Spring allergies - how to treat spring allergies and the effects they have on the respiratory tract
Article by Becky Windell
Spring allergies – peak season of the year-round battle
As obligate nasal breathers horses are predisposed to inhaling respirable dust, mould, pollen and other irritants from the environment. Whilst they have defence mechanisms to deal with it, the horse can be overloaded with the amount they are exposed to.
Springtime brings an array of newfound pollen from trees, grasses, and crops including the infamous oilseed rape (OSR). This pollen offensive comes in addition to the other allergens in the horse’s environment often surpassing the threshold of irritant load. This can result in respiratory based “spring allergies” with inflammation in the airways leading to allergen based equine asthma. Either subtle signs such as poor performance and reduced stamina will appear and/or more obvious clinical signs such as coughing and nasal discharge. Horses will tire early due to the reduced amount of oxygen being taken up by the blood from the lungs.
Plants are polyploids and show many gene duplications so cross reactivity among species in which different antigens appear similar to the immune system can amplify the horse’s response to pollen and is particularly the case for grass pollens.
Generally intact pollen grains range from 10–100 μm in size, this is bigger than respirable particles which are classified respirable at <5 μm. Therefore, pollen has not generally been implicated in Equine Asthma and tends to be considered more of an irritant than allergen. However, a study by White et al identified an association with pollen in a group of horses with Severe Equine Asthma (SEA) while looking at bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples compared to healthy horses2. The effects of pollen on the horse is an area where more research is needed.
Oilseed rape on the decline
It’s well documented that oilseed rape (OSR) is a concern for trainers with some experiencing underperforming horses while surrounding fields are flowering oilseed rape crops.
Whilst it’s still unclear if there’s truly an allergic component to it, it certainly seems to irritate a lot of horses and vets see pollen in the tracheal washes when OSR is in flower.
A study in people comparing spring allergy symptoms of people living near OSR and those living far away, found small but significant excesses of cough, wheeze, and headaches in spring in the oilseed rape area. Interestingly they also found counts of fungal spores were mostly higher in the rape than the non-rape areas so perhaps pollen is not the culprit but fungal spores on the crop…?
This is worth noting as fungi is proven to cause respiratory problems in horses. A study by Dauvillier et al found horses with fungal elements observed on the tracheal wash (TW) cytology had 2 times greater chance of having equine asthma than horses without fungi. They also found the risk of being diagnosed and likelihood of fungi in TW were higher when horses were bedded on straw or fed dry hay which are key sources of fungi in the horse’s environment.
Practical solutions to OSR have been for trainers to purchase neighbouring fields or pay their neighbouring farmer not to grow the OSR.
From the farmer’s perspective OSR has been an essential part of the arable crop rotation for many years now. It is a crop specially planted to give the cereal crops a ‘break’ from the cycle of weeds, pests and disease that build up in the soil. This helps to improve the yield of the crops that are grown afterwards, such as wheat.
It used to be good for removing grass weeds too but has become less useful for this purpose in recent years due to weed resistance. In fact, a number of previously positive reasons to grow OSR are no longer standing up. A flea beetle which previously could be treated with a neonicitinoid is no longer licenced for this use, soil borne diseases have become a problem, and the crop does not do well in the wetter winters.
Ultimately it is now less profitable. This is good news for trainers with farmers starting to use the crop less often and perhaps grow it every 6th year rather than ever 3rd year in a field. Its use is on the decline in UK/Ire and this can been seen in government figures, in 2023-24 all regions in England saw decreases in the oilseed rape area with the largest proportional decrease seen in the North East and the overall decrease of OSR grown in the UK of 27%. While in Ireland Winter oilseed rape declined by 30% in 20246.
Now the interesting question in time is how much will the incidence of spring allergies reduce with the reduction in oil seed rape?
Global Warming
Dr. Emmanuelle Van Erck Westergren, founder of Equine Sports Medicine Practice in Belgium cautions about the effects of global warming on seasonal allergies. Global warming is altering fungal behaviour and distribution, offering conditions that provide opportunities for fungi such as Apergillus and increases the risk of mycotoxins. In addition the burden of pollen is increased by warming temperatures.
