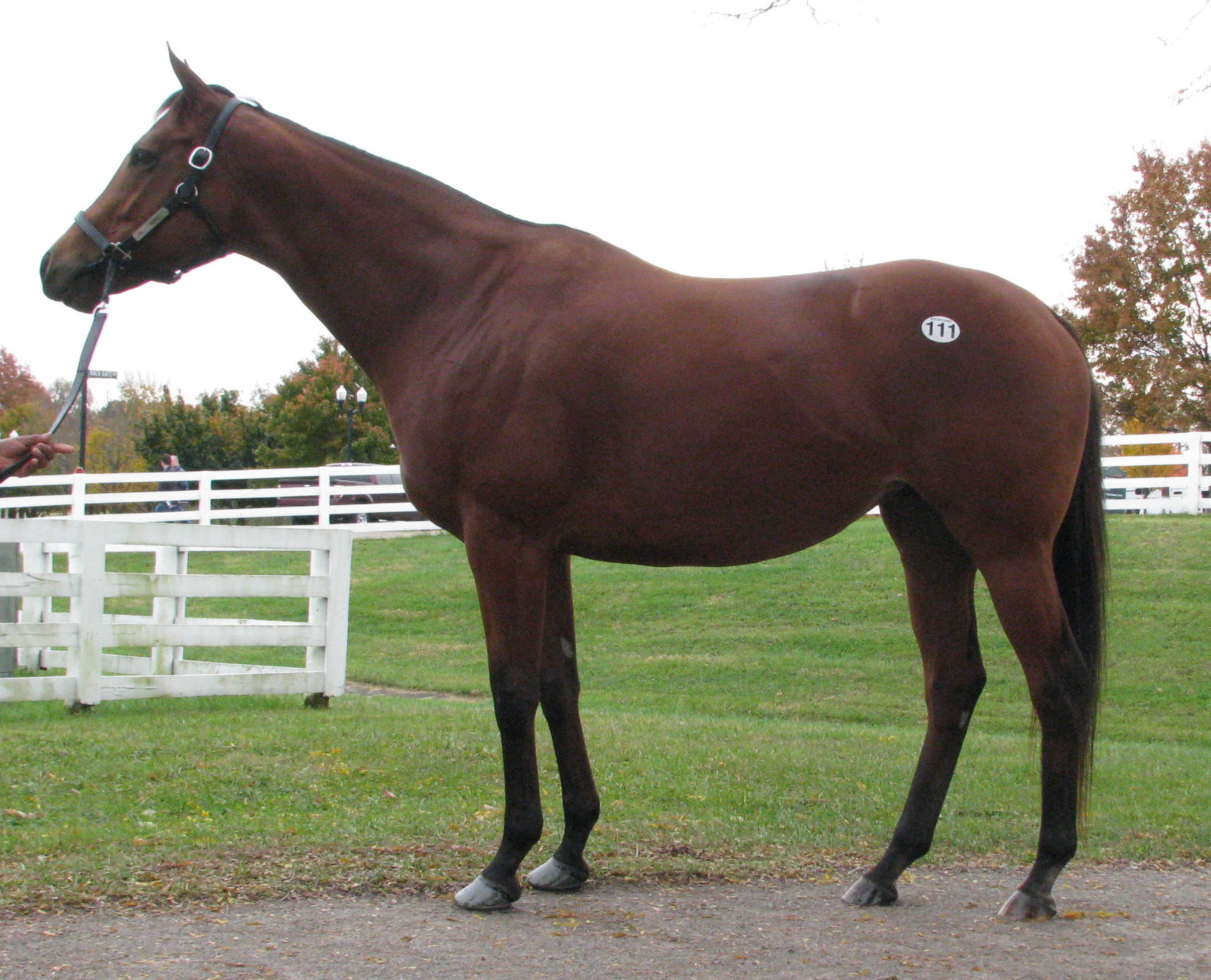
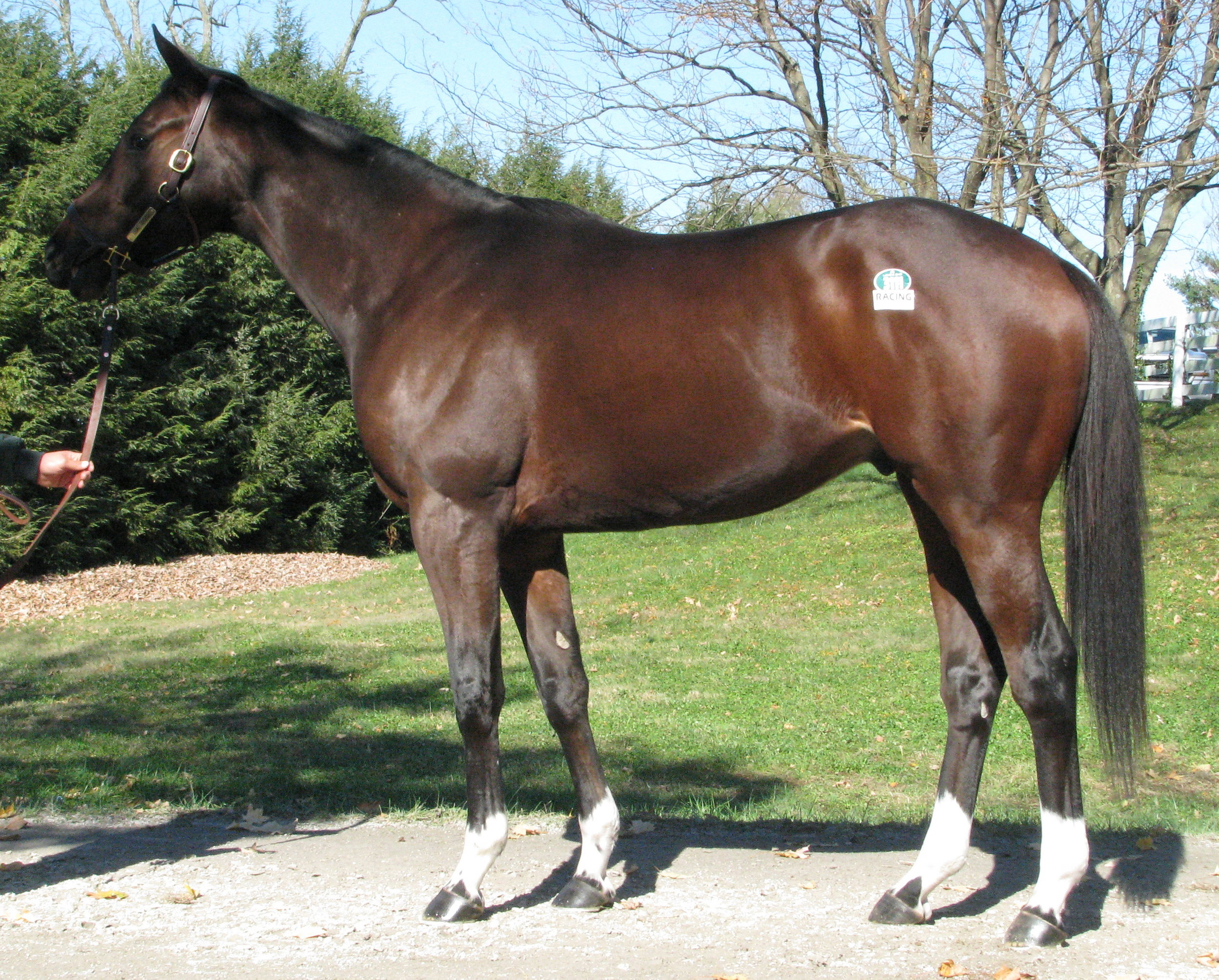



After considerable thought, these three horses were selected: Tiznow (Horse #1) twice won the Breeders’ Cup Classic (1¼ miles) ; Lady Eli (Horse #2) won the Juvenile Fillies Turf and was twice second in the Filly and Mare Turf (13/8 miles); while our third example (Horse #3) did not earn enough to pay his way on the track. Let’s see if we can explain the commonalities and the differences so that we can apply that knowledge in the future.
Factors for Athleticism
If we consider the horse’s hindquarters to be the motor, then we should consider the connection between hindquarters and body to be the horse’s transmission. Like in a vehicle, if the motor is strong, but the transmission is weak, the horse will either have to protect the transmission or damage it.
According to Dr. Hilary M. Clayton (BVMS, PhD, MRCVS), the hind limb rotates around the hip joint in the walk and trot and around the lumbosacral joint in the canter and gallop. “The lumbosacral joint is the only part of the vertebral column between the base of the neck and the tail that allows a significant amount of flexion [rounding] and extension [hollowing] of the back. At all the other vertebral joints, the amount of motion is much smaller. Moving the point of rotation from the hip joint to the lumbosacral joint increases the effective length of the hind limbs and, therefore, increases stride length.” From a functional perspective, that explains why a canter or gallop is loftier in the forehand than the walk or the trot.
In order to establish an objective measure, I use the lumbosacral (LS) gap, which is located just in front of the high point of the croup. This is where the articulation of the spine changes just in front of the sacrum, and it is where the majority of the up and down motion along the spine occurs. The closer a line drawn from the top point of one hip to the top point of the other hip comes to bisecting this palpable gap, the stronger the horse’s transmission. In other words, the stronger the horse’s coupling.