Diagnosing spring allergies
Regular, routine tracheal washes (TW) are useful as a quick and easy “screening” procedure. They help monitor how inflamed the airways are by looking at the neutrophils and macrophage cells. Normal samples are typically of low to moderate numbers of nucleated cells, the nucleated cells being mostly macrophages, with <10% neutrophils. An elevated proportion of neutrophils in the TW is considered to indicate airway inflammation, and cutoff values for neutrophil percentage have been set at 20% for TW.
Ian Beamish partner at Baker McVeigh Lambourn equine practice says he uses the tracheal wash to see “how the army is looking” in terms of number of cells and how many of those cells are dying on the battlefield.
He also warned “Ultimately, it can be a struggle to determine the actual cause of inflammation of the airways. Whilst spring allergies is a strong possibility at this time of year it could be any number of allergens from the environment causing it or simply the addition of more burdening the system. And then it could also be a virus! It’s important to remember racehorses are immune suppressed from being in full training so they are susceptible to low grade viral disease which can present with similar poor performance.”
To establish if the horse is truly allergic or if it is simply an irritation of the airways there is a diagnostic blood test for allergens. Measuring allergen-specific IgE antibodies present in the serum, can help to identify environmental allergens for both allergen avoidance purposes and to select for inclusion in allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT). This can be a helpful aid for diagnosing allergic disease but has been known to give occasional false positives so cannot be relied upon. Establishing the specific allergy is unfortunately very difficult.
Performance Horse Consultant and highly experienced equine vet Peter ‘Spike’ Milligan advises to first and foremost control what you can.
“Reducing contact with pollen can be extremely challenging so first focus on what you can control. Irrespective of the time of year, regularly re-evaluate the stable environment as well as the forage and bedding quality. This includes how they are stored, prepared and used to ensure the allergen and irritant load is as low as possible.”
A useful tool
The pollen count measures the number of pollen grains in a given volume of air and can indicate if it is a day the horse will be exposed to high concentrations of pollen. Pollen count is affected by the season, weather and even the time of day. The largest concentrations of pollen are found on days of high radiation and wind, early in the morning when pollen is first shed when the air is warming and rising and in the evening as the pollen in the air descends to nose level with the afternoon air-cooling.
The pollen count can be checked daily on weather apps. Where possible, it’s advisable to adapt the horses training schedule in line with the pollen count and keep training sessions less strenuous on the days the pollen count is high.
Treating spring allergies
Treatment of horses with allergen-induced equine asthma focuses mainly on decreasing and controlling airway inflammation. The standard and effective cornerstone treatment is to give a systemic or inhaled corticosteroid and if necessary, a bronchodilator can also be used.
The preferred method to administer these tends to be via a nebuliser because inhaled therapy delivers the drug directly to the lungs and helps to loosen mucous. In addition, a lower dose can be used reducing the chance of side effects and shortening the drug withdrawal time required prior to racing.
Recent advances in treatment include a specifically designed inhaler with a different inhaled steroid, ciclesonide, studies have demonstrated improved clinical signs in a group of horses with mild to severe equine asthma.
However, whilst corticosteroids are very effective and efficient at relieving airway obstruction, they have limited residual effect after treatment stops and long‐term administration is usually limited due to the risk of laminitis, immunosuppression, and interactions with endocrine metabolism9. The drug withdrawal period also impacts the racing schedule. So, what treatments can be used which interfere less with their training and racing plan?
Firstly, creating a barrier between the horse’s airways and the pollen with Nostrilvet or similar and/or the use of a nose-net are low-cost options for training that could be worth a try. This could help to reduce the irritant load on non-race days.
If the horse is truly allergic to certain pollens, then de-sensitisation injections can be used with no withdrawl period necessary. Known as allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) it is a safe long-term treatment which has been used successfully for allergen-induced Equine Asthma. The efficacy of the treatment can vary however, studies suggest that approximately 75% of cases treated showed a good response, with either no need or a reduced need for steroids.
Immunotherapy aims to make the horse tolerant to the environmental allergens that have been diagnosed as responsible for their clinical signs by introducing increasing amounts of the allergen to which they are sensitive. These desensitisation vaccines are administered to the horse subcutaneously. The initial treatment lasts for approximately 10 months, with a dosage regime that gradually increases until the maximum tolerated dose is reached. This is then followed by maintenance treatment. The length of time for a response has been reported to vary between individual horses and can be anywhere from 4 and 12 months. Treatment can be ongoing as premature discontinuation may result in the clinical signs recurring.
Developments in orthobiologics has brought a new non-corticosteroid anti-inflammatory alternative for use in affected horses. Alpha-2-macroglobulin (α2M) is a naturally occurring protein within the blood and is the horses natural defence against inflammation. Plasma proteins are filtered from the horse’s own blood, leaving an isolated, concentrated alpha-2-macroglobulin product which can be nebulised using a Flexineb. It’s high-priced and still early days for this product but offers a potential drug-free way to treat. It is also an effective anti-inflammatory in joint disease.
Principally the greatest threat to respiratory health year-round is from environmental sources which you can control – the forage, the bedding and the overall stable hygiene environment, this should never be overlooked.
References
Couetil L, Cardwell J, Garber V, et al. Inflammatory airway disease of horses— Revised consensus statement. J Vet Intern Med 2016;30:503-515
White S, Moore-Colyer M, Marti E, Coüetil L, Hannant D, Richard EA, Alcocer M. Development of a comprehensive protein microarray for immunoglobulin E profiling in horses with severe asthma. J Vet Intern Med. 2019 Sep;33(5):2327-2335. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15564. Epub 2019 Aug 20. PMID: 31429513; PMCID: PMC6766494.
Soutar A, Harker C, Seaton A, Brooke M, Marr I. Oilseed rape and seasonal symptoms: epidemiological and environmental studies. Thorax. 1994 Apr;49(4):352-6. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.4.352. PMID: 8202906; PMCID: PMC475369.
Dauvillier J, Ter Woort F, van Erck-Westergren E. Fungi in respiratory samples of horses with inflammatory airway disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2019 Mar;33(2):968-975. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15397. Epub 2018 Dec 21. PMID: 30576012; PMCID: PMC6430897.
Gov.uk website - Accredited official statistics Cereal and oilseed areas in England at 1 June 2024. Updated 29 August 2024 https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/cereal-and-oilseed-rape-areas-in-england/cereal-and-oilseed-rape-areas-in-england-at-1-june-2023#:~:text=1.7%20Oilseed%20crops,244%20thousand%20hectares%20in%202024.
Teagasc Crop Report www.teagasccropreport.ie Harvest report 2024. https://teagasccropreport.ie/reports/harvest-report-2024#:~:text=The%20area%20of%20winter%20oilseed,of%2021%2C600%20ha%20in%202023.
Lavoie J, Bullone M, Rodrigues N, et al. Effect of different doses of inhaled ciclesonide on lung function, clinical signs related to airflow limitation and serum cortisol levels in horses with experimentally induced mild to severe airway obstruction. Equine Vet J 2019;51:779-786.
Ciclesonide [prescribing information] Duluth, GA: Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc. 2020.
Mainguy-Seers S, Lavoie JP. Glucocorticoid treatment in horses with asthma: A narrative review. J Vet Intern Med. 2021 Jul;35(4):2045-2057. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16189. Epub 2021 Jun 3. PMID: 34085342; PMCID: PMC8295667.
Alpha-2 Macroglobulin for the Management of Equine Asthma Summary Results of a Pilot Study Dan Dreyfuss, DVM
Air Quality and Air Pollution’s Impact on Your Horse’s Lungs
There’s nothing like hearing a horse cough to set people scurrying around the barn to identify the culprit. After all, that cough could mean choke, or a respiratory virus has found its way into the barn. It could also indicate equine asthma. Yes, even those “everyday coughs” that we sometimes dismiss as "summer cough" or "hay cough" are a wake-up call to the potential for severe equine asthma.
Formerly known as heaves, broken wind, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or recurrent airway obstruction (RAO), this respiratory condition is now called severe equine asthma (sEA). These names reflect how our scientific and medical understanding of this debilitating disease has changed over the years. We now consider heaves to be most comparable to severe asthma in people.
But what if your horse only coughs during or after exercise? This type of cough can mean that they have upper airway irritation (think throat and windpipe) or lower airway inflammation (think lungs) meaning inflammatory airway disease (IAD), which is now known as mild-to-moderate equine asthma (mEA). This airway disease is similar to childhood asthma, meaning that it can go away on its own. However, it is still very important to call your veterinarian out to diagnose mEA. This disease causes reduced athletic performance, and there are different subtypes of mEA that benefit from specific medical therapies. In some cases, mEA progresses to sEA.