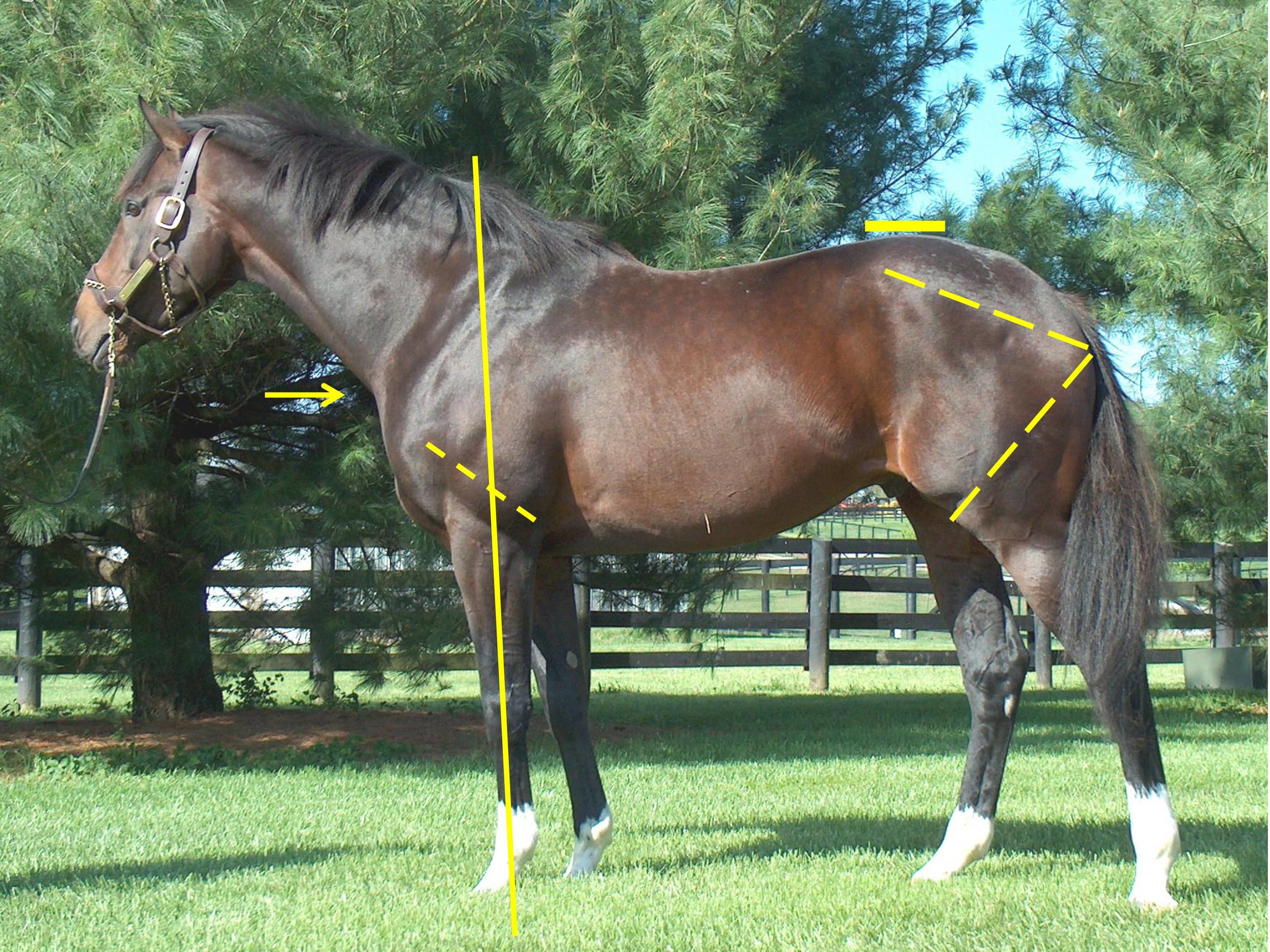

We can see that the first two horses have an LS gap (just in front of the high point of the croup as indicated) that is essentially in line with a line drawn from the top of one hip to the top of the opposing hip. This gives them the ability to transfer their power both upward (lifting of the forehand) and forward (allowing for full extension of the forehand and the hindquarters). Horse #3 shows an LS gap considerably rearward of the top of his hip, making him less able to transfer his power and setting him up for a sore back.
You may also notice that all three of these sample horses display an ilium side (point of hip to point of buttock), which is the same length as the femur side (point of buttock to stifle protrusion)—meaning that they produce similar types of power from the rear spring as it coils and releases when in stride. We can examine the variances in these measures in more detail in future articles, when we start to delve into various ranges of motion as well as other factors for soundness or injury.
Factors for Distance Preferences…