Equine Asthma and Air Quality
What does equine asthma have to do with air quality? A lot, it turns out. Poor air quality, or air pollution, includes the barn dusts—the allergens and moulds in hay and the ground-up bacteria in manure, as well as arena dusts and ammonia from urine. Also, very importantly for both people and horses, air pollution can be from gas and diesel-powered equipment. This includes equipment being driven through the barn, the truck left idling by a stall window, or the smog from even a small city that drifts nearly invisibly over the surrounding farmland. Recently, forest-fire smoke has been another serious contributor to air pollution.
Smog causes the lung inflammation associated with mEA. Therefore, it is also likely that air pollution from engines and forest fires will also trigger asthma attacks in horses with sEA. Smog and smoke contain many harmful particulates and gases, but very importantly they also contain fine particulate matter known as PM2.5. The 2.5 refers to the diameter of the particle being 2.5 microns. That’s roughly 30 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair. Because it is so small, this fine particulate is inhaled deeply into the lungs where it crosses over into the bloodstream. So, not only does PM2.5 cause lung disease, but it also causes inflammation elsewhere in the body including the heart. Worldwide, even short-term exposure is associated with an increased risk of premature death from heart disease, stroke, and lung cancer. This PM2.5 stuff is not trivial!
In horses, we know that PM2.5 causes mEA, so it’s logical that smog and forest-fire smoke exposure could exacerbate asthma in horses, but we don’t know about heart disease or risk of premature death.
Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests and Treatments
Equine asthma manifests with a spectrum of symptoms that vary in severity and the degree of debilitation they cause. Just like in people with asthma, the airways of horses with mEA and sEA are “hyperreactive.” This means that the asthmatic horse’s airways are extra sensitive to barn dusts that another horse’s lungs would just “ignore.” The asthmatic horse’s airways constrict, or become narrower, in response to these dusts. This narrowing makes it harder to get air in and out of the lungs. Think about drinking through a straw. You can drink faster with a wider straw than a skinnier one. It’s the same with air and the airways. In horses with mEA, the narrowing is mild. In horses with sEA, the constriction is extreme and is the reason why they develop the “heaves line”; they have to use their abdominal muscles to help squeeze their lungs to force the air back out of their narrow airways. They also develop flaring of their nostrils at rest to make their upper airway wider to get more air in. Horses with mEA do not develop a heaves line, but the airway narrowing and inflammation do cause reduced athletic ability.
The major signs of mEA are coughing during or just after exercise that has been going on for at least a month and decreased athletic performance. In some cases, there may also be white or watery nasal discharge particularly after exercise. Often, the signs of mEA are subtle and require a very astute owner, trainer, groom, or rider to recognise them.
Another very obvious feature of horses with sEA is their persistent hacking cough, which worsens in dusty conditions. “Hello dusty hay, arena, and track!” The cough develops because of airway hyperreactivity and because of inflammation and excess mucus in the airways. Mucus is the normal response of the lung to the presence of inhaled tiny particles or other irritants. Mucus traps these noxious substances so they can be coughed out, which protects the lung. But if an asthma-prone horse is constantly exposed to a dusty environment, it leads to chronic inflammation and mucus accumulation, and the development or worsening of asthma along with that characteristic cough.
Accurately Diagnosing Equine Asthma
Veterinarians use a combination of the information you tell them, their observation of the horse and the barn, and a careful physical and respiratory examination that often involves “rebreathing.” This is a technique where a bag is briefly placed over the horse’s nose, causing them to breathe more frequently and more deeply to make their lungs sound louder. This helps your veterinarian hear subtle changes in air movement through the lungs and amplifies the wheezes and crackles that characterise a horse experiencing a severe asthma attack. Wheezes indicate air “whistling” through constricted airways, and crackles mean airway fluid buildup. The fluid accumulation is caused by airway inflammation and contributes to the challenge of getting air into the lung.
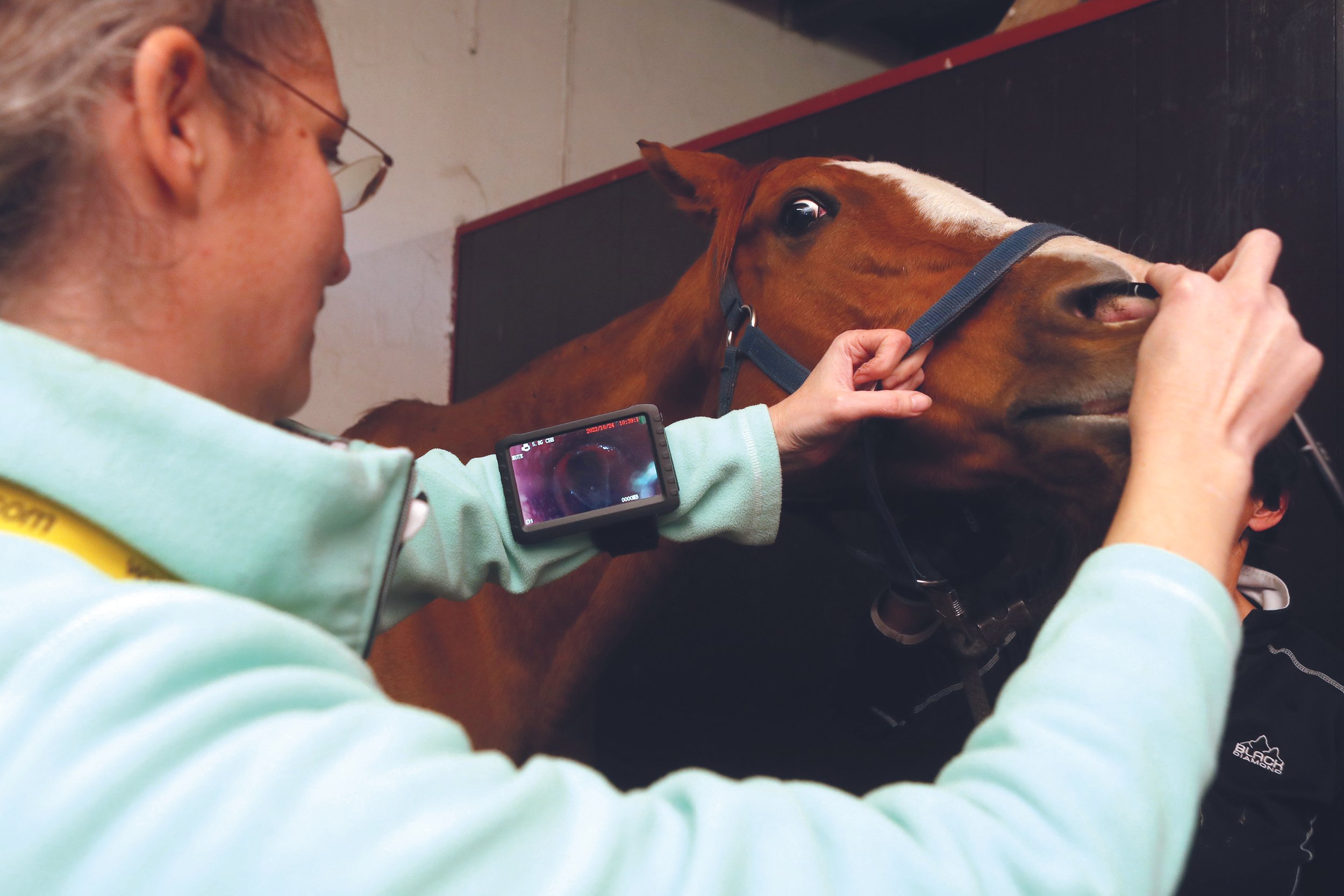
Other tests your veterinarian might use are endoscopy, bronchoalveolar lavage, and in the specialist setting, pulmonary function testing. They will also perform a complete blood count and biochemical profile assay to help rule out the presence of an infectious disease.
Endoscopy allows your veterinarian to see the mucus in the trachea and large airways of the lung. It also lets them see whether there are physical changes to the shape of the airways, which can be seen in horses with sEA.
Bronchoalveolar lavage, or “lung wash” is how your veterinarian assesses whether there is an accumulation of mucus and inflammatory cells in the smallest airways that are too deep in the lung to be seen using the endoscope. Examining lung wash fluid is a very important way to differentiate between the different types of mEA, between sEA in remission and an active asthma attack, and conditions like pneumonia or a viral lung infection.
Finally, if your veterinarian is from a specialty practice or a veterinary teaching hospital, they might also perform pulmonary function testing. This allows your veterinarian to determine if your horse’s lungs have hyperreactive airways (the hallmark of asthma), lung stiffening, and a reduced ability to breathe properly.
Results from these tests are crucial to understanding the severity and prognosis of the condition. As noted earlier, mEA can go away on its own; but medical intervention may speed healing and the return to athletic performance. With sEA, remission from an asthmatic flare is the best we can achieve. As the disease gets worse over time, eventually the affected horse may need to be euthanised.
Management, Treatment and Most Importantly—Prevention
Successful treatment of mEA and sEA flares, as well as long-term management, requires a multi-pronged approach and strict adherence to your veterinarian’s recommendations.
Rest is important because forcing your horse to exercise when they are in an asthma attack further damages the lung and impedes healing. To help avoid lung damage when smog or forest-fire smoke is high, a very useful tool is your local, online, air quality index (just search on the name of your closest city or town and “AQI”). Available worldwide, the AQI gives advice on how much activity is appropriate for people with lung and heart conditions, which are easily applied to your horse. For example, if your horse has sEA and if the AQI guidelines say that asthmatic people should limit their activity, then do the same for your horse. If the AQI says that the air quality is bad enough that even healthy people should avoid physical activity, then do the same for you AND your horse. During times of poor air quality, it is recommended to monitor the AQI forecast and plan to bring horses into the barn when the AQI is high and to turn them out once the AQI has improved.
Prevent dusty air. Think of running your finger along your tack box – whatever comes away on your finger is what your horse is breathing in. Reducing dust is critical to preventing the development of mEA and sEA, and for managing the horse in an asthmatic flare.
Logical daily practices to help reduce dust exposure:
Turn out all horses before stall cleaning
Wet down the aisle prior to sweeping
Never sweep debris into your horse’s stall
Use low-dust bedding like wood shavings or dust-extracted straw products, which should also be dampened down with water
Reduce arena, paddock, and track dust with watering and maintenance
Consider low-dust materials when selecting a footing substrate
Steam (per the machine’s instructions) or soaking hay (15–30 minutes and then draining, but never store steamed or soaked hay!)
Feed hay from the ground
Feed other low-dust feeds
Avoid hay feeding systems that allow the horse to put their nose into the middle of dry hay—this creates a “nosebag” of dust
Other critical factors include ensuring that the temperature, humidity and ventilation of your barn are seasonally optimised. Horses prefer a temperature between 10–24 ºC (50–75 ºF), ideal barn humidity is between 60–70%. Optimal air exchange in summer is 142 L/s (300 cubic feet/minute). For those regions that experience winter, air exchange of 12–19 L/s (25–40 cubic feet/minute) is ideal. In winter, needing to strip down to a single layer to do chores implies that your barn is not adequately ventilated for your horse’s optimal health. Comfortable for people is often too hot and too musty for your horse!
Medical interventions for controlling asthma are numerous. If your veterinarian chooses to perform a lung wash, they will tailor the drug therapy of your asthmatic horse to the results of the wash fluid examination. Most veterinarians will prescribe bronchodilators to alleviate airway constriction. They will also recommend aerosolised, nebulised or systemic drugs (usually a corticosteroid, an immunomodulatory drug like interferon-α, or a mast cell stabilisers like cromolyn sodium) to manage the underlying inflammation. They may also suggest nebulising with sterile saline to help loosen airway mucus and may suggest feed additives like omega 3 fatty acids, which may have beneficial effects on airway inflammation.
New Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is paramount to expanding our knowledge of what causes equine asthma and exploring innovative medical solutions. Scientists are actively investigating the effects of smog and barn dusts on the lungs of horses. They are also working to identify new targeted therapies, immunotherapies and other treatment modalities to improve outcomes for affected horses.
Conclusion
Both mild and severe equine asthma are caused and triggered by the same air pollutants, highlighting the need for careful barn management. The alarming rise in air pollution levels poses an additional threat to equine respiratory health. Recognising everyday coughs as potential warning signs and implementing proper diagnostic tests, day-to-day management practices and medical therapies are crucial in combating equine asthma. By prioritising the protection of our horse’s respiratory health and staying informed about the latest research, we can ensure the well-being of our equine companions for years to come.